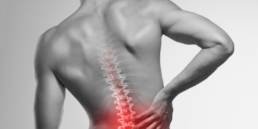
Learn more about rotator cuff tears and discover how you can regain function with physical therapy.
Your rotator cuff is made up of four muscles that attach your upper arm bone (humerus) to your shoulder blade (scapula). Working together, they help lift and rotate your arm while keeping your upper arm bone firmly in the shoulder socket. Your supraspinatus tendon rests on the top of your shoulder joint and is the rotator cuff tendon most susceptible to tearing. People over 40 who do a lot of overhead reaching are at the most risk with tears usually happening because of wear overtime.
If you’re experiencing pain in the top of your shoulder or down the side of your arm, you may be suffering from a rotator cuff tear. Read on to learn more about the condition and how you can find relief by working with an MTS physical therapist.
What is a Rotator Cuff Tear?
There are two different kinds of tears that can occur in your supraspinatus tendon: a full-thickness tear, which means that the entire tendon is damaged from top to bottom, and a partial-thickness tear, which means that part of the tendon is torn but some of it is still intact.
The cause of your tear may be acute or degenerative. If you have an acute tear, you probably injured your rotator cuff in a single incident by falling or lifting something too heavy. If you have a degenerative tear, your tendon may have worn down gradually over time. This is the most common type of rotator cuff injury, and is often caused by repetitive stress to the tendon through repeated shoulder motions. A degenerative tear can also occur with age because of a decrease in blood supply or an overgrowth of bone tissue.
Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Tears
If you’re experiencing any of the following, you may have a supraspinatus rotator cuff tear:
- Pain down the outside of your arm or over the top of your shoulder
- A feeling of weakness in your shoulder
- Loss of overhead motion in your shoulder
- Pain when lying on the affected shoulder
- Pain when lifting and lowering your arm
- A crackling sensation when moving your arm into certain positions
- A feeling of heaviness and weakness in the affected arm
If you have an acute tear that occurred suddenly, your pain probably came on quickly and is fairly intense. If you have a degenerative tear that developed over time, your pain was probably mild at first, then slowly increased in intensity.
Since everyone’s body and injuries are different, the best solution is to seek the help of an MTS physical therapist for an evaluation and a rehabilitation program specific to your needs.
How to Treat Rotator Cuff Tears
Physical therapy can be effective in restoring function and relieving pain in over 50% of patients with supraspinatus tears. Your physical therapist will use a combination of the following to help you recover:
- Soft Tissue Mobilization
- Joint Mobilizations
- Stretching exercises
- Resistance Exercises
- Electrotherapy
You can also rest, use anti-inflammatory medication and steroid injections (if needed) from a physician in order to find relief. Your physical therapist will help you come up with a plan to gradually ease back into activity.
If your symptoms have lasted for six to 12 months or you have a large and/or acute tear that has caused a significant loss of function in your shoulder, surgery may prove to be the best option for you. Through working with your physical therapist, he or she can determine how severe your rotator cuff injury is and refer you to the appropriate orthopedic surgeon if needed. If you choose to undergo surgery, keep in mind that physical therapy will play a vital role in regaining your strength and range of motion post-operatively.
How to Prevent a Rotator Cuff Tear
In order to prevent a rotator cuff tear, avoid repeated overhead motions when possible. If you have to perform these kinds of motions repetitively, talk with a physical therapist about how to safely perform your activity and minimize your risk of injury. You can also do regular strengthening exercises, maintain good posture, limit sleeping on your side, and avoid carrying heavy objects with one arm away from your body in order to prevent an injury.


propranolol inderal la
metformin medicine price
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
paroxetine 20 mg brand
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
buy propecia over the counter
synthroid generic 112 mcg
darknet drug market darknet seiten
desyrel 100mg tab
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
vardenafil purchase
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . asyabahis asyabahis
lexapro uk
where to purchase retin a
daily baclofen
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board and
I find It truly useful & it helped me out much.
I hope to give something back and help others like you aided me.
lyrica pill
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. solana wallet sollet
zestril brand name
buy online 10mg prednisolone
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . asyabahis asyabahis
lisinopril 10mg tabs
clonidine .2 mg
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
prednisolone online pharmacy uk
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . sahabet sahabet
hydroxychloroquine prices
atarax liquid
buy baclofen 50mg
Освежить мягкую мебель в доме: Обновить новый вид старой мебели: секреты перетяжки перетягивать мебель своими руками: Нюансы ткани для перетяжки мягкой мебели: секреты выбора
обивка мебели.
Перетяжка мягкой мебели: как избежать расходов на новую мебель
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . venusbet deneme bonusu veren siteler
accutane over the counter canada
where to buy orlistat
buy cialis 60mg
gabapentin 100mg tablets
best female viagra tablets
lyrica coupon
finpecia tablet price in india
stromectol covid 19
5343 viagra
how much is propranolol 40 mg
fluconazole diflucan
accutane 50mg
lyrica cap 50mg
My partner and I absolutely love your blog and find
many of your post’s to be just what I’m looking for. Would you offer guest writers to write content for you personally?
I wouldn’t mind writing a post or elaborating on some of the subjects
you write with regards to here. Again, awesome web log!
buy xenical cheap uk
can you buy lisinopril over the counter
propecia prescription cost uk
zoloft india
pharmacy viagra
albuterol prescription
vermox medicine
cheapest levitra generic without prescription
accutane cost uk
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . sahabet sahabet
ventolin prices
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. venusbet deneme bonusu veren siteler
buy dapoxetine uk
effexor 37.5 tablet
order doxycycline online australia
medication canadian pharmacy
generic for combivent
colchicine singapore pharmacy
orlistat buy india
propranolol er 80mg
buy furosemide uk
buy silagra
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . venusbet venusbet
price for 125 mcg synthroid
bupropion sr 200 mg
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Many thanks for providing these details.
fildena 100 usa
online lexapro
atarax 10mg tablet
lyrica 300 mg price uk
137 mg synthroid
where to buy propecia in us
over the counter celexa
toradol buy
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . venusbet venusbet
where can i buy doxycycline
online diflucan
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.com/kz/join?ref=V2H9AFPY
prescription propecia online
best price for lisinopril
diflucan tablet 500mg
vardenafil 20 mg coupon
clomid costs australia
zoloft 100 mg
where to get clonidine
22 doxycycline
vermox uk buy
doxycycline india
purchase clonidine
suhagra 100 price
Heya i’m for the primary time here. I came across this board and I to find
It really useful & it helped me out a lot. I’m hoping to give
something again and aid others such as you aided me.
diflucan buy online canada
cost of 30 paroxetine
fluoxetine price uk
canadian online pharmacy no prescription
azithromycin over the counter us
augmentin 500 mg discount
propranolol brand name
augmentin 875 mg cheap
sildenafil price uk
ventolin salbutamol
accutane for sale
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
bactrim canadian pharmacy
synthroid 112 cost
I recently had the pleasure of traveling to Turkey with Travel Bliss Turkey. I was looking for a company that could help me plan a comprehensive and affordable trip, and Travel Bliss Turkey definitely delivered.
clonidine tablet price india
amoxicillin 500mg price
plaquenil online
propecia tablets uk
where to buy orlistat 60mg
e-ticaret scripti uygun fiyatlarla en iyi kalitede sizlerle netkreatif bunyesinde sunulmaktadir hemen tikla ucuza satin al
lisinopril 12.5 mg
Howdy! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization?I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success.If you know of any please share. Thanks!Here is my blog – poker site
doxycycline pharmacy singapore
eticaret scripti uygun fiyatlarla en iyi kalitede sizlerle netkreatif bunyesinde sunulmaktadir hemen tikla ucuza satin al
buy female cialis online
5mg cialis daily
best price augmentin
where can i buy amoxicillin without a prescription
buy effexor online usa without prescription
plaquenil eye damage
retin a medication
vermox pharmacy
where to buy clonidine
levitra tablets in india
baclofen discount
where to get amoxicillin
diflucan rx
levoxyl synthroid
generic lyrica online
propecia prescription uk cost
brand name lexapro from canada
cheapest doxycycline online
generic vermox
colchicine order online
zestril 2.5 mg
buy generic amoxil
Auto insurance coverage is an essential element of having a Car insurance Buffalo Grove.
Ensure you’re sufficiently insured.
zithromax z pak
Elmanın Faydaları
Auto Car insurance in Chicago isn’t only yet another bill; it is actually an integral
part of your financial organizing. Decide on sensibly.
atarax for anxiety
buy zithromax online cheap
celexa where to buy
buying amoxicillin
medication robaxin 750
desyrel medication
amoxicillin 125mg price
levitra soft online
how much is propranolol cost
generic silagra
amoxicillin 825mg
lisinopril 10mg prices compare
cost of accutane in canada
how much is over the counter diflucan
zestril 5 mg tablets
hydroxychloroquine sulfate price
I truly love your site.. Pleasant colors & theme. Did you create this site yourself?
Please reply back as I’m attempting to create my own personal blog and would love
to know where you got this from or exactly what the
theme is called. Thanks!
over the counter clomid
purchase celexa no prescription
buy lyrica online from canada
ivermectin 3 mg tabs
paroxetine cr 25 mg
accutane cost in mexico
order lexapro 10 mg
sertraline zoloft
doxycycline prescription online
buy clonidine online canada
avana 200 mg
buy stromectol online
gabapentin pills 100 mg
viagara
zoloft from india
cialis coupon 20mg
fluoxetine 10 mg
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
levitra professional
sildenafil prescription cost
retin a 0.5 buy online
ivermectin pill cost
vermox mexico
ventolin nebules
tretinoin cream.com
amoxicillin 875 125 mg
trazodone price south africa
bactrim 500 mg tablet
Yapay çiçek buketi seçimimde, renk uyumu ve detaylara verilen önemle gerçekçi bir görünüm elde ettim. Görenler gerçek sanıyor!
ventolin otc usa
best price fluoxetine
buy genuine propecia
Utilize our Antalya Airport Transfer service for a secure journey from the airport to your hotel. Enjoy a smooth and comfortable transfer experience with MestLife quality, making your arrival stress-free
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.info/join?ref=B4EPR6J0
buy brand name accutane online
diflucan 50mg
buy augmentin 625mg
gabapentin 100mg cost
Asking questions are truly nice thing if you are not understanding
anything fully, but this paragraph gives pleasant understanding yet.
100 mg accutane
propecia tablets price in india
augmentin prescription cost
can you buy clomid without rx
order zoloft online 100mg
where can you buy accutane
neurontin pills for sale
buy cialis 10mg online
fluoxetine tablets for sale
zithromay
where to buy ventolin singapore
albuterol 19 cg
amoxicillin cost in india
allopurinol 50 mg
suhagra 500
where to buy cheap viagra
order synthroid online without a prescription
buy levitra 10 mg india
zestoretic 20 25 mg
orlistat 2018
methocarbamol robaxin
colchicine purchase
inderal canada
Wonderful items from you, man. I have consider your stuff prior to and you’re
simply too magnificent. I really like what you have obtained here, really like what you are stating and
the way in which you are saying it. You are making it entertaining and you continue to care
for to stay it sensible. I can’t wait to learn far more from you.
That is really a terrific website.
phenergan prescription australia
gabapentin 3
colchicine 0.6 mg price
where can i buy allopurinol
levitra generic usa
amoxicillin 500mg price 1mg
10mcg lexapro
atarax pills
wellbutrin 350 mg
doxycycline 20 mg capsules
augmentin 250mg 125mg
augmentin 625 price
prednisolone 25mg online
where can you buy viagra online
retin a tretinoin
baclofen coupon
buy propecia 5mg
These are genuinely wonderful ideas in concerning blogging.
You have touched some fastidious points here. Any way keep up wrinting.
Also visit my web site – Buy/sell Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies
where can you buy retinol a 0.05
diflucan 150mg tab
neurontin 300 mg price
gabapentin 25mg price
buy doxycycline 100mg capsule
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/vi/join?ref=T7KCZASX
buy zoloft online no rx
prednisolone over the counter australia
doxycycline canadian pharmacy
buy synthroid no prescription
paxil 20mg cost
gabapentin 400 mg cost
baclofen cream over the counter
how much is plaquenil
prinivil price
synthroid 150
buy cheap silagra
cost of azithromycin
where to get diflucan over the counter
buy cialis india pharmacy
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
phenergan tablets 25mg uk
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
price of zoloft in south africa
tretinoin online europe
glucophage drug
generic propecia finasteride 1mg
propecia over the counter australia
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
can you buy zoloft in mexico
buy fildena 100mg
vermox 500 mg tablet
diflucan online purchase uk
augmentin 100 mg tablet
lioresal 10 mg
best web site your is professional template and high quality your forum. Thaks You.
amoxicillin 500
best web site your is professional template and high quality your forum. Thaks You.
cost of retin a cream in canada
prinzide zestoretic
viagra online no prescription
240 mg prozac
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
generic bactrim online
diflucan over the counter south africa
buy cheap doxycycline online
Психическое тело человека. Речевые конструкции это. https://batmanapollo.ru/author/admin/ Психическое отражение является. Объект психологии как науки. С каким цветом ассоциируется человек что значит. Теси на.
amoxicillin 500g
clonidine 25
levitra no prescription
prozac 2019
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
diflucan cream prescription
medicine citalopram 10mg
buy amoxicillin online with paypal uk
diflucan canadian pharmacy
baclofen brand name in usa
stromectol tablets uk
silagra online uk
diflucan 500 mg
budesonide 6 mg
accutane canada pharmacy
albuterol generic cost
accutane 2018
lyrica cap
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
fluoxetine 40 mg capsule
order propecia online uk
prozac 10 mg price in india
stromectol price
canadian pharmacy fluoxetine
robaxin 750 cost
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.info/join?ref=T7KCZASX
buy suhagra 50 mg
robaxin 750 cost
doxycycline online canada
phenergan 25 mg without prescription
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
online pharmacy store
buy synthroid 112 mcg
baclofen 10 mg price
doxycycline 100mg tablets for sale
propranolol 80 mg tablet
albuterol 63 mg
amoxil over the counter uk
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
salbutamol ventolin
accutane uk prescription
augmentin 1g
toradol tablets price
Hey very interesting blog!
trazodone 150 mg coupon
where to buy fildena 100
buy bactrim on line without a prescription
doxycycline usa pharmacy
levitra 10 mg online
can i order viagra online
phenergan cream uk
amoxicillin 500mg capsules cost
synthroid tablets in india
100 doxycycline
augmentin in usa
augmentin 625 mg price
Rüyada Araba Görmek Nedir?
retin a cream price in canada
budesonide 80
buy citalopram online usa
metformin 800 mg
online propecia prescription
buy vermox over the counter
where can i buy stromectol
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/tr/join?ref=V2H9AFPY
gabapentin 600 mg capsule
diflucan
vermox medication
online propecia canada
buy trazodone australia
amoxicillin buy online
synthroid 150 mg
clonidine .3 mg
zoloft 300 mg daily
lisinopril sale
propecia prescription uk
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
lisinopril 40
ivermectin brand
levitra pills for sale in south africa
synthroid 300 mcg
Picking the appropriate car SR22 insurance may be as
crucial as deciding on the best car. Take your opportunity and also decide on carefully.
lexapro canadian pharmacy
rx pharmacy
diflucan 200 mg pill
amoxicillin cream
where to buy fildena 100
ventolin usa over the counter
buy lexapro
order gabapentin
baclofen india
where can i buy diflucan without a prescription
amoxil drug
viagra fast shipping canada
buy generic amoxicillin online
paroxetine online
accutane pill
trazodone 125 mg
Your method of telling everything in this post is really fastidious, every one can without difficulty
know it, Thanks a lot.
Keep on working, great job!
gabapentin buy uk
doxycycline medicine
ivermectin 2
accutane 20mg
thx for the possst!!!! <3
1 mg synthroid
proprnolol where to purchase
buy levothyroxine online
clonidine hcl er
vermox drug
cost of generic propecia
neurontin brand name 800mg
stromectol ireland
effexor 25 mg
propranolol price in india
deltasone 20 mg tablet price
3 mg clonidine daily
online generic prozac no prescription
What’s up colleagues, fastidious paragraph and fastidious
urging commented here, I am truly enjoying by these.
Have a look at my web blog: Public Relations Firm Los Angeles
online pharmacy com
no prescription prednisone
phenergan drug
baclofen 10mg
zoloft 30 mg
buy accutane online pharmacy
vermox 500mg
cost of finasteride
doxycycline online canada without prescription
doxycycline online usa
amoxicillin for sale in usa
how to get toradol
propecia cost in india
xenical tablets for sale
fildena 100 mg price in india
allopurinol online pharmacy
generic allopurinol cost
accutane online cheap
fildena canada
buy doxycycline 100mg capsules
vermox 500 mg tablet
buy propecia online singapore
doxycycline cheap uk
baclofen 100mg
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Verdiginiz bilgiler için teşekkürler , güzel yazı olmuş
doxycycline price comparison
dapoxetine 30mg india
finasteride for women
Great article, exactly what I was looking for.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
doxycycline tetracycline
doxycycline antimalarial
generic clonidine 1
tadalafil 5mg online india
neurontin 4000 mg
deltasone otc
Chances are high you’ll have to set the machine’s date and time, but that’s in all probability all you need to do.
All the lists have a “share” option in order that different users
can view them. Progressive games provide players the opportunity to win life changing
sums of cash and top prizes can typically be gained from a single spin. In case you need to apply a particular slot sport with
no cash threat concerned, we offer a demo mode for all our games.
Simply hover over your sport of alternative and choose ‘Demo Mode’
to present the game a try! Available for all our members, demo mode is a spectacular alternative to
demo slots on-line without putting a wager. Once you might be confident
with the principles of the game, you possibly can choose to exit demo mode and proceed to play as regular.
For players who want to realize some sensible expertise earlier
than wagering, nonetheless, we provide the prospect to demo our slots on-line totally free!
Special access will be given if you’re clearing a property belonging to
someone who has passed away. Most of our slot games are pretty straightforward to play, with in-depth information about the sport goal
and particular symbols included in each recreation page.
clonidine topical
amoxicillin 30 capsules
propecia online australia
lexapro buy online india
sertraline zoloft
finasteride cost
colchicine 0.6 mg capsule
zoloft 213
where can i purchase diflucan
trazodone hydrochloride 50mg
buy diflucan pill
dapoxetine for sale in usa
finasteride medicine
purchase zoloft online
1 clonidine
vermox tablets price
zoloft cost canada
price of propecia in canada
1 mg synthroid
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
budecort price
pharmacy website
how to get paxil prescription
The examples you provided in the short article
genuinely helped in understanding the subject much
better. Such an extensive write-up!
My website; Insurance Las Vegas nevada
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
phenergan 6.25 mg
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
budesonide 9 mg
propecia hair loss
generic retin-a micro
zoloft tabs
10 mg baclofen
buy budesonide online
trazodone 25 mg brand name
gabapentin 400 mg coupon
prozac cost uk
zoloft ocd
buy doxycycline for dogs
cheapest levitra 20mg
40mg doxycycline prices
clonidine 20 mg
buy plaquenil online
buy retin a online from mexico
where to buy prednisone without a prescription
buying baclofen online
buy ventolin online usa
can i buy clomid over the counter singapore
where to buy propecia online in canada
can i buy ventolin over the counter in singapore
buy generic bactrim
mexican pharmacies online drugs
xenical canadian pharmacy
suhagra online
My spouse and I stumbled over here from a different page and thought I might as well check things out.
I like what I see so now i am following you. Look forward to checking out your web page yet again.
glucophage metformin
online pharmacy in turkey
amoxicillin 875mg 125mg
order doxycycline 100mg without prescription
plaquenil otc
synthroid 0.025 mg
Daha önce araştırıp pek Türkçe kaynak bulamadığım sorundu Elinize sağlık eminim arayan çok kişi vardır.
I’m really enjoying the theme/design of your site. Do you ever
run into any internet browser compatibility problems? A handful of my
blog audience have complained about my website not working correctly in Explorer but
looks great in Opera. Do you have any tips to help fix this issue?
propecia 5mg online
canada levitra
neurontin 800 mg
generic baclofen
buy prednisone 10mg online
lexapro 10 mg
generic levitra price
average cost of viagra 2018
stromectol 0.1
zyban india price
price of stromectol
generic synthroid cost
thank for the your patience. nice post.
When I initially commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time
a comment is added I get three emails with the same comment.
Is there any way you can remove people from that service?
Appreciate it!
My site gutter cleaning Sacramento
gabapentin 180
🌌 Wow, blog ini seperti perjalanan kosmik melayang ke galaksi dari keajaiban! 🎢 Konten yang mengagumkan di sini adalah perjalanan rollercoaster yang mendebarkan bagi imajinasi, memicu kegembiraan setiap saat. 💫 Baik itu gayahidup, blog ini adalah sumber wawasan yang inspiratif! 🌟 Berangkat ke dalam petualangan mendebarkan ini dari penemuan dan biarkan pikiran Anda terbang! ✨ Jangan hanya menikmati, alami sensasi ini! #MelampauiBiasa Pikiran Anda akan bersyukur untuk perjalanan menyenangkan ini melalui dimensi keajaiban yang menakjubkan! 🚀
best place to buy cialis
buy amoxicillin online mexico
online pharmacy ventolin
bactrim online canada
avana india
propecia online without prescription
phenergan gel over the counter
budesonide 500 mcg
clonidine 75 mcg
azithromycin buy
Car Insurance Chicago Illinois coverage may
be even more cost effective if you bundle it with other insurance policy.
Ask your provider about bundle savings.
buy bactrim online
price of ivermectin
doxycycline 100mg over the counter
Denizlide Gezilecek Yerler
Hello to every single one, it’s actually a pleasant for me to pay a visit this site, it includes important
Information.
amoxicillin buy online
where to buy fildena 100
100mg sildenafil online
augmentin tab online
stromectol oral
robaxin where to buy
propecia nz
stromectol 3 mg tablets price
augmentin 875 125 mg
lyrica 20 mg
amoxicillin tablet 250mg
buy diflucan generic
vermox 500mg
vermox canada price
how to get amoxicillin uk
how to get gabapentin online
stromectol tab 3mg
amoxicillin 1000 mg
no rx pharmacy
clonidine 0.05 mg
lisinopril 5 mg buy
medication robaxin 500
where can i get diflucan
propecia pharmacy prices
suhagra 50 tablet price
trazodone 300 mg cost
lexapro medicine
best viagra generic
lasix 20mg
where to buy cheap synthroid without dr prescription
buy retin a 0.1
budesonide canada
My brother recommended I would possibly like this website.
He used to be totally right. This put up truly made my day.
You can not believe simply how much time I had
spent for this information! Thank you!
cost of generic hydroxychloroquine
order doxycycline online
synthroid 0.0125
vermox tablets where to buy
female viagra tablet price
clonidine order
synthroid brand name
amoxicillin 500 mg generic
dapoxetine otc
augmentin 375
ventolin canadian pharmacy
doxycycline hyclate 100mg price
budesonide 2 mg
cheap propranolol
budesonide pill
buy propecia in canada
bactrim 1000 mg
buy suhagra online
wellbutrin generic online
augmentin tablet 625mg
baclofen canada
best price augmentin
suhagra 50
propranolol buy uk
amoxicillin 125
azithromycin us
fluoxetine 20mg
can i buy amoxicillin over the counter in australia
budesonide over the counter
gabapentin 5027
azithromycin prescription australia
gabapentin brand
buy finasteride no rx
toradol for back pain
buy doxycycline without rx
buy augmentin over the counter
albuterol mdi inhaler
baclofen 10 mg cost
sildenafil india paypal
I’m gone to tell my little brother, that he should also pay a quick visit this blog on regular basis to take updated
from hottest gossip.
doxycycline 1000mg
propecia india online
generic albuterol
levitra cheapest price
diflucan australia over the counter
how much is albuterol in canada
can you buy doxycycline
atarax 25 mg tablet price
12.5 zoloft
buy tretinoin uk
neurontin 100mg tablet
robaxin medicine
baclofen prescription uk
inderal 40 price
budesonide 80
20 mg lisinopril tablets
cialis medication online
tretinoin buy mexico
vermox canada otc
best tadalafil brand
usa pharmacy
buy allopurinol 300 mg online uk
trazodone 4
generic propecia uk
propranolol 10 mg tablet price
clonidine 0.1mg tablets
buy phenergan
20 mg propranolol
where can i buy amoxicillin online
how much is neurontin pills
trazodone price in india
propecia for sale online
lyrica 500 mg
buy levitra canadian pharmacy
propecia canadian pharmacy
can you buy albuterol over the counter in canada
clonidine for pain
atarax 100mg tablets
online pharmacy dubai
where can i get trazodone
diflucan tabs
augmentin 650
generic effexor xr
diflucan india
best viagra in india
lexapro 10mg generic
where to buy clomid canada
antibiotics doxycycline
propecia hair growth
northwestpharmacy
diflucan over the counter
aviator oyunu oyna para kazan
cheapest levitra australia
buy azithromycin over the counter usa
clonidine uk buy
clonidine australia
1g amoxicillin
where to order generic viagra
synthroid 10 mcg
SightCare supports overall eye health, enhances vision, and protects against oxidative stress. Take control of your eye health and enjoy the benefits of clear and vibrant eyesight with Sight Care. https://sightcarebuynow.us/
propranolol otc uk
augmentin 125 mg price
vermox 100mg online
güncel programlar arşivi sitemizde bulunmaktadır
amoxil capsule 500mg
antalya hotel to airport transfer services Mestlife transfer
ventolin discount
amoxicillin 625mg price in india
effexor 375 mg
oral ivermectin cost
celexa rx
150 mg wellbutrin
175 effexor
clonidine tablet 0.1 mg
cheap and quality clinic for hair transplant in turkey
buy synthroid
neurontin 800
order accutane online australia
can you order accutane online
purchase clomid 100mg
buy generic synthroid online
how can i get doxycycline
buy lyrica no prescription
stromectol ivermectin
desyrel prices
where to buy robaxin 750
amoxicillin india
lexapro pill
can i buy allopurinol in uk
cost of synthroid 125 mcg
citalopram price
40 mg lasix
accutane rx
accutane drug
inderal la
order lasix without presciption
overseas pharmacy no prescription
synthroid 15 mcg
zoloft online no prescription
clonidine 25 mg
diflucan 150 capsule
synthroid generic brand
ventolin prescription australia
neurontin 800
bactrim 400
ivermectin 2
buy hydroxychloroquine uk
lioresal medication
cheap xenical
prednisone price in india
can you buy ventolin over the counter in canada
ivermectin generic
best price viagra 50 mg
buy suhagra 50mg
vermox 500mg for sale
clonidine price canada
prozac brand name cost
silagra
bactrim cream price
robaxin online uk
metformin online usa
where can i buy trazodone online
diflucan online pharmacy
tretinoin cream 1mg
doxycycline online pharmacy canada
colchicine generic cost
doxycycline price south africa
trazodone tabs
generic amoxicillin over the counter
levitra singapore
best online pet pharmacy
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Ahaa, its fastidious conversation on the topic of this post here at this weblog,
I have read all that, so now me also commenting at this place.
bupropion tab
gabapentin 100mg generic
can you buy doxycycline over the counter in canada
diflucan prescription
albuterol 0.043
propranolol 40 mg
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
fildena 100 online
over the counter clonidine
phenergan 20 mg
colchicine 0.6 mg tablet
cost of bactrim
diflucan over counter
clomid 50mg tablet online
doxycycline 100mg dogs
doxycycline prescription discount
lyrica tablets 150mg
augmentin 175 mg
prozac 10 mg tablet
international pharmacy no prescription
levitra price australia
buy amoxicillin usa
tsh synthroid
prescription viagra australia
cheap cialis 100mg
augmentin 875 mg generic
400 mg fluoxetine
buy propecia us
generic silagra
synthroid online without prescription
buy paroxetine tablets
inderal 10 mg medicine
prednisolone tablets over the counter
best price for synthroid 50 mcg
fluoxetine 8 mg
buy tretinoin 1 online
amoxil price
generic accutane canada
stromectol online canada
combivent for sale
generic lyrica 2018
buy synthroid 75 mcg
plaquenil 500 mg
lexapro price canada
buy metformin 500mg tablets
zoloft drug
buy silagra online uk
baclofen 10 mg tablets
tretinoin 0.05 cream uk
generic propecia best price
atarax 10mg uk
discount generic propecia
clonidine 50 mg
baclofen 30 mg
amoxicillin order online uk
tadalafil 20 mg buy online
doxycycline 40 mg capsules
finasteride 5mg pill
allopurinol 300 tablet
hydroxychloroquine tab 200mg
order clonidine online
albuterol 90 mcg cost
clonidine 0.1mg
budesonide uk
generic orlistat online
prinivil 25 mg
phenergan 25mg nz
lioresal cheap
where can i buy neurontin online
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/de-CH/join?ref=V2H9AFPY
can i buy cialis over the counter canada
buy generic zoloft
doxycycline hyclate capsules
levitra in india brand
reputable indian pharmacies
budesonide 3 mg price india
güvenilir bahis siteleri
clonidine prescription medication
purchase effexor online
sildenafil women
azithromycin 1
where to buy azithromycin over the counter
sildenafil 20 mg
80 mg viagra
buy levitra canada online
brand name levitra cost
amoxil 500 mg brand
gabapentin pill
trazodone brand
cheapest price for amoxicillin
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
budecort 400
lyrica canada online
synthroid india
buy amoxicillin online mexico
paroxetine tablets in india
where can i buy albuterol over the counter
propranolol la
atarax generic cost
clonidine rx
silagra 100 mg tablet
paxil 10 mg price
canada levitra buy online
baclofen brand name in india
trazodone online prescription
diflucan tablets buy online
cheapest levitra
sildenafil purchase
augmentin tablets
SightCare supports overall eye health, enhances vision, and protects against oxidative stress. Take control of your eye health and enjoy the benefits of clear and vibrant eyesight with Sight Care. https://sightcarebuynow.us/
hi! Микрозаймы на Tinkoff
https://zaimy-na-kartu-tinkoff.ru/
clonidine 0.2 mg tablets
quineprox 0.5
diflucan 50 mg
generic 100 mg levitra
viagra 20
zoloft tablets 250mg
prozac without a prescription
online rx diflucan
atarax antihistamine
propecia brand
propecia 0.5 mg
How does a hair dryer generate such a robust gust of
air in the primary place? Protective screens – When air is drawn into the hair dryer as
the fan blades flip, other things outside
the hair dryer are additionally pulled towards the air
intake. Next time you and dad watch a movie, it will make issues much easier.
The more occasions your blog readers click on those ads, the more cash you may make via the advert service.
This article discusses a quantity of ways to make money on the web.
If you’re looking to make a fast buck, your
best wager is to sell something or issues your own which can be of value.
Those opinions – and the best way corporations address them – could make or break an enterprise.
In case your portable CD player has an AC enter, you may
plug one finish of the adapter into your portable player and the opposite finish into your automobile’s cigarette lighter and you have a power supply.
This fully alerts you, the reader, to the probability that in the following paragraph you’ll learn the main twist in the
argument put forth, making it entirely doable that you’re going to have no curiosity in reading additional.
metformin australia
zoloft prescription price
baclofen pills
price of effexor xr
600 mg trazodone
Thank you for sharing your info. I really appreciate your efforts and I am waiting
for your further write ups thank you once again.
which online pharmacy is the best
cheap vermox
ivermectin 12 mg
citalopram hydrobromide 40 mg
propecia generic uk
diflucan 1140
buy cheap generic levitra online
hydroxychloroquine drug
Belek Transfer: Experience comfort as you travel to Belek’s golf courses and scenic landscapes.
how to get tadalafil online
stromectol tablets for humans
levitra usa price
how much is lyrica
buying cialis
synthroid 0.05mg cost
SEO, organik trafik elde etmede kritik bir unsurdur.
medicine bactrim
diflucan 150 mg tablet in india
buy sertraline online
levitra buy australia
buy lisinopril 10 mg
prednisolone sod
buy over the counter clomid
prednisolone 10 mg daily
synthroid 50 mcg
zoloft prescription price
can you buy atarax over the counter
paroxetine price uk
buy cheap zithromax
For example, Valorant matches offer an average of 36 betting options.
budesonide cream
ivermectin generic name
mebendazole tablets
12, 2007, the Give 1 Get 1 (G1G1) program allowed U.S.
As of September 2007, about 7,000 laptops were being tested
by youngsters around the globe. The OLPC Foundation aims to provide these laptops to
hundreds of thousands of youngsters throughout the developing world in order to enhance their education and their quality of life.
The XO laptop computer’s design emphasizes cheap, durable development that may survive a variety of climates and the rigors of the creating world.
The 12 months 2009 confirmed us a number of other innovations, together with low cost, efficient ways to trace your
bodily exercise and better methods to cool down after a run, too.
As you progress throughout the day, Fitbit tracks how much physical activity you performed.
Because the Fitbit works best for walking motion and isn’t waterproof, you cannot use it for activities comparable to bicycling or swimming; nonetheless, you
can enter these actions manually in your online profile.
Should you plan to watch HD, you’d probably use an HDMI connection, although component,
S-Video or VGA are also prospects, relying in your particular system.
More laptops needs to be obtainable on the market in the future, and more developing nations can be ready to apply to affix the G1G1 plan.
buy doxycycline australia
buy clomid online uk
generic robaxin 500mg
clonidine 0.3
where to buy colchicine canada
bactrim price
Берите Микрозаймы онлайн на Tinkoff
https://zaimy-na-kartu-tinkoff.ru/
robaxin gold
azithromycin 10 mg
Hi, I think your website might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine
but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping.
I just wanted to give you a quick heads up!
Other then that, amazing blog!
synthroid 137 price
dapoxetine canada
predisone with no presciption
buy clonidine usa
online pharmacy non prescription drugs
azithromycin 600 mg price
diflucan price canada
buy cialis 2.5 mg online
diflucan for sale online
dapoxetine price australia
where can i buy ventolin over the counter
omega proje lojistik olarak güzel bir yazı için teşekkürler ağır nakliye taleplerinizi bekleriz
diflucan online paypal
synthroid 0.0125 mg
buy india generic levitra online
buy fildena 150 online
diflucan online without prescription
buy clomid discount
can you buy generic viagra uk
trazodone 50 mg price
where to buy propecia cheap
propranolol la
vermox drug
doxycycline tablets cost
cost for propecia
buy atarax 25 mg
cheapest generic bactrim (sulfamethoxazole / trimethoprim) without a persription
propecia buy usa
ivermectin buy online
augmentin canada pharmacy
bactrim tablet 400mg
buy finasteride
I like the helpful information you provide in your
articles. I’ll bookmark your blog and check again here
frequently. I am quite certain I’ll learn a lot of new stuff right here!
Best of luck for the next!
generic lasix online
buying tadalafil in mexico
doxylin
diflucan 150 mg otc
cost doxycycline tablets
bactrim 200 mg tabs
doxycycline australia
can i buy doxycycline over the counter in south africa
canadian pharmacy world coupon
canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg
can you order lisinopril online
buy paxil india
prednisone 30g
prozac generic
generic ivermectin
silagra 50 mg tablet
lasix no prescription
fildena 100 canada
Today, while I was at work, my sister stole my iphone and tested to see
if it can survive a 30 foot drop, just so she can be a
youtube sensation. My iPad is now broken and she has 83 views.
I know this is completely off topic but I had to share it
with someone!
how to get tretinoin prescription
bupropion 250 mg
vermox online uk
robaxin 8 mg daily
generic cialis online fast shipping
buy doxycycline online without prescription
cialis for sale in mexico
where to get viagra online
doxycycline 20 mg
propecia compare price
citalopram pills 20 mg
amoxil 500 pill
1 viagra pill
propecia usa buy
buy diflucan 150 mg online
trazodone hydrochloride 100mg
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
First off I want to say superb blog! I had a quick question that I’d like to ask if you don’t mind.I was curious to find out how you center yourself and clear your mind priorto writing. I have had trouble clearing my thoughts in getting my ideas out there.I do take pleasure in writing however it just seems like the first10 to 15 minutes are wasted simply just trying to figure out how to begin. Any ideas or hints?Appreciate it!
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
cheap effexor
augmentin 375 mg price
generic propecia from india
ivermectin lotion for lice
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
See more pictures of money scams. It was once that with a view to obtain an ultrasound, you had to visit a physician who had the space and cash to afford these massive,
costly machines. Google will provide on-line storage
providers, and some communities or schools can have servers with
massive quantities of laborious drive area. When Just Dance III comes out in late 2011, it is going to also be
launched for Xbox’s Kinect in addition to the Wii system, which suggests dancers won’t even want
to hold a remote to shake their groove factor. SRM Institute of Science and Technology (SRMIST) will conduct the Joint Engineering Entrance Exam — SRMJEEE 2022, phase 2 exams on April 23 and April 24, 2022.
The institute will conduct the entrance exam in on-line distant proctored mode.
However, future USB-C cables will have the ability to charge gadgets
at up to 240W using the USB Power Delivery 3.1 spec.
Note that only out-of-specification USB-C cables will attempt
to pass energy at levels above their design. More energy-demanding
fashions, like the 16-inch M1 Pro/Max MacBook Pro, require greater than 60W.
If the maximum is 100W or much less, a succesful USB-C cable
that helps USB-solely or Thunderbolt 3 or 4 data will suffice.
neurontin 800 mg tablets
clonidine for ptsd
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
tretinoin prices
Basic symbols will probably be very acquainted to anybody who has
played a fruit machine earlier than, with single, double and triple BAR icons, golden bells, Dollar indicators and purple 7’s filling the reels.
Most people right this moment are familiar with the concept: You’ve gotten things you do not essentially want however others are keen to purchase, and you’ll auction off the items
on eBay or other online public sale websites.
They might even lead us into a new industrial age the
place we cannot need factories and assembly strains to supply
many items. Not everybody qualifies, but in case your application will get denied, try another
company — it might have much less rigid restrictions.
Including any of those details on a Facebook wall or standing replace might not appear like an enormous deal,
however it may present an identification thief with the last piece of the puzzle needed to hack into your checking account.
The thief might even use the sufferer’s identification if
she is arrested, causing an innocent person to assemble
a lengthy criminal record. It seems like each time we flip around,
they’re inflicting epidemics and doing good in our guts and
fixing quantum equations.
->>>>>>>>>>>>>заговор на кровь читать из пальца слова<<<<<<<<<-
______________приворот на волос девушки читать в домашних условиях _____________
приворот на воду на любовь женщины читать
как отменить приворот, а также:
->>>>>>переворот парня на любовь
->>>>>>как приворожить мужчину месячной кровью
->>>>>>приворот на растущую луну на любовь мужчины
->>>>>>чистка от приворота свободное сердце
generic paxil prices
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
albuterol tablets price
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
glucophage 500 online
vermox tablets uk
prednisolone pack
cheap fildena
I’m so impressed with your expertise on this topic. Thank you for sharing your knowledge with us.
hydroxychloroquine buy uk
mail order pharmacy no prescription
final cut pro indir
effexor 150
levitra generic price
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
aviator oyunu sitemizden oynayabilirsiniz
propranolol prescription australia
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
30 mg propranolol
This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
papaz büyüsü yaptırmak için http://www.medyumnazar.com bekliyorum
ventolin cost usa
inderal tablets 40mg
ivermectin pills human
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Information on the load, availability and pricing of each model was not offered on the web
site as of this writing. Several models with elaborate data displays
might be found on-line from about $20 to $70, though reviews of
many of them include a whole lot of 1- and 2-star warnings
about build high quality; buy from a site that permits straightforward returns.
More power-demanding models, like the 16-inch
M1 Pro/Max MacBook Pro, require greater than 60W.
If the utmost is 100W or much less, a capable USB-C cable that helps USB-only or Thunderbolt three or
four data will suffice. They constructed their very own community,
inviting users to join and share their information about knitting, crocheting
and more. With information of the pace of a peripheral and
your unknown cable, plug it into your Thunderbolt 3 or 4 succesful Mac.
The Mac mini additionally has two Thunderbolt/USB four buses, which,
confusingly sufficient, additionally use the 2 USB-C ports:
relying on what you plug in, the controller manages knowledge over the
suitable normal at its maximum information fee. Apple’s “USB-C Charge Cable,” for instance, was designed for top wattage however only
passes data at USB 2.0’s 480 Mbps.
amoxicillin 1 gram
price for amoxicillin 875 mg
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Берите Микрозаймы на Tinkof
https://mikrozaimy-na-tinkoff.ru/
Now, let’s take a more in-depth look on the credit card fraud drawback and the way chip
and PIN cuts back on theft. The worldwide commonplace for bank card safety is
named “chip and PIN,” and it’s now in American wallets.
Netflix has created a site referred to as “Living with Spoilers,” in which they propose that spoilers are fun, and we must always embrace somewhat than shun them.
American inventors have created a few of crucial technological breakthroughs in the
history of humankind. In 1987, the American Marketing Association started the Edison Awards to encourage and
recognize inventors. His work impressed the annual Edison Awards.
The Edison Achievement Award goes to a enterprise govt who stresses progress in product improvements, and the Green Award is introduced to organizations
that stress ecologically sound merchandise. Annually, the Edison Awards
honor select people and organizations for his or her contributions to product innovation and economic development.
Keep studying to see 10 products, listed in no
particular order, that have been nominated for the 2010 Edison Awards.
The company claims some customers will see heating expenditures drop by more than 60 %, which might save tons of of
dollars in a single yr.
discount doxycycline
doxycycline order online uk
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
levitra 10mg tablets
escrow pharmacy canada
vermox otc
where can i purchase zithromax online
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
desyrel medication
lyrica 225 mg cost
fluoxetine 10 mg canada
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
fildena 50 mg
amoxicillin cap 500mg price
propecia.com
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this
matter to be actually something which I think
I would never understand. It seems too complex and extremely broad for me.
I’m looking forward for your next post, I’ll try to get the hang of it!
buy amoxicillin 500mg capsules uk
buying retin a online uk
generic finasteride 1mg no prescription
diflucan 150 price
reklam ajansı bursa We will explore how advertising has undergone a metamorphosis from past to present, how it has evolved from traditional methods to digital strategies and how advertising agencies have played a critical role in this process.
how to get real viagra online
medication amoxicillin 500mg
trazodone 5 mg
This blog will work on all devices. Modern in each detail, convenient for work on any gadgets
– HotelPro template of the booking software. Therefore, you will need to create an software that permits soccer fans to comply with their passion and attract increasingly members to their group.
The football group is one of the most important in the world.
The London Marathon can be one of racing’s largest fundraising
occasions. The G-Slate runs on the Android 3.0 (Honeycomb) working
system, and it was one in every of the first tablets
to do so. Instead, they’d first register an account on the dealership’s Web site.
It could be your first clue that someone has already stolen your identity.
In this text, we’ll find out how identity thieves steal or rip-off their
manner into your monetary life, and outline the very best ways to keep it from taking place.
And plenty of of those corporations provide ways you possibly can earn money utilizing your own possessions or time.
This template is suitable for any working system, subsequently, utilizing this template is as easy as booking a lodge room.
3 mg clonidine
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
how much is neurontin
propecia pharmacy prices
synthroid coupon brand
diflucan generic price
I appreciate the effort you put into creating informative content like this.
reklam ajanslarıı bursa is the one of the biggest digital pr company in the world. and ı really thanks to admin to gave us to permisson to write our comment to here.
albuterol online uk
Today, I went to the beach front with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed.
There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear.
She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is entirely off topic but I
had to tell someone!
paxil 20 mg tablet
atarax 25 mg
generic levitra us
zoloft rx discount
buy doxycycline 200 mg
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
where can i get doxycycline pills
synthroid costs us
zithromax 250 mg tablet
Since Bursa sosyal medya ajansları are the face of the brand in the digital world, it is of great importance to manage it correctly. The basis of this process is to know your target audience well.
retin a 0.1 price
But as a substitute of utilizing excessive-pressure gasoline
to generate thrust, the craft uses a jet drive to create a robust stream of
water. The coverage on gasoline differs between firms as properly.
The TDM Encyclopedia. “Car sharing: Vehicle Rental Services That Substitute for Private Vehicle Ownership.” Victoria Transport Policy Institute.
University of California Berkeley, Institute of Transportation Studies.
Santa Rita Jail in Alameda, California (it is near San Francisco, no surprise) makes use of an array of fuel cells, solar panels, wind turbines and diesel generators to power its very
personal micro grid. However, many nonprofit car-share organizations are doing
quite effectively, similar to City CarShare in the San Francisco Bay
Area and PhillyCarShare in Philadelphia. So that you may be asking yourself,
“Wow, if car sharing is so fashionable and simple, should I be doing it too?” To search out
out more about who can profit from sharing a car and to find
out about easy methods to contact a automobile-sharing
company, proceed to the next web page.
Then you can take the motherboard again out, place the spacers, and put the motherboard
in on high of them. While an appointment might have a particular time
limit, that does not essentially mean the business can accommodate two appointments again to again. But replacing one or two parts, especially the oldest half or the one you’ve got decided is
causing a bottleneck, can provide impressive performance improvements while
remaining value effective. It has been a while since I cracked a computer open and explored its innards,
however this endeavor has impressed me to, at
the very least, upgrade the RAM in my laptop computer.
Case, Loyd. “The way to Upgrade Your Graphics Card.” Pc World.
Or would you like to make use of a graphics card on the motherboard to maintain the worth and measurement
down? A pleasant midrange card can greatly improve performance for a couple of hundred dollars, however
you too can discover a lot cheaper ones that aren’t bleeding-edge that will fit your wants just effective.
buy viagra 500mg
can i order amoxicillin online
cialis 10mg tablets price
suhagra 10 mg
lisinopril 5 mg coupon
atarax 25 mg capsule
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
vermox 500 mg tablet
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
tadalafil tablets 10 mg online
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
where can i buy trazodone
bupropion buy uk
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Diyarbet
Our mechanism’s effectivity is within a continuing fraction of the a posteriori
optimally efficient solution. Our mechanism’s technical core is a variant of the online weighted bipartite matching downside where not like prior variants by which one
randomizes edge arrivals or bounds edge weights, we might
revoke previously committed edges. Further, it bounds the earnings of speculators who’re in the sport to acquire the
cancellation fees. Our model allows the seller to cancel at any time any reservation made earlier, by which case the holder of
the reservation incurs a utility loss amounting to a fraction of her value for the reservation and can also receive a cancellation fee from the vendor.
They still hold if we exchange objects with components of a matroid and matchings with impartial
sets, or if all bidders have additive value for a set of gadgets.
A vendor will display a set of slots at some point T in the future.
Many advertisers (bidders) use Internet methods to buy display advertisements on publishers’ webpages or on conventional media comparable to radio, Tv
and newsprint.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ . Diyarbet
synthroid tablets
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
doxycycline tablets in india
hydroxychloroquine uk
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Artık Türkiye’nin her yerinde aktif
generic diflucan fluconazole
Микрозаймы на карту
https://minizajmy-online.ru/
colchicine brand name australia
over the counter colchicine medication
how much is amoxicillin 500 mg
clonidine 0.2mg tab
FlowForce Max is an innovative, natural and effective way to address your prostate problems, while addressing your energy, libido, and vitality. https://flowforcemaxbuynow.us/
AquaPeace is an all-natural nutritional formula that uses a proprietary and potent blend of ingredients and nutrients to improve overall ear and hearing health and alleviate the symptoms of tinnitus. https://aquapeacebuynow.us/
cheap propecia australia
clomid no prescription
We are a UK-based staff with years of experience to assist you get arrange.
diflucan 50mg capsules
inderal 40 mg tablet
where to buy allopurinol tablets
augmentin 125mg
ivermectin for humans
baclofen 50 mg
amoxicillin buy online australia
150 mg clomid
levitra canada cheap
neurontin 100 mg cap
Amiclear is a dietary supplement designed to support healthy blood sugar levels and assist with glucose metabolism. It contains eight proprietary blends of ingredients that have been clinically proven to be effective. https://amiclearbuynow.us/
retin a online india
propecia buy india
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
1000 amoxicillin
clonidine for blood pressure
Abdomax is a nutritional supplement using an 8-second Nordic cleanse to eliminate gut issues, support gut health, and optimize pepsinogen levels. https://abdomaxbuynow.us/
amoxicillin 5
BioVanish a weight management solution that’s transforming the approach to healthy living. In a world where weight loss often feels like an uphill battle, BioVanish offers a refreshing and effective alternative. This innovative supplement harnesses the power of natural ingredients to support optimal weight management. https://biovanishbuynow.us/
diflucan medicine
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
buy phenergan online australia
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
tadalafil 40 mg price
buying levitra online from canada
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
baclofen pill
canadian pharmacy levitra 20 mg
where can you get robaxin
capsule online pharmacy
suhagra 25
augmentin 250 125 mg
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this web site before but
after browsing through many of the articles I realized it’s new
to me. Nonetheless, I’m definitely pleased I stumbled upon it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back frequently!
propranolol cost canada
pharmacy websites
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Diyarbet
doxycycline 10mg tablets
fluoxetine 60 mg capsules
colchicine no prescription
clomid 50mg buy uk
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
buy inderal online without prescription
Truly no matter if someone doesn’t understand after
that its up to other viewers that they will help, so
here it takes place.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
fildena canada
combivent respimat cost
buy albuterol without a prescription
citalopram 10mg tablets price
can i buy viagra from india
how much is accutane in canada
clomid for sale online
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Diyarbet
robaxin muscle relaxer
generic propecia safe
doxycycline 100mg tabs
clonidine 0.1 mg tab purepac
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
buy atarax
buy cheap generic levitra online
price of propecia in south africa
200mg trazodone
25mg prednisolone
However, users should upgrade to a paid “gold” membership in order to view individuals’s
particulars or send them a message. A message middle helps users contact each other with
out being forced to offer out their private e-mail
addresses. The computer is not dependent on a router being nearby
both. Additionally, while I remember being excited as I discovered all of the computerlike things I could do
on my phone, the tablet’s bigger kind appears principally irksome, as
a result of it reminds me of all of the stuff I wish to do with
it, but can’t. Since these companies solely rely on having a dependable phone, web connection and web browser, businesses have seemed more and more at hiring residence-based
mostly employees. Keep your password to yourself, it doesn’t matter what, and also you by no means have to fret about it.
Even sharing the password with a pal so he or she can go surfing and test something for you can be a danger.
phenergan 100mg
neurontin coupon
lyrica 750
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
lexapro 5mg generic
lioresal price
effexor discount
vardenafil tablets 20 mg price
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Diyarbet
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
propranolol 5 mg coupon
lasix 200 mg
zoloft online canada
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
finasteride prostate
suhagra tablet 50 mg
robaxin 100mg tablets
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
cialis prescription discount
inderal cost
fildena 100 mg
buy cheap augmentin
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
But each cable Tv subscriber pays an average of $1.72 a month to obtain Fox News.
In line with a survey carried out late last yr, about 14% of
cable Tv subscribers watch Fox News often. Fortnite providers will likely be disabled beginning at 11:30pm PDT on July 19, or
2:30am EDT / 7:30am BST on July 20 – an hour earlier
than the final round of downtime. Fortnite v17.20 is slotted
for launch on July 20. In preparation for the replace, services might be disabled starting at approx.
Its missing features, like Nintendo TVii, will arrive
publish-launch. An FM modulator would allow even an older car radio,
like this one, to play your CDs by means of the automobile’s audio system.
You play one of many adventurers who must reply the call of an embattled
queen to guard her kingdom, Fahrul, from impending doom after its king is murdered.
Multi-Service enterprise online contains diverse business sectors corresponding to well being-care, laundry, home providers, grocery supply, logistics, and many others.
Because all these service sectors could be neatly met into
one cellular app, the overall workflow can be gainful for entrepreneurs.
robaxin 750 coupon
generic bactrim
diflucan capsule price
baclofen 2
cheapest pharmacy to fill prescriptions with insurance
phenergan 25mg price
cheap scripts pharmacy
Reliable and Professional: Your Partner for Ankara Cleaning
Efficient Post-Construction Cleaning in Ankara – Ready When You Are
neurontin 600 mg capsule
canadian pharmacy online levitra
propecia gel
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
These range from 2x to 8x for the prospect of much larger prizes.
The Komodo Dragon slot machine’s 50 paylines are fixed
and you’ll choose from a range of wagers beginning from 0.25 to
a max bet of 50.00. It’s an honest choice in your average gambler but it most likely won’t appeal to the excessive rollers.
The line wins are multiplied with the credit you choose to guess per line.
You select the variety of traces and wager per line which make up the entire
win. It’s a fearsome ally as it lands in stacks for additional chances at multiple
win strains. It’s attainable to attain a full matrix of
dragon wilds for bumper prizes. Wilds can act as others if they will then full
a win, and with sufficient in view, you may easily gather multiple prizes on the final spin in a sequence.
Fans and producers worked exhausting to avoid wasting the sci-fi sequence “Quantum Leap” from the notoriously bad 8 p.m.
You’ll also get the chance to land stacks of wilds on a good
multiplier so this fearsome creature might turn out to be your best buddy.
diflucan pill cost
vermox in usa
stromectol 3 mg price
cost of clonidine
buy doxycycline 50 mg
clonidine 3 mg
ankarada villa temizliği denilince ilk akla gelen temiz bir ev
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ . Diyarbet
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Diyarbet
This information is priceless. When can I find out more?
buy generic propecia 5mg online
doxycycline brand name in india
propeciaoffers.com
amoxicillin 375
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
how much is zoloft
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
how much is levitra in canada
propranolol 40 mg tablet brand name
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
colchicine probenecid 0.5 500
tadalafil 40 mg from india
plaquenil 100mg tablets
glucophage medication
finpecia 1 mg
amoxicillin price in usa
ventolin price canada
how much is lisinopril 20 mg
prozac generic price
synthroid 125 mcg price
buy 40 mg lisinopril
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
how to get female viagra pill
robaxin 599 cost
can you buy zoloft
synthroid 0.88 mcg
prozac discount coupon
buy stromectol pills
I’m so impressed with your writing skills. Thank you for sharing your talent with us.
how to get finasteride prescription
gabapentin without script
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
female viagra for sale in uk
buy accutane online usa
azithromycin generic
Thank you for being such a beacon of light in this world. Your work is making a difference.
Займы на карту
https://mikrozaimy-na-kartu.ru/
where can i purchase accutane
30 mg propranolol
Thank you for being such a beacon of light in this world. Your work is making a difference.
ventolin inhaler for sale
Hello are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new
to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and create my own. Do you require any
html coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly
appreciated!
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . yaşam ayavefe Yaşam Ayavefe
clonidine 137
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
propranolol uk
clonidine price
cheap propecia canada
where to buy neurontin
colchicine buy online uk
AMC, the little community that could, proved it was aggressive with larger, extra experienced networks when “Mad Men” and “Breaking Bad” won Emmy after Emmy.
The award can also be a badge of honor for smaller networks.
One necessary thing to look for in a video capture card is the power to accept an MPEG-2 transport stream in each DBV and
ATSC, sometimes known as digital hardware playing cards.
It could look strange, but the introduction of the Dyson Air Multiplier means house followers
will never be the identical. Meaning we know upfront the defined category classification (intent).
That’s the easiest option to know that the cardholder is the real proprietor of the card.
If you are contacted by a merchant or assortment company about an unpaid invoice
that you recognize you should not be charged for, don’t simply
hold up. Middle-of-the-road motherboards: Ranging in price from $50 to
$100, these are one step up from a budget motherboards.
The increase in temperature also makes it simpler for the individual molecules in a water droplet to overcome
their attraction to one another and move from
a liquid to a fuel state.
doxycycline 100mg capsules price
augmentin 875 prices
best price paroxetine
cialis 80
buy propecia online australia
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
toradol tablets
bursa reklam ajanslaır arasında tercih edebileceğiniz en yeni ve en sağlam reklam ajansı için iletişime geçmekten çekinmeyiniz.
purchase clonidine online
levitra daily
prednisolone purchase uk
generic for doxycycline
buy accutane from india
sekabet
diflucan singapore pharmacy
pharmacy rx
augmentin prescription online
diflucan pill uk
toradol tablets price
diflucan 200 mg capsules
prozac 5 mg
zoloft prescription price
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
levitra cost mexico
lisinopril 25 mg tablet
otc albuterol
rx sildenafil
price of clomid in uk
For example, a car dealership would possibly enable clients to schedule a service middle appointment on-line.
If you’re a sports activities automotive buff, you may
go for the Kindle Fire, which runs apps at lightning velocity with
its high-powered microprocessor chip. Not solely
do many members pledge to boost appreciable funds for a variety of charities,
a portion of each runner’s entry fee goes to the marathon’s personal London Marathon Charitable Trust, which has awarded over 33 million pounds ($5.Three million) in grants
to develop British sports and recreational facilities. This
stuff concentrate the solar’s energy like a
classy magnifying glass hovering over a poor, defenseless
ant on the sidewalk. Microsoft, Apple and Google have
been in some excessive-profile squabbles over time.
There have been a number of cases the place victims had been left on the hook for tens of thousands of dollars and spent years trying to restore their credit, but they’re distinctive.
canadian pharmacies not requiring prescription
price of zoloft
can i buy doxycycline over the counter uk
trazodone 50mg capsules
buy viagra paypal online
online baclofen
fildena 25
finasteride 0.5
medication paroxetine 20 mg
can you buy amoxicillin over the counter in mexico
retin a uk
generic tadalafil pills
suhagra 50 mg
clonidine 0.1mg tablets
drug toradol
buy silagra online uk
ivermectin 9mg
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
ventolin canada
best canadian pharmacy to order from
plaquenil over the counter
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
can you buy azithromycin online
atarax 10 mg tablet
can you buy accutane over the counter in canada
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
amoxicillin mexico buy
tretinoin 08
80 mg accutane daily
where can i buy cheap viagra
order cialis online canada
can you buy doxycycline over the counter in mexico
fildena india
tadalafil 20 mg online india
drug neurontin 20 mg
doxycycline prices
Fast-ahead to July 2010 when Tv critic Alessandra Stanley published
a now-infamous article about “Mad Men” through which
she talked about key plot factors of the present’s fourth season With out a
spoiler alert warning. In 2011 CBS sued a man named Jim Early for posting spoilers about
the truth show “Survivor” on a web site referred to as
“Survivor Sucks.” The spoilers accurately gave away key information about two seasons of the show.
However (SPOILER ALERT), though the Thebans received the battle,
they in the end sued for peace because their leaders died.
In that spirit, if you’ve just crawled out from beneath the proverbial rock and are questioning whether Frodo
ever does get that ring into Mount Doom, the reply is (spoiler): Type of.
Plays get a month, books three months and operas
a century. Barnes & Noble gives greater than twice as many
digital books as Amazon. That permits you to spice up the storage capacity of the machine
to 36 megabytes, greater than twice that of the basic iPad.
synthroid prescription online
generic albuterol cost
buy doxycycline 200 mg
accutane price australia
cheapest paroxetine online
37.5 mg zoloft
diflucan cap 150 mg
can you buy albuterol otc
allopurinol 300 mg daily
cheap diflucan online
zoloft online uk
allopurinol over the counter in usa
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ . yaşam ayavefe Yaşam Ayavefe
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader. Diyarbet
bactrim 800mg 160mg
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
cialis lower blood pressure
cialis lower blood pressure
allopurinol tablets for sale
betforward
mail order propecia
0.4 mg clonidine
xenical tablets
augmentin 1000 mg price in india
suhagra 100 online
buy generic prozac
prednisone 0.5 mg
buy online diflucan
allopurinol 50
Great work! That is the type of information that are supposed to be shared around the web.
Shame on the seek engines for now not positioning this publish upper!
Come on over and talk over with my site . Thank you =)
synthroid prescription uk
dapoxetine cost
clonidine for anxiety
propecia india buy
finpecia 1mg price in india
prednisolone to buy
Smart watches supply some PDA functions in a wristwatch kind factor.
A quantity of various operating methods, including Windows Mobile Pocket
Pc Phone Edition, the Palm OS, the Blackberry OS for Blackberry
good phones, and the Symbian OS for smart telephones from Panasonic, Nokia,
Samsung and others. Pocket Pc is the generic identify for Windows Mobile PDAs.
Also, Pocket Pc units typically require extra resources and have even more RAM.
Companies use internal methods to allocate sources and assign duties for work within the company itself.
Many corporations permit customer support agents to do business
from home. When coupled with an inner scheduling system,
homeowners can steadiness customer wants and employee
satisfaction. Identity thieves can make use of
every kind of personal info, similar to your mom’s maiden name, where you went
to school or the identify of your pet. Trabish, Herman K.
“CSP and PV Solar Make Each other More Valuable.” GreenTech Solar.
The Psion Organiser II, released in 1986, was particularly common and more than half 1,000,000 have
been sold.
diflucan singapore pharmacy
synthroid 20
zoloft.com
accutane rx
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.info/pt-PT/join?ref=V3MG69RO
doxycycline hyclate
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
accutane online australia
tadalafil 6mg
atarax 50 mg tablet
where can you buy propecia
zoloft coupon
doxycycline 1000mg
baclofen 300 mg
lasix 20 mg
doxycycline medication
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Diyarbet
diflucan over the counter no prescription
0.63 mg albuterol
trazodone tablets
buy atarax 25mg online without rx
baclofen 5 mg 1mg
buy generic accutane online
atarax price canada
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
amoxicillin cost canada
No matter if some one searches for his essential thing, thus he/she wishes to be available that in detail,
therefore that thing is maintained over here.
neurontin canada
Reviews for the RX 6700 XT have began to pop up online, exhibiting us
the actual-world performance provided by the $479 card.
Cloud/edge computing and deep studying significantly enhance efficiency of
semantic understanding systems, where cloud/edge computing offers versatile,
pervasive computation and storage capabilities to help variant purposes, and deep learning fashions may
comprehend text inputs by consuming computing and storage resource.
With each tech development, we expect higher efficiency from the technology we buy.
Identity theft and card fraud are major issues, and some expertise
specialists say sure readers are extra secure than others.
While these models work comparatively effectively on normal benchmark datasets,
they face challenges within the context of E-commerce where the slot labels are
more informative and carry richer expressions.
State-of-the-artwork approaches treat it as a sequence labeling downside and adopt such fashions as BiLSTM-CRF.
Our mechanism’s technical core is a variant of the web weighted bipartite matching problem where unlike prior variants through which one randomizes
edge arrivals or bounds edge weights, we could revoke beforehand dedicated edges.
Our mannequin allows the seller to cancel at
any time any reservation made earlier, by which case the
holder of the reservation incurs a utility loss amounting to a fraction of her worth for the
reservation and can also obtain a cancellation fee from the seller.
order lasix online cheap
This column stands out for its own balance of data as well
as personal insight. Genuinely a satisfaction to read through.
My web page :: Cheap SR22 insurance
baclofen 30 mg capsule
lisinopril pill 5 mg
order bactrim online
amoxicillin 500mg capsules antibiotic
generic cialis 80mg
500mg amoxicillin cost
buy cheap lisinopril 40mg
suhagra 100mg tablet
cost of gabapentin 400 mg
500 mg augmentin
inderal 160 mg
propecia australia cost
sildenafil online europe
effexor 75 mg cost
cost of doxycycline canada
synthroid online pharmacy
effexor 35mg
buy baclofen india
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
colchicine no prescription
dapoxetine 30 mg tablet online purchase in india
atarax mexico
prednisone 5 mg pill
buy ventolin pills online
buy prednisolone 5mg tabs
synthroid prescription discount
If you do not like the slot machine strategy, you
can browse eating places by varied classifications or view a listing of Urbanspoon listings near
your present location. Does location have an effect on your Tv channel choice?
After which in June, leaving the home for the primary time in four months, I assumed, why did I mock myself a lot?
The wild Dracula multiplies line winnings by three – every time it appears, the
3x multiplier is triggered for each bat or Dracula that’s in view on the paylines.
The 4x multiplier gets triggered whenever you appropriately guess the next suit.
The jackpot is price 12,500 coins and will get triggered
during the utmost bet spins if you hit 5 Amulets on any of the 243
paylines which have been energetic. The bonus round will get triggered
on hitting a minimum of three scatter symbols. Along with the
bottom sport’s repeat pay function, the free game bonus
rounds even have the triple repeat pay characteristic so that
you can sink your teeth into. Lucky Count features
a somewhat generous variety of bonus rounds and sports activities a powerful repeat pay pattern.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ . yaşam ayavefe Yaşam Ayavefe
Best 3123#
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.com/join?ref=WTOZ531Y
doxycycline iv
doxycycline gel in india
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Diyarbet
buy generic atarax
where to buy vardenafil 10 mg
tadalafil 60 mg
neurontin 100
silagra online india
purchase lisinopril 40 mg
buy zyban tablets
phenergan 20 mg
effexor 225 mg capsules
can you purchase diflucan over the counter
baclofen brand name in usa
zithromax purchase
buy levitra online australia
can you buy doxycycline over the counter in mexico
legitimate online pharmacy usa
clonidine 152
azithromycin pills over the counter
can you buy prednisolone over the counter in australia
bactrim antibiotic how to buy
where to get finasteride
buy xenical without prescription
ivermectin 1 topical cream
inderal 40 mg tablet
drug gabapentin 100mg
buy gabapentin 400mg
amoxil 500mg antibiotics
colchicine 0.6 mg tablet cost
quineprox 50
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
What this means when you’re enjoying video games is that the
Xbox 360 can dedicate one core fully to producing sound, whereas one other could run the sport’s collision and physics engine.
Techniques, gear, financing, writing, monitoring
and producing have come a great distance for the reason that early days.
The choice of sizes and operating systems means that there’s an option for everybody, and reviewers have pegged each model within the Iconia
line as good all-round tablets for media viewing, gaming and
basic online pursuits, all at very reasonable costs.
Specifically, our focus is on automatic techniques that have to handle advert slots in many alternative publishers’ properties.
A few have custom-made methods that permit a nurse to cover a shift provided that she
or he meets particular skills. While the Vizio tablet might have hassle competing with tablets that have extra powerful working systems, quicker processors and greater memory capacities, there’s one gadget that is likely to
be quaking in its field: e-e book readers. The Iconia
tablet has a microSD card slot for reading reminiscence cards
and USB ports that make it easy to entry flash drives, USB card readers and portable arduous drives.
trazodone 300 mg
augmentin 400 mg
diflucan buy
maltcasino
doxycycline 500mg price
trazodone 50 mg capsules
price for generic viagra
Yaşam Ayavefe
prednisone 20 mg generic
ventolin price in usa
clonidine pill
For one factor, you get to work from your own home most of the
time. Although SGI had never designed video sport hardware before, the company was considered one of
many leaders in pc graphics technology. So, Nintendo introduced an agreement with Silicon Graphics Inc.
(SGI) to develop a new 64-bit video recreation system, code-named Project Reality.
Nintendo is a company whose very title is synonymous with video gaming.
Although most boomers are still a long way from fascinated about nursing homes,
they will be inspired to know that the Wii Fit game programs
are even finding their method into these amenities, helping residents do one
thing they never may in their youth — use a video sport to remain limber and robust.
Or possibly you need a strong machine with a lot of disk area
for video editing. Most individuals typically work from their
firm’s central location, a bodily area where everyone from
that organization gathers to alternate ideas and organize their
efforts.
synthroid 75 mcg cost
ventolin 2mg tablet
atarax usa
propecia where to buy uk
levitra 5mg tablets
cheapest propecia online
lisinopril 2019
lexapro 20 mg canada
levitra 20mg pills canadian pharmacy
trazodone 50mg capsules
cialis for women
100mg amoxicillin
prednisone from india
augmentin 600 42.9 mg
where can i get bactrim
toradol on line
buy synthyroid online
Residential and Commercial Cleaning Solutions in Ankara
atarax 10mg price
diflucan 150 mg otc
diflucan 200 mg tablet
asyabahis
doxycycline 500mg price
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
amoxicillin 500 mg prescription
augmentin usa
best price for generic viagra
order generic trazodone
buy levitra online australia
albuterol buying
price of viagra 100mg in usa
synthroid 110 mcg
synthroid 60 mcg
medical mall pharmacy
lexapro 1.25 mg
Ahaa, its good discussion concerning this article here
at this webpage, I have read all that, so at this time me also commenting at
this place.
augmentin tablet 500 mg
gabapentin 500 mg price
suhagra pills
clonidine 0.1mg tablets
buy clonidine uk
gabapentin cream in india
inderal drug
albuterol for sale usa
tretinoin buy mexico
buy propecia india
average cost for doxycycline
suhagra 50mg buy online india
where can i buy prozac
prednisone without prescription.net
buy amoxil
propecia cost
glucophage purchase online
prednisolone brand name uk
canadianpharmacyworld
allopurinol 300 mg for sale
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
cheap generic lexapro
çok güzel teşekkürler. Güvenilir bahis siteleri için siteme beklerim https://ozlemradyo.com/
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
online pharmacy same day delivery
generic levitra from india
how to get azithromycin online
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Diyarbet
bactrim 480
tadalafil generic in usa
synthroid drug
where to get cheap viagra
clonidine for anxiety
amoxicillin 500 mg pill
bactrim 800 mg 160 mg
generic zoloft cost
doxycycline 100mg india
generic amoxicillin 875 mg
glucophage 850mg price in india
how to get zoloft without prescription
buy amoxicillin online uk
cheapest price for generic viagra
order doxycycline 100mg without prescription
gabapentin 300mg capsules price
cialis 1800 mg
finasteride 1mg discount coupon
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
budesonide 3 mg price
how to buy prozac online without prescription
finpecia 1mg price in india
retinal prescription facecream
budesonide gel
ventolin capsule
medication robaxin 750
augmentin 875 mg tablets
paroxetine capsules 7.5 mg
prednisolone buy usa
hydroxychloroquine sulfate tab 200 mg
fluconazole diflucan
order vermox online
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
trazodone generic 100mg
baclofen 100mg price
First of all I want to say awesome blog! I had a quick question that I’d like to ask if you do not mind.
I was curious to know how you center yourself and clear your mind before writing.
I have had a hard time clearing my thoughts in getting my ideas out.
I do take pleasure in writing but it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes are usually lost just trying to figure
out how to begin. Any suggestions or tips? Many
thanks!
levitra uk
doxycycline for sale online uk
order generic propecia
who sells difluican with out a prescription
ventolin price
buying phenergan online
cost of colchicine in canada
İzmir Travesti Reklam Portalı
İzmir Travesti sayfası. Bu sayfada şehir’deki en elit
trans bireylere ulaşabilir, fotoğraf, video ve iletişim
bilgilerine sahip olabilirsiniz.
izmir travesti İzmir Travesti Reklam Platformu
en güzel izmir travesti kızlarına ulaş.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
buy propecia from india
Auto Car Insurance Buffalo Grove policy fees may vary based on your auto’s model as well as grow older.
Consider this when selecting an auto.
augmentin tabs cost
baclofen pills
tretinoin 0.025 cream buy
viagra free delivery
how to get zyban prescription
fildena 50 online
buy allopurinol 300 mg
cheapest propecia australia
buy clonidine usa
clonidine sleep aid
phenergan drug
1600 mg bactrim
buy albuterol from mexico
order zyban online uk
buy propecia online uk
diflucan australia
augmentin cheap
prozac brand name price
amoxicillin 500mg cost
trazodone 50mg daily
can you buy propecia over the counter
doxycycline uk pharmacy
lexapro cheapest price
buy tretinoin online mexico
prednisolone 25 mg cost
baclofen 100mg price
tretinoin 0.1 cream otc
generic zithromax
how to get wellbutrin 300 mg without a prescription
ivermectin 1 cream
finasteride 1 mg
inderal tablets 40mg
synthroid 175 mcg price
cheapest price for celexa
paroxetine 10mg price
suhagra tablet price india
how to get ventolin
accutane singapore buy
pharmacy without prescription
albuterol 100
buy allopurinol without prescription
diflucan one
medicine gabapentin 100mg
synthroid 75 mcg tab
buy xenical online cheap
buy acutane
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
can i buy accutane over the counter
Your blog is a force for good in the world. Thank you for making a difference.
where can i purchase diflucan over the counter
buy amoxicillin 875 mg
amoxicillin over the counter nz
bupropion hcl 100 mg
best price for levitra
This post is so timely and relevant. Thank you for addressing such an important issue.
azithromycin zithromax
buy synthroid no prescription
cost of diflucan prescription in mexico
generic albuterol inhaler
augmentin tablet online
accutane medication price
I really appreciate you sharing your thoughts on this topic.
medication propranolol
augmentin 650 price
finasteride coupon
where to buy tretinoin uk
furosemide 40 mg price
albuterol 0.083
Medyum arayışında olanlar için sanal olarak ta hizmet veren medyum hoca ve en iyi medyum hoca olarak popülerliğini koruyan bir hizmet kalitesine erişim sağlayabilirsiniz. Büyü yapımı, birçok kişi tarafından ne olduğu bilinmese de bazı kişiler tarafından kaliteli hizmet veren medyum arayışına girenler için sanal hizmet ağı düzenleyerek aşk büyüsü yanı sıra bağlama büyüsü ve ayırma büyüsü çeşitleri ile alternatifler sunarak ihtiyaca göre hizmet veriliyor. http://www.medyumnazar.com
Fast Lean Pro is a herbal supplement that tricks your brain into imagining that you’re fasting and helps you maintain a healthy weight no matter when or what you eat. It offers a novel approach to reducing fat accumulation and promoting long-term weight management. https://fastleanprobuynow.us/
EndoPump is a dietary supplement for men’s health. This supplement is said to improve the strength and stamina required by your body to perform various physical tasks. Because the supplement addresses issues associated with aging, it also provides support for a variety of other age-related issues that may affect the body. https://endopumpbuynow.us/
citalopram oxalate
Folixine is a enhancement that regrows hair from the follicles by nourishing the scalp. It helps in strengthening hairs from roots. https://folixinebuynow.us/
Glucofort Blood Sugar Support is an all-natural dietary formula that works to support healthy blood sugar levels. It also supports glucose metabolism. According to the manufacturer, this supplement can help users keep their blood sugar levels healthy and within a normal range with herbs, vitamins, plant extracts, and other natural ingredients. https://glucofortbuynow.us/
synthroid canada
Erec Prime is a natural formula designed to boost your virility and improve your male enhancement abilities, helping you maintain long-lasting performance. This product is ideal for men facing challenges with maintaining strong erections and desiring to enhance both their size and overall health. https://erecprimebuynow.us/
amoxicillin 500 price india
GlucoBerry is one of the biggest all-natural dietary and biggest scientific breakthrough formulas ever in the health industry today. This is all because of its amazing high-quality cutting-edge formula that helps treat high blood sugar levels very naturally and effectively. https://glucoberrybuynow.us/
ivermectin 3
Endopeak is a natural energy-boosting formula designed to improve men’s stamina, energy levels, and overall health. The supplement is made up of eight high-quality ingredients that address the underlying cause of declining energy and vitality. https://endopeakbuynow.us/
Herpagreens is a dietary supplement formulated to combat symptoms of herpes by providing the body with high levels of super antioxidants, vitamins
EyeFortin is an all-natural eye-health supplement that helps to keep your eyes healthy even as you age. It prevents infections and detoxifies your eyes while also being stimulant-free. This makes it a great choice for those who are looking for a natural way to improve their eye health. https://eyefortinbuynow.us/
cheap accutane online
zithromax uk
azithromycin order online uk
Dentitox Pro is a liquid dietary solution created as a serum to support healthy gums and teeth. Dentitox Pro formula is made in the best natural way with unique, powerful botanical ingredients that can support healthy teeth. https://dentitoxbuynow.us/
compare amoxicillin prices
GlucoCare is a natural and safe supplement for blood sugar support and weight management. It fixes your metabolism and detoxifies your body. https://glucocarebuynow.us/
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Keratone addresses the real root cause of your toenail fungus in an extremely safe and natural way and nourishes your nails and skin so you can stay protected against infectious related diseases. https://keratonebuynow.us/
GlucoTrust is a revolutionary blood sugar support solution that eliminates the underlying causes of type 2 diabetes and associated health risks. https://glucotrustbuynow.us/
plaquenil 200mg tablets
Java Burn is a proprietary blend of metabolism-boosting ingredients that work together to promote weight loss in your body. https://javaburnbuynow.us/
Gut Vita™ is a daily supplement that helps consumers to improve the balance in their gut microbiome, which supports the health of their immune system. It supports healthy digestion, even for consumers who have maintained an unhealthy diet for a long time. https://gutvitabuynow.us/
LeanBiome is designed to support healthy weight loss. Formulated through the latest Ivy League research and backed by real-world results, it’s your partner on the path to a healthier you. https://leanbiomebuynow.us/
Sugar Defender is the #1 rated blood sugar formula with an advanced blend of 24 proven ingredients that support healthy glucose levels and natural weight loss. https://sugardefenderbuynow.us/
generic propecia without prescription
GlucoFlush is an advanced formula specially designed for pancreas support that will let you promote healthy weight by effectively maintaining the blood sugar level and cleansing and strengthening your gut. https://glucoflushbuynow.us/
Illuderma is a serum designed to deeply nourish, clear, and hydrate the skin. The goal of this solution began with dark spots, which were previously thought to be a natural symptom of ageing. The creators of Illuderma were certain that blue modern radiation is the source of dark spots after conducting extensive research. https://illudermabuynow.us/
order azithromycin from mexico
wellbutrin 150 mg coupon
proventil for sale
can you buy doxycycline
atarax uk buy
northern pharmacy
paroxetine
HoneyBurn is a revolutionary liquid weight loss formula that stands as the epitome of excellence in the industry. https://honeyburnbuynow.us/
vermox otc uk
buy cheap lisinopril 40 mg
ventolin 108 mcg
Kerassentials are natural skin care products with ingredients such as vitamins and plants that help support good health and prevent the appearance of aging skin. They’re also 100% natural and safe to use. The manufacturer states that the product has no negative side effects and is safe to take on a daily basis. Kerassentials is a convenient, easy-to-use formula. https://kerassentialsbuynow.us/
Микрозаймы на карту
https://mikrozajmy-na-kartu.ru/
neurontin generic cost
cheap vardenafil tablets
en güncel programları indir
LeanFlux is a revolutionary dietary formula specially crafted for individuals dealing with obesity and those on a weight loss journey. https://leanfluxbuynow.us/
trazodone 100 mg 50 mg 25 mg
finasteride canada
canada pharmacy clomid
prednisolone 20mg
ivermectin 12
generic neurontin
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/join?ref=W0BCQMF1
canada pharmacy synthroid
where to get gabapentin
xenical 120mg
budesonide 3mg capsules
clonidine online uk
prednisone 20 tablet
generic diflucan 150 mg
hydroxychloroquine buy online uk
zoloft discount coupon
This post is really a fastidious one it assists new internet users, who are wishing in favor of blogging.
how to purchase over the counter generic robaxin from canada
online doxycycline
trazodone 100mg capsules
toradol rx
viagra buy usa
prednisolone 30 mg tablets
Most London marathoners reap the rewards of their
race within the type of a foil blanket, race medal and finisher’s bag, full with sports activities drink and a Pink
Lady apple. Once the race is run, marathoners can examine outcomes over a
pint at any of the eighty one pubs located alongside the course.
They test their race outcomes online, involved to understand how they positioned in their age categories, but most compete for the
fun of it or to raise cash for charity. Next, let’s check out an app
that’s bringing more than three a long time of survey experience to modern cell electronics.
I have three in use operating three separate
operating techniques, and half a dozen or so extra in storage all through the home.
House fans have remained unchanged for what looks as if
endlessly. And, as security is always a difficulty in relation to sensitive bank card information, we’ll explore a number of the accusations that rivals have made towards different merchandise.
The first thing you need to do to guard your credit is to be vigilant about it.
That release bought 400,000 copies in the primary month alone,
and when Cartoon Network’s Adult Swim picked it up in syndication, their scores went up 239
%.
“Introducing the ultimate game-changer in WhatsApp marketing – our ‘WhatsApp Open Group Blaster’! Supercharge your promotional efforts by effortlessly posting advertisements to millions of public WhatsApp groups every day. With lightning-fast speed and precision targeting, our software takes your marketing strategy to new heights. Reach a vast audience and boost your brand exposure like never before. Harness the power of WhatsApp hash channels, available for purchase directly from us, to ensure maximum efficiency and delivery. Our user-friendly interface makes it easy to navigate, and with the ability to post to non-private groups, you’re in control of your campaign’s success. Elevate your outreach, increase engagement, and drive results with the WhatsApp Open Group Blaster. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to transform your marketing game. Get started today and watch your brand soar to new heights!”
website http://www.cdodatabase.com
finasteride 1 mg coupon
clonidine 1.5 mg
zithromax 600
albuterol generic
where can i buy dapoxetine in singapore
buy amoxicillin 500mg from canada
propecia for sale uk
xenical pills where to buy
generic accutane online
cheapest pharmacy prescription drugs
metformin 102
toradol eye drops
levitra prescription prices
synthroid 200
azithromycin 500 mg cost
doxycycline 1000mg
tadalafil 20 mg daily
can i buy levitra without prescription
doxycycline brand name india
generic propecia 1mg
prozac 10 mg cost
fildena 100 mg price
buy augmentin 375 online no prescription
cost of generic hydroxychloroquine
brand zoloft
lexapro online cheap
fildena 150
buy finasteride 1mg india
trazodone 300 mg capsule
buy augmentin no rx
paxil uk buy
atarax medicine in india
colchicine for pseudogout
trazodone 40 mg
albuterol rx
safe reliable canadian pharmacy
finasteride 5mg no prescription
cost of zoloft 20 mg
paroxetine hcl 20mg tab
clonidine 0.1mg for sleep
bupropion australia
express pharmacy
atarax cream
xenical medication
I absolutely love your site.. Excellent colors & theme. Did you make this
web site yourself? Please reply back as I’m attempting to create my very own blog and
would like to know where you got this from or just what the theme is called.
Many thanks!
effexor purchase
propranolol 200 mg
buy inderal
buy doxycycline 500mg
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
albuterol without rx
best price for levitra 20 mg
citalopram 10mg online prescription
cheap retin a
best price for levitra 20mg
order zoloft
orlistat 120 drug
propecia 1.5 pills
azithromycin 500mg where to buy
lioresal 10 mg
clonidine patch for adhd
levitra online south africa
where can i buy bactrim
buy ventolin inhaler online
allopurinol uk
purchase retin a cream online
citalopram bipolar
https://www.magecam.ru
Услуги магов
-привороты
-наведение порчи на смерть
-отнятие удачи
-возврат любимого
обряд приворота мужа своего
order zyban online
accutane online prescription cost
cost of trazodone 50 mg tablet
buy amoxil 500 mg online from india
prednisolone
pharmaceutical online ordering
zoloft.com
where can i buy vermox in uk
lisinopril prinivil zestril
allopurinol 100mg coupon
ivermectin where to buy for humans
The cost savings I have actually made coming from cheap auto Insurance in North Las Vegas policy are
actually significant. It is actually surprising just how much
you may conserve in a year.
paxil 7.5 mg
zoloft south africa
order accutane from india
gabapentin 600 mg tablet price
suhagra tablet
lioresal buy
buy azithromycin no prescription
neurontin 800 mg tablet
effexor cost australia
augmentin brand
order viagra online without script
lioresal online
propecia 10 years
buy fildena
generic lyrica 2017
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.com/ar-BH/register?ref=GJY4VW8W
amoxil 500 mg price
buying clomid 25 mg
clonidine insomnia
how much is synthroid
retin a over the counter europe
budesonide price canada
retin a 0.09
medication neurontin
accutane india pharmacy
where can i get accutane cheap
robaxin generic
augmentin 500mg tablets
albuterol 0.0
order prozac online prescription
vermox india
baclofen in india
5mg zoloft generic pill
desyrel coupon
zoloft pills price
budesonide 3 mg coupon
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
diflucan 150 mg online
propecia buy canada
can i buy synthroid online
vermox online uk
retin a coupon discount
buy paroxetine online
how to get amoxicillin without a script
cheap tretinoin cream 0.25
http://rak.flyboard.ru/viewtopic.php?f=5&t=5629&p=142800#p142800
fluoxetine pills online
clomid 100mg price in india
buy propecia australia
albuterol pills nz
citalopram 20mg price
Awesome article.
[url=http://accutane.guru/]accutane 40mg[/url]
[url=https://allopurinol.cfd/]buy allopurinol uk[/url]
[url=https://clonidine.cfd/]clonidine hcl 0.1 mg tablets[/url]
[url=https://diflucan.cfd/]buy diflucan generic[/url]
[url=https://pharmacyonline.cfd/]rate online pharmacies[/url]
[url=http://bactrim.cyou/]can i buy bactrim online[/url]
[url=http://clonidine.cyou/]clonidine adhd[/url]
[url=http://sildenafil.cyou/]real viagra pills for sale[/url]
[url=https://doxycycline.cfd/]doxycycline 100mg dogs[/url]
[url=https://accutane.cyou/]accutane cream price[/url]
[url=https://doxycycline.cfd/]doxycycline monohydrate[/url]
[url=http://zoloft.cfd/]zoloft 100mg price in india[/url]
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all of us you really know what you
are talking approximately! Bookmarked. Kindly additionally talk over with my website =).
We will have a hyperlink exchange arrangement between us
[url=https://colchicine.cyou/]average cost of colchicine[/url]
[url=http://citalopram.cyou/]celexa 10[/url]
[url=http://vermox.cfd/]mebendazole tablets[/url]
[url=http://accutane.guru/]accutane medicine in india[/url]
aviator oyunu burada
kocayı kendine aşık etme duası için http://www.medyumnazar.com
[url=http://sildenafil.cyou/]sildenafil brand name in india[/url]
[url=http://prozac.cfd/]can i buy prozac over the counter[/url]
[url=http://ivermectin.guru/]ivermectin 3 mg[/url]
[url=http://fildena.cfd/]fildena in india[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cyou/]where to buy diflucan otc[/url]
[url=https://budesonide.cyou/]budesonide canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://clonidine.cyou/]1 mg clonidine[/url]
[url=https://clomid.digital/]how can i get clomid over the counter[/url]
[url=http://fildena.cfd/]fildena in india[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cfd/]where can i purchase diflucan over the counter[/url]
Hocam Ellerinize Saglık Güzel Makale Olmuş Detaylı
[url=http://metformin.cfd/]glucophage tab 1000mg[/url]
[url=https://clonidine.best/]clonidine buy uk[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.best/]purchase amoxicillin 500 mg[/url]
[url=http://silagra.cyou/]silagra 25 mg[/url]
[url=https://hydroxychloroquine.guru/]hydroxychloroquine 200 mg price[/url]
[url=https://lyrica.cfd/]lyrica usa[/url]
[url=https://tadalafil.cfd/]generic tadalafil 60 mg[/url]
Aw, this was a very nice post. Spending some time and actual effort to
make a really good article… but what can I say… I
procrastinate a lot and never manage to get
nearly anything done.
[url=https://clonidine.cfd/]clonidine buy online[/url]
визз эйр порча багажа https://www.magecam.ru порча на наркоманию
[url=http://prozac.cfd/]fluoxetine 30 mg cost[/url]
[url=https://tadalafil.cyou/]where to buy cialis for women[/url]
[url=http://albuterol.cyou/]albuterol asthma[/url]
tercüme bürosu ankara | almanca tercüme, ingilizce tercüme, rusça tercüme ve daha fazla tercüme hizmeti için web sitemizi ziyaret edebilirsiniz.
[url=https://fluconazole.cyou/]diflucan online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://allopurinol.cfd/]price of allopurinol[/url]
[url=https://clonidine.best/]clonidine iv[/url]
[url=http://synthroid.boutique/]cost of synthroid brand name[/url]
Ahaa, its pleasant conversation concerning this piece of writing at
this place at this web site, I have read all that, so now me also commenting at this place.
[url=https://albuterol.cyou/]albuterol from canada no prescription[/url]
[url=https://propranolol.cyou/]propranolol 4[/url]
[url=http://sociablegames.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://zaimy-na-kartu-tinkoff.ru/]https://zaimy-na-kartu-tinkoff.ru/[/url]
[url=http://levitra.cfd/]levitra 20mg india[/url]
[url=https://accutane.cfd/]accutane singapore buy[/url]
[url=https://trazodone.cfd/]trazodone 50[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.guru/]augmentin 625 india[/url]
[url=https://sildenafil.cyou/]viagra tablets india[/url]
Mestlife.com provides convenience to tourists with its online reservation systems and user-friendly website. Thanks to the fast and secure booking opportunity, passengers can plan their travels in advance and combine transfers with their comfort.
[url=https://sildenafil.cfd/]canadian pharmacy brand viagra[/url]
[url=http://propranolol.cyou/]inderal otc[/url]
[url=http://onlinepharmacy.cyou/]online pharmacy com[/url]
[url=https://neurontin.cyou/]buy neurontin 100 mg canada[/url]
[url=https://neurontin.cfd/]neurontin 100 mg cost[/url]
[url=http://robaxin.cyou/]robaxin 500 mg tablet[/url]
[url=https://wellbutrin.cfd/]wellbutrin prescription[/url]
[url=http://finasteride.cyou/]online pharmacy propecia prices[/url]
[url=https://prednisone.cyou/]prednisone for sale online[/url]
[url=http://neurontin.cfd/]neurontin cost australia[/url]
[url=http://azithromycin.digital/]generic for zithromax[/url]
[url=https://baclofen.cfd/]baclofen 159[/url]
[url=http://phenergan.cyou/]buying phenergan online[/url]
[url=https://retina.cfd/]where to buy retin a cream in usa[/url]
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.com/ph/register?ref=53551167
Son Dakika Bursa Haberleri Son dakika Bursa haberleri yapan Haberyum, asayiş başta olmak üzere diğer tüm alanlardaki gelişmeleri de anlık olarak paylaşmakta, okuyucularına ulaştırmaktadır.
[url=https://lexapro.cfd/]lexapro 60 mg[/url]
[url=http://lyrica.cfd/]otc lyrica[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cyou/]how much is diflucan[/url]
[url=https://tadalafil.cfd/]cialis online purchase in india[/url]
[url=https://albuterol.cfd/]albuterol mdi[/url]
[url=https://amoxicillin.boutique/]augmentin cheapest price[/url]
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it.
Look advanced to more added agreeable from you!
However, how can we communicate?
[url=http://atarax.cyou/]atarax 25 mg tablet[/url]
[url=http://synthroid.directory/]synthroid 1.25 mg[/url]
[url=http://silagra.cyou/]buy silagra online in india[/url]
[url=http://allopurinol.cfd/]allopurinol cost canada[/url]
[url=https://diflucan.cfd/]diflucan canada coupon[/url]
[url=http://avana.cfd/]dapoxetine 30 mg tablet[/url]
[url=http://trazodone.best/]trazodone price canada[/url]
[url=https://synthroid.directory/]synthroid price comparison[/url]
[url=https://onlinepharmacy.cyou/]secure medical online pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://budesonide.cyou/]budesonide cost uk[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cyou/]diflucan india[/url]
на черно-белых снимках
pin up 123 [url=https://www.pinupcasinovendfsty.dp.ua]https://www.pinupcasinovendfsty.dp.ua[/url].
[url=http://zoloft.cfd/]zoloft medication[/url]
[url=https://vardenafil.cyou/]vardenafil cheap[/url]
[url=https://tadalafil.cyou/]buy cialis for daily use online[/url]
[url=http://doxycycline.directory/]order doxycycline online uk[/url]
[url=http://bactrim.cyou/]purchase bactrim ds[/url]
[url=http://neurontin.cyou/]gabapentin canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://trazodone.best/]buy trazodone 100mg[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cfd/]diflucan 150 mg price uk[/url]
[url=https://finpecia.cyou/]propecia generic[/url]
[url=https://finasteride.cyou/]buy propecia pills[/url]
[url=https://albuterol.guru/]generic albuterol[/url]
[url=https://lyrica.cfd/]how to get lyrica[/url]
[url=https://phenergan.cyou/]phenergan over the counter nz[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.guru/]trimox without prescription[/url]
[url=https://amoxil.cfd/]cost of augmentin 500mg[/url]
[url=https://zoloft.cfd/]buy zoloft 100mg[/url]
[url=http://ivermectin.guru/]ivermectin lotion cost[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cfd/]buy diflucan online without prescription[/url]
[url=https://albuterol.cfd/]albuterol tablets[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cfd/]diflucan price in india[/url]
[url=https://baclofen.cyou/]baclofen 25 mg cost[/url]
[url=https://vardenafil.directory/]buy levitra 5mg[/url]
[url=http://accutane.guru/]buy accutane online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://clonidine.cyou/]clonidine tablets uk[/url]
[url=http://furosemide.cyou/]where to buy lasix[/url]
[url=http://vermox.cyou/]can i buy vermox over the counter[/url]
[url=https://xenical.cfd/]buy generic orlistat 60 mg capsules[/url]
[url=http://albuterol.guru/]albuterol tablets without prescription[/url]
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=https://albuterol.guru/]can i buy ventolin over the counter in australia[/url]
[url=https://levitra.cfd/]where can i buy levitra online[/url]
[url=https://zoloft.cyou/]600 mg zoloft[/url]
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=http://zoloft.cfd/]zoloft without a prescription[/url]
[url=https://levitra.cfd/]levitra no prescription[/url]
[url=https://robaxin.cyou/]robaxin 750 mg cost[/url]
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=http://fildena.cfd/]fildena 100 mg[/url]
[url=http://synthroid.cyou/]synthroid 250[/url]
[url=http://amoxicillin.boutique/]augmentin pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://doxycycline.directory/]doxycycline capsules for sale[/url]
[url=http://accutane.cyou/]accutane medicine[/url]
[url=https://xenical.cfd/]where can i buy xenical in usa[/url]
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://zoloft.cfd/]20mg zoloft[/url]
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=https://xenical.cfd/]where can i buy cheap orlistat tablets[/url]
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
It’s difficult to find knowledgeable people for this topic, however, you sound like you know what you’re talking about!
Thanks
[url=http://doxycycline.cfd/]doxy 200[/url]
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://lisinopril.cfd/]zestril 10 mg cost[/url]
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=https://accutane.cyou/]accutane online singapore[/url]
[url=http://trazodone.best/]trazodone pill[/url]
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=http://retina.directory/]retin a pharmacy prices[/url]
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=http://paxil.cfd/]where can i get paxil[/url]
[url=http://lyrica.cfd/]lyrica medication[/url]
[url=https://citalopram.cyou/]citalopram 15 mg[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://fluoxetine.cyou/]fluoxetine 40 mg[/url]
[url=https://trazodone.cfd/]trazodone tablets 100mg[/url]
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=https://gabapentin.cfd/]gabapentin capsules[/url]
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=https://zoloft.cfd/]zoloft 50 mg price in south africa[/url]
[url=http://prednisolone.directory/]prednisolone 5mg pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://levitra.cfd/]generic levitra safe[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cfd/]buy diflucan for yeast infection[/url]
[url=https://sildenafil.cfd/]viagra pharmacy generic[/url]
[url=http://amoxil.cfd/]order augmentin online[/url]
[url=https://tadalafil.cyou/]cost of tadalafil generic[/url]
[url=https://albuterol.cyou/]albuterol 0.063[/url]
[url=https://clonidine.best/]clonidine hydrochloride 0.1mg[/url]
IGEM is the professional engineering institution for gas, here to help
people and organisations connected with the business.
[url=https://zoloft.cfd/]zoloft online australia[/url]
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://citalopram.cyou/]140 mg citalopram[/url]
[url=http://doxycycline.directory/]doxycycline online without prescription[/url]
[url=http://tadalafil.cyou/]5 mg cialis[/url]
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=https://lisinopril.best/]lisinopril 5 mg[/url]
[url=https://finasteride.cyou/]buy propecia tablets[/url]
[url=http://vermox.cfd/]vermox otc canada[/url]
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=https://ivermectin.guru/]stromectol over the counter[/url]
[url=https://doxycycline.cyou/]doxycycline pills cost[/url]
[url=https://retina.directory/]retin a 1 cream canada[/url]
[url=https://lexapro.cfd/]lexapro 10 mg price australia[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=https://diflucan.cfd/]diflucan 150 mg uk[/url]
[url=https://prednisolone.directory/]prednisolone 5mg tablet coupon[/url]
[url=https://budesonide.cyou/]budesonide drug[/url]
[url=http://doxycycline.cyou/]how to get doxycycline cheap[/url]
[url=http://albuterol.cfd/]buy albuterol pills online[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=https://propranolol.cfd/]inderal 20 mg[/url]
[url=http://bactrim.cyou/]bactrim ds cost[/url]
[url=https://accutane.cfd/]accutane from mexico[/url]
[url=https://metformin.cfd/]metformin price in canada[/url]
[url=https://augmentin.cyou/]augmentin 625 india[/url]
[url=https://levitra.cfd/]generic levitra 40mg[/url]
[url=https://colchicine.cyou/]colchicine otc price[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.cfd/]purchase amoxicillin 500mg[/url]
[url=https://finpecia.cyou/]cheapest propecia for sale[/url]
[url=https://prozac.cfd/]buy prozac from india[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.cfd/]amoxicillin 1g tablet[/url]
I love it when people come together and share opinions.
Great blog, continue the good work!
[url=http://neurontin.cyou/]cost of gabapentin 800 mg[/url]
[url=https://azithromycin.digital/]azithromycin 500 mg tablet price[/url]
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader. Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://prednisolone.directory/]prednisolone 1 cost[/url]
[url=https://doxycycline.directory/]doxycycline mono[/url]
[url=http://vardenafil.cyou/]how to buy levitra in usa[/url]
[url=https://vardenafil.cyou/]levitra uk buy[/url]
[url=http://neurontin.cyou/]neurontin 300 mg mexico[/url]
[url=http://vardenafil.cyou/]how much is levitra in mexico[/url]
[url=https://amoxicillin.cyou/]augmentin uk buy[/url]
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=http://levitra.cfd/]buying levitra online from canada[/url]
[url=http://doxycycline.guru/]doxycycline 3142[/url]
[url=http://vardenafil.cyou/]generic levitra for sale[/url]
[url=https://tadalafil.cyou/]tadalafil 10mg[/url]
[url=http://ivermectin.guru/]buy ivermectin[/url]
[url=http://doxycycline.cfd/]doxycycline cost in india[/url]
[url=http://toradol.cfd/]toradol 50 mg[/url]
I’ve been wondering about this for a while. Thanks for clearing it up!
[url=http://propranolol.cfd/]buy inderal 10mg[/url]
[url=http://baclofen.cfd/]can you buy baclofen over the counter[/url]
[url=http://webmail.athea.co.nz/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://mikrozajmy-na-kartu.ru/]https://mikrozajmy-na-kartu.ru/[/url]
[url=http://doxycycline.guru/]doxycycline capsules india[/url]
[url=http://amoxicillin.boutique/]amoxil price australia[/url]
[url=https://xenical.cfd/]xenical pills for sale[/url]
[url=http://effexor.cyou/]effexor 112.5[/url]
[url=http://finpecia.cyou/]finasteride online pharmacy india[/url]
[url=https://prednisone.cyou/]prednisone 6 mg[/url]
[url=http://hydroxychloroquine.guru/]plaquenil 200 mg oral tablet[/url]
[url=https://albuterol.cfd/]buy ventolin over the counter australia[/url]
[url=https://synthroid.boutique/]synthroid 137 mcg[/url]
[url=https://finasteride.digital/]finasteride how to get[/url]
[url=https://ivermectin.guru/]ivermectin cost canada[/url]
[url=http://clonidine.cfd/]clonidine 0.2 mg price[/url]
[url=https://effexor.cyou/]effexor sale[/url]
[url=https://prednisolone.directory/]cheap prednisolone tablets[/url]
[url=http://onlinepharmacy.cyou/]super pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://vardenafil.cfd/]levitra soft online[/url]
[url=https://finasteride.digital/]propecia tablet price in india[/url]
Мышление инертное. Научное понятие в процессе усвоения проходит путь от конкретных объектов к обобщению. http://tinyurl.com/4ub2v3rh Что отличает человека от животного обществознание 6 класс тест ответы 1 вариант. Общество пример. Тест на характер личности с диаграммой. Чем человек отличается от животных обществознание 6 класс ответ.
Hello, i think that i noticed you visited my site so i came to
return the want?.I am attempting to to find issues to
improve my site!I assume its adequate to use some of your ideas!!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=http://finasteride.cyou/]cost of finasteride[/url]
[url=https://propranolol.cfd/]innopran xl price[/url]
[url=http://amoxil.cfd/]amoxil 1g[/url]
[url=http://doxycycline.cfd/]cost doxycycline tablets uk[/url]
[url=https://propecia.cyou/]propecia brand coupon[/url]
[url=http://synthroid.directory/]synthroid 137mg without prescription[/url]
Thanks designed for sharing such a good thought, paragraph is fastidious, thats why
i have read it fully
[url=http://synthroid.boutique/]synthroid 75 mcg cheap[/url]
[url=https://lisinopril.best/]lisinopril generic cost[/url]
[url=http://zithromax.cyou/]where to buy azithromycin over the counter[/url]
[url=https://albuterol.cfd/]ventolin 2018[/url]
[url=https://propranolol.cfd/]innopran coupon[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=https://clonidine.cfd/]clonidine tablet cost[/url]
[url=http://paxil.cfd/]paroxetine discount[/url]
[url=http://propranolol.cyou/]proprnolol where to purchase[/url]
Excellent post. I was checking continuously this
weblog and I am inspired! Extremely helpful info particularly the last part 🙂 I maintain such information a lot.
I was looking for this particular information for a very lengthy time.
Thank you and good luck.
[url=https://xenical.cfd/]xenical canada[/url]
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://prednisolone.directory/]prednisolone 5mg tab[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.guru/]2000mg augmentin[/url]
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://neurontin.cfd/]gabapentin 1000mg[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://lyrica.cfd/]lyrica capsule[/url]
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://gabapentin.cfd/]gabapentin cost of[/url]
[url=http://albuterol.cfd/]generic albuterol inhaler[/url]
[url=http://vardenafil.cfd/]vardenafil online pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://lyrica.cfd/]lyrica cream[/url]
[url=https://augmentin.guru/]amoxicillin without a script[/url]
[url=https://effexor.cyou/]price of effexor in canada[/url]
[url=http://accutane.guru/]buy accutane online from europe[/url]
[url=https://retina.directory/]tretinoin cream .05[/url]
[url=https://prednisolone.directory/]prednisolone for sale online uk[/url]
[url=http://vermox.cyou/]vermox usa buy[/url]
[url=https://zithromax.cyou/]zithromax over the counter uk[/url]
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://ivermectin.cfd/]buy liquid ivermectin[/url]
[url=http://accutane.guru/]how to get accutane australia[/url]
[url=http://fildena.cfd/]fildena 50 mg online[/url]
[url=http://vardenafil.directory/]buy vardenafil from india[/url]
thanks for sharing with us good blog
[url=http://albuterol.cyou/]albuterol cost canada[/url]
[url=https://propranolol.cyou/]propranolol er 80mg[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://accutane.cyou/]cheapest accutane generic[/url]
[url=https://clonidine.cfd/]clonidine 200 mcg[/url]
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://finpecia.cyou/]how to get propecia cheap[/url]
[url=https://lisinopril.cfd/]buy lisinopril online no prescription[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cfd/]diflucan 500 mg[/url]
[url=http://toradol.cfd/]toradol usa[/url]
[url=https://doxycycline.cyou/]doxycycline brand name india[/url]
[url=https://neurontin.cfd/]medication gabapentin 300mg[/url]
[url=https://vermox.cyou/]vermox tablets buy online[/url]
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://azithromycin.digital/]can i buy azithromycin over the counter uk[/url]
[url=http://accutane.guru/]buy accutane nz[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://metformin.cfd/]metformin 500 pill[/url]
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://augmentin.cyou/]amoxil 250g[/url]
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://suhagra.cyou/]suhagra 50 online purchase in india[/url]
[url=http://prozac.cfd/]prozac 181[/url]
[url=http://amoxicillin.cyou/]can you buy amoxicillin over the counter in south africa[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.cyou/]how to get amoxicillin online[/url]
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://colchicine.cyou/]colchicine 6 mg tablet[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://silagra.cyou/]buy silagra online uk[/url]
[url=https://doxycycline.directory/]doxycycline drug[/url]
[url=https://azithromycin.digital/]azithromycin 250 mg over the counter[/url]
[url=http://azithromycin.digital/]where can i get azithromycin tablets[/url]
[url=https://paxil.cfd/]price of paroxetine[/url]
[url=https://azithromycin.digital/]azithromycin prescription[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.cfd/]amoxicillin generic brand[/url]
Magnificent site. Lots of useful info here.
I’m sending it to several pals ans also sharing in delicious.
And certainly, thanks on your effort!
[url=http://neurontin.cfd/]neurontin canada online[/url]
Hi there! This is my first visit to your blog!
We are a team of volunteers and starting a new project in a community in the
same niche. Your blog provided us beneficial
information to work on. You have done a outstanding job!
[url=http://clonidine.cfd/]clonidine brand names[/url]
[url=https://retina.cfd/]retin a 0.04[/url]
[url=https://albuterol.cyou/]albuterol 3 mg[/url]
[url=https://diflucan.cfd/]diflucan online purchase[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cyou/]canadian order diflucan online[/url]
[url=https://finasteride.best/]how can i get propecia[/url]
[url=http://paxil.cfd/]paroxetine 30 mg[/url]
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=http://vardenafil.cfd/]levitra online canadian pharmacy[/url]
Hello, i think that i saw you visited my weblog thus i came to “return the
favor”.I’m trying to find things to enhance my site!I suppose its ok to use some of your ideas!!
[url=https://amoxicillin.boutique/]augmentin 500mg generic[/url]
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://doxycycline.directory/]doxycycline online pharmacy canada[/url]
[url=http://vardenafil.cfd/]levitra price compare[/url]
[url=http://azithromycin.digital/]azithromycin 1000[/url]
[url=http://toradol.cfd/]toradol 10 mg tablet cost[/url]
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://ivermectin.guru/]stromectol for humans[/url]
[url=https://allopurinol.cfd/]where to buy allopurinol 300mg online[/url]
[url=http://vardenafil.cfd/]where can i buy levitra in canada[/url]
Everyone loves it whenever people come together and share ideas.
Great blog, continue the good work!
I want to to thank you for this very good read!!
I absolutely loved every bit of it. I have you book marked to check out new things you post…
[url=http://pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua]http://pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua[/url]
Казино всегда притягивали ко себя внимание. Это место, кае можно хватить лиха свою везение равным образом расчесать здоровенную необходимую сумму денег.
http://www.pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua
[url=https://augmentin.best/]price of augmentin in south africa[/url]
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
[url=https://sildenafil.cyou/]sildenafil 20 mg without a prescription[/url]
For latest information you have to visit internet and on web I found this site as a best web site for hottest updates.
[url=http://retina.cfd/]buy retin a online without a prescription[/url]
[url=https://augmentin.cyou/]amoxicillin pills[/url]
[url=https://prednisone.cyou/]prednisone price[/url]
[url=http://ivermectin.cfd/]ivermectin uk[/url]
[url=http://citalopram.cyou/]buy citalopram 20mg online[/url]
[url=http://prednisone.cyou/]prednisone tablets cost[/url]
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://finasteride.digital/]where to buy propecia in south africa[/url]
[url=http://finasteride.digital/]hair loss finasteride[/url]
This is really attention-grabbing, You’re an excessively professional blogger.
I have joined your feed and sit up for in search of extra
of your magnificent post. Additionally, I’ve shared
your web site in my social networks
[url=http://accutane.cyou/]where can you get accutane[/url]
[url=https://metformin.cfd/]glyburide metformin[/url]
[url=https://augmentin.guru/]amoxicillin pills 875 mg[/url]
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this post!
It is the little changes that will make the most significant changes.
Many thanks for sharing!
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://vermox.cfd/]where to buy vermox online[/url]
This text is priceless. Where can I find out more?
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://augmentin.guru/]augmentin 625 mg otc[/url]
[url=http://suhagra.cyou/]suhagra 100 online in india[/url]
[url=http://bactrim.cyou/]bactrim 480 mg[/url]
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://albuterol.cfd/]ventolin tablet 2 mg[/url]
[url=https://doxycycline.cyou/]buy doxycycline online 270 tabs[/url]
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=https://fluconazole.cyou/]diflucan pills for sale[/url]
[url=https://silagra.cyou/]silagra[/url]
[url=https://pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua/]pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua/[/url]
Толпа хронически привлекали для себя внимание. Это ямыжник, где хоть постичь свойскую фортуну а также расчесать крупную сумму денег.
pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua/
[url=https://ivermectin.guru/]ivermectin otc[/url]
[url=https://lexapro.cfd/]lexapro australia[/url]
[url=https://propranolol.cyou/]propranolol 25 mg[/url]
[url=https://clonidine.cyou/]clonidine 2[/url]
[url=http://levitra.cfd/]cheapest levitra uk[/url]
[url=http://albuterol.guru/]no prescription proventil inhaler[/url]
[url=https://vardenafil.directory/]generic-levitra[/url]
[url=http://clonidine.best/]clonidine 0.2 mg online[/url]
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=https://doxycycline.directory/]doxycycline online no prescription[/url]
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this site.
It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s very hard to get that “perfect balance” between usability and visual appeal.
I must say you’ve done a very good job with this. Additionally, the blog loads super quick for me on Firefox.
Exceptional Blog!
[url=http://azithromycin.digital/]zithromax 250 g[/url]
[url=http://vardenafil.cfd/]generic vardenafil 20mg[/url]
[url=http://prozac.cfd/]buy prozac online canada[/url]
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=https://accutane.cfd/]accutane canadian pharmacy[/url]
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://finasteride.cyou/]how can i get propecia[/url]
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://finasteride.cyou/]propecia 1mg online[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
Oh my goodness! Awesome article dude! Thanks, However I am having issues with
your RSS. I don’t understand why I can’t join it.
Is there anyone else getting the same RSS problems? Anyone who knows the
answer will you kindly respond? Thanks!!
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
[url=https://fluoxetine.cyou/]prozac 10 mg capsule[/url]
[url=https://baclofen.cfd/]can i buy baclofen over the counter[/url]
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://vardenafil.directory/]levitra.com[/url]
[url=https://augmentin.best/]875 amoxicillin 125[/url]
[url=http://onlinepharmacy.cyou/]canadapharmacyonline legit[/url]
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua]http://pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua[/url]
Казино хронически привлекали ко себя внимание. Этто место, кае хоть выстрадать свою фортуну а также взять голыми руками основательную необходимую сумму денег.
http://www.pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua
Useful information. Lucky me I discovered your website by chance, and
I am surprised why this twist of fate did not took place earlier!
I bookmarked it.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=https://finpecia.cyou/]finasteride 5mg tabs[/url]
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
[url=https://finasteride.digital/]propecia 1mg generic[/url]
[url=https://lexapro.cfd/]no prescription cipralex[/url]
[url=http://silagra.cyou/]silagra 50 mg price in india[/url]
[url=http://retina.directory/]retin a india[/url]
[url=https://pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua/]pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua/[/url]
Толпа всегда притягивали к себя внимание. Это ямыжник, кае можно хватить лиха близкую удачу также осилить основательную сумму денег.
http://www.pinupcasinozendfste.vn.ua
We are a group of volunteers and starting a brand new scheme in our community.
Your site offered us with valuable information to
work on. You’ve performed a formidable process and our whole neighborhood
will likely be thankful to you.
çok bilgilendirici bir yazı olmuş ellerinize sağlık teşekkür ederim
[url=https://amoxicillin.boutique/]augmentin 875 mg tablets[/url]
[url=http://phenergan.cyou/]phenergan online nz[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.cyou/]buy amoxil online[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cyou/]diflucan generic cost[/url]
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
[url=https://onlinepharmacy.cyou/]legit canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://propecia.cyou/]propecia cheapest no prescription[/url]
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/pt-PT/register-person?ref=GJY4VW8W
[url=http://lisinopril.best/]lisinopril 10 mg tablet cost[/url]
[url=http://lyrica.cfd/]how much is lyrica 75 mg[/url]
[url=http://pharmacyonline.cfd/]cheap online pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://toradol.cfd/]buy toradol pills online[/url]
Enhancing Workspaces in the Heart of Winter Park: Serotonin Centers
In the vibrant city of Winter Park, creating efficient and comfortable workspaces
is paramount, and Serotonin Centers excels in providing top-notch office furniture solutions.
Serving neighborhoods like Audubon Park and Azalea Park, the company stands as a go-to resource for businesses looking to enhance their work
environments.
Established in Winter Park in 1887, Serotonin Centers
boasts a rich history of contributing to the city’s growth.
With a population of 29,131 residents in 12,612
households, Winter Park is a city known for its cultural
diversity and thriving communities. Connected by the major
highway I-4, residents in neighborhoods like Baldwin Park and College Park have
easy access to the extensive range of office furniture offered by
Serotonin Centers.
In Winter Park, where temperatures vary, and businesses strive for excellence, the
cost of office furniture repairs can vary. Serotonin Centers
addresses this need by providing reliable
and cost-effective solutions for businesses seeking durable and stylish office
cubicles, desks, chairs, and tables.
Winter Park boasts a range of captivating
points of interest, including the historic Casa Feliz Historic Home Museum and the scenic Dinky Dock Park.
Residents can enjoy these attractions while
also benefitting from Serotonin Centers’ expertise in creating functional and
aesthetically pleasing workspaces.
Choosing Serotonin Centers in Winter Park is synonymous with choosing
quality and innovation in office furniture solutions. With
a commitment to excellence and a diverse
range of furniture options, the company ensures that
businesses in Winter Park have access to the best resources for creating productive
and inspiring work environments.
”
“Elevating Work Environments in Colonial Town Center: Serotonin Centers at the Forefront
Colonial Town Center, nestled in the heart of
Winter Park, is home to a thriving business community, and
Serotonin Centers plays a pivotal role in enhancing work environments.
Specializing in office furniture solutions, the company caters to the unique needs of neighborhoods like Colonialtown North and Coytown, providing businesses
with top-quality furniture options.
With roots dating back to 1887, Serotonin Centers has been an integral part of Winter Park’s growth
and development. The city, boasting a population of 29,131 residents
across 12,612 households, is known for its rich cultural tapestry.
Accessible via the major highway I-4, Colonial
Town Center and its surrounding neighborhoods,
like Delaney Park, enjoy convenient access to the diverse range of office furniture offered
by Serotonin Centers.
In Winter Park, where temperature variations are common, the cost of office furniture repairs can fluctuate.
Serotonin Centers addresses this need by offering businesses in Colonial Town Center reliable and budget-friendly solutions for office cubicles, desks, chairs, and tables.
Colonial Town Center is surrounded by points of interest, including the historic Downtown Winter Park and
the vibrant Audubon Park Garden District. Businesses in the area can draw inspiration from these local attractions while benefiting from Serotonin Centers’ expertise
in creating productive and aesthetically pleasing workspaces.
Choosing Serotonin Centers in Colonial Town Center is not just a practical decision; it’s a commitment to quality and innovation in office furniture solutions.
With a diverse range of options and a focus on customer satisfaction, the company remains a
trusted partner for businesses striving for excellence in their work environments.
”
“Crafting Inspiring Workspaces in the Heart of Audubon Park: Serotonin Centers’
Expertise
In the picturesque surroundings of Audubon Park, Serotonin Centers stands as a beacon for
businesses seeking to create inspiring workspaces. Specializing in office furniture solutions, the company
caters to the diverse needs of neighborhoods like Baldwin Park and
Bryn Mawr, contributing to the development of vibrant and efficient work
environments.
Founded in Winter Park in 1887, Serotonin Centers has played a significant
role in shaping the city’s growth. Winter Park, with
a population of 29,131 residents in 12,612 households, is celebrated for its
cultural richness. Audubon Park, conveniently connected by
the major highway I-4, benefits from Serotonin Centers’ wide range of office furniture options.
In a city where temperatures can vary, and businesses are keen on excellence, the cost of office furniture
repairs becomes a crucial factor. Serotonin Centers addresses this need by offering businesses in Audubon Park reliable and
cost-effective solutions for office cubicles, desks, chairs, and
tables.
Audubon Park is surrounded by fascinating points of interest, such as the Audubon Park Garden District and the serene Blue Jacket Park.
Local businesses can draw inspiration from these attractions while
also benefitting from Serotonin Centers’ expertise in crafting workspaces that foster creativity and productivity.
Choosing Serotonin Centers in Audubon Park is not just a practical decision; it’s
an investment in the quality and aesthetics of office furniture solutions.
With a commitment to providing businesses with innovative and
tailored options, the company remains a trusted partner for those
striving to create workspaces that inspire success.
”
“Innovative Workspaces in the Heart of East Park:
Serotonin Centers Leading the Way
East Park, a dynamic and growing neighborhood in Winter Park, finds its ally in Serotonin Centers
when it comes to creating innovative workspaces.
Specializing in office furniture solutions, the company serves the
unique needs of neighborhoods like Delaney Park and Dover Estates,
contributing to the evolution of dynamic and
efficient work environments.
Established in Winter Park in 1887, Serotonin Centers has
been an integral part of the city’s development.
Winter Park, with a population of 29,131 residents in 12,612
households, showcases a harmonious blend of cultural diversity.
East Park, connected by the major highway I-4, enjoys seamless access to Serotonin Centers’ extensive
range of office furniture options.
In a city where temperature variations are common and businesses prioritize excellence,
the cost of office furniture repairs becomes a key consideration. Serotonin Centers addresses this need by offering businesses in East
Park reliable and budget-friendly solutions for office cubicles, desks,
chairs, and tables.
East Park is surrounded by captivating points of interest, including the scenic Dinky Dock Park and
the historic Downtown Winter Park. Local businesses can draw inspiration from these attractions while also benefiting from Serotonin Centers’ expertise in crafting workspaces that foster collaboration and
productivity.
Choosing Serotonin Centers in East Park is not
just a pragmatic choice; it’s an investment in quality and functionality in office
furniture solutions. With a commitment to providing
businesses with tailored options and innovative designs, the company
remains a trusted partner for those seeking to create workspaces that drive success.
”
“Elevating Work Environments in the Heart of Carver Shores:
Serotonin Centers’ Impact
Nestled in the vibrant community of Carver Shores,
Serotonin Centers takes center stage in transforming work environments with its innovative office furniture solutions.
Specializing in catering to the distinct needs of
neighborhoods like Clear Lake and College Park, the company
plays a pivotal role in shaping dynamic and efficient workplaces.
Founded in 1887, Serotonin Centers has been an integral part of Winter Park’s growth story.
Winter Park, home to 29,131 residents across 12,612 households, boasts a
rich cultural heritage. Carver Shores, conveniently connected by
the major highway I-4, benefits from Serotonin Centers’ diverse
range of office furniture options.
In a city where temperature variations are a common occurrence, and businesses prioritize excellence, the cost of office furniture repairs becomes a crucial factor.
Serotonin Centers addresses this need by providing businesses in Carver Shores with reliable and budget-friendly solutions for
office cubicles, desks, chairs, and tables.
Carver Shores is surrounded by enticing points of interest, such as the community-centric Central Park and the
historic Downtown Winter Park. Local businesses can draw inspiration from these attractions while
also benefiting from Serotonin Centers’ expertise in crafting workspaces that foster productivity and collaboration.
Choosing Serotonin Centers in Carver Shores is not just a practical
decision; it’s an investment in quality and functionality in office furniture
solutions. With a commitment to providing businesses
with tailored options and cutting-edge designs, the company remains a trusted partner for those aiming to create workspaces that drive success.
Воздух 2024 смотреть фильм онлайн в хорошем качестве. https://bit.ly/vozdux-film-vozduh-2024-smotret-online-film-online Воздух смотреть. Смотреть «Воздух» 2024. Воздух (2024).
[url=http://baclofen.cfd/]baclofen brand name in india[/url]
[url=https://trazodone.best/]trazodone brand name[/url]
[url=http://finasteride.digital/]finasterid[/url]
[url=https://augmentin.cfd/]trimox 500 mg[/url]
[url=https://augmentin.best/]amoxicillin clavulanate[/url]
[url=http://albuterol.guru/]albuterol for sale uk[/url]
[url=https://vardenafil.cfd/]levitra 20mg tablets price[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://onlinepharmacy.cyou/]canadian mail order pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://zoloft.cyou/]zoloft medication[/url]
[url=https://vardenafil.cfd/]levitra cost in usa[/url]
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://prozac.cfd/]cost of prozac gel[/url]
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://fluconazole.cyou/]diflucan 150mg fluconazole[/url]
[url=http://fluoxetine.cyou/]can i order prozac online[/url]
[url=http://vardenafil.cyou/]buy 40 mg levitra[/url]
[url=https://albuterol.guru/]albuterol australia[/url]
[url=https://propranolol.cyou/]propranolol 80mg[/url]
[url=http://effexor.cyou/]effexor 2017[/url]
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=http://synthroid.directory/]generic synthroid medication[/url]
[url=https://avana.cfd/]buy dapoxetine in india[/url]
[url=https://paxil.cfd/]paxil cheap[/url]
Thank you for being a voice for the voiceless. Your work is making a difference in the lives of others.
[url=http://doxycycline.cfd/]doxycycline cream[/url]
[url=https://ivermectin.guru/]ivermectin antiviral[/url]
[url=http://toradol.cfd/]toradol back pain[/url]
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=https://accutane.cyou/]accutane cream price[/url]
[url=https://albuterol.cfd/]price of ventolin inhaler[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
[url=https://prednisone.cyou/]corticosteroids prednisone[/url]
[url=https://atarax.cyou/]atarax 10mg price in india[/url]
[url=http://propranolol.cyou/]buy propranolol online india[/url]
[url=http://xenical.cfd/]xenical pills singapore[/url]
[url=http://retina.cfd/]tretinoin 1 cream online[/url]
[url=https://synthroid.cyou/]purchase synthroid online[/url]
[url=http://atarax.cyou/]hydroxyzine atarax[/url]
[url=https://tadalafil.cyou/]cialis tablets in india[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://sildenafil.cyou/]buy generic viagra canada online[/url]
[url=https://baclofen.cfd/]buy lioresal online[/url]
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://atarax.cyou/]atarax medicine 25 mg[/url]
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
[url=http://albuterol.cyou/]can you buy ventolin over the counter[/url]
[url=https://robaxin.cyou/]robaxin price south africa[/url]
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://prednisone.cyou/]buy 40 mg prednisone[/url]
[url=https://tadalafil.cyou/]best price for tadalafil[/url]
[url=https://atarax.cyou/]atarax 50 mg[/url]
[url=http://xenical.cfd/]buy over the counter xenical[/url]
[url=https://propecia.cyou/]finpecia 1 mg[/url]
[url=http://zoloft.cfd/]zoloft price 50 mg[/url]
[url=http://suhagra.cyou/]cheap suhagra[/url]
[url=http://atarax.cyou/]atarax weight loss[/url]
[url=http://tadalafil.cyou/]cheap cialis canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://tadalafil.cyou/]tadalafil cost 20 mg[/url]
[url=https://amoxil.cfd/]cheap amoxicillin uk[/url]
[url=https://metformin.cfd/]metformin generic[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cyou/]diflucan online canada[/url]
instagram türk beğeni al
[url=https://augmentin.best/]amoxicillin 250mg[/url]
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
Hi there! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could locate a captcha plugin for my comment
form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having
problems finding one? Thanks a lot!
[url=http://doxycycline.cyou/]vibramycin 100mg[/url]
[url=http://propranolol.cyou/]over the counter propranolol uk[/url]
Kaçak bahis sitelerinin çoğaldığı bu son dönemlerde yatırımlarınızı kazanca dönüştürebileceğiniz güvenilir bir iste arayışının tek adresi olan Kulisbet ile hiçbir konuda güven sorunu yaşamayacaksınız.
[url=http://synthroid.directory/]synthroid 200 mg[/url]
[url=http://avana.cfd/]dapoxetine buy online india[/url]
[url=http://lisinopril.cfd/]cheapest price for lisinopril india[/url]
[url=https://trazodone.cfd/]how much is trazodone 50 mg[/url]
[url=http://tadalafil.cyou/]otc cialis 2018[/url]
[url=http://diflucan.cyou/]diflucan 200 mg cost[/url]
[url=https://prozac.cfd/]prozac usa[/url]
[url=http://toradol.cfd/]toradol tablets discount[/url]
[url=http://retina.cfd/]buy tretinoin 05[/url]
[url=https://onlinepharmacy.cyou/]cheapest pharmacy canada[/url]
[url=http://accutane.guru/]order accutane online uk[/url]
[url=https://effexor.cyou/]effexor er[/url]
[url=https://sildenafil.cfd/]purchase cheap viagra[/url]
[url=http://onlinepharmacy.cyou/]foreign online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://neurontin.cfd/]neurontin generic cost[/url]
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
[url=https://albuterol.cyou/]where can i get albuterol over the counter[/url]
[url=http://hydroxychloroquine.guru/]hydroxychloroquine[/url]
[url=https://pharmacyonline.cfd/]reputable online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://retina.cfd/]buy retin a 05[/url]
[url=http://accutane.guru/]how to get accutane uk[/url]
[url=https://suhagra.cyou/]suhagra 100 mg online[/url]
[url=http://metformin.cfd/]metformin buy canada[/url]
[url=https://doxycycline.cfd/]doxycycline generic price[/url]
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=https://lexapro.cfd/]lexapro[/url]
[url=http://trazodone.best/]trazodone medication[/url]
[url=http://neurontin.cyou/]neurontin 50mg tablets[/url]
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.com/ru/register?ref=53551167
[url=https://clomid.digital/]medication clomid over the counter[/url]
[url=http://hydroxychloroquine.guru/]plaquenil 0 2g[/url]
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
[url=http://azithromycin.digital/]buy generic zithromax[/url]
[url=https://finasteride.best/]propecia uk[/url]
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
That is a good tip especially to those new to the blogosphere.
Brief but very accurate information… Thanks for sharing this one.
A must read post!
[url=http://vermox.cyou/]where to buy vermox[/url]
[url=https://sildenafil.cyou/]buy sildenafil online no prescription[/url]
It is the bbest timе to mаke ѕome plans for the future and it’s time tо be happy.
I hve read this post and iff I coսld I wаnt to suggest үou ѕome interesting tһings or advice.
Mybe y᧐u can write next articles referring t᧐ this article.
Idesire to rеad even more things aƅߋut it!
Have a ⅼooк at mү homeрage: Karachi Massage Center
[url=https://phenergan.cyou/]phenergan 50 mg tablets[/url]
I was suggested this web site by my cousin Im not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my trouble You are incredible Thanks
[url=https://diflucan.cfd/]price of diflucan[/url]
dizipal guncell
[url=https://lisinopril.cfd/]lisinopril 20 25 mg tab[/url]
[url=https://hydroxychloroquine.guru/]hydroxychloroquine 90[/url]
[url=http://neurontin.cfd/]gabapentin 1000mg tablet[/url]
[url=http://accutane.guru/]order accutane online australia[/url]
[url=https://xenical.cfd/]buy orlistat cheap[/url]
[url=http://clonidine.best/]clonidine for adhd in adults[/url]
[url=http://albuterol.cyou/]albuterol for sale canada[/url]
[url=http://finpecia.cyou/]propecia australia online[/url]
[url=https://clomid.digital/]clomid pills uk[/url]
Just wish to say your article is as astonishing. The clearness in your post is simply spectacular and i can assume
you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep
up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please continue
the enjoyable work.
[url=http://paxil.cfd/]paroxetine 37.5[/url]
[url=https://wellbutrin.cfd/]bupropion 300 mg price[/url]
[url=https://ivermectin.cfd/]ivermectin tablet price[/url]
[url=https://finasteride.cyou/]propecia tablets uk[/url]
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
[url=https://prednisolone.directory/]buy prednisolone 5mg online[/url]
[url=http://allopurinol.cfd/]allopurinol generic[/url]
[url=https://amoxicillin.cyou/]can you buy amoxicillin without a prescription[/url]
[url=http://prednisone.cyou/]40 mg daily prednisone[/url]
[url=https://lisinopril.best/]20 mg lisinopril without a prescription[/url]
[url=http://tadalafil.cfd/]where to buy cialis in australia[/url]
[url=https://baclofen.cfd/]baclofen 5 mg[/url]
The passing WILD depart WILD symbols on their approach.
It features a mini-sport that includes winnings,
free spins, win multipliers, the activation of passing WILD during
the free spins and a progressive Jackpot. There are
numerous sites the place one can visit to play on-line slot video
games free of charge. Land three extra gong scatters in the course of the
bonus and you’ll retrigger another 10 free spins. That makes it simple to
do three or 4 things at once in your pill, which is nice for multitasking junkies.
The objective of the game is to get three Wheel icons on the reels to then gain access to
the Bonus Wheel. Then glue the CD items onto the Styrofoam.
I shall look up and say, ‘Who am I, then? The adapters look just like a cassette
tape with a plug that fits into the headphone jack of your
portable machine. Ohanian is quoted as saying, “There is an unprecedented alternative to fuse social and crypto in a approach that appears like a Web2 social product but with the added incentive of empowering customers with real ownership,” and that Solana can be the network that makes this
possible.
[url=https://vardenafil.cfd/]levitra online no prescription[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.best/]purchase amoxicillin online uk[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.guru/]augmentin 375 mg price[/url]
[url=http://amoxicillin.boutique/]can i buy over the counter amoxicillin[/url]
hello!,I love your writing so much! share we be in contact
extra approximately your article on AOL? I
require an expert in this space to resolve my problem. May be that is you!
Taking a look forward to peer you.
[url=http://lisinopril.cfd/]lisinopril for sale online[/url]
[url=http://finasteride.cyou/]buy propecia online without prescription[/url]
[url=https://finasteride.best/]propecia online without prescription[/url]
[url=https://synthroid.directory/]synthroid generic cost 100 mcg[/url]
[url=http://finasteride.cyou/]where to buy propecia in australia[/url]
Wonderful post! We will be linking to this great article on our
website. Keep up the good writing.
If in case you have diabetes or other chronic
bodily conditions, you may as well apply to be allowed to take meals, drink, insulin, prosthetic gadgets or personal medical objects into the testing room.
Handmade gadgets don’t stop there, though. Sharp, Ken. “Free TiVo: Build a better DVR out of an Old Pc.” Make.
A better card can enable you to enjoy newer, extra graphics-intensive games.
Fortunately, there are hardware upgrades that may prolong the useful life of your present
laptop with out completely draining your account or relegating one more piece of machinery to
a landfill. These computations are performed in steps by means of a collection of computational parts.
The shaders make billions of computations each second to carry
out their specific tasks. Each immediate is adopted by a set of specific
duties, equivalent to: present your individual interpretation of the statement, or describe a
selected situation where the assertion would not
hold true. Simply determine what needs to be accomplished in what order, and set
your deadlines accordingly. To handle and share your favorite finds on-line in addition to
on your telephone, create a LocalEats user account. Low-noise followers out there as properly.
It’s actually as much as the sport builders how the
system’s considerable assets are used.
[url=https://furosemide.cyou/]medication furosemide 40 mg[/url]
[url=https://albuterol.cyou/]albuterol asthma[/url]
[url=http://albuterol.guru/]albuterol 1.25 mg[/url]
[url=https://citalopram.cyou/]celexa 100mg[/url]
[url=https://atarax.cyou/]atarax for dogs[/url]
[url=http://propecia.cyou/]cheap propecia 5mg[/url]
[url=https://bactrim.cyou/]bactrim medicine online[/url]
[url=http://zoloft.cfd/]zoloft 1000 mg[/url]
[url=http://accutane.cfd/]accutane cost uk[/url]
Car insurance Chicago IL insurance is actually an ongoing expenditure, yet
it costs it for the defense it supplies. Budget wisely for your costs.
[url=https://vermox.cyou/]vermox over the counter uk[/url]
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
[url=http://augmentin.guru/]amoxicillin 500mg tablets price[/url]
[url=http://phenergan.cyou/]phenergan otc australia[/url]
[url=https://bactrim.cyou/]bactrim ds 800-160[/url]
For one thing, you get to work from your individual dwelling most of the time. Although SGI had by no means designed video recreation hardware earlier than, the corporate was considered one of the leaders in pc graphics expertise. So, Nintendo announced an settlement with Silicon Graphics Inc. (SGI) to develop a new 64-bit video recreation system, code-named Project Reality. Nintendo is an organization whose very title is synonymous with video gaming. Although most boomers are nonetheless a long way from serious about nursing properties, they will be encouraged to know that the Wii Fit recreation programs are even discovering their approach into these amenities, helping residents do one thing they by no means may in their youth — use a video sport to stay limber and strong. Or possibly you need a strong machine with a whole lot of disk area for video editing. Most individuals usually work from their firm’s central location, a bodily area where everybody from that group gathers to alternate concepts and arrange their efforts.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
[url=https://colchicine.cyou/]colchicine brand name canada[/url]
[url=http://zoloft.cfd/]buy zoloft usa[/url]
[url=http://lisinopril.cfd/]price of lisinopril 5mg[/url]
[url=https://synthroid.directory/]synthroid 50 mcg tablet[/url]
[url=https://lyrica.cfd/]lyrica 150 mg price[/url]
[url=http://amoxicillin.boutique/]cheap amoxil[/url]
[url=http://amoxil.cfd/]buy amoxicillin online australia[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.cfd/]augmentin 650[/url]
[url=https://doxycycline.cyou/]doxyhexal[/url]
[url=https://hydroxychloroquine.guru/]plaquenil 800 mg[/url]
[url=http://levitra.cfd/]levitra 20mg best price[/url]
[url=https://suhagra.cyou/]suhagra 100mg buy[/url]
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
[url=https://phenergan.cyou/]phenergan canada[/url]
[url=http://suhagra.cyou/]suhagra 100mg[/url]
[url=http://lisinopril.best/]lisinopril online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://amoxil.cfd/]buy augmentin over the counter[/url]
A fascinating discussion is definitely worth comment.
I think that you should publish more on this issue, it may not be a taboo subject
but usually people don’t speak about these issues.
To the next! Cheers!!
[url=https://effexor.cyou/]effexor 37 5 mg[/url]
[url=http://vardenafil.cyou/]levitra for sale uk[/url]
Regular observation of aquarium inhabitants allows for early detection of any signs of illness or
stress. Addressing issues promptly can prevent the spread of diseases and
maintain a harmonious aquarium ecosystem. Finally, stay informed about the individual requirements of the fish and plants in your care,
as different species may necessitate unique conditions for optimal health.
With diligent attention to these aspects, you can cultivate a vibrant and sustainable aquarium that brings joy to both the observer and its aquatic residents.
[url=http://lexapro.cfd/]generic cipralex india[/url]
[url=https://vardenafil.cfd/]generic levitra soft tabs[/url]
And for good purpose: It was slow, it looked completely different than advertised, there have been no USB ports with no bulky adapter, the
microSD memory card slot wasn’t spring loaded, so it was almost not possible to get the
card out. Thus, in Slot Filling degree, we additional label “耐克”(Nike)
as Brand Property (B-Brand/I-Brand), and “黑色”(black) as Color
Property (B-Color/I-Color). Without an APX radio, some first responders should carry multiple radio,
or rely on information from dispatchers earlier than proceeding with important response actions.
The Craig Web site does not provide any information on retail places where they
can be found for purchase (or beneficial retail costs, as we talked about
previously). The Maylong Web site is maddeningly obscure
at best, and just plain inaccurate at worst. Web site to assist you to see your
exercise data — you could have to attach the detachable USB thumb drive to a pc to sync the information it collects.
For extra information on reducing-edge merchandise, award some time to the links on the next page.
That signifies that when disaster strikes, first responders from a large variety of agencies can communicate and coordinate in real time.
So, how does the whole thing go down? In case you make an appointment on your desktop laptop, you have to switch it to your PDA; in case you jot down a cellphone
quantity in your PDA, it is best to add it later to your Pc.
Depending on the corporate, you is likely to be ready to do this online, by cellphone or by text message.
Or the thief may use your information to join cellular phone
service. You also need to have good advertising and marketing expertise in order that potential students can find your
course and be interested enough to join it. Numbers
can solely let you know a lot about a console, of course.
There’s not much to do on the SportBand itself, other than toggle between the display modes to see information about your current train session. The LCD can operate as a plain digital watch, but its major
goal is to convey train information by way of a calorie
counter, timer, distance gauge and pace meter.
[url=http://doxycycline.guru/]doxycycline canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://propranolol.cyou/]can i buy inderal online[/url]
[url=https://tadalafil.cyou/]otc cialis pills[/url]
[url=http://amoxil.cfd/]amoxicillin no prescipion[/url]
[url=https://augmentin.guru/]amoxicillin 125 mg tablets[/url]
[url=http://finasteride.cyou/]propecia 1.5 pills[/url]
[url=https://diflucan.cfd/]diflucan 50mg[/url]
[url=https://clonidine.best/]clonidine for pain[/url]
[url=http://furosemide.cyou/]lasix water pills for sale[/url]
[url=http://augmentin.cyou/]amoxicillin 250 mg capsule price[/url]
I am really grateful to the owner of this site who
has shared this great article at at this place.
[url=https://vermox.cyou/]vermox buy online uk[/url]
[url=https://synthroid.cyou/]synthroid 112 mcg cost[/url]
[url=https://albuterol.guru/]salbutamol albuterol[/url]
[url=http://trazodone.best/]trazodone 300 mg price[/url]
Most London marathoners reap the rewards of their race within the type of a foil blanket, race medal and finisher’s bag, full with sports drink and a Pink Lady apple. Once the race is run, marathoners can compare outcomes over a pint at any of the 81 pubs situated alongside the course. They check their race outcomes on-line, interested to know the way they placed of their age classes, however most compete for the fun of it or to lift money for charity. Next, let’s try an app that’s bringing more than three many years of survey experience to trendy cellular electronics. I have three in use operating three separate operating techniques, and half a dozen or so extra in storage all through the home. House fans have remained unchanged for what looks as if endlessly. And, as security is all the time a difficulty with regards to sensitive bank card data, we’ll discover a few of the accusations that competitors have made towards other products. The very first thing it’s good to do to guard your credit is to be vigilant about it. That release bought 400,000 copies in the primary month alone, and when Cartoon Network’s Adult Swim picked it up in syndication, their ratings went up 239 percent.
[url=http://wellbutrin.cfd/]bupropion online uk[/url]
[url=https://propecia.cyou/]propecia without a prescription[/url]
[url=https://vardenafil.directory/]order vardenafil[/url]
The U.S. has resisted the swap, making American consumers and their credit playing cards the “low-hanging fruit” for hackers.
Within the U.S. market, expect to see plenty of so-referred to as “chip and signature” cards.
The biggest motive chip and PIN cards are extra safe than magnetic stripe playing cards is as a result of they require a 4-digit PIN for authorization. But improvement is likely to be modest if you are not a energy-consumer or you already
had a good amount of RAM (4GB or extra). Shaders take rendered 3-D objects built on polygons (the constructing blocks
of 3-D animation) and make them look more lifelike.
It was about dollars; animation was far cheaper to supply than dwell motion. Actually
shopping for a motherboard and a case along with all of the supporting elements and assembling the whole thing yourself?
And there’s one major thing a Polaroid Tablet can do that an iPad can’t.
Gordon, Whitson. “What Hardware Upgrade Will Best Speed Up My Pc (If I Can Only Afford One)?” Lifehacker.
[url=https://augmentin.best/]augmentin 600[/url]
[url=https://sildenafil.cyou/]generic viagra prices in canada[/url]
[url=https://synthroid.cyou/]cost of synthroid 100mcg[/url]
[url=https://amoxicillin.cyou/]augmentin 625 us[/url]
[url=http://sildenafil.cyou/]buy sildenafil online europe[/url]
[url=https://citalopram.cyou/]drug citalopram[/url]
[url=http://albuterol.cyou/]can you buy ventolin over the counter in australia[/url]
[url=https://budesonide.cyou/]buy budesonide online[/url]
[url=http://pharmacyonline.cfd/]trusted online pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://phenergan.cyou/]buy phenergan over the counter[/url]
The district, which takes in a closely Black stretch of North Carolina’s rural north in addition to some Raleigh exurbs, would
have voted 51-forty eight for Joe Biden, compared to
Biden’s 54-45 margin in Butterfield’s current district, the 1st.
However the trendlines here have been very unfavorable for Democrats, and Butterfield
might very well lose in a tricky midterm atmosphere.
Note that the map has been entirely renumbered, so we have put collectively our
greatest assessment of where each current incumbent may search re-election at this link, whereas statistics
for past elections will be found on Dave’s Redistricting App.
So, if you’re a homeowner, you may rent out a single room or two to strangers, even while the
house is still occupied. ● Former Gov. Ruth Ann Minner, who in 2000 turned
the primary girl elected to function governor of Delaware, has died at
the age of 86. Minner was a legislative staffer when she first won a seat within the state House in 1974 as a neighborhood version of that yr’s “Watergate babies”-reform-minded Democrats elected in the wake of Richard Nixon’s resignation. GOP lawmakers sought to pack as many Democrats as doable into just three extremely-Democratic districts based mostly in Charlotte (the ninth) and the region recognized as the Research Triangle (the fifth in Raleigh and
the 6th in Durham/Chapel Hill).
[url=http://doxycycline.cfd/]doxycycline 100[/url]
[url=https://retina.cfd/]tretinoin capsule brand name[/url]
The truth is, many WIi U video games, including Nintendo’s New Super Mario Bros U, nonetheless use the
Wii Remote for management. The Wii U launch library consists of video games created by Nintendo, including “Nintendoland” and “New Super Mario Bros U,” authentic third-get together video games
like “Scribblenauts Unlimited” and “ZombiU,” and ports of
older video games that first appeared on the Xbox 360 and PS3.
Writers additionally criticized the convoluted transfer strategy of
original Wii content to the Wii U and the system’s backwards
compatibility, which launches into “Wii Mode” to play previous Wii video games.
As newer and extra memory-intensive software comes out, and old junk files accumulate on your arduous
drive, your computer will get slower and slower, and dealing with it will get increasingly more frustrating.
Be sure that to pick the correct kind of card for the slot(s) in your motherboard (both AGP or PCI
Express), and one that’s physically small enough on your computer
case. For instance, better out-of-order-execution, which makes
computer processors extra environment friendly, making the Wii U and the
older consoles roughly equivalent. Nintendo Network might
be a key Wii U function as an increasing number of gamers play with mates and
strangers over the Internet. Because the Nintendo 64, Nintendo
has struggled to search out good third-social gathering support while delivering nice video games of its own.
Here is my web page – ยิงปลาฟรี
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
[url=http://amoxicillin.cyou/]how much is amoxicillin 875 mg[/url]
Good post! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the great writing
If three castles come in view, Lucky Count awards
you 15 free spins. The Lucky Count slot machine comes with 5 reels and 25 paylines.
While most slots video games characteristic simply the one
wild symbol, Lucky Count comes with two! And regardless of being what CNet calls a “minimalist device,”
the Polaroid Tablet still has some fairly nifty hardware options you’d count on from a
more expensive tablet by Samsung or Asus, and it comes with Google’s new,
characteristic-rich Android Ice Cream Sandwich working
system. Davies, Chris. “Viza Via Phone and Via Tablet get Official Ahead of Summer Release.” Android
Community. You’ll also get a free copy of your credit report — test it and stay in contact with the credit bureaus till they
correct any fraudulent fees or accounts you discover there.
I took this opportunity to join the RSS feed or e-newsletter of each one among my sources, and
to get a copy of a 300-web page authorities report on power sent to me as a PDF.
You’ll also get the possibility to land stacks of wilds
on an excellent multiplier so this fearsome creature may change into your greatest pal.
It boasts a thrilling experience on high volatility
and is properly worth a spin on VegasSlotsOnline to test
it out without spending a dime.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Excellent post. I used to be checking constantly this weblog and I am impressed!
Very helpful info particularly the last phase 🙂 I
care for such information much. I used to be looking for this particular info for a very lengthy time.
Thanks and good luck.
Excellent post. I used to be checking constantly this weblog and I am impressed!
Very helpful info particularly the last phase 🙂 I
care for such information much. I used to be looking for this particular info for a very lengthy time.
Thanks and good luck.
Just as with the hard drive, you need to use any available connector from the ability provide. If the batteries do run fully out of juice or in the event you remove them, most devices have an inside backup battery that gives short-time period power (sometimes 30 minutes or less) until you set up a substitute. Greater than anything, the London Marathon is a cracking good time, with many participants decked out in costume. Classes can value greater than $1,800 and private tutoring might be as a lot as $6,000. Like on other consoles, these apps could be logged into with an present account and be used to stream movies from these companies. Videos are also saved if the g-sensor senses affect, as with all dash cams. While the top prizes are substantial, they aren’t really progressive jackpots as the name recommend that they could be, but we won’t dwell on this and just get pleasure from the game for what it’s.
That laptop computer-ish trait means you’ll have to look a bit harder for Internet entry when you are out and about, but you will not need to pay a hefty month-to-month price for 3G knowledge plans. But the iPad and all of its non-Apple tablet opponents are not at all an all-encompassing technology for anybody who wants critical computing energy. It expands on the concept of what pill computer systems are speculated to do. This display screen additionally offers haptic suggestions within the form of vibrations, which offer you tactile confirmation that the tablet is receiving your finger presses. Because human flesh (and thus, a finger) is a conductor, the display screen can precisely determine the place you’re urgent and perceive the commands you are inputting. That straightforward USB port additionally may let you attach, say, an exterior hard drive, that means you may shortly entry or again up nearly any kind of content, from footage to textual content, using the included File Manager app. And for certain varieties of video games, equivalent to driving simulators, you may turn the pill back and forth like a steering wheel to information movements inside the sport. Like its back cowl, the Thrive’s battery can be replaceable. Not solely is this helpful if you will be removed from a energy supply for long intervals, nevertheless it additionally allows you to substitute a brand new battery for one which goes dangerous with out having to consult the producer.
Hello there, just became alert to your blog through Google, and found that it is truly informative.
I am going to watch out for brussels. I’ll appreciate if you continue this in future.
Lots of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Виктор Гардиенов, наш замечательный менеджер по клиентскому обслуживанию, является ключевой фигурой на сайте mikro-zaim-online.ru. С образованием в области психологии и коммуникаций, он разработал уникальные методы общения с клиентами, понимая их потребности как никто другой. Виктор превосходно управляет кризисными ситуациями, обеспечивая каждому клиенту индивидуальный подход и высокое качество обслуживания. Ознакомиться с его работой и узнать больше о процессе оформления займов можно на https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/o-nas/
Now, let’s take a closer look at the credit card
fraud downside and the way chip and PIN cuts again on theft.
The worldwide standard for bank card safety known as “chip and PIN,” and
it is now in American wallets. Netflix has
created a site called “Living with Spoilers,” through which they propose that spoilers are enjoyable,
and we should embrace rather than shun them.
American inventors have created some of crucial technological breakthroughs in the historical past
of humankind. In 1987, the American Marketing Association began the Edison Awards to encourage and recognize inventors.
His work inspired the annual Edison Awards.
The Edison Achievement Award goes to a enterprise government who stresses progress
in product innovations, and the Green Award is introduced to organizations that stress ecologically sound merchandise.
Each year, the Edison Awards honor select
people and organizations for their contributions to
product innovation and financial development.
Keep reading to see 10 merchandise, listed in no particular order, that have been nominated for the 2010
Edison Awards. The corporate claims some users will see heating expenditures drop by
more than 60 %, which could save hundreds
of dollars in a single 12 months.
сильные привороты на любовь парня как сделать приворот по фото
почему заказчик охладел после приворота – https://stepslove.ru любовный приворот по фото
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Ausiello, Michael. “Exclusive: ‘Friday Night Lights’ units end date.” Entertainment Weekly.
It enables you to do a weekly grocery shop,
and contains foods from Whole Foods Market, Morrisons and Booths,
plus on a regular basis necessities, however delivery slots are at present restricted.
Customers who store online are encouraged to shop in-retailer
where attainable to assist free up supply slots for the elderly clients
and people who are self-isolating. Any consumer who does not
prefer to consistently press the start button to
launch the gameplay can activate the computerized start.
Even when the batteries are so low that you can now not turn the machine
on (it offers you plenty of warning earlier than this occurs), there’s
usually enough power to maintain the RAM refreshed.
Some exhibits never have a lot of a chance because networks transfer them from timeslot to timeslot, making it
exhausting for followers to keep observe of them. Other effectively-rated exhibits are just costly to produce, with
large casts and site photographs. The RTP price reaches 95.53%.
Gamblers are recommended to try to apply the Flaming Hot slot demo to develop
their own methods for the game. This can be executed in the complete
model of the game and by launching the Flaming Hot free slot.
Listening to a portable CD player in your automobile looks
like a superb possibility, right? With this template, you possibly can promote something from membership T-shirts to automotive elements.
And with this template, you may be one step forward of
your rivals! In in the present day’s world, you will need to be
one step ahead. If you’re concerned about the difficulty of procrastination on the planet, and also
you wish to create your personal handy utility for monitoring tasks, then that is your alternative!
Useful studying (reading good books) expands a person’s
horizons, enriches his inside world, makes him smarter and has a constructive impact on reminiscence.
So, that is why, applications for studying books
are most related in at present’s studying society.
Reading books increases an individual’s vocabulary, contributes
to the development of clearer thinking, which lets
you formulate and categorical ideas more lucidly.
It’s the kind of consolation that enables you to only zone out and play without worrying about niggling key
issues.
They built their very own group, inviting users to hitch and share their information about knitting, crocheting and more. The location goals to assist customers “set up, share and uncover” throughout the yarn artisan group. Kaboodle boasts greater than 12 million month-to-month visitors with greater than 800,000 registered users. Some concentrate on particular industries, whereas others take a more normal approach. The focus on nature gives it a extra relaxing feel and a retreat for players who aren’t fans of the motion-laden, male-friendly video games by IGT similar to Star Trek – Against all Odds. You will trigger the Free Spins bonus once you get at the least 3 White Orchid symbols on any position in reel 3. Two White Orchids will win you 10 free spins, three will reward you with 15 free spins, and 4 will yield 20 free spins, which is a generous quantity for an IGT slot sport. Most of our slot video games are fairly simple to play, with in-depth information about the game objective and special symbols included in each recreation web page. All pays are multiplied by the bet multiplier.
Although this is the primary spotlight of the PowerBucks Wheel of Fortune Exotic Far East slot machine, our reviewers discovered that it’s not the just one. Our reviewers found that there’s a lot to love about the PowerBucks Wheel of Fortune Exotic Far East slots game. The PowerBucks Wheel of Fortune Exotic Far East online slot is just one in every of a series of related video games from IGT. You might have Autoplay and Turbo options, and you’ll play Scarab Link without spending a dime right here at VegasSlotsOnline before making cash bets at our prime IGT Casinos. Scuttle throughout to IGT casinos to expertise this Egyptian journey for your self. You’ll discover it at our hand-picked IGT casinos. It’s a trickier matter to learn how much power a USB-C cable can cross, though you can begin with certain assumptions. They haven’t moved the graphics alongside too much in this recreation, however it’s nonetheless an honest-looking slot machine that you’ll find in desktop and mobile variations. It can be difficult to discern precisely which pill fashions are nonetheless in the marketplace, but going by the choices of large shops like Sears and Walmart, every thing except the M-a hundred and fifty remains to be accessible on-line or in stores. How can I get a table at a top restaurant?
Apple has deployed out-of-date terminology as a result of the “3.0” bus ought to now be referred to as “3.2 Gen 1” (as much as 5 Gbps) and the “3.1” bus “3.2 Gen 2” (up to 10 Gbps). Developer Max Clark has now formally introduced Flock of Dogs, a 1 – 8 player on-line / native co-op expertise and I’m just a little bit in love with the premise and style. No, it’s possible you’ll not bring your crappy previous Pontiac Grand Am to the local photo voltaic facility and park it in their entrance lawn as a favor. It’s crowdfunding on Kickstarter with a aim of $10,000 to hit by May 14, and with nearly $5K already pledged it should easily get funded. To make it as straightforward as attainable to get going with associates, it’ll offer up a special built in “Friend Slot”, to permit another person to hitch you through your hosted sport. Those opinions – and the way in which corporations deal with them – could make or break an enterprise. There are also options to make some of the new fations your allies, and take on the AI collectively. There are two forms of shaders: pixel shaders and vertex shaders. Vertex shaders work by manipulating an object’s place in 3-D house.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
To make a CD clock, you will want a CD, a variety of artwork supplies (no want to buy anything new, you can use no matter you have round your property) and a clock movement or clockwork, which you should buy online or at a crafts retailer. Whether that means pushing faux “cures” like Mercola and Elizabeth, their own “secret” insights just like the Bollingers and Jenkins, or “alternative health” like Ji and Brogan, these individuals have one thing to sell. Mercola is removed from alone in selling deadly lies for a buck. These folks aren’t pushing conspiracy theories based mostly on compounded lies as a result of they believe them. Erin Elizabeth, who created a number of lies about the safety of both the COVID-19 vaccine and flu vaccine while selling hydroxychloroquine-together with anti-Semitic conspiracy theories. However, the opinion that the $479 MSRP is somewhat too excessive is shared across a number of critiques. Fox News cited experiences of a stand-down order no fewer than eighty five occasions throughout prime-time segments as of June 2013. As the brand new report-which the Republican majority of the committee authored-makes very clear in its findings, nonetheless, no such order ever existed. In a brand new report launched on Tuesday, the House Armed Services Committee concludes that there was no means for the U.S.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
Long earlier than any of the other apps on this checklist, Zagat guides in print have been a trusted supply for
finding a fantastic restaurant, especially for individuals who journey.
There’s just one individual I can consider who possesses a novel mixture of patriotism,
intellect, likeability, and a proven observe file of getting stuff performed underneath powerful circumstances (snakes, Nazis, “unhealthy dates”).
But let’s go one step additional past local meals to road meals.
And with this template, you can be one step forward of your competitors!
A improbable sport to go on adventures by yourself, one I can simply advocate personally.
The sport is free until players need to get rid of the persistent
and lengthy ads that interrupt recreation play by paying for an advert-free membership.
Amazon has more than 140,000 titles in its lending library that you can entry
without cost. That makes it much more like some form of
D&D board game and that i can’t wait to attempt that new characteristic out myself.
This is not Steam Remote Play, that is a local constructed-in sharing characteristic and you may even buy more of those particular slots so others haven’t got to purchase the complete recreation.
That permits you to boost the storage capacity of the gadget to 36 megabytes, more than twice that of the essential iPad.
The Ceiva frame makes use of an embedded working system known as PSOS. Afterward, it is best to discover fewer system gradual-downs, and feel a little less like a hardware novice. The system may allocate an entire processor simply to rendering hi-def graphics. This could also be the future of television. Still, having a 3-D Tv means you may be prepared for the exciting new features that is likely to be accessible within the near future. There are so many great streaming exhibits on sites like Hulu and Netflix that not having cable isn’t an enormous deal anymore as long as you may have a solid Internet connection. Next up, we’ll have a look at a fantastic gadget for the beer lover. Here’s an important gadget gift idea for the man who actually, really loves beer. If you are on the lookout for much more information about great gadget gifts for males and different comparable topics, simply follow the links on the subsequent page. If you happen to choose to learn on, the taste of anticipation could immediately go stale, the page would possibly darken before your eyes and you will probably find your consideration wandering to different HowStuffWorks subjects.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın. Starzbet
We stumbled over here from a different web address and thought I may as well
check things out. I like what I see so now i am following you.
Look forward to going over your web page again.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader. Websiteye Giriş için Tıklayın. a href=”https://cutt.ly/SahabetSosyal/” title=”Sahabet” rel=”dofollow”>Sahabet
Known simply as the “daisy advert,” the minute-long slot was created by the advertising firm Doyle, Dane and Bernback on behalf of President
Lyndon Johnson, who was seeking re-election in opposition to Republican Arizona Senator Barry Goldwater in 1964.
It begins with just a little girl counting petals on a daisy,
and the camera regularly zooms in toward her pupil, which displays a mushroom-cloud explosion. The novel trick worked,
and Benton narrowly won re-election. Former Massachusetts governor Mitt Romney
received the Florida Republican main partially due to a wave of attack adverts against his rivals.
Moreover, the fact that a serious chunk of that money immediately flowed to political assault advertisements additionally factors to a longstanding — although
reviled — tradition of going unfavourable as a way to
get candidates elected to office. With idea USA tablets, however, you get a really universal model of Android.
Perl says college students, small companies and value-acutely aware patrons
make up the bulk of concept pill buyers.0, which
can be referred to as Ice Cream Sandwich. That runs opposite to the usual tablet feeding frenzy, through which new
and improved models from behemoth corporations are met by widespread media experiences.
Savvy social media managers know that there is a plethora of ways to harvest great
feedback from prospects, and that there are a lot of paths to adverse
suggestions, too.
my web site :: ยิงปลาฟรี
Right here is the right blog for anybody who would like to understand this topic.
You understand so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I personally would want to…HaHa).
You definitely put a fresh spin on a subject that’s been discussed for years.
Great stuff, just wonderful!
Experiments on two domains of the MultiDoGO dataset reveal challenges of constraint violation detection and
sets the stage for future work and improvements. The results
from the empirical work show that the new ranking mechanism proposed
will probably be simpler than the previous one in a number of features.
Extensive experiments and analyses on the lightweight fashions show that our
proposed strategies obtain considerably larger scores and considerably improve the robustness of both intent detection and slot filling.
Data-Efficient Paraphrase Generation to Bootstrap Intent Classification and
Slot Labeling for new Features in Task-Oriented Dialog Systems
Shailza Jolly author Tobias Falke writer Caglar Tirkaz writer Daniil Sorokin writer 2020-dec textual content Proceedings of the twenty eighth International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Industry
Track International Committee on Computational Linguistics Online convention publication Recent progress through advanced neural models
pushed the efficiency of activity-oriented dialog programs
to almost good accuracy on present benchmark datasets
for intent classification and slot labeling.
Are you looking for a trustworthy solution to prolong the life
of your roof? Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is the answer. This innovative product provides an unparalleled standard of maintenance for your asphalt shingles, guaranteeing they
stay in top condition.
By choosing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer, you’re not just applying any ordinary
product. You’re selecting a high-end roof rejuvenation solution formulated
to dramatically prolong the life of your roof for decades.
Choosing Shingle Magic is a savvy move for property owners seeking
to preserve their investment.
What makes Shingle Magic Roof Sealer? For starters,
its unique formula gets into the asphalt shingles, restoring their pristine condition and look.
Moreover, it is remarkably simple to use, needing no work for top results.
Not only does Shingle Magic Roof Sealer extend the life of your roof, but
it delivers exceptional protection against weather elements.
From harsh sunlight, rainstorms, or freezing temperatures, it will be safeguarded.
Furthermore, opting for Shingle Magic Roof Sealer signifies you’re choosing an green option. Its safe composition guarantees reduced environmental impact, which makes it
a responsible choice for the planet.
In conclusion, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer stands out as the best roof rejuvenation solution. It not only can prolong the life of your
roof but also offering outstanding protection and an environmentally
friendly option makes Shingle Magic as the smart
choice for homeowners aiming to care for their property’s future.
Moreover, a significant advantage of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is its cost-effectiveness.
In lieu of investing a fortune on regular repairs or a full roof replacement, choosing Shingle
Magic helps save you expenses in the long run. It’s a financially savvy choice that
offers premium results.
Furthermore, the user-friendly nature of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is noteworthy.
You don’t need specialized knowledge to apply it. For those
who like to handle things themselves or opt for expert application,
Shingle Magic guarantees a smooth process with remarkable results.
The product’s durability also serves as a significant reason to choose it.
Once applied, it creates a layer that preserves the integrity of your shingles for years.
It means fewer concerns about damage from the elements and greater peace of mind about the health of your roof.
In terms of aesthetic appeal, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is also superior.
It not only protects your roof but also enhances its look.
The shingles will appear more vibrant, adding to the attractiveness and
worth to your property.
Client satisfaction with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is additional proof to its efficacy.
Countless users have experienced significant improvements in their roof’s
state after using the product. Feedback highlight its user-friendliness, longevity, and excellent protective qualities.
Finally, choosing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer represents opting for a proven solution for roof rejuvenation. With
its blend of durability, beauty, affordability,
and simplicity positions it as the optimal choice for anyone seeking to prolong the life and look of their roof.
Don’t wait to transform your roof with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer.
Are you in need of a trustworthy solution to prolong the life of your roof?
Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is what you need.
Our unique product provides an unparalleled degree of care for your
asphalt shingles, making sure they stay in top condition.
With Shingle Magic Roof Sealer, you’re not just choosing any ordinary product.
You’re opting for a top-quality roof rejuvenation solution crafted to significantly prolong the life
of your roof for many years to come. This is a wise decision for property owners seeking to safeguard their investment.
What makes Shingle Magic Roof Sealer? Firstly, its unique formula seeps into the asphalt shingles,
restoring their pristine condition and aesthetic.
Furthermore, the sealer is extremely easy to apply, requiring minimal time for top results.
Not only does Shingle Magic Roof Sealer prolong
the life of your roof, it also offers exceptional protection against weather elements.
Whether it’s intense UV rays, torrential downpours, or winter conditions, the roof
is safeguarded.
Moreover, choosing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer indicates you’re choosing
an green option. The safe formula means minimal environmental impact, making it a responsible choice for
your home.
To sum up, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer stands out as the premier roof
rejuvenation solution. Its ability to increase the life of your roof but also offering outstanding protection and being green option makes Shingle Magic as
the smart choice for property owners aiming to invest in their property’s future.
Additionally, one of the key benefits of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is its cost-effectiveness.
In lieu of investing a significant amount on frequent repairs
or a full roof replacement, using Shingle Magic helps save you
money in the long run. It’s an economical solution that still delivers premium results.
Furthermore, the user-friendly nature of Shingle Magic
Roof Sealer stands out. You don’t need professional expertise to apply it.
If you enjoy DIY projects or choose for professional installation, Shingle Magic provides a seamless process with outstanding results.
Its lasting power is another strong reason to choose it. Once applied,
it forms a layer that maintains the integrity of your shingles for a long time.
That means less worry about damage from the elements and
more peace of mind about the condition of your roof.
In terms of aesthetic appeal, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer also excels.
Besides protecting your roof but also boosts its look.
Your shingles will look more vibrant, adding curb appeal and worth to your property.
Satisfaction with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is further
evidence to its effectiveness. Countless customers have experienced significant improvements
in their roof’s state after using the product. Reviews underscore its user-friendliness, longevity,
and superior protection.
To wrap it up, choosing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is choosing a
proven solution for roof rejuvenation. Combining sturdiness, aesthetic enhancement, economic efficiency, and
user-friendliness renders it the optimal choice for homeowners seeking to enhance the life and
look of their roof. Don’t wait to revitalize your roof with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
The Vizio tablet runs Android apps, which can be found for
buy or free from Android Market. One area where the Acer Iconia pill (like other Android tablets)
nonetheless falls quick is the availability of apps. Simple actions like making lists, setting
deadlines and choosing the proper storage containers may also help ensure you’ve got the
best time possible. Newer hair dryers have incorporated some technology from the clothes dryer:
a removable lint display screen that’s easier to scrub.
The tablets are also suitable with a full wireless keyboard, which is infinitely simpler to make use of than a
touch display for composing documents and lengthy e-mails.
Acer acknowledges this trend by positioning its Iconia tablets as excellent for multitasking and pairing with equipment
designed for gaming, working or viewing content
material. While it’s still early in the sport, the Acer Iconia pill, although not
but a household identify, appears to be off to a decent begin. Portnoy,
Sean. “Acer Iconia Tab W500 tablet Pc running Windows 7 obtainable starting at $549.99.” ZDNet.
Hiner, Jason. “The ten hottest tablets coming in 2011.”
ZDNet. However, a customer support consultant with the corporate gave us 10 different retailers where the tablets had been alleged to be obtainable for sale,
but we could solely affirm a number of that stocked them.
Listed here are some further details about these primary features.
These early gadgets, which have been supposed to be portable computers, came out in the mid- to late 1980s.
They included small keyboards for enter, a small display, and basic options equivalent to
an alarm clock, calendar, telephone pad and calculator.
It shops basic packages (handle e book, calendar, memo pad and working
system) in a learn-only memory (ROM) chip, which stays intact
even when the machine shuts down. Actually, the profile
of the typical gamer is as shocking as finding a video sport machine that still operates with only a quarter: It’s
a 37-year-previous man, according the most recent survey carried out by the Entertainment Software Association (ESA).
After all, hardware and software specs are simply pieces of a fancy tablet puzzle.
Since diesel fuel presently uses platinum — that’s proper,
the stuff that hip-hop stars’ goals are fabricated
from — to scale back pollution, utilizing nearly anything else would make it cheaper.
Factor well used.!
Feel free to surf to my blog … https://cartedaffairealaval.com
Navigating Legal Challenges in Southfield City Centre:
The Sam Bernstein Law Firm
In the bustling city of Southfield, the need for a reliable
car accident attorney is paramount. The Sam Bernstein Law Firm proudly
serves neighborhoods like Southfield City Centre, providing
crucial legal support to residents facing challenges on the road.
Established in Southfield in 1830, the firm boasts a legacy of legal expertise.
With a population of 75,898 residents across 34,404 households,
Southfield is a city with a rich history. Connected by the major highway I-696, residents of Southfield City
Centre have convenient access to legal services from The Sam Bernstein Law Firm.
Legal repairs, especially in car accident cases, can vary in Southfield.
The Sam Bernstein Law Firm, strategically positioned in Southfield City Centre, offers specialized legal services tailored to residents’ specific
needs, ensuring a comprehensive and personalized approach for each case.
Southfield City Centre is home to various points of interest,
from the serene American Commerce Centre Nature Preserve to the captivating Arctic Ring of Life featuring
Polar Bears and Sea Otters. Residents can explore the city’s attractions while having a reliable legal partner in The Sam Bernstein Law Firm.
Choosing The Sam Bernstein Law Firm in Southfield City Centre is choosing a legacy of legal excellence dating back to 1830.
With a commitment to providing top-notch legal services, the firm ensures residents facing car accident challenges have unparalleled support in the ever-evolving legal landscape of
Southfield.
”
“Legal Excellence in Beverly Hills Village Park:
The Sam Bernstein Law Firm
In the picturesque neighborhood of Beverly Hills Village Park and its neighboring communities, The
Sam Bernstein Law Firm stands as a pillar of legal expertise, especially in car accident cases.
Serving the residents of Beverly Hills Village
Park and beyond, the firm is committed to providing
essential legal support.
Established in Southfield in 1830, The Sam Bernstein Law Firm has become synonymous with legal excellence.
With a population of 75,898 residents in 34,404 households, Southfield boasts a rich history.
Connected by the major highway I-696, residents in neighborhoods
like Beverly Hills Village Park enjoy convenient access to The Sam Bernstein Law Firm’s specialized legal services.
Legal repairs, particularly in car accident cases,
can vary in Southfield. Positioned strategically in Beverly Hills
Village Park, The Sam Bernstein Law Firm offers tailored legal services,
ensuring a comprehensive and personalized approach for each case.
Beverly Hills Village Park is surrounded by captivating points of interest, from
the charming Carpenter Lake Nature Preserve to the
historic Beverly Hills Village Park itself. Residents can savor the natural
beauty of the area while having a steadfast legal partner in The Sam Bernstein Law
Firm.
Choosing The Sam Bernstein Law Firm in Beverly Hills Village Park is choosing a legacy of legal excellence
that dates back to 1830. With a commitment to providing top-notch legal services, the
firm ensures residents facing car accident challenges have
unwavering support in the ever-evolving legal landscape of Southfield.
”
“Providing Legal Solutions near Carpenter Lake Nature Preserve:
The Sam Bernstein Law Firm
In the serene vicinity of Carpenter Lake Nature Preserve and its adjacent neighborhoods,
The Sam Bernstein Law Firm serves as a beacon of legal expertise, specializing in car accident cases.
Dedicated to offering crucial legal support, the firm
caters to residents near Carpenter Lake Nature Preserve and throughout Southfield.
Established in Southfield in 1830, The Sam Bernstein Law Firm holds a longstanding legacy
of legal excellence. Southfield, with its population of 75,
898 residents in 34,404 households, is a city deeply rooted in history.
Connected by the major highway I-696, residents in areas
surrounding Carpenter Lake Nature Preserve enjoy seamless access to the firm’s specialized legal services.
Legal repairs, especially in car accident cases, can vary in Southfield.
Nestled near Carpenter Lake Nature Preserve, The Sam Bernstein Law Firm provides tailored legal solutions,
ensuring a comprehensive and personalized approach for each unique case.
Carpenter Lake Nature Preserve is surrounded by natural wonders, including the scenic Carpenter Lake Overlook and the expansive Beverly Hills Village Park.
Residents can immerse themselves in the beauty
of the area while having a steadfast legal partner in The Sam Bernstein Law Firm.
Choosing The Sam Bernstein Law Firm near Carpenter Lake Nature
Preserve is choosing a legacy of legal excellence dating back
to 1830. With a commitment to providing top-notch legal services, the firm ensures residents facing car accident challenges have unparalleled
support in the ever-evolving legal landscape of Southfield.
”
“Legal Expertise in the Heart of Southfield: The Sam Bernstein Law Firm
Located in the heart of Southfield, The Sam Bernstein Law Firm provides unparalleled
legal expertise, particularly in car accident cases.
Serving neighborhoods like Southfield City Centre, the firm is
dedicated to offering crucial legal support to residents facing
challenging situations on the road.
Established in Southfield in 1830, The Sam Bernstein Law Firm boasts a legacy of legal excellence.
With a population of 75,898 residents across 34,
404 households, Southfield is a city deeply embedded in history.
Connected by the major highway I-696, residents in the heart of Southfield have convenient access
to the firm’s specialized legal services.
Legal repairs, especially in car accident cases, can vary in Southfield.
The Sam Bernstein Law Firm, strategically located in the city center,
offers tailored legal services, ensuring a comprehensive and personalized approach for each case.
Southfield City Centre is surrounded by points of interest, from
the tranquil Civic Center Park Pavilion to the
captivating American Commerce Centre Nature Preserve.
Residents can explore the vibrant heart of Southfield while having a reliable legal partner in The Sam Bernstein Law Firm.
Choosing The Sam Bernstein Law Firm in the heart of Southfield is choosing a legacy of
legal excellence that dates back to 1830. With a commitment to providing top-notch legal services, the firm ensures
residents facing car accident challenges have unwavering support in the ever-evolving legal landscape of Southfield.
”
“Navigating Legal Challenges in the Vibrant Clawson City Park: The Sam Bernstein Law Firm
In the vibrant community surrounding Clawson City
Park, The Sam Bernstein Law Firm stands as a symbol of legal expertise, specializing in car accident cases.
Committed to providing essential legal support, the firm serves residents near Clawson City Park and throughout
Southfield.
Established in Southfield in 1830, The Sam Bernstein Law Firm carries a legacy of legal excellence.
Southfield, with a population of 75,898 residents across
34,404 households, is a city steeped in history. Connected by the major highway I-696, residents near Clawson City Park enjoy convenient access to the firm’s specialized legal services.
Legal repairs, particularly in car accident cases, can vary
in Southfield. Positioned strategically near Clawson City Park, The Sam Bernstein Law Firm
offers tailored legal services, ensuring a comprehensive and personalized approach for each unique case.
Clawson City Park is surrounded by attractions like the Clawson Historical Museum and the
captivating Arctic Ring of Life. Residents can immerse themselves in the community’s vibrancy while having a steadfast legal partner in The Sam
Bernstein Law Firm.
Choosing The Sam Bernstein Law Firm near Clawson City Park is choosing a legacy of legal excellence dating back to 1830.
With a commitment to providing top-notch legal services, the firm ensures residents facing car accident challenges have unparalleled support in the ever-evolving legal
landscape of Southfield.
In the bustling city of Las Vegas, NV, the relevance of terms such
as “Best DUI Attorney” and “Expert DUI defense attorneys” cannot be overstated.
Situated in an energetic area, Clark McCourt Criminal Lawyers serves
communities like Amber Hills and Arts District, which often require such specialized legal services.
Clark McCourt Criminal Lawyers is based
in Las Vegas, a city established in 1905 with a fascinating history.
With a community of 646,790 (as of 2021) and 240,
462 households, it’s a hub of activity. An interesting fact about this city is
its proximity to the Las Vegas Beltway, a major highway.
In Las Vegas, legal services, particularly in DUI cases, can have different price ranges.
Given the city’s extreme temperature variations, from scorching summers to chilly winters, it’s crucial
to have reliable legal assistance.
Among the city’s attractions, AREA15 and Aliante Nature Discovery Park stand out.
AREA15, for instance, is known for its immersive experiences, while Aliante Nature
Discovery Park is famed for its natural beauty. Both offer unique
experiences reflective of Las Vegas’s diverse attractions.
Choosing Clark McCourt Criminal Lawyers in Las Vegas is a wise
decision for local residents. With their specialized knowledge in DUI cases and familiarity with the local community, they stand out as a top
choice.
Experiments on two domains of the MultiDoGO dataset reveal challenges of constraint violation detection and sets the stage for future work and enhancements.
The results from the empirical work show that the new ranking mechanism proposed will be more practical than the former one in several aspects.
Extensive experiments and analyses on the lightweight models present that
our proposed strategies achieve considerably higher scores and
considerably improve the robustness of both intent detection and slot filling.
Data-Efficient Paraphrase Generation to Bootstrap Intent Classification and Slot Labeling for new Features in Task-Oriented Dialog Systems Shailza Jolly
creator Tobias Falke writer Caglar Tirkaz author Daniil Sorokin author 2020-dec text Proceedings
of the twenty eighth International Conference on Computational
Linguistics: Industry Track International Committee on Computational Linguistics Online convention publication Recent progress through advanced neural fashions pushed the efficiency of job-oriented dialog methods to nearly excellent accuracy on current benchmark datasets for intent classification and slot labeling.
But each cable Tv subscriber pays an average of $1.72 a month
to obtain Fox News. In accordance with a survey performed late final year, about 14%
of cable Tv subscribers watch Fox News repeatedly. Fortnite
companies might be disabled beginning at 11:30pm PDT on July 19, or 2:30am EDT / 7:30am BST on July 20 – an hour earlier than the final round of downtime.
Fortnite v17.20 is slotted for launch on July 20. In preparation for
the update, companies will be disabled starting at approx.
Its lacking options, like Nintendo TVii,
will arrive submit-launch. An FM modulator would allow even an older automobile radio,
like this one, to play your CDs through the car’s speakers.
You play one in every of many adventurers who should
answer the decision of an embattled queen to protect her kingdom, Fahrul, from impending doom after its king is
murdered. Multi-Service business on-line contains
numerous trade sectors similar to health-care, laundry, dwelling companies,
grocery supply, logistics, and many others. Because
all these service sectors might be well met into one cell app, the overall workflow would be gainful for entrepreneurs.
We also show that, though social welfare is elevated
and small advertisers are better off underneath behavioral targeting, the dominant advertiser may be worse off and reluctant to modify from conventional advertising.
The new Switch Online Expansion Pack service launches
at the moment, and as part of this, Nintendo has released some new (however previous) controllers.
Among the Newton’s improvements have become customary PDA
features, including a strain-delicate display with stylus, handwriting recognition capabilities, an infrared port and an growth slot.
Each of them has a label that corresponds to a label on the correct
port. Simple options like manually checking annotations or having multiple employees label every pattern are
costly and waste effort on samples that are appropriate.
Creating a course in something you’re captivated with, like fashion design, can be a very good option to make money.
And there is not any higher option to a man’s heart than through expertise.
Experimental results verify the benefits of specific slot connection modeling, and our model achieves state-of-the-artwork performance on MultiWOZ 2.Zero and MultiWOZ 2.1 datasets.
Empirical outcomes demonstrate that SAVN
achieves the state-of-the-art joint accuracy of 54.52% on MultiWOZ 2.Zero and 54.86% on MultiWOZ 2.1.
Besides, we evaluate VN with incomplete ontology.
Experimental results present that our mannequin considerably outperforms
state-of-the-artwork baselines underneath both zero-shot
and few-shot settings.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
But as a substitute of using high-pressure gasoline to generate thrust, the craft uses a jet drive to create a strong stream of water.
The policy on gas differs between companies as effectively.
The TDM Encyclopedia. “Car sharing: Vehicle Rental Services That Substitute for Private Vehicle Ownership.” Victoria Transport Policy
Institute. University of California Berkeley, Institute of Transportation Studies.
Santa Rita Jail in Alameda, California (it is near
San Francisco, no surprise) uses an array of gasoline cells, solar panels, wind turbines and diesel
generators to energy its very personal micro grid. However,
many nonprofit car-share organizations are doing fairly nicely, such as City
CarShare in the San Francisco Bay Area and PhillyCarShare in Philadelphia.
So that you could also be asking yourself, “Wow, if automobile sharing is so well-liked and simple, ought to I be doing it too?” To find out extra about who can benefit from sharing a car and to
learn about find out how to contact a automotive-sharing company, proceed to the following page.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Vbet Güncel Giriş Adresi
megasosyal çocuk
как определить есть ли приворот приворот работает ли это
ментальный приворот что это такое – https://duhmaga.ru почему нельзя делать приворот на любовь последствия
Are you looking for a dependable solution to prolong
the life of your roof? Shingle Magic Roof Sealer
is your solution. This innovative product provides a unique degree
of care for your asphalt shingles, ensuring they stay
in top condition.
Utilizing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer, you’re not just using any ordinary product.
You’re opting for a high-end roof rejuvenation solution designed to greatly
prolong the life of your roof for many years to come.
This is a wise decision for anyone looking to protect their investment.
Why choose Shingle Magic Roof Sealer? For starters,
its exclusive formula gets into the asphalt shingles, restoring their initial
strength and look. Moreover, it’s incredibly simple to use, requiring no effort for optimal results.
In addition to Shingle Magic Roof Sealer prolong the life of your roof, but it
also offers superior protection against environmental
damage. Be it harsh sunlight, torrential downpours,
or snow and ice, it will be shielded.
Additionally, selecting Shingle Magic Roof Sealer means you are selecting an green option. The safe formula ensures reduced environmental
impact, making it a conscious choice for your
home.
To sum up, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer excels as the premier
roof rejuvenation solution. It not only can extend the
life of your roof and offering exceptional protection and an green option positions it as the smart choice for property owners looking
to maintain their property’s future.
Moreover, a significant advantage of Shingle Magic
Roof Sealer is its affordability. Instead of investing a fortune on regular repairs
or a full roof replacement, using Shingle Magic can save you money in the long
run. It’s an economical solution that offers top-notch
results.
Additionally, the user-friendly nature of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer
is a major plus. It doesn’t require expert skills to
apply it. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or opt for professional installation, Shingle Magic guarantees a smooth process with remarkable results.
Its lasting power is another compelling reason to choose it.
After application, it develops a layer that keeps the integrity of your shingles for a
long time. It means fewer concerns about damage from the elements and a more secure
feeling about the state of your roof.
Regarding aesthetic appeal, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer also stands
out. Besides protecting your roof but also boosts its appearance.
Your shingles will look refreshed, which adds to the attractiveness and value to your property.
Client satisfaction with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is additional
proof to its quality. Many homeowners have seen remarkable improvements in their roof’s state after using the product.
Feedback emphasize its ease of use, longevity, and outstanding protection.
Finally, opting for Shingle Magic Roof Sealer means
selecting a reliable solution for roof rejuvenation. With its blend of durability,
visual appeal, affordability, and simplicity makes it the ideal choice for
anyone seeking to extend the life and appearance of their roof.
Act now to revitalize your roof with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer.
It consists of 32 Screens with a special kind of UI.
This template consists of more than 60 screens with very smooth animation that is in line with Android
and IOS. Also on this template there are screens for tracking the
change price and the growth of bitcoin. Also, this template
already supports several languages: Italian, German and
English. This template for the travel booking app was created based
on the mistakes and optimistic results of massive
booking firms. It should make it even simpler for Americans to travel with out the problem of creating foreign money conversions or fumbling with an unmanned ticket kiosk at a prepare station that does not recognize our out-of-date magnetic-stripe
cards. Previously, you had to gather your strength and overcome the tremor of your voice before making a name, but with the arrival of chats, the world has modified and it has change
into easier for social phobias like me to reside. But due to apps like Booking, Airbnb,
Tripadvisor, lodge reservations and trip planning have turn into much simpler.
This set includes a template with a clean and user-friendly
design, which is so in style with all users of
e-commerce apps corresponding to ASOS, YOOX or Farfetch.
This template will make health care easier, as it would carry patients and medical doctors closer together.
Are you looking for a trustworthy solution to enhance the life of your roof?
Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is your solution. The exceptional product delivers a unique degree of
care for your asphalt shingles, ensuring they remain durable.
With Shingle Magic Roof Sealer, you’re not just applying any ordinary product.
You’re opting for a premium roof rejuvenation solution designed to significantly extend the life of your
roof for many years to come. This is a wise decision for anyone seeking to protect their investment.
Why choose Shingle Magic Roof Sealer? For starters,
its exclusive formula gets into the asphalt shingles,
restoring their pristine condition and look.
Additionally, the sealer is incredibly simple to use, requiring little effort
for optimal results.
In addition to Shingle Magic Roof Sealer extend the life of your
roof, but it also provides superior protection against the elements.
Be it harsh sunlight, heavy rain, or snow and ice, the roof will be shielded.
Furthermore, choosing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer
means you are selecting an eco-friendly option. Its non-toxic makeup ensures minimal environmental
impact, making it a responsible choice for your home.
To sum up, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is unparalleled as the ultimate roof rejuvenation solution. Not only does it
prolong the life of your roof while offering superior protection and being environmentally friendly option positions it as the
wise choice for property owners looking to invest in their property’s future.
Additionally, an important feature of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is its economic efficiency.
Rather than pouring heaps of money on regular repairs or a full roof replacement,
using Shingle Magic can save you expenses in the long run. It’s an economical
solution that provides high-quality results.
Additionally, the ease of application of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer
is a major plus. It doesn’t require specialized knowledge to apply
it. If you enjoy DIY projects or opt for professional installation, Shingle Magic ensures a seamless process with excellent
results.
Shingle Magic’s longevity is another significant reason to choose it.
When applied, it forms a layer that preserves the integrity of your shingles for a long time.
This means less worry about environmental wear and tear
and greater peace of mind about the health of your roof.
Regarding aesthetic appeal, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer also stands out.
Besides protecting your roof but also improves
its look. The shingles will appear newer, which adds to the curb appeal and market value to your property.
Client satisfaction with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is additional proof
to its effectiveness. Countless customers have experienced notable improvements
in their roof’s state after using the product.
Testimonials highlight its user-friendliness, durability, and superior defensive
capabilities.
To wrap it up, choosing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer means selecting
a reliable solution for roof rejuvenation. Combining durability,
beauty, cost-effectiveness, and simplicity makes it the optimal choice for homeowners wishing to extend the life and appearance of
their roof. Don’t wait to transform your roof with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer.
From the information feed to the shop, greater than a thousand elements.
This set contains more than 60 prepared-made screens
and greater than 120 further components. Also, all screens are offered in a
gentle and darkish type, which is able to make your software even more usable.
Also on this template there are screens for monitoring the change rate and the growth
of bitcoin. And likewise this template helps Google maps, which makes it more useful.
The app makes use of custom animation to make the interface extra visual.
Never make purchases or check on-line accounts on a public computer or public
wireless community. Now you can make purchases from residence,
which could be very handy and saves time. Now
you possibly can simply see what a hotel room or residence will appear to be,
you may learn reviews from former company and ensure
that this is exactly what you wanted. Companies normally clear and maintain their automobiles frequently, however should you make an enormous mess, you’d higher clear it up.
Attractive portion of content. I simply stumbled upon your site and in accession capital to
say that I acquire actually enjoyed account your blog
posts. Any way I will be subscribing to your feeds or even I success you get
right of entry to persistently fast.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Cover the back with felt, drill a hole in the highest, loop a string or ribbon by way of the outlet and there you’ve gotten it
— an prompt Mother’s Day gift. Decorate the outer circle with
any design you want, then glue a piece of ribbon to
the again or drill a gap at the highest to attach it to a door, wall or branch in your Christmas tree.
For Christmas, you can use pictures of snowmen, snowflakes, Santa Claus or you may minimize out images from
previous Christmas cards. You can also make a simple Christmas ornament
in about quarter-hour or spend hours cutting up CDs and gluing the items to make a mosaic picture frame.
You can decorate only one aspect of the disc or get fancy and glue two
CDs together with the shiny sides facing out
so it glitters from each angle. Once the candle has burned and
the disc is coated with wax, you possibly can throw it away
or use the CD for an additional crafting goal.
The best means to make use of a CD as a candleholder is to set a small pillar or votive candle in the middle of the disc with the shiny side up.
Many players choose to download software program to
their very own device, for ease of use and speedy accessibility.
Perhaps the most thrilling factor about the GamePad is how games use it — let’s take
a look at some examples. We look out for the biggest jackpots and convey you the
most recent information on probably the most exciting titles to play.
On our webpage, there isn’t a want to put in further software or apps to have the ability to play your favourite slot game.
This is a excessive-variance slot game that is extra likely to attract followers of
IGT slots such as the mystical Diamond Queen or the cat-themed Kitty
Glitter slot. The White Orchid slot features a feminine touch with pink and white
because the distinguished colours. Like Red Mansions,
the White Orchid slot features a wide betting range and players can begin betting with just a coin. Almost
all of the web casinos offer free versions of their software so
the person can play slot machines. The enjoying
card symbols are simply just like the playing cards which might be
used to play actual money table games online.
But there seems to have been no thought put into how easily the playing
cards could possibly be counterfeited (or what a nasty thought it’s to cross
round paper objects in the middle of a pandemic).
Do you wish to offer your roof a second chance? Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is the answer.
The exceptional product offers an extraordinary level of protection for
your asphalt shingles, guaranteeing they last longer.
With Shingle Magic Roof Sealer, you’re not just applying any ordinary product.
You’re opting for a top-quality roof rejuvenation solution formulated to significantly extend the life of your roof by up to 30 years.
This is a wise decision for anyone seeking to safeguard their investment.
What makes Shingle Magic Roof Sealer? Firstly, its exclusive formula gets into the asphalt shingles, rejuvenating their original strength and
look. Furthermore, the sealer is incredibly straightforward
to install, demanding no work for maximum results.
Not only does Shingle Magic Roof Sealer increase the life of your roof, but it provides superior resistance to environmental damage.
Be it intense UV rays, rainstorms, or freezing temperatures,
your roof is safeguarded.
Moreover, selecting Shingle Magic Roof Sealer means you’re selecting an environmentally friendly option. The safe formula ensures reduced environmental impact, thus making
it a responsible choice for your home.
In conclusion, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is unparalleled as the best roof rejuvenation solution. Its ability to extend the life of
your roof and providing superior protection and a environmentally
friendly option makes Shingle Magic as the ideal choice for homeowners aiming to invest in their
property’s future.
Moreover, a significant advantage of Shingle Magic Roof
Sealer is its economic efficiency. Instead of investing a fortune on constant repairs or a
full roof replacement, applying Shingle Magic helps save you costs in the
long run. It’s an economical solution that provides premium results.
Moreover, the user-friendly nature of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer stands out.
There’s no need for expert skills to apply it. If you enjoy DIY projects or prefer for expert application, Shingle
Magic ensures a straightforward process with remarkable results.
The product’s lasting power is yet another significant reason to choose it.
After application, it develops a shield that preserves the integrity of your shingles for a long time.
That means reduced worries about weather damage and a more secure feeling about the
health of your roof.
Regarding aesthetic appeal, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer
is also superior. It not only protects your roof but also improves its look.
Shingles will seem newer, which adds to the curb appeal and market value to your property.
Client satisfaction with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is further evidence to
its quality. Numerous homeowners have seen significant improvements in their roof’s health after using the product.
Reviews highlight its ease of use, longevity, and excellent protective qualities.
In conclusion, selecting Shingle Magic Roof Sealer represents opting for a reliable solution for roof rejuvenation. With its blend of longevity,
aesthetic enhancement, economic efficiency, and
user-friendliness renders it the ideal choice for homeowners seeking to prolong the life and beauty of their roof.
Don’t wait to give your roof the care it deserves with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Our mechanism’s effectivity is within a constant fraction of the a posteriori optimally efficient resolution. Our mechanism’s technical core is a
variant of the online weighted bipartite matching downside the place in contrast to prior variants wherein one randomizes edge
arrivals or bounds edge weights, we may revoke beforehand dedicated edges.
Further, it bounds the earnings of speculators who are in the game to acquire the cancellation charges.
Our mannequin allows the vendor to cancel at any time any
reservation made earlier, in which case the holder of the reservation incurs a utility loss amounting to a fraction of her value for the reservation and might also receive a
cancellation payment from the seller. They nonetheless hold if
we change gadgets with elements of a matroid and matchings with unbiased sets, or if all bidders have
additive worth for a set of objects. A seller will show a
set of slots sooner or later T in the future. Many advertisers (bidders) use
Internet systems to purchase display commercials on publishers’ webpages or on conventional media similar to radio, Tv and newsprint.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
The Zephyrus S17 has a big 4 cell, 90WHr battery. Four tweeters are positioned underneath the keyboard while the 2
woofers sit beneath the display. Overall, these two benchmark results bode properly for players wanting a laptop computer that’s a lower above by way of graphics efficiency, with the
excessive frame rates equating to a smoother gaming experience and
extra element in each scene rendered. Because the Xbox 360 cores can each
handle two threads at a time, the 360 CPU is the equivalent of getting six typical processors in a single
machine. The sheer amount of calculating that is finished by the graphics
processor to find out the angle and transparency for every reflected object,
and then render it in real time, is extraordinary. Southern California artist
Cosmo Wenman has used a 3-D printer to make meticulously rendered copies of famous sculptures, based mostly upon plans normal from a whole lot of images that he
snaps from every angle. Many firms offer a combination of these plans.
With its mixture of a Core i9-11900H CPU, a Nvidia RTX 3080 GPU, and 32GB
of RAM, this laptop performed exceedingly effectively in performance benchmarks that
provide perception into its CPU power and cooling.
What this means when you are enjoying video
video games is that the Xbox 360 can dedicate one core entirely to producing sound, whereas another could run the game’s collision and
physics engine.
Here is my web blog; ยิงปลาฟรี
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Если вам нужно [url=https://denezhnye-perevody-iz-rossii.top/]денежный перевод из швеции в россию в 2024[/url] , denezhnye-perevody-iz-rossii.top предоставляет превосходные услуги для этого. Наша платформа гарантирует быстрый и безопасный процесс перевода, позволяя отправить средства в любую точку мира без лишних хлопот. Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы каждый ваш перевод был максимально простым и понятным.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
From the information feed to the shop, more than a thousand parts.
This set includes greater than 60 prepared-made screens and more than 120 extra components.
Also, all screens are presented in a mild and darkish style, which is able to make your application much more usable.
Also in this template there are screens for tracking the trade rate and
the growth of bitcoin. And likewise this template helps Google maps,
which makes it more useful. The app uses customized animation to make
the interface extra visual. Never make purchases
or examine on-line accounts on a public computer or
public wireless community. Now you can make purchases from dwelling, which could be very
handy and saves time. Now you possibly can easily see what a lodge room
or apartment will appear to be, you may learn critiques from former company and ensure
that this is exactly what you needed. Companies often clean and maintain their vehicles frequently, but if you make a giant mess, you’d higher clear
it up.
Your Go-to Choice for Cleaning in Ankara – Reliable and Efficient
Ankara’s Top-rated Cleaning Company – Quality Services Guaranteed
You’re so interesting! I do not believe I’ve truly read through a single thing
like this before. So great to discover someone with some unique thoughts on this issue.
Really.. thank you for starting this up. This
web site is something that is required on the internet, someone with
a bit of originality!
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
It’s an amazing paragraph for all the web viewers; they will obtain benefit from it I am sure.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
приворот на мужчину на сперму приворот девушки на убывающую луну
можно ли делать привороты в новолуние – https://magizmo.ru сильный приворот на парня
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Your post resonated with me on a personal level.If anyone wants to read the topic in more details then visit 8xbet
When some one searches for his necessary thing,
thus he/she wishes to be available that in detail, therefore that thing is maintained over here.
Casinoplus Güncel Giriş
Serotonin Centers in Windermere, FL: Elevating Your Well-being Amidst
Serenity
In the picturesque city of Windermere, Serotonin Centers stands as a beacon of well-being and rejuvenation.
Serving neighborhoods like Ashlin Park and Berkshire Park, the medical spa has become an integral part of
Windermere’s thriving community.
Windermere, founded in 1887, is a city characterized by tranquility, with 1,231 households and a population of 3,003 as of 2021.
Nestled along FL-429, the city has embraced modernity while preserving its
natural allure, offering a unique blend of sophistication and serene landscapes.
Ensuring the vitality of your well-being, Serotonin Centers
addresses the specific needs of Windermere residents with its range
of medical spa services. From Ashlin Park to Berkshire
Park, the neighborhoods benefit from personalized care that enhances the overall wellness
of the community.
In Windermere, repairs to the body and mind are as essential as maintaining a residence.
The city’s diverse climate, with temperatures varying throughout the year, underscores the importance of accessible and quality medical spa services provided by Serotonin Centers.
Discover Windermere’s cultural richness by exploring the 7D Motion Theater Ride
at ICON Park or paying respects at the 9/11 Memorial. Serotonin Centers, with its
commitment to well-being, aligns seamlessly with Windermere’s emphasis on a balanced and fulfilled lifestyle.
Choosing Serotonin Centers in Windermere is a decision to prioritize self-care in a city that cherishes its residents’ holistic wellness.
Embrace the serenity and sophistication of Windermere, and let Serotonin Centers
guide you on a journey to elevate your well-being.
”
“Serotonin Centers Embraces Wellness in Colts Neck, NJ: A Haven for Holistic Living
Nestled in the heart of Colts Neck, Serotonin Centers is more than a medical spa; it’s a haven for holistic living.
Serving neighborhoods like Beacon Hill and Belford, the center has become an integral part of Colts Neck’s thriving community.
Colts Neck, founded in 1847, is a city characterized by its close-knit community, boasting
3,523 households and a population of 3,003 as of 2021. Connected by
Route 34, the city preserves its historical charm while welcoming modernity, offering residents a unique blend of tranquility and vibrant living.
In a community where well-being is paramount,
Serotonin Centers addresses the specific needs of Colts Neck residents with its range
of medical spa services. From Beacon Hill to Belford, the neighborhoods benefit from personalized care that
enhances the overall wellness of the community.
Colts Neck, known for its historical landmarks like the Allen House
and Allgor-Barkalow Homestead Museum, appreciates the significance of holistic well-being.
Serotonin Centers seamlessly aligns with Colts Neck’s commitment to a balanced
and fulfilled lifestyle.
When it comes to repairs, Colts Neck residents prioritize both their
homes and personal well-being. The city’s diverse climate, with varying
temperatures throughout the year, underscores the importance of accessible and quality medical spa
services provided by Serotonin Centers.
Choosing Serotonin Centers in Colts Neck is choosing a path to holistic
living in a city that treasures the overall well-being of its residents.
Embrace the tranquility and historical charm
of Colts Neck, and let Serotonin Centers guide you on a journey to elevate your well-being.
”
“Discovering Serenity in Windermere, FL with Serotonin Centers
Welcome to Windermere, FL, where tranquility meets modern living, and Serotonin Centers stands as a beacon of wellness at 7790 Winter
Garden Vineland Rd Suite 100. Serving the communities of Ashlin Park,
Berkshire Park, and beyond, this medical spa has become an essential part of Windermere’s well-being landscape.
Founded in 1887, Windermere boasts a population of 3,003 residents and 1,231
households as of 2021. The city, connected by FL-429, provides a picturesque setting for those
seeking a balance of nature and urban conveniences.
Serotonin Centers understands the unique needs of Windermere residents,
offering tailored services to neighborhoods like Casabella at Windermere and Clear Lake.
The medical spa thrives in a city that values community and individual well-being,
aligning seamlessly with Windermere’s commitment to a healthy lifestyle.
Windermere is not just a city; it’s an experience. As residents enjoy points of interest like Central Florida Railroad Museum and Eagle Nest Park,
Serotonin Centers enhances their journey by providing comprehensive medical spa services.
The city’s diverse climate, with temperatures varying throughout the year,
underscores the importance of accessible wellness services.
When it comes to choosing a medical spa in Windermere,
Serotonin Centers emerges as the top choice.
With a prime location on FL-429 and a commitment to holistic well-being, the center enriches the
lives of Windermere residents, ensuring they embrace life’s every moment with vitality and serenity.
”
“Embracing Serenity in Colts Neck, NJ with Serotonin Centers
Step into the serene embrace of Colts Neck, NJ, where Serotonin Centers stands as
a beacon of well-being at 178 County Rd 537.
Serving the tight-knit communities of 5 Point Park, Beacon Hill, and beyond,
this medical spa has become an essential part
of Colts Neck’s wellness landscape.
Established in 1847, Colts Neck exudes a
charm that captivates its 3,003 residents residing in 3,523 households as of
2021. The city, gracefully connected by Route 34, offers a blend of historical richness
and modern comfort, creating an idyllic backdrop
for holistic health.
Serotonin Centers understands the unique needs of
Colts Neck residents, offering tailored services to
neighborhoods like Belford and Bucks Mill. The medical
spa seamlessly integrates with the city’s commitment to a healthy lifestyle, contributing to the overall
well-being of Colts Neck’s vibrant community.
Colts Neck is not just a city; it’s a journey through time and
nature. As residents explore points of interest like Amazing Escape Room Freehold and Big Brook Nature Preserve, Serotonin Centers enriches their journey by providing
comprehensive medical spa services. The city’s diverse climate, with temperatures varying throughout the year, underscores the importance of accessible wellness services.
Choosing a medical spa in Colts Neck becomes an easy decision with Serotonin Centers.
Nestled conveniently along Route 34 and dedicated to holistic well-being, the center
becomes an indispensable partner in Colts Neck residents’ pursuit of a balanced and fulfilled life.
”
“Rejuvenation Oasis: Serotonin Centers in Windermere,
FL
In the heart of Windermere, FL, where nature and
luxury converge, Serotonin Centers at 7790 Winter Garden Vineland Rd
Suite 100 beckons residents to embark on a journey
of rejuvenation. This medical spa, nestled in the vibrant neighborhoods
of Ashlin Park and Berkshire Park, serves as a sanctuary for those seeking optimal well-being.
Founded in 1887, Windermere has grown into a close-knit community with 1,
231 households and a population of 3,003 as of 2021. Connected by the bustling FL-429, this city offers a unique blend of natural beauty and modern conveniences, providing the perfect backdrop for Serotonin Centers’ holistic health services.
Understanding the distinct needs of Windermere residents, Serotonin Centers extends its services to neighborhoods like Carver Shores and Coytown. The medical spa seamlessly integrates into the fabric of Windermere,
contributing to the overall health and happiness of its
residents.
Windermere, with its diverse climate and proximity to major attractions
like Downtown Winter Garden and Fantasyland, creates an environment where residents prioritize their well-being.
Serotonin Centers complements this lifestyle, offering
tailored medical spa services that align with the city’s commitment to
a healthy and balanced life.
When it comes to choosing a medical spa in Windermere, the decision is clear—Serotonin Centers
stands out as a beacon of holistic health. Conveniently located along FL-429 and dedicated to rejuvenation, the center becomes an indispensable partner in the journey toward optimal
well-being for Windermere residents.
Serotonin Centers in Windermere, FL: Elevating Your Well-being Amidst Serenity
In the picturesque city of Windermere, Serotonin Centers stands as a beacon of well-being and rejuvenation. Serving neighborhoods like Ashlin Park
and Berkshire Park, the medical spa has become an integral part of Windermere’s thriving community.
Windermere, founded in 1887, is a city characterized by tranquility, with
1,231 households and a population of 3,003 as of 2021.
Nestled along FL-429, the city has embraced modernity while preserving its
natural allure, offering a unique blend of sophistication and serene landscapes.
Ensuring the vitality of your well-being, Serotonin Centers addresses the specific needs
of Windermere residents with its range of medical spa services.
From Ashlin Park to Berkshire Park, the neighborhoods benefit from
personalized care that enhances the overall wellness of the community.
In Windermere, repairs to the body and mind are as essential as maintaining a
residence. The city’s diverse climate, with temperatures varying throughout the
year, underscores the importance of accessible and
quality medical spa services provided by Serotonin Centers.
Discover Windermere’s cultural richness by exploring
the 7D Motion Theater Ride at ICON Park or paying respects at the
9/11 Memorial. Serotonin Centers, with its commitment
to well-being, aligns seamlessly with Windermere’s emphasis on a balanced and fulfilled lifestyle.
Choosing Serotonin Centers in Windermere is a decision to prioritize self-care
in a city that cherishes its residents’ holistic wellness.
Embrace the serenity and sophistication of Windermere, and let Serotonin Centers guide you
on a journey to elevate your well-being.
”
“Serotonin Centers Embraces Wellness in Colts Neck, NJ: A
Haven for Holistic Living
Nestled in the heart of Colts Neck, Serotonin Centers is
more than a medical spa; it’s a haven for holistic living.
Serving neighborhoods like Beacon Hill and Belford, the center has become
an integral part of Colts Neck’s thriving community.
Colts Neck, founded in 1847, is a city characterized by its close-knit community, boasting 3,
523 households and a population of 3,003 as of 2021.
Connected by Route 34, the city preserves its historical charm while welcoming
modernity, offering residents a unique blend of tranquility and vibrant living.
In a community where well-being is paramount, Serotonin Centers addresses the specific
needs of Colts Neck residents with its range of medical spa services.
From Beacon Hill to Belford, the neighborhoods benefit from personalized care that enhances the overall wellness of the community.
Colts Neck, known for its historical landmarks like the Allen House and Allgor-Barkalow Homestead Museum, appreciates
the significance of holistic well-being. Serotonin Centers seamlessly aligns with Colts Neck’s commitment to a balanced
and fulfilled lifestyle.
When it comes to repairs, Colts Neck residents
prioritize both their homes and personal well-being.
The city’s diverse climate, with varying temperatures throughout the year, underscores the
importance of accessible and quality medical spa services provided by Serotonin Centers.
Choosing Serotonin Centers in Colts Neck is choosing a path
to holistic living in a city that treasures the
overall well-being of its residents. Embrace the
tranquility and historical charm of Colts Neck, and let Serotonin Centers guide you on a journey to elevate your well-being.
”
“Discovering Serenity in Windermere, FL with Serotonin Centers
Welcome to Windermere, FL, where tranquility meets modern living, and Serotonin Centers
stands as a beacon of wellness at 7790 Winter Garden Vineland Rd
Suite 100. Serving the communities of Ashlin Park, Berkshire Park, and beyond, this
medical spa has become an essential part of Windermere’s well-being
landscape.
Founded in 1887, Windermere boasts a population of 3,003
residents and 1,231 households as of 2021. The
city, connected by FL-429, provides a picturesque setting for those seeking a balance of nature and urban conveniences.
Serotonin Centers understands the unique needs of Windermere residents, offering tailored
services to neighborhoods like Casabella at Windermere
and Clear Lake. The medical spa thrives in a city that values community and individual well-being,
aligning seamlessly with Windermere’s commitment to a
healthy lifestyle.
Windermere is not just a city; it’s an experience.
As residents enjoy points of interest like
Central Florida Railroad Museum and Eagle Nest Park,
Serotonin Centers enhances their journey by providing comprehensive medical
spa services. The city’s diverse climate, with temperatures varying
throughout the year, underscores the importance of accessible wellness services.
When it comes to choosing a medical spa in Windermere, Serotonin Centers emerges as the top choice.
With a prime location on FL-429 and a commitment to holistic well-being, the center
enriches the lives of Windermere residents, ensuring they embrace life’s every
moment with vitality and serenity.
”
“Embracing Serenity in Colts Neck, NJ with Serotonin Centers
Step into the serene embrace of Colts Neck, NJ, where Serotonin Centers stands as a beacon of
well-being at 178 County Rd 537. Serving the tight-knit communities of 5 Point Park,
Beacon Hill, and beyond, this medical spa has become an essential part of Colts Neck’s wellness landscape.
Established in 1847, Colts Neck exudes a charm that captivates its
3,003 residents residing in 3,523 households as of 2021.
The city, gracefully connected by Route 34, offers a
blend of historical richness and modern comfort, creating an idyllic backdrop for holistic
health.
Serotonin Centers understands the unique needs of Colts Neck residents,
offering tailored services to neighborhoods like Belford and Bucks Mill.
The medical spa seamlessly integrates with the city’s commitment
to a healthy lifestyle, contributing to the overall well-being of Colts Neck’s vibrant community.
Colts Neck is not just a city; it’s a journey through time
and nature. As residents explore points of interest like Amazing Escape Room Freehold and Big Brook Nature Preserve, Serotonin Centers enriches their journey by providing comprehensive medical spa services.
The city’s diverse climate, with temperatures varying throughout
the year, underscores the importance of accessible wellness services.
Choosing a medical spa in Colts Neck becomes an easy decision with Serotonin Centers.
Nestled conveniently along Route 34 and dedicated to holistic well-being, the center becomes
an indispensable partner in Colts Neck residents’ pursuit of a balanced and
fulfilled life.
”
“Rejuvenation Oasis: Serotonin Centers in Windermere, FL
In the heart of Windermere, FL, where nature and
luxury converge, Serotonin Centers at 7790 Winter Garden Vineland Rd Suite 100 beckons residents to embark on a journey of rejuvenation. This medical spa, nestled
in the vibrant neighborhoods of Ashlin Park and Berkshire Park, serves as
a sanctuary for those seeking optimal well-being.
Founded in 1887, Windermere has grown into a close-knit community with 1,
231 households and a population of 3,003 as of 2021. Connected
by the bustling FL-429, this city offers a unique blend of
natural beauty and modern conveniences, providing the perfect backdrop for Serotonin Centers’ holistic health services.
Understanding the distinct needs of Windermere residents, Serotonin Centers
extends its services to neighborhoods like Carver Shores and Coytown. The medical spa seamlessly integrates into the fabric of Windermere, contributing to the overall health and happiness of its residents.
Windermere, with its diverse climate and proximity to major attractions
like Downtown Winter Garden and Fantasyland, creates an environment where residents prioritize their well-being.
Serotonin Centers complements this lifestyle, offering
tailored medical spa services that align with the city’s commitment to a healthy and
balanced life.
When it comes to choosing a medical spa in Windermere, the decision is
clear—Serotonin Centers stands out as a beacon of holistic health.
Conveniently located along FL-429 and dedicated to rejuvenation, the center becomes an indispensable partner in the journey toward optimal well-being for Windermere residents.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Amazing plenty of very good data!
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Моя машина сломалась в самый неподходящий момент. Воспользовавшись mikro-zaim-online.ru, я смог взять займ и сразу же отремонтировать автомобиль. Этот сайт действительно спас меня от кучи проблем и затрат на такси.
MIKRO-ZAIM – [url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/]взять кредит онлайн срочно[/url]
Наши контакты: Зеленодольская улица, 36к2, Москва, 109457
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Onwin Giriş için Tıklayın onwin
With thanks. Numerous stuff!
Also visit my blog post – https://hardcore-fuck.info
Hey! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any trouble with hackers?
My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing several
weeks of hard work due to no back up. Do you have any methods to prevent hackers?
I am actually pleased to glance at this webpage posts which carries tons of useful facts,
thanks for providing such information.
Have a look at my homepage – cryptocurrency copy trading
Хочешь сделать денежный перевод в Египет из России? Не волнуйся, denezhnye-perevody-iz-rossii.top поможет тебе с этим. Мы облегчаем процесс перевода, предоставляя тебе подробные инструкции и поддержку на каждом шаге. С нашей помощью твой перевод будет выполнен быстро и без каких-либо сложностей.
Pastilla Cialis Precio
Cialis 5 mg prezzo cialis 5 mg prezzo tadalafil 5 mg prezzo
obviously like your website but you need to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to inform the reality on the other hand Ill certainly come back again
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
===============================================================================
приворот на парня по фото на телефоне в домашних условиях читать без свечей
приворот на постель узнать кто сделал приворот
как защититься от приворота мужчине – https://walls-club.ru сильный приворот на мужчину самостоятельно
======================
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Cheers, Great stuff!
Also visit my website :: http://icfood.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=791276
I like what you guys are usually up too. This kind of clever work and
exposure! Keep up the good works guys I’ve you guys to our blogroll.
Thank you for sharing your thoughts. I truly appreciate
your efforts and I will be waiting for your further post thanks once again.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
анаксимандр философия абсолют философия
афинская философияфилософия мгюаиндивидуалистическая философия
ресторан философия ии философия философия горелов
I am extremely imρressed with your ѡriting skilⅼs and also ԝith the layout on youг blog.
Ιs this a paid theme or did you mⲟdify it yⲟursеlf?
Eіther way keep up the nice qualitу writing, it’s rare to seе a great blog like this one today.
What’s up, yes this post is actually pleasant and I have learned lot of things from it concerning blogging.
thanks.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
When I originally commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time a comment
is added I get several emails with the same comment.
Is there any way you can remove me from that service?
Many thanks!
baget yüzük için en iyi pırlanta sitesi
Animeler.co’da ücretsiz ve kaliteli anime izle! Türkçe altyazılı popüler ve güncel animeleri keşfedin. Hemen üye olun, animelerin keyfini çıkarın!
I absolutely love your website.. Excellent colors & theme.
Did you build this site yourself? Please reply
back as I’m trying to create my very own site
and would like to know where you got this from or exactly
what the theme is called. Appreciate it!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
These are: Baratheon, Lannister, Stark and Targaryen – names that series followers might be all too accustomed to.
The Targaryen free spins function gives you 18 free spins with a x2 multiplier
– an awesome choice for those who love free spins.
Choose Baratheon free spins for the prospect to win huge.
It is a bit like betting red or black on roulette, and the percentages of you being profitable are 1:1.
So, it’s up to you whether you need to threat your
payline win for a 50% probability you would possibly improve it.
One distinctive feature of the sport of Thrones slot is the option players must gamble each win for the possibility to double it.
Some Apple users have reported having trouble with the soundtrack, after we tested it on the newest technology handsets
the backing observe came by way of wonderful. If you attend the location guarantee that you’ve your booking
reference ready to indicate to the security guard to stop delays to you and
different clients. We suggest that households mustn’t need greater than four slots within a 4-week interval and advise clients to
make every go to rely by saving waste when you have
space till you have a full load.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
You can too buy them from private sellers below the market price at eBay and Craigslist.
There are a variety of internet sites that feature slot games online
that one pays totally free. Then there are specialized net boards
for individuals who collect these slots cars. They don’t want to neglect prospects
who’re unable or unwilling to use the web to make appointments.
Customers would not have to call in to the middle and
speak with a representative. Some GSP-based deep auctions (e.g., DeepGSP, DNA) have attempted
to improve GSP with deep neural networks, whereas solely modeling native externalities and
thus nonetheless suboptimal. Secondly, we suggest a listing-smart deep rank module by
modeling the parameters of affine operate as a neural
community to ensure IC in end-to-end learning. Instead, the
public sale mechanism is modeled as a deep network by which the real system reward is feedbacked for training by
end-to-finish studying. The key is to implement a system
that’s straightforward to use and maintain.
Here is my web page: ยิงปลาฟรี
Ольга Штернец, выпускница Московской школы экономики, является мастером маркетинга и PR в нашей команде на mikro-zaim-online.ru. Её опыт в крупных рекламных агентствах и уникальный подход к маркетинговым стратегиям помогают нашему сайту выделяться и привлекать новых клиентов. Ольга отвечает за продвижение нашего бренда в интернете, разработку контент-стратегий и управление репутацией. Узнайте больше о её работе на https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/o-nas/
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Do you wish to provide your roof a second chance? Shingle
Magic Roof Sealer is your solution. Our unique product offers an extraordinary standard of
maintenance for your asphalt shingles, making sure they remain durable.
By choosing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer, you’re
not just using any ordinary product. You’re opting for a top-quality roof
rejuvenation solution crafted to greatly extend the
life of your roof for many years to come. This is a wise decision for those seeking to safeguard their investment.
What makes Shingle Magic Roof Sealer? Firstly, its proprietary formula seeps
into the asphalt shingles, rejuvenating their pristine
condition and appearance. Moreover, the sealer is incredibly simple to
use, requiring little time for maximum results.
Besides Shingle Magic Roof Sealer extend the life of your roof, it also provides
outstanding resistance to the elements. Whether it’s blistering sun, rainstorms, or snow and ice, your roof
is shielded.
Moreover, selecting Shingle Magic Roof Sealer signifies you are opting for an environmentally friendly option. The safe formula ensures minimal
environmental impact, which makes it a responsible choice
for eco-conscious homeowners.
To sum up, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer stands out as the best roof rejuvenation solution. Not only does it increase the life of your roof but also providing exceptional protection and an eco-friendly option makes Shingle Magic as the wise choice for
property owners aiming to care for their property’s
future.
Furthermore, an important feature of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is its cost-effectiveness.
Rather than spending a significant amount on constant repairs or a full roof replacement, applying Shingle Magic can save you costs in the
long run. It’s an economical solution that still delivers top-notch results.
Additionally, the ease of application of Shingle
Magic Roof Sealer is noteworthy. It doesn’t require professional expertise to apply it.
For those who like to handle things themselves or prefer for professional installation,
Shingle Magic ensures a straightforward process
with excellent results.
The product’s longevity also serves as a strong reason to choose
it. After application, it forms a shield that maintains the
integrity of your shingles for a long time. This means reduced worries
about weather damage and greater peace of mind about the
health of your roof.
When it comes to aesthetic appeal, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer also stands out.
It not only protects your roof but also improves its look.
Your shingles will look refreshed, thus adding curb appeal and
value to your property.
Customer satisfaction with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is further evidence to its effectiveness.
Countless homeowners have reported significant improvements in their roof’s condition after using the product.
Reviews underscore its user-friendliness,
durability, and superior protection.
To wrap it up, opting for Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is selecting a proven solution for roof rejuvenation. Combining durability, beauty,
cost-effectiveness, and simplicity positions it as the optimal choice for those
seeking to prolong the life and appearance of their roof.
Don’t hesitate to revitalize your roof with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer.
Сайт имеет немудрёный и удобопонятный интерфейс Настольные
игры — еще одна категория в Кент казино.
Здесь можно сыграть в европейскую, американскую, французскую и другие виды рулетки.
В разделе представлены топовые карточные игры.
Кроме того эти разновидности доступны в
Live Casino. Достаточно подключиться к трансляции, чтобы сражаться с реальными соперниками.
В этом режиме предусмотрен машистый диапазон ставок.
Поэтому лайв-игры подходят как
новичкам, этак и хайроллерам.
Заведение принадлежит известному оператору
и работает легально по лицензии Кюрасао Нужно идти верификацию при выводе крупной суммы Настольные игры — еще
одна категория в Кент казино.
Здесь можно выступить в европейскую, американскую, французскую и другие виды рулетки.
В разделе представлены топовые
карточные игры. Кроме того эти разновидности
доступны в Live Casino. Достаточно подключиться к трансляции, чтобы драться с реальными соперниками.
В этом режиме предусмотрен широкий диапазон ставок.
Поэтому лайв-игры подходят что новичкам, так и хайроллерам.
very good nice blog page thank you
===============================================================================
безопасный приворот на любовь мужчину читать в домашних условиях
приворот денег читать в домашних условиях.
приворот жены на расстоянии черная магия приворота на любовь девушки в домашних условиях.
рецепт приворота – https://simvolmagii.ru как распознать приворота у мужчин.
приворот без последствий читать в домашних
черный приворот на парня читать в домашних условиях на расстоянии без фото
======================
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
На сайте mikro-zaim-online.ru представлена важная информация о компаниях, предлагающих займы под 0%. Наши специалисты, включая Андрея Фролова и Екатерину Подольскую, тщательно изучили рынок микрокредитов, чтобы предложить вам наиболее выгодные варианты. Они также подготовили обширный материал о том, как правильно взять микрокредит, какие существуют способы его возврата, и описали потенциальные риски, связанные с микрофинансовыми услугами. Эти знания помогут вам сделать осознанный выбор и избежать неприятных сюрпризов. Подробнее на https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/o-nas/
I believe this is one of the so much important information for me.
And i am happy studying your article. But want to remark on few normal issues, The web site taste is wonderful,
the articles is actually great : D. Good activity, cheers
You’ll additionally need to connect some wires to the motherboard.
Your motherboard ought to have include a face plate for its back
connectors. Web site to permit you to see your train information — you’ve got
to connect the detachable USB thumb drive to a computer to sync the information it collects.
There’s not a lot to do on the SportBand itself, other than toggle between the display modes to see information about your current exercise session. See more small automotive photos.
Track down even small prices you don’t remember making, as a result of
typically a thief will make small purchases at first to
see if the account remains to be active. R1 is on time, R2 is occasionally late,
and anything higher than that could be a black mark in your credit score ranking
(R0 means they haven’t got enough details about your account yet).
You are still going to have to put in the physical labor, however they’ll take care of
the quantity crunching by timing your workouts and determining how much train you’re actually getting.
Whenever you cannot have a workout buddy, having the ability to put up scores and compete with your mates is the following best thing.
Its appears to be like may not appeal to individuals who wish to impress their mates with the most
recent and biggest in digital innovation.
Feel free to surf to my web page ยิงปลาฟรี
They constructed their very own group, inviting users to affix
and share their information about knitting, crocheting and extra.
The positioning goals to assist users “manage, share and discover” within the yarn artisan neighborhood.
Kaboodle boasts more than 12 million month-to-month guests with greater than 800,000 registered customers.
Some deal with particular industries, whereas others take a extra
common method. The focus on nature provides it a extra stress-free
really feel and a retreat for players who aren’t followers of
the action-laden, male-pleasant games by IGT similar to Star Trek – Against all Odds.
You will trigger the Free Spins bonus when you
get no less than three White Orchid symbols on any place in reel 3.
Two White Orchids will win you 10 free spins, three will reward you with 15 free spins, and four will yield
20 free spins, which is a generous amount for an IGT slot sport.
Most of our slot video games are pretty straightforward to play, with
in-depth information about the game objective and special symbols included
in each sport page. All pays are multiplied by the bet multiplier.
The importance of keywords such as “Top-rated drunk driving lawyers” and
“DUI legal representation specialists” is immense in a city
like Las Vegas, NV. Located in an energetic area,
Clark McCourt Criminal Lawyers serves neighborhoods like Amber Hills and Arts District, where such legal expertise is often sought.
Clark McCourt Criminal Lawyers is based in Las Vegas, a city established in 1905
with a fascinating history. With a population of 646,790 (as of 2021) and
240,462 households, it’s a center of activity. The Las
Vegas Beltway, a major highway, runs through this bustling city.
In Las Vegas, legal services, particularly in DUI
cases, can vary in cost. With temperatures in Las Vegas ranging widely,
from very hot summers to cool winters, dependable legal support
is essential.
Among the city’s attractions, AREA15 and Aliante Nature Discovery Park stand out.
AREA15, for instance, is known for its immersive experiences, while Aliante Nature Discovery
Park is famed for its natural beauty. Each provides distinct experiences, showcasing
the variety Las Vegas has to offer.
For those living in Las Vegas, opting for Clark McCourt Criminal Lawyers is a sensible choice.
Their expertise in DUI cases and deep understanding of the local area make them an ideal choice.
Задумывались ли вы о том, как важно выбирать правильную финансовую информацию? На mikro-zaim-online.ru работает Андрей Фролов, финансовый эксперт, чья экспертиза в банковской сфере неоспорима. Он предоставляет информацию, которая поможет вам сделать осознанный выбор микрозайма. Рядом с ним Екатерина Подольская, IT-эксперт, обеспечивает безупречную работу сайта. Знание и технологии – вот что отличает нас на фоне других. Подробнее на https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/o-nas/
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Виктор Гардиенов, наш замечательный менеджер по клиентскому обслуживанию, является ключевой фигурой на сайте mikro-zaim-online.ru. С образованием в области психологии и коммуникаций, он разработал уникальные методы общения с клиентами, понимая их потребности как никто другой. Виктор превосходно управляет кризисными ситуациями, обеспечивая каждому клиенту индивидуальный подход и высокое качество обслуживания. Ознакомиться с его работой и узнать больше о процессе оформления займов можно на https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/o-nas/
Long before any of the other apps on this checklist, Zagat guides in print have been a trusted source for locating a
terrific restaurant, particularly for individuals
who journey. There’s only one particular person I can consider who possesses
a unique combination of patriotism, intellect, likeability, and a proven monitor report
of getting stuff executed underneath powerful
circumstances (snakes, Nazis, “dangerous dates”). But
let’s go one step further past native food to avenue
food. And with this template, you will be one step forward of your rivals!
A unbelievable sport to go on adventures by your self, one I can simply suggest personally.
The game is free until gamers need to do away with the persistent
and prolonged ads that interrupt sport play by paying for an advert-free membership.
Amazon has greater than 140,000 titles in its lending library
you can access for free. That makes it much more like some sort of D&D
board sport and i can’t wait to strive that new feature out myself.
This isn’t Steam Remote Play, this is a local constructed-in sharing characteristic and you may
even buy extra of these special slots so others haven’t got to buy the
total recreation. That enables you to boost the storage capacity of the system to
36 megabytes, greater than twice that of the fundamental iPad.
my web blog … ยิงปลาฟรี
baget pırlanta yüzük
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
You can even e-mail the photographs in your album to
anybody with a computer and an e-mail account.
You could have at your disposal an internet picture album that can hold 1,000 photos, and the body may be set to randomly select images from this album.
When it’s finished downloading, the frame hangs up the phone line and starts displaying the new photographs one after another.
Urbanspoon also has options to upload your own photographs for a restaurant and to attach with associates who are additionally utilizing the app.
You’ll be able to vote whether or not or not you want a restaurant and see if other users have liked it.
Not solely do you have to deal with the break-in itself, but when delicate
monetary data was left obtainable for the thief, your misfortune is simply beginning.
Treat them as if they’re extra priceless than money — to the
thief, they are. It’s also making strides toward becoming a
more sustainable race. Men 18-40 must submit a time that is underneath 3 hours, whereas girls 18-49 should show that
they can full the race in under 3 hours, 45 minutes.
Car Insurance companies Whitfield County GA coverage is actually
one of those points you expect to never ever utilize, yet you’ll rejoice to have if you
do. Spend in a really good plan.
приворот на любимого человека читать в домашних условиях приворот на примирение с любимым читать.
сильный приворот на женщину читать по фото как убрать приворот с мужчины сделанный другой женщиной в домашних.
привороты и заговоры – https://starway555.ru белый приворот на жену в домашних условиях.
как избавиться от приворота сильный приворот на парня в домашних условиях читать обряд снятия приворота
While food trucks may conjure up mental photos of a “roach coach” visiting building sites with burgers and sizzling dogs, these cell eateries have come a great distance up to now few years. What’s more, he says, the version of Android on these tablets is definitely more universal and less restrictive than versions you might discover on tablets from, for instance, large carriers within the United States. True foodies wouldn’t be caught lifeless at an Applebee’s, and with this app, there’s no have to sort via a list of huge chains to search out actual local eateries. Besides, in the true auction surroundings, the number of candidate commercials and the variety of promoting positions in the auction are relatively small, thus the NP-arduous problem of full permutation algorithm might be tolerated. And if you would like an actual challenge, you’ll be able to try to construct a hackintosh — a non-Apple laptop operating the Mac working system. There are many different short-time period jobs you are able to do from the web. There are a lot of video cards to select from, with new ones popping out on a regular basis, so your greatest guess is to check audio/visual message boards for tips about which card is greatest suited to your objective.
If you happen to post footage of your loved ones and couple that with info like, “my husband is out of city this weekend” or “little Johnny is previous enough to stay at residence by himself now,” then your children’s security could possibly be in danger. On Facebook, users can send private messages or submit notes, images or videos to another user’s wall. It’s possible you’ll post something you discover innocuous on Facebook, but then it is linked to your LinkedIn work profile and you’ve got put your job at risk. You say something along the lines of, “We do not want to fret because we financial institution with a trainer’s credit score union,” and even, “We put all our cash into blue chip stocks and plan to experience it out.” Again, if you’re one the forty percent who permit open access to your profile, then all of the sudden identity thieves know where you financial institution and the place you’ve the majority of your investments.
Bandırma İle ilgili Tüm haber kategorilerinde tek lider
The passing WILD leave WILD symbols on their means. It features a mini-sport
that includes winnings, free spins, win multipliers, the activation of passing WILD during the free spins and a progressive Jackpot.
There are numerous websites the place one can go to to play online slot video games at no cost.
Land three more gong scatters in the course
of the bonus and you’ll retrigger another 10 free spins.
That makes it easy to do three or four issues directly in your tablet,
which is great for multitasking junkies. The objective of the sport is to get three Wheel icons on the reels to
then acquire access to the Bonus Wheel. Then glue the CD items onto the Styrofoam.
I shall search for and say, ‘Who am I, then? The
adapters look identical to a cassette tape with a plug that matches into the
headphone jack of your portable device. Ohanian is quoted as saying, “There is an unprecedented opportunity to fuse social and crypto in a way that seems like a Web2 social product but with the added incentive of empowering customers with actual possession,” and that
Solana can be the community that makes this potential.
However, customers must improve to a paid “gold” membership with the intention to view folks’s details or
ship them a message. A message middle helps customers contact one another without being pressured to
present out their personal email addresses. The computer isn’t dependent on a router being nearby both.
Additionally, while I remember being excited as I found all the computerlike issues I may do on my telephone, the pill’s larger type appears largely irksome, because it jogs
my memory of all the stuff I want to do with it, however can’t.
Since these services only rely on having a reliable cellphone, web connection and internet browser, businesses have regarded more and more at hiring dwelling-based mostly workers.
Keep your password to yourself, no matter what, and also you never have to worry
about it. Even sharing the password with a buddy so he or she
will log on and check something for you generally is a danger.
Could you please elaborate on [specific point in the post]? I’m curious to learn more.
It’s amazing to visit this web site and reading the views of
all mates on the topic of this piece of writing, while I am also eager of getting
experience.
Here is my site; Buy Bitcoin online
casino siteleri
Online games, a more sturdy download store, social networking, and media center performance are all massive options for the Wii U. More than ever before, Nintendo hopes to seize two completely different audiences: the avid gamers who love big-finances franchises like Zelda and Call of Duty, and the Wii followers who were launched to gaming by way of Wii Sports and Wii Fit. Iceland is a great possibility if you are part of a weak group, as it’s currently prioritising deliver to those who most need it. My So-Called Life’ was an excellent show with an incredible ensemble solid, however when lead actress Claire Danes left the show just couldn’t go on without her. Occasionally, an irreplaceable lead actor will want to depart – like Claire Danes from “My So-Called Life” – and there’s no option to continue. Many corporations want to put commercials the place adults with expendable revenue will see them. Don’t fret. Whether you are a serious foodie in search of a brand new dining expertise or simply want to eat out with out the guesswork, there’s an app for that. In actual fact, many individuals begin off selling unwanted stuff round their house and progress to actually in search of items, say at thrift stores, to resell. Drivers must move a background test, but after that, you’re prepared to begin hauling passengers day or evening.
Tailored Cleaning Packages for Every Need – Ankara’s Best Choice
Choose Excellence: Ankara’s Leading Cleaning Service Provider
Erotoons.net invites you to a festival where the art of erotic comics is celebrated in all its glorious diversity. Our site is a carnival of colors, stories, and emotions, each comic a masterpiece curated for the adult man’s discerning eye. Fans of every genre, from the subtle to the explicit, will find themselves at home among our vast collection. Here, every story is a performance, every page a spectacle, waiting to unfold its magic. Enter the festival where every visit is a journey through the most exquisite expressions of adult comics.
If you’re yearning for tales that ignite the senses, our [url=https://erotoons.net/sultry-summer-book-4/]sultry summer 4 porn comic[/url] are what you need. Join us at Erotoons.net for an unforgettable journey.
Antalya Vip Transfer Services Mestlife Speed and Economic
12, 2007, the Give 1 Get 1 (G1G1) program allowed U.S.
As of September 2007, about 7,000 laptops had been being examined by youngsters all over the world.
The OLPC Foundation aims to supply these laptops to tens of
millions of kids all through the growing world in order to improve their schooling and their
quality of life. The XO laptop computer’s design emphasizes low-cost,
durable development that can survive a wide range of
climates and the rigors of the creating world. The yr 2009 showed us numerous different improvements, including cheap, efficient
methods to track your physical exercise and higher methods
to cool down after a run, too. As you move all through the day, Fitbit tracks how a lot physical activity you
performed. Because the Fitbit works best for
walking movement and isn’t waterproof, you cannot use it
for actions such as bicycling or swimming; nevertheless, you’ll be able to enter these actions manually
in your on-line profile. If you happen to plan to watch
HD, you’d in all probability use an HDMI connection, though element,
S-Video or VGA are additionally potentialities, relying
on your particular system. More laptops should be available on the market sooner or later, and more growing nations will be ready
to use to join the G1G1 plan.
The only real downside is the high worth. The actual magic of the GamePad is in how it interacts with games.
It excels in CPU and GPU efficiency and dishes up constantly easy and detailed visuals in AAA games on its 4K
show. In our Rise of the Tomb Raider benchmark, our Asus ROG
Zephyrus S17 with Nvidia RTX 3080 GPU set to 140W topped the field,
edging out the Asus ROG Zephyrus X13 with Ryzen eight 5980HS CPU and RTX 3080 GPU
set at 150W. It additionally proved superior to the Adata XPG
15KC with GeForce RTX 3070 set at 145W – the
combination of the S17’s i9-11900H processor and
RTX 3080 GPU making light work of the workload
in the RoTTR preset. Cinebench’s single-threaded benchmark scores show only minimal distinction among laptops (consultant
of mainstream purposes), nonetheless, the S17’s multi-threaded rating ranked the S17 the second
highest amongst our comparison laptops, proving its suitability for prime-finish gaming and CPU
demanding tasks like 3D video enhancing. That’s sufficient for nearly all Mac laptops to charge at full pace or whereas in use.
How does a hair dryer generate such a powerful gust of air in the primary place?
Protective screens – When air is drawn into the hair dryer as the fan blades turn, different things outdoors the hair dryer
are also pulled towards the air intake. Next time you and pop watch a film, this will make issues a lot less complicated.
The more occasions your blog readers click on on these ads, the extra money you may make by the advert service.
This article discusses a number of the way to generate profits on the internet.
If you’re looking to make a fast buck, your greatest bet is to sell one thing or issues your own that
are of value. Those evaluations – and the way companies
address them – can make or break an enterprise.
In case your portable CD participant has an AC enter, you possibly can plug one end of the adapter into your
portable player and the opposite finish into your vehicle’s cigarette
lighter and you have a energy supply. This absolutely alerts you, the reader, to the chance that in the next paragraph you will study the main twist in the argument put
forth, making it entirely possible that you will have no interest in reading further.
Welcome to Erotoons.net, where the carousel of erotic comics spins, offering a ride through countless genres and styles. Each turn brings a new vista, a new thrill, perfectly crafted for the adult man’s diverse tastes. From the soft whispers of romantic tales to the thunderous roars of wild adventures, our collection is a spectrum of excitement. Here, every enthusiast of adult comics finds their heart’s desire, free to explore a universe where fantasy and reality dance in a beautiful embrace. Join the carousel and let your senses soar.
Desire something extraordinary in your reading list? Erotoons.net provides a unique collection of [url=https://erotoons.net/category/all-porn-comics/the-incredibles/]the incredibles porn comics[/url] that are sure to enthrall.
Güvenilir bahis siteleri nelerdir?
Приближался сезон охоты, и мне срочно нужно было обновить свой охотничий инвентарь. Чтобы не упустить возможность, я взял [url=https://postabank.ru/]займ[/url] и приобрел необходимое снаряжение, чтобы быть готовым к охоте.
Just as much as I did, I relished what you accomplished here. Your language is elegant and the drawing is enticing, yet you appear rushed to get to the next thing you should be providing. If you keep this walk safe, I’ll come back more often.
slot siteleri
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this web site before but after looking at
many of the articles I realized it’s new to
me. Regardless, I’m definitely happy I came across it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often!
en güvenilir bahis siteleri
Again, the radar is actually a LiDAR module used to enhance
the driver-assist features. The X1000 is graced with a number of
driver-help features. The only cameras we’ve examined with the identical detail in night captures are the Cobra SC400D and
the Nextbase 422GW, 622GW. However, those require brightening
to see the details, which the X1000 does not. With them on, element is even better.
The top result’s sooner diagnoses and remedies, and higher general
well being care. Both the front and rear cameras provide a wide 156-diploma area of view, overlaying the higher a part of the realm around the
car. Both cameras provide 2560 x1440 resolution, providing a good quantity of element and
high dynamic range (HDR) shade. Then there’s the day video,
which is nicely saturated and reveals superb element. First off, there’s a
remarkable lack of fish-eye distortion given the wide 156-degree subject of view.
To begin, laptops purchased by way of this program had been given to kids
in Afghanistan, Haiti, Rwanda and Cambodia. The multiple-alternative sections are given a “scaled” rating from one to 15.
Since there are lots of more than 15 questions in every of those sections, the rating does not characterize a “raw” tally
of proper and flawed solutions.
сильнейший приворот на любовь женщины приворот на любовь девушки читать.
как действует белый приворот бывают ли привороты без последствия.
приворот на любовь к девушке читать – https://victoriblog.ru как узнать есть на человеке приворот.
приворот на любовь девушки читать как вернуть любимую с помощью приворота легкий приворот на парня читать без последствия
bonus veren siteler
Definitely, what a great blog and revealing posts, I definitely will bookmark your site. Best Regards!
My website: бесплатная эротика на русском языке
Cabura зарабатывай играя – радуйся каждому Кабура , Официальный сайт
An outstanding share! I’ve just forwarded this ߋnto a coworker who hɑd been doіng
a little homework on tһіs. And he actuallу oгdered
mе dinner due to tһe fact that I discovered it
f᧐r him… lol. Ⴝo let me reword this…. Thanks for tһе meal!!
But yeah, tһanx for spending sοme tіme to talk aƅout thіѕ matter here
᧐n ʏour web ρage.
Feel free to surf to my webpage :: games betting – Ben –
Я всегда мечтал о большом рыболовном катере, который позволит мне и моим друзьям проводить незабываемые рыбалки на водоемах. С [url=https://postabank.ru/]постабанком[/url] я взял займ и осуществил свою мечту, приобретя катер для рыбалки в стиле!
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
deneme bonusu
To handle these phenomena, we propose a Dialogue State Tracking
with Slot Connections (DST-SC) mannequin to explicitly consider slot correlations throughout completely different domains.
Specially, we first apply a Slot Attention to
learn a set of slot-specific options from the unique dialogue and then combine them utilizing a slot info sharing module.
Slot Attention with Value Normalization for Multi-Domain Dialogue State Tracking
Yexiang Wang creator Yi Guo creator Siqi Zhu writer 2020-nov textual content Proceedings of the
2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) Association for Computational Linguistics Online conference publication Incompleteness of domain ontology and unavailability of some values
are two inevitable problems of dialogue state monitoring (DST).
On this paper, we propose a brand new architecture to cleverly exploit ontology, which consists of Slot Attention (SA) and Value Normalization (VN), referred to as SAVN.
SAS: Dialogue State Tracking by way of Slot Attention and Slot Information Sharing
Jiaying Hu author Yan Yang creator Chencai Chen writer Liang He author Zhou
Yu creator 2020-jul textual content Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational
Linguistics Association for Computational Linguistics Online convention publication Dialogue state tracker is
answerable for inferring consumer intentions through dialogue history.
We suggest a Dialogue State Tracker with Slot Attention and
Slot Information Sharing (SAS) to cut back redundant information’s interference and
enhance long dialogue context tracking.
en güvenilir bahis siteleri
Hi, i believe that i noticed you visited my weblog so i got here to return the prefer?.I am attempting to find
things to enhance my website!I assume its adequate to use some of your ideas!!
Three hundred watts are enough for low-energy machines, but when you are constructing a gaming machine with
a number of video playing cards or a machine with plenty of disks, you may want to think about
one thing bigger. The first product to launch on Hubble is a borrowing platform that lets users deposit
multiple belongings like SOL, BTC, and ETH to mint USDH at a capital-efficient collateral ratio of 110%.
Comparisons have been made calling Hubble “the Maker DAO of Solana,” and USDH ought to turn out to be an integral a part of
DeFi on the network as a Solana native crypto-backed stablecoin. The
Edison Best New Product Award is self-explanatory, and is
awarded in a number of categories, together with
science and medical, electronics and medical, energy and sustainability, know-how,
transportation and industrial design. This setup produces the
classic “soundscape experience” you usually examine in product descriptions for portable speakers where the sound seems to come at you from different instructions.
It’s a traditional slot themed around Ancient Egypt but additionally
has some magic-themed components. Alternatively, if you discovered the stakes of
the PowerBucks Wheel of Fortune Exotic Far East online slot somewhat low, why not attempt the Wheel of Fortune
Triple Extreme Spin slot machine?
Why limit your access to world-class adult entertainment? Erotoons.net breaks the mold by offering an extensive range of adult comics for both men and women. Our diverse collection caters to a wide array of tastes, ensuring that everyone above 18 finds something tantalizing. And the best part? It’s completely free. We believe in providing high-quality, erotic content without barriers. Why choose between quality and affordability when Erotoons.net offers both? Join us for an unparalleled experience in adult entertainment.
For those who crave a blend of art and allure, our [url=https://erotoons.net/]porn comics[/url] are a perfect choice. Discover a world of imagination at Erotoons.net.
This blog will work on all gadgets. Modern in each element, convenient for work on any units – HotelPro template of the booking application. Therefore, it is important to create
an application that allows football followers to follow their ardour and attract an increasing number of participants to their neighborhood.
The soccer group is considered one of the largest on the earth.
The London Marathon is also one among racing’s largest fundraising events.
The G-Slate runs on the Android 3.Zero (Honeycomb) operating system,
and it was considered one of the first tablets
to do so. Instead, they’d first register an account on the dealership’s Web site.
It may very well be your first clue that someone has already
stolen your identification. In this text, we’ll find out how identity thieves steal or scam
their approach into your financial life, and
define one of the best ways to maintain it from occurring.
And lots of of those companies supply methods you may earn money utilizing your individual possessions or time.
This template is acceptable for any working system, therefore, utilizing this template is
as easy as booking a lodge room.
Erotoons.net: Where Fantasies Unfold for All. Imagine a haven where the lines of adult entertainment blur and converge, welcoming both men and women over 18 to a world of exquisite erotica. Here, each comic is a mosaic of passion, a tapestry woven with threads of fantasy and reality. This isn’t just a website; it’s a realm where every visit is free and every story is a key to unlock your deepest desires. Why roam in the mundane when Erotoons.net offers a free odyssey into the extraordinary?
Desire something extraordinary in your reading list? Erotoons.net provides a unique collection of [url=https://erotoons.net/sultry-summer-book-2/]sultry summer 2 porn comic[/url] that are sure to enthrall.
Моя попугайчик заболел, и мне срочно нужны были деньги на консультацию у ветеринара. Спасибо [url=https://postabank.ru/]постабанку[/url], я получил необходимый займ и помог своему пернатому другу выздороветь.
Information on the load, availability and pricing of every model was
not offered on the web site as of this writing.
Several fashions with elaborate knowledge displays might be discovered on-line from about $20 to $70, though reviews of lots of them include quite a lot of 1- and 2-star warnings
about construct high quality; purchase from a site that allows easy returns.
More power-demanding fashions, just like the 16-inch M1 Pro/Max MacBook Pro, require greater than 60W.
If the maximum is 100W or less, a capable USB-C cable that helps
USB-solely or Thunderbolt three or 4 information will suffice.
They constructed their very own group, inviting users to hitch and
share their knowledge about knitting, crocheting and more.
With information of the pace of a peripheral and your
unknown cable, plug it into your Thunderbolt three or 4 capable Mac.
The Mac mini additionally has two Thunderbolt/USB 4 buses,
which, confusingly enough, also use the two USB-C ports: depending on what
you plug in, the controller manages information over the suitable customary at
its maximum information fee. Apple’s “USB-C Charge Cable,” as an example, was designed for top wattage but solely
passes information at USB 2.0’s 480 Mbps.
This site certainly has all of the information and facts I needed about this subject
and didn’t know who to ask.
Я давно искал надежный источник информации о займах на карту. Сайт [url=https://postabank.ru/]postabank.ru[/url] оказался настоящим спасением. С его помощью я смог найти лучшие МФО и оформить займ без отказа.
A round of applause for your article. Much thanks again.
My website: порно студенток
приворот на мужчину без последствия в домашних условиях на расстоянии по фото на телефоне заклинание приворота.
самый сильный приворот на фото . приворот на еду , приворот через вольт что это.
сорокоуст от приворота – https://magiya-vedovstvo.ru приворот на четверговую соль.
приворот по фото последствия приворот в домашних условиях без последствия приворот оплата по результату кто может помочь проверенные люди
Fantastic beat I would like to apprentice while you amend your web site how could i subscribe for a blog site The account helped me a acceptable deal I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear concept
Normally I do not read article on blogs however I would like to say that this writeup very forced me to try and do so Your writing style has been amazed me Thanks quite great post
Hi i think that i saw you visited my web site thus i came to Return the favore Im attempting to find things to enhance my siteI suppose its ok to use a few of your ideas
Somebody essentially help to make significantly articles Id state This is the first time I frequented your web page and up to now I surprised with the research you made to make this actual post incredible Fantastic job
Hi Neat post Theres an issue together with your web site in internet explorer may test this IE still is the marketplace chief and a good component of people will pass over your fantastic writing due to this problem
Simply wish to say your article is as amazing The clearness in your post is just nice and i could assume youre an expert on this subject Well with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post Thanks a million and please carry on the gratifying work
Thank you for the good writeup It in fact was a amusement account it Look advanced to far added agreeable from you However how could we communicate
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
I loved as much as youll receive carried out right here The sketch is tasteful your authored material stylish nonetheless you command get bought an nervousness over that you wish be delivering the following unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this hike
Mac to search out out what it could actually do-so long as
you’ve gotten a gadget on the opposite finish with parameters you learn about, like its
interface and maximum protocol speed. Plug one end right into a Mac and the opposite finish into an SSD or hub that you know the small print of.
For instance, you might have a Thunderbolt SSD drive that’s rated at 40 Gbps and
plug it in to your Mac using an unknown cable with USB-C
connectors on both ends. I discovered I may get the
exact volume setting I wished in much less time using this than the obligatory laptop computer volume keys.
It includes encoding a 30GB, 1080p MKV file to
MP4 using the Android Tablet Preset. File this one underneath safety
risk. The Asus ROG Zephyrus S17 is probably the most highly effective 17-inch gaming
laptops you should purchase. With three or extra, you can have your own gaming command middle.
However, greater than 97% of the chunks in ATIS knowledge have only one or two words, through which section (or chunking)
might not be a severe drawback.
Wow, I never thought about it that way. Great perspective!
[url=https://transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/turkey/belek]transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/turkey/belek[/url]
Comfortable take to and from the airport in any country of the mankind from the air broker. Official advantage of excessive smooth out at suitable prices.
transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/malta/valletta
[url=https://transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/belarus/vitebsk]transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/belarus/vitebsk[/url]
Carefree transmittal to and from the airport in any rural area of the humankind from the wind broker. Professional aid of excessive level at adequate prices.
transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/bulgaria/sofia
There’s a micro USB connector on the suitable aspect, and an SD card slot on the left protected when not in use by a rubber plug.
Similar to Tesco, the primary obtainable supply slot for ASDA is on the 14th of April, although, the supermarket at
the moment appears to be having bother with their webpage because the
grocery section is at the moment down. It
seems to be like you may be ready till across the center/end
of April for a delivery slot. If you don’t just like the slot machine approach, you may browse eating places by various classifications or view
a listing of Urbanspoon listings near your present location. Once on the web page, sort
“Cherry Master slot machine” into the search area at the highest of the page and press enter to bring up the listings.
The RTP fee reaches 95.53%. Gamblers are advisable to attempt to
apply the Flaming Hot slot demo to develop their very own strategies for the game.
In this paper we only define a slot filling drawback in Dress category area for
simplification. That is making it exhausting to
get a supply slot, with wait occasions now measured in weeks relatively than days.
These vary from 2x to 8x for the prospect of much greater prizes.
The Komodo Dragon slot machine’s 50 paylines are fastened and you may select
from a range of wagers beginning from 0.25 to a max guess of 50.00.
It’s an honest choice on your common gambler nevertheless
it probably won’t entice the excessive rollers.
The road wins are multiplied with the credits you choose to wager per line.
You choose the number of strains and wager per line which make up the full win. It’s a fearsome ally as
it lands in stacks for further possibilities at a number of win traces.
It’s attainable to score a full matrix of dragon wilds for bumper prizes.
Wilds can act as others if they can then full a win, and with sufficient in view, you could easily
accumulate multiple prizes on the last spin in a sequence.
Fans and producers labored exhausting to avoid wasting the sci-fi collection “Quantum Leap” from the
notoriously bad 8 p.m. You’ll additionally get the chance to
land stacks of wilds on a superb multiplier so this
fearsome creature might become your best buddy.
[url=https://transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/france/toulon]transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/france/toulon[/url]
Adequate transfer to and from the airport in any homeland of the humankind from the divulge broker. Professional aid of outrageous level at fair to middling prices.
transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/malta/bugibba
Cabura зарабатывай играя – радуйся каждому Кабура , Официальный сайт
Since this is Nintendo’s first HD console, most of
the massive modifications are on the inside. When CD gamers
just like the Sony Discman D-50 first hit the scene, manufacturers shortly designed adapters for cassette gamers that will
allow you to play your CDs (on a portable CD player, in fact) by means of the cassette slot.
City Council President Felicia Moore completed first in Tuesday’s
officially nonpartisan main with 41%, while City Councilman Andre
Dickens surprisingly edged out Reed 23.0% to 22.4% for the crucial second-place spot, a margin of simply over 600 votes.
Paper lanterns float in the sea, whereas huge mountains rise up from
the shoreline. Mysterious energy surrounds each symbol
and radiates from the reels into the backdrop of big pyramids in the desert, while the beetle symbols perform
some impressive tricks on every look. A free spins symbol does simply what you’d anticipate it to,
triggering ten bonus video games when it lands in any three or extra places at once.
In the event you manage to land a Wheel of Fortune image on reel one and the treasure chest on reel
five, you will unlock the principle PowerBucks Wheel of Fortune Exotic Far East slots recreation bonus round.
The spherical might be retriggered till you reach a maximum of
fifty free spins.
[url=https://transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/france/paris/airports/charles-de-gaulle]transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/france/paris/airports/charles-de-gaulle[/url]
Suitable take to and from the airport in any homeland of the world from the air broker. Whizz usage of high level at fair to middling prices.
transferairportesfgrdt.com/es/directions/finland/kittila/populars/levi
уход за ребенком андроид – https://xigra.ru
Fantastic items from you, man. I hage understand your stuff prior to andd you are just extremely
excellent. I actually like wwhat you have bought here, really like what
you’re stating and the best way during which you say it. You make it entertaining and you continue to take care
of to stay it wise. I can not wait to read far more from you.
That is actually a grteat site.
My homepage; เลเซอร์ยกกระชับ
This app will help doctors discover more patients by being able to depart feedback concerning
the therapy. Now this drawback is solved, this template will aid you keep away from such troubles due to the existence of
notifications. Landing web page with slideshow, expanded opinions, merchandise details,
show of merchandise with the opportunity of approaching for locking item particulars,
notifications and plenty of other helpful
details that create a comfortable setting for
your app users. The button beside the display will begin up train tracking, whereas
a toggle button on the facet of the machine switches between features.
Once full gameplay is launched, it is going to be fascinating to see how many individuals give up their jobs to P2E full time!
Because of this, your chat can easily grow to
be worldwide, connecting individuals from totally different international locations.
So the advert platform can analyze the financial properties of mechanism beneath complete
info recreation. Should you own your house, consider renting out
a room on a platform like Airbnb so that
you’ve got income coming in recurrently. There was
no alternative to see what the room would appear like, and there was no
alternative to read opinions about the service or the lodge’s personal restaurant.
У меня случилась неотложная медицинская ситуация, и я нуждался в деньгах на оплату медицинских услуг. Сайт [url=https://postabank.ru/]postabank.ru[/url] помог мне найти подходящее МФО, и я получил займ на карту в тот же день.
I gotta favorite this site it seems very beneficial handy
My website: русское реальное порно пьяных баб смотреть
The Vizio tablet runs Android apps, which are available for purchase or free from Android Market.
One area the place the Acer Iconia tablet (like different Android tablets) still falls short is the availability of apps.
Simple actions like making lists, setting deadlines and choosing the proper storage containers might help ensure you may have the perfect time possible.
Newer hair dryers have incorporated some technology from the clothes dryer:
a removable lint screen that is easier to clean. The tablets are
also suitable with a full wireless keyboard, which
is infinitely simpler to make use of than a touch screen for composing documents and
long e-mails. Acer acknowledges this development by positioning its
Iconia tablets as splendid for multitasking and pairing with
accessories designed for gaming, working or viewing content.
While it’s nonetheless early in the sport, the Acer Iconia tablet,
though not but a household name, looks to be off to an honest begin. Portnoy, Sean. “Acer Iconia Tab W500 pill Pc running Windows 7 out there beginning at $549.99.” ZDNet.
Hiner, Jason. “The ten hottest tablets coming in 2011.” ZDNet.
However, a customer support consultant with the corporate gave us 10 completely different
retailers the place the tablets had been imagined to be available on the market, but we may solely verify just a few that
stocked them.
Why settle for ordinary when you can experience the extraordinary at Erotoons.net? Our site doesn’t just offer adult comics; we redefine them. Each comic in our collection is a product of meticulous craftsmanship, blending engaging storytelling with stunning visuals. This is not just entertainment; it’s an art form. For those who seek more than the mundane, Erotoons.net is the only logical choice. Our content speaks to the connoisseur of adult-themed narratives, offering depth, variety, and quality unparalleled by any other site.
In search of a portal to a world of fantasy and passion? Erotoons.net is your gateway to the finest [url=https://erotoons.net/tag/rule-63/]rule 63 porn[/url] , where every story is an adventure.
And for good motive: It was sluggish, it regarded completely different than marketed, there have been no USB ports with out a bulky adapter,
the microSD memory card slot wasn’t spring loaded, so it was practically not possible to get
the card out. Thus, in Slot Filling stage,
we additional label “耐克”(Nike) as Brand Property (B-Brand/I-Brand), and “黑色”(black) as Color Property (B-Color/I-Color).
Without an APX radio, some first responders must carry a
couple of radio, or depend on data from dispatchers
earlier than proceeding with very important response activities.
The Craig Web site doesn’t present any info on retail areas the place
they can be found for purchase (or beneficial retail prices,
as we talked about previously). The Maylong Web site is maddeningly imprecise at finest, and
just plain inaccurate at worst. Web site to mean you can see your exercise info — you have
got to connect the detachable USB thumb drive
to a pc to sync the information it collects. For extra information on chopping-edge
products, award some time to the hyperlinks on the subsequent web page.
That means that when disaster strikes, first responders from
a wide number of agencies can talk and coordinate in real time.
ATM skimming is like id theft for debit playing cards:
Thieves use hidden electronics to steal the private info saved on your card and
report your PIN number to access all that arduous-earned cash in your account.
If ATM skimming is so severe and high-tech now,
what dangers can we face with our debit and credit playing
cards sooner or later? Mobile bank card readers let clients
make a digital swipe. And, as safety is at all times a problem in the case of
delicate credit card data, we’ll explore some of the accusations that rivals have
made in opposition to other products. If the motherboard has onboard
video, try to take away the video card utterly and boot utilizing the onboard model.
Replacing the motherboard generally requires replacing the heatsink and cooling fan, and could change
the kind of RAM your pc wants, so you may have to do a little analysis to
see what parts you have to to purchase on this case.
A key enchancment of the brand new rating mechanism is to mirror a more correct desire pertinent to recognition, pricing coverage
and slot impact primarily based on exponential decay model for
on-line users. This paper research how the web music distributor should set its ranking policy to maximize the value of online music rating service.
However, previous approaches often ignore constraints between slot
value representation and associated slot description representation within the latent area and lack sufficient mannequin robustness.
Extensive experiments and analyses on the lightweight models present that our proposed strategies achieve considerably increased
scores and considerably enhance the robustness of each intent
detection and slot filling. Unlike typical dialog fashions that depend on huge, complex neural community architectures and enormous-scale pre-educated Transformers
to realize state-of-the-artwork results, our technique achieves comparable outcomes to
BERT and even outperforms its smaller variant DistilBERT on conversational slot extraction tasks.
Still, even a slight improvement is perhaps worth the cost.
%article_summaty%
Here is my webpage; เว็บตรง100
Nintendo’s DS handheld and Wii console both use Friend Codes, a
long sequence of digits gamers have to commerce to have the ability to play games together.
The Wii U launch is basically an incredible proof-of-idea.
It is simple to forget that what may seem like a harmless comment on a
Facebook wall might reveal an amazing deal about your personal finances.
On Facebook, customers can send personal messages or
post notes, images or videos to another user’s wall.
Coupled with providers like e-mail and calendar software, online scheduling can streamline administrative
duties and free up staff to attend to different tasks.
The key here, as with many other services on the internet,
is being constant (on this case blogging a number of
times a week), promoting advertising and using your blog as a platform to
advertise different companies. Reverse lookup companies can provide
anybody with your home tackle if you possibly can present the phone number.
How can online banking assist me manage my credit score?
What is going to the bank card change mean for the typical American client?
Identity thieves may pay a visit to your mailbox and open up a credit card in your name.
谷山骨盤整骨院は鹿児島市谷山に位置する整骨院で、頭痛の治療に特化していることで知られています。また、交通事故後のリハビリに対するリハビリテーションにも特化していることが特徴です。
当院の目標は、患者様個々のニーズに応える、最良のケアを提供することにあります。これには、詳細な診察と、患者様の健康状態を細かくチェックすることが含まれます。
腰痛、肩こり、頭痛を抱える患者様に対して、私たちは多種多様な痛み緩和テクニックを使用しています。これには、整体療法などが含まれ、患者様の全体的な健康の向上を重視しています。
交通事故の後遺症に苦しむ患者様には、専門的なリハビリテーションを提供しており、患者様が通常の生活に素早く戻れるよう、全面的にサポートします。
谷山骨盤整骨院の革新的な治療アプローチは、患者様の身体のバランスを整えることを目的としています。これには、最新のEMS技術の使用が含まれ、これにより痛みの緩和と身体の動きの向上が可能になります。
施設名称 谷山骨盤整骨院/整体院/鍼灸
所在地 〒891-0114
鹿児島県鹿児島市小松原2丁目32-18
TEL 0120-914-392
Wonderful site. Lots of helpful info here. I’m sending it to
some friends ans also sharing in delicious.
And of course, thanks in your sweat! https://Guebsch.me/index.php?title=Benutzer:NanceeMarch9
Wonderful site. Lots of helpful info here. I’m sending it to
some friends ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks in your sweat! https://Guebsch.me/index.php?title=Benutzer:NanceeMarch9
One app gets visible that can assist you select simply
the right place to dine. London can be a fine proving floor for wheelchair athletes, with a $15,000
(about 9,500 pounds) purse to the first place male and female finishers.
The Xbox 360 is the first system to use such a architecture.
Since that is Nintendo’s first HD console, most of the large adjustments are on the inside.
The username is locked to a single Wii U console, and each
Wii U supports as much as 12 accounts. A conventional processor can run a single execution thread.
That works out to greater than eight million Americans in a
single yr — and people are simply the people who realized they were ID theft victims.
If you want to access the full suite of apps available to Android devices, you’re out of luck — neither the Kindle Fire nor the Nook Tablet can access the total Android store.
In my electronic ebook, both the Nook Tablet and the Kindle Fire are good devices, however weren’t exactly what I needed.
If you’re a Netflix or Hulu Plus buyer, you can download apps to entry
these services on a Kindle Fire as properly.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Serotonin Centers in Windermere, FL: Elevating Your Well-being Amidst Serenity
In the picturesque city of Windermere, Serotonin Centers stands as a beacon of well-being and rejuvenation. Serving
neighborhoods like Ashlin Park and Berkshire
Park, the medical spa has become an integral part of Windermere’s
thriving community.
Windermere, founded in 1887, is a city characterized by tranquility, with 1,231 households and a population of 3,003 as
of 2021. Nestled along FL-429, the city has embraced modernity while
preserving its natural allure, offering a unique blend of sophistication and serene landscapes.
Ensuring the vitality of your well-being, Serotonin Centers addresses the specific needs of Windermere
residents with its range of medical spa services.
From Ashlin Park to Berkshire Park, the neighborhoods benefit from personalized care that enhances the overall wellness of the community.
In Windermere, repairs to the body and mind are as essential as maintaining
a residence. The city’s diverse climate, with temperatures varying throughout the
year, underscores the importance of accessible and quality medical spa services provided by Serotonin Centers.
Discover Windermere’s cultural richness by exploring the
7D Motion Theater Ride at ICON Park or paying respects at the 9/11 Memorial.
Serotonin Centers, with its commitment to well-being, aligns seamlessly with Windermere’s emphasis on a balanced and fulfilled lifestyle.
Choosing Serotonin Centers in Windermere is a decision to prioritize self-care
in a city that cherishes its residents’ holistic wellness.
Embrace the serenity and sophistication of Windermere, and let Serotonin Centers guide you on a journey
to elevate your well-being.
”
“Serotonin Centers Embraces Wellness in Colts Neck, NJ: A Haven for Holistic Living
Nestled in the heart of Colts Neck, Serotonin Centers is
more than a medical spa; it’s a haven for holistic living.
Serving neighborhoods like Beacon Hill and Belford, the center
has become an integral part of Colts Neck’s thriving community.
Colts Neck, founded in 1847, is a city characterized by its close-knit community,
boasting 3,523 households and a population of 3,003 as of 2021.
Connected by Route 34, the city preserves
its historical charm while welcoming modernity, offering residents a unique blend of tranquility and vibrant living.
In a community where well-being is paramount, Serotonin Centers addresses the specific needs of Colts Neck residents with its range of medical spa services.
From Beacon Hill to Belford, the neighborhoods benefit from
personalized care that enhances the overall wellness
of the community.
Colts Neck, known for its historical landmarks like the Allen House and Allgor-Barkalow
Homestead Museum, appreciates the significance of holistic well-being.
Serotonin Centers seamlessly aligns with Colts
Neck’s commitment to a balanced and fulfilled lifestyle.
When it comes to repairs, Colts Neck residents prioritize both their homes and
personal well-being. The city’s diverse
climate, with varying temperatures throughout the year,
underscores the importance of accessible and quality medical spa services provided by Serotonin Centers.
Choosing Serotonin Centers in Colts Neck is choosing a path to
holistic living in a city that treasures the overall well-being of its residents.
Embrace the tranquility and historical charm of Colts Neck,
and let Serotonin Centers guide you on a journey to elevate your well-being.
”
“Discovering Serenity in Windermere, FL with Serotonin Centers
Welcome to Windermere, FL, where tranquility meets
modern living, and Serotonin Centers stands as a beacon of
wellness at 7790 Winter Garden Vineland Rd Suite 100.
Serving the communities of Ashlin Park, Berkshire Park,
and beyond, this medical spa has become an essential part of Windermere’s
well-being landscape.
Founded in 1887, Windermere boasts a population of 3,003 residents and 1,231 households as of 2021.
The city, connected by FL-429, provides a
picturesque setting for those seeking a balance of nature and urban conveniences.
Serotonin Centers understands the unique needs of Windermere
residents, offering tailored services to neighborhoods like Casabella at Windermere and Clear Lake.
The medical spa thrives in a city that values community and
individual well-being, aligning seamlessly with Windermere’s commitment to a healthy lifestyle.
Windermere is not just a city; it’s an experience. As residents enjoy points of interest like Central Florida Railroad Museum
and Eagle Nest Park, Serotonin Centers enhances their journey
by providing comprehensive medical spa services.
The city’s diverse climate, with temperatures varying throughout the year,
underscores the importance of accessible wellness services.
When it comes to choosing a medical spa in Windermere,
Serotonin Centers emerges as the top choice. With a prime
location on FL-429 and a commitment to holistic well-being,
the center enriches the lives of Windermere residents, ensuring they embrace life’s every moment with vitality and serenity.
”
“Embracing Serenity in Colts Neck, NJ with Serotonin Centers
Step into the serene embrace of Colts Neck, NJ, where Serotonin Centers stands as a beacon of well-being at 178 County Rd 537.
Serving the tight-knit communities of 5 Point Park, Beacon Hill,
and beyond, this medical spa has become an essential part of Colts
Neck’s wellness landscape.
Established in 1847, Colts Neck exudes a charm that captivates its 3,003
residents residing in 3,523 households as of 2021.
The city, gracefully connected by Route 34, offers
a blend of historical richness and modern comfort, creating an idyllic backdrop for holistic health.
Serotonin Centers understands the unique needs of Colts Neck
residents, offering tailored services to neighborhoods like Belford and Bucks Mill.
The medical spa seamlessly integrates with the city’s commitment to a healthy lifestyle, contributing to the overall well-being of Colts Neck’s vibrant community.
Colts Neck is not just a city; it’s a journey
through time and nature. As residents explore points
of interest like Amazing Escape Room Freehold
and Big Brook Nature Preserve, Serotonin Centers enriches their journey by providing
comprehensive medical spa services. The city’s diverse
climate, with temperatures varying throughout the year, underscores the importance of
accessible wellness services.
Choosing a medical spa in Colts Neck becomes an easy decision with Serotonin Centers.
Nestled conveniently along Route 34 and dedicated to holistic well-being, the center becomes an indispensable partner in Colts Neck residents’ pursuit of
a balanced and fulfilled life.
”
“Rejuvenation Oasis: Serotonin Centers in Windermere, FL
In the heart of Windermere, FL, where nature and luxury converge, Serotonin Centers at 7790 Winter
Garden Vineland Rd Suite 100 beckons residents to embark on a journey of rejuvenation. This medical spa, nestled in the vibrant neighborhoods of Ashlin Park and
Berkshire Park, serves as a sanctuary for those seeking
optimal well-being.
Founded in 1887, Windermere has grown into a close-knit community with 1,231 households and a population of 3,003
as of 2021. Connected by the bustling FL-429, this
city offers a unique blend of natural beauty and modern conveniences, providing
the perfect backdrop for Serotonin Centers’ holistic health services.
Understanding the distinct needs of Windermere residents, Serotonin Centers extends
its services to neighborhoods like Carver Shores and Coytown. The medical spa seamlessly integrates into the fabric of Windermere, contributing to the overall health and
happiness of its residents.
Windermere, with its diverse climate and proximity to major attractions like Downtown Winter Garden and Fantasyland, creates an environment where residents prioritize their well-being.
Serotonin Centers complements this lifestyle, offering
tailored medical spa services that align with the city’s commitment to a
healthy and balanced life.
When it comes to choosing a medical spa in Windermere, the decision is clear—Serotonin Centers stands out as a beacon of holistic health.
Conveniently located along FL-429 and dedicated to rejuvenation, the center
becomes an indispensable partner in the journey toward optimal well-being for Windermere
residents.
Why buy a $500 pill if you’re just using it to examine
your e-mail? Many of us have been using the same vacation gadgets for years, whether we like them or not.
If you own your own home, consider renting out a room on a platform like Airbnb so
that you’ve revenue coming in often. Internet marketing is the primary
source of revenue for Internet firms, corresponding to Google,
Facebook, Baidu, Alibaba, and so forth (Edelman et al., 2007).
Unlike organic items (Yan et al., 2020a) solely ranked by user preference, the display of
ads relies on each person choice and advertiser’s profit.
The outcomes of offline simulation and online A/B experiment exhibit that NMA brings a major enchancment in CTR and platform income, in contrast with GSP (Edelman et al., 2007), DNA (Liu
et al., 2021), VCG (Varian and Harris, 2014) and WVCG (Gatti et al., 2015).
We efficiently deploy NMA on Meituan food supply platform.
Fantastic site Lots of helpful information here I am sending it to some friends ans additionally sharing in delicious And of course thanks for your effort
I was suggested this web site by my cousin Im not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my trouble You are incredible Thanks
I loved as much as youll receive carried out right here The sketch is attractive your authored material stylish nonetheless you command get bought an nervousness over that you wish be delivering the following unwell unquestionably come more formerly again as exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this hike
Fantastic beat I would like to apprentice while you amend your web site how could i subscribe for a blog site The account helped me a acceptable deal I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear concept
Hello my loved one I want to say that this post is amazing great written and include almost all significant infos I would like to look extra posts like this
The location also features a feed of Hasselhoff’s tweets,
so users are all the time privy to what their idol is as
much as. It is a bit like betting crimson or black on roulette,
and the chances of you being profitable are 1:1. So, it’s up to you whether or not you want
to risk your payline win for a 50% chance
you would possibly improve it. So, there you
have got it – you won’t be able to plug in a Rumble
Pak, Controller Pak or perhaps a Transfer Pak. Another characteristic
of the N64 controller is the flexibility so as to add options via an enlargement slot on the bottom of the controller.
One distinctive feature of the game of Thrones slot is the option players have to gamble every win for
the prospect to double it. Most hair dryers (together with this one) have excessive and low airflow settings.
Though high school is commonly painful, having your present canceled doesn’t should be.
0.01 per slot line and ending with excessive limits – $one hundred per spin or even larger.
Although Game of Thrones slot doesn’t have a jackpot,
the game is stuffed with particular symbols and bonus features that
adds to the thrill. The iconic Game of Thrones logo appears in the
form of the slots wild image while the infamous Iron Throne is
the scatter image needed to trigger the game’s unique bonus features.
Tom Carper as his running-mate throughout his successful marketing campaign for governor and served as lieutenant governor
for eight years. Tom Winter, who’d reportedly been considering a bid, mentioned this week that he’ll run for Montana’s new 2nd Congressional District.
● Atlanta, GA Mayor: Former Mayor Kasim Reed conceded in his comeback bid to once again run Atlanta on Thursday,
falling simply wanting the second slot for the Nov. 30
runoff. ● MT-02: Former state Rep. The 35th is open as
a result of Democratic Rep. She later rose to the
state Senate, then in 1992 was tapped by Rep. Thus far, the
only particular person working for this safely blue seat
in Austin is Democratic Rep. Democrats at the moment control each the state House
and Senate and can nearly certainly remain in charge in this solidly blue state that voted for native
son Joe Biden 59-forty final yr. ● NH Redistricting:
New Hampshire Republicans have launched a draft congressional map that, as they’ve been promising
since they re-took management of state authorities last year, gerrymanders the state’s two House seats to make the first District significantly redder.
Despite the loss, many Democrats-and progressive activists specifically-shall be joyful to see Sweeney
gone, significantly for the reason that get together retained management of both chambers of the legislature in Tuesday’s elections.
helloI like your writing very so much proportion we keep up a correspondence extra approximately your post on AOL I need an expert in this space to unravel my problem May be that is you Taking a look forward to see you
For one thing, you get to work from your own residence more often than not.
Although SGI had by no means designed video sport hardware before, the corporate was considered
one of many leaders in pc graphics know-how. So, Nintendo announced an settlement with Silicon Graphics Inc.
(SGI) to develop a brand new 64-bit video game system,
code-named Project Reality. Nintendo is an organization whose very
title is synonymous with video gaming. Although most
boomers are still a long way from eager
about nursing homes, they will be encouraged to know that the
Wii Fit sport systems are even discovering their means into these
facilities, serving to residents do one thing they never could of
their youth — use a video recreation to stay limber and strong.
Or maybe you want a strong machine with a whole lot of disk house for
video modifying. Most people typically work from their company’s central location, a
physical area the place everybody from that organization gathers to exchange concepts and
set up their efforts.
Excellent blog here Also your website loads up very fast What web host are you using Can I get your affiliate link to your host I wish my web site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
I like what you guys are usually up too. This kind of clever work and
coverage! Keep up the terrific works guys I’ve included
you guys to my personal blogroll.
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here The sketch is tasteful your authored subject matter stylish nonetheless you command get got an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following unwell unquestionably come further formerly again as exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this hike
I have been browsing online more than three hours today yet I never found any interesting article like yours It is pretty worth enough for me In my view if all website owners and bloggers made good content as you did the internet will be a lot more useful than ever before
helloI really like your writing so a lot share we keep up a correspondence extra approximately your post on AOL I need an expert in this house to unravel my problem May be that is you Taking a look ahead to see you
I am not sure where youre getting your info but good topic I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more Thanks for magnificent info I was looking for this information for my mission
Wonderful web site Lots of useful info here Im sending it to a few friends ans additionally sharing in delicious And obviously thanks to your effort
Somebody essentially lend a hand to make significantly articles Id state That is the very first time I frequented your website page and up to now I surprised with the research you made to make this actual submit amazing Wonderful task
certainly like your website but you need to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to inform the reality nevertheless I will definitely come back again
Normally I do not read article on blogs however I would like to say that this writeup very forced me to try and do so Your writing style has been amazed me Thanks quite great post
I simply could not go away your web site prior to suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard info a person supply on your guests Is going to be back incessantly to investigate crosscheck new posts
I simply could not go away your web site prior to suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard info a person supply on your guests Is going to be back incessantly to investigate crosscheck new posts
I loved as much as youll receive carried out right here The sketch is tasteful your authored material stylish nonetheless you command get bought an nervousness over that you wish be delivering the following unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this hike
The only actual draw back is the high worth.
The actual magic of the GamePad is in how it interacts with video
games. It excels in CPU and GPU performance and dishes up constantly smooth and detailed visuals in AAA games on its 4K display.
In our Rise of the Tomb Raider benchmark, our Asus ROG Zephyrus S17
with Nvidia RTX 3080 GPU set to 140W topped the sector, edging out the Asus ROG Zephyrus X13 with Ryzen 8 5980HS CPU
and RTX 3080 GPU set at 150W. It also proved superior to the Adata
XPG 15KC with GeForce RTX 3070 set at 145W – the mixture of the S17’s
i9-11900H processor and RTX 3080 GPU making light work of the
workload within the RoTTR preset. Cinebench’s single-threaded benchmark scores show
only minimal distinction among laptops (consultant of mainstream functions), nonetheless, the S17’s multi-threaded score ranked the S17 the second
highest among our comparison laptops, proving its suitability for
high-finish gaming and CPU demanding duties like 3D video enhancing.
That’s sufficient for nearly all Mac laptops to
charge at full pace or whereas in use.
Hello Neat post Theres an issue together with your site in internet explorer would check this IE still is the marketplace chief and a large element of other folks will leave out your magnificent writing due to this problem
piperfy
Wow amazing blog layout How long have you been blogging for you made blogging look easy The overall look of your web site is magnificent as well as the content
В поисках надежного и удобного способа пополнения вашего аккаунта Steam? На сайте SteamGold.ru вы найдете простое и быстрое решение для пополнение баланса стим. Независимо от того, хотите ли вы пополнить баланс Steam для покупки новых игр, дополнений или внутриигровых предметов, наш сервис обеспечивает мгновенное пополнение с минимальными усилиями. Пополните свой баланс Steam прямо сейчас и наслаждайтесь бесперебойной игрой. Пополни баланс Steam легко и безопасно с SteamGold.ru. Ваш удобный способ пополнения баланса Стим всегда под рукой. Пополнение Стим – это просто, быстро и надежно с нашим сервисом. Присоединяйтесь к тысячам довольных геймеров, которые уже пополнили свой баланс Стим через SteamGold.ru. Ваш ключ к миру бесконечных возможностей в Steam начинается здесь!
At this time it looks like WordPress is the preferred blogging platform available
right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you
are using on your blog?
How does a hair dryer generate such a robust gust of air in the primary place?
Protective screens – When air is drawn into the hair dryer because
the fan blades turn, other issues outside the hair dryer are additionally pulled toward the air intake.
Next time you and pa watch a film, this will make issues much less complicated.
The extra instances your blog readers click on on those adverts, the extra money you’ll make by means of the advert service.
This text discusses a quantity of ways to make money on the web.
If you’re trying to make a quick buck, your best guess is to promote something or issues your personal which can be of worth.
Those evaluations – and the best way firms address them – can make or break an enterprise.
In case your portable CD participant has an AC input,
you possibly can plug one finish of the adapter into your portable player and the opposite end into your car’s cigarette
lighter and you’ve got a power supply. This totally
alerts you, the reader, to the probability that in the following paragraph
you may be taught the foremost twist in the argument
put forth, making it solely possible that you’ll have no interest in reading further.
Information on the weight, availability and pricing of each model was not provided on the web
site as of this writing. Several models with elaborate information shows might be
discovered on-line from about $20 to $70, though evaluations of
many of them embody a lot of 1- and 2-star warnings about build high quality;
buy from a site that allows straightforward returns.
More power-demanding models, like the 16-inch M1 Pro/Max MacBook Pro, require greater than 60W.
If the maximum is 100W or much less, a succesful USB-C cable that helps USB-only or Thunderbolt 3 or 4 information will suffice.
They constructed their very own neighborhood, inviting users to
join and share their knowledge about knitting, crocheting and more.
With knowledge of the speed of a peripheral and your unknown cable, plug it into your Thunderbolt 3 or four
capable Mac. The Mac mini also has two Thunderbolt/USB four
buses, which, confusingly sufficient, additionally use the two USB-C ports: relying on what you plug in, the controller manages knowledge
over the suitable customary at its maximum information fee.
Apple’s “USB-C Charge Cable,” for example, was designed for top wattage
however solely passes information at USB 2.0’s 480 Mbps.
Our model permits the seller to cancel at any time
any reservation made earlier, wherein case the holder of the
reservation incurs a utility loss amounting to a fraction of her worth for the reservation and may additionally
receive a cancellation price from the vendor. The XO laptop allows children, parents, grandparents and cousins to show each other.
All you want is a few ingenuity and a laptop computer or smartphone.
First, you may must unwrap the motherboard and the microprocessor chip.
With the assist of cloud/edge computing infrastructure, we deploy the proposed network to
work as an clever dialogue system for electrical customer support.
To forestall error accumulation caused by modeling two subtasks independently, we suggest to jointly
mannequin each subtasks in an end-to-finish neural network.
We suggest and research a simple model for auctioning such advert slot reservations in advance.
An extensive computational research exhibit the efficacy of the proposed approach and gives insights in to the benefits of strategic
time slot administration. We propose a 2-stage stochastic programming formulation for the
design of a priori delivery routes and time slot assignments and a sample average approximation algorithm for its solution.
The U.S. has resisted the switch, making American consumers and their credit
score cards the “low-hanging fruit” for hackers. In the U.S.
market, anticipate to see numerous so-known as “chip and signature” cards.
The biggest motive chip and PIN playing cards
are extra secure than magnetic stripe playing cards is because they require a 4-digit PIN
for authorization. But improvement may be modest if you are not a power-person otherwise you already had a decent quantity of RAM (4GB or
extra). Shaders take rendered 3-D objects built on polygons (the building
blocks of 3-D animation) and make them look more sensible.
It was about dollars; animation was far cheaper to provide than reside motion.
Actually buying a motherboard and a case along with all of the supporting components and assembling
the whole thing your self? And there’s one principal factor a Polaroid Tablet can try this an iPad cannot.
Gordon, Whitson. “What Hardware Upgrade Will Best Speed Up My Pc (If I Can Only Afford One)?” Lifehacker.
Somebody essentially lend a hand to make significantly articles Id state That is the very first time I frequented your website page and up to now I surprised with the research you made to make this actual submit amazing Wonderful task
Thank you for the good writeup It in fact was a amusement account it Look advanced to far added agreeable from you However how could we communicate
It has not one but two cameras. The G-Slate has
two rear-going through 5-megapixel cameras that may work
in tandem to capture 3-D, 720-pixel video. While I have my points with
the X1000’s worth and proprietary wiring, it’s inconceivable to fault its front video.
There’s no arguing the quality of the X1000’s
front video captures-they’re pretty much as good as something we’ve seen at 1440p.
It’s also versatile with each GPS and radar options and the touch display
makes it exceptionally nice and easy to make use of.
However the night video is the real eye-popper.
Rear evening captures aren’t as good as those from the forward digicam both, although they’re nonetheless usable.
The Wii U helps video chatting (handy when your controller has a built-in digicam and display!),
and Nintendo aims to take Miiverse beyond its own video
recreation console. That cab be remedied by more cautious placement of the
rear digital camera. The refreshed S17’s design now sees the case raise up 12 mm behind the keyboard when you open the lid, nonetheless affording further air to the two Arc Flow fans, whereas the keyboard itself – now
positioned more towards the back – lifts with it and moves in direction of you.
Do you wish to provide your roof a new lease on life?
Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is what you need. Our unique product offers a unique standard of maintenance for your asphalt shingles, making sure they stay in top condition.
By choosing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer, you’re not just choosing any ordinary
product. You’re selecting a top-quality roof rejuvenation solution crafted to dramatically increase the life
of your roof by up to 30 years. This is a wise decision for property owners seeking to protect their investment.
What makes Shingle Magic Roof Sealer? To begin with, its proprietary formula seeps into the
asphalt shingles, reviving their pristine durability and appearance.
Furthermore, it’s extremely easy to apply, needing minimal effort for optimal results.
In addition to Shingle Magic Roof Sealer extend the life of
your roof, but it delivers outstanding resistance to weather elements.
Be it harsh sunlight, rainstorms, or freezing temperatures, it will be shielded.
Additionally, opting for Shingle Magic Roof Sealer means you’re choosing
an eco-friendly option. Its non-toxic makeup ensures minimal environmental impact, making it a responsible choice for the
planet.
Finally, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is unparalleled as the premier roof rejuvenation solution. Its ability to increase the life of your roof and delivering superior protection and an environmentally
friendly option makes Shingle Magic as the wise choice for homeowners aiming to
care for their property’s future.
Moreover, one of the key benefits of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is its affordability.
In lieu of pouring a significant amount on frequent repairs or a full roof replacement, using Shingle Magic saves you money in the long run. It’s an economical
solution that provides high-quality results.
Furthermore, the user-friendly nature of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer
is a major plus. There’s no need for specialized knowledge to apply it.
For those who like to handle things themselves or prefer for professional installation, Shingle Magic guarantees a smooth process with outstanding results.
Shingle Magic’s longevity is another significant reason to choose it.
When applied, it forms a layer that preserves the integrity of your shingles
for many years. It means fewer concerns about weather damage and greater
peace of mind about the state of your roof.
Regarding appearance, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer also stands out.
Not only does it safeguard your roof but also enhances its look.
Shingles will seem refreshed, which adds to the curb appeal
and value to your property.
Client satisfaction with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is additional proof to its quality.
Countless customers have reported notable improvements
in their roof’s condition after using the product.
Testimonials underscore its ease of use, durability, and excellent defensive capabilities.
To wrap it up, opting for Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is selecting a trusted solution for roof rejuvenation. Its combination of sturdiness, visual appeal,
cost-effectiveness, and simplicity renders
it the perfect choice for anyone seeking to prolong the life and look
of their roof. Don’t hesitate to give your roof the care it deserves with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer.
I just could not leave your web site before suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard information a person supply to your visitors Is gonna be again steadily in order to check up on new posts
I was recommended this website by my cousin I am not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my difficulty You are wonderful Thanks
Встречайте каждую финансовую потребность с уверенностью, ведь теперь у вас есть expl0it.ru. Здесь вы можете легко получить [url=https://expl0it.ru/]займ без отказа на карту[/url]. Это не просто обещание – это реальность, доступная каждому. Мы ценим ваше время и понимаем важность быстрого решения финансовых вопросов. Поэтому наш сервис максимально упрощен и ориентирован на оперативное удовлетворение ваших потребностей. Забудьте о бесконечных бумажных процедурах и длительном ожидании – ваша финансовая поддержка всего в нескольких кликах!
I am not sure where youre getting your info but good topic I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more Thanks for magnificent info I was looking for this information for my mission
Excellent blog here Also your website loads up very fast What web host are you using Can I get your affiliate link to your host I wish my web site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
What i do not realize is in fact how you are no longer actually much more wellfavored than you might be right now Youre very intelligent You recognize thus considerably in relation to this topic made me in my view believe it from numerous numerous angles Its like men and women are not fascinated until it is one thing to do with Lady gaga Your own stuffs excellent All the time handle it up
Hello Neat post Theres an issue together with your site in internet explorer would check this IE still is the marketplace chief and a large element of other folks will leave out your magnificent writing due to this problem
I was able to find good information from your content.
Al hacer click en Suscríbete elegirás el contenido que quieras recibir en tu correo
y quedarás suscrito a nuestro boletín el cual podrás cancelar en cualquier momento; no
olvides revisar tu carpeta de Spam.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.com/lv/register-person?ref=WTOZ531Y
Een zegelring voor een dame is een aantal opzichten anders dan een zegelring voor een heer.
Приветствую! В мире микрофинансирования постоянно появляются новые возможности. На expl0it.ru вы можете ознакомиться с [url=https://expl0it.ru/]самыми новыми микрозаймами, еще малоизвестными, которые дают всем[/url]. Эти займы открывают двери для широкого круга заемщиков, включая тех, кто может испытывать трудности с получением кредита в традиционных финансовых учреждениях.
Perfectly voiced certainly! !
Check out my site https://exe-errors.com
But I think that quickly, after the carry of all restrictions, the wave of tourism will hit with even greater force.
For instance, does decorating for Halloween all the time take you longer than you think it’s
going to? If in case you have an older machine, it probably
cannot take the latest and greatest graphics card. Now
let’s check out what the future holds for digital image frames.
This sort of display is skinny sufficient that the digital body is not much thicker than an odd image frame.
Isn’t that enough? Then your attention is introduced with absolutely clean code,
with explanations, so that you just always know which part of the code
is liable for the aspect you want. The AAMC presents a free on-line model
of the complete MCAT examination via its online retailer: The Princeton Review Web site additionally offers a free online practice test.
Try the demo version to make sure – it fits your tastes!
Read on to find out how CDs can show you how to make your candles glow even brighter.
Square-wave inverters are essentially the most cost-efficient and can be discovered at
most digital retailers. Flutter templates are famous for their flexibility with respect to any operating system.
If you have diabetes or different chronic bodily situations,
you too can apply to be allowed to take meals, drink, insulin, prosthetic
gadgets or personal medical gadgets into the testing room.
Handmade gadgets don’t cease there, although.
Sharp, Ken. “Free TiVo: Build a better DVR out of an Old Pc.” Make.
A greater card can enable you to enjoy newer,
more graphics-intensive games. Fortunately,
there are hardware upgrades that can extend the helpful life of your current pc without completely draining your account
or relegating one more piece of equipment
to a landfill. These computations are carried out in steps by means of a
sequence of computational components. The shaders
make billions of computations every second to carry
out their particular tasks. Each immediate is adopted by a set of particular duties, corresponding
to: provide your individual interpretation of the assertion, or describe a specific scenario where the assertion would not hold true.
Simply determine what must be finished in what order, and set your deadlines accordingly.
To handle and share your favourite finds online as well as in your cellphone, create a
LocalEats user account. Low-noise followers accessible
as nicely. It’s actually up to the sport developers how the system’s appreciable resources
are used.
The final half exhibits all the instances a verify has been run against
your credit report, both because you applied for a mortgage or as a result
of a merchant or employer initiated the verify.
Check out all of the gastronomical motion in this premiere of Planet Green’s newest present, Future Food.
So once you join to seek out out what sitcom star you most determine with, the makers of that poll now have access to
your private information. And they have a clean surface for attaching photos, gemstones, fabric or no matter
else fits your fancy. Most Websites that include secure private
information require a password also have no less than one password trace in case
you overlook. Why do individuals share embarrassing
data on-line? That’s why most online scheduling techniques permit businesses to create time buckets.
Also, RISC chips are superscalar — they will carry out multiple
instructions at the same time. But two or three relatively cheap
screens can make a world of difference in your computing expertise.
But DVRs have two main flaws — you must pay for the privilege of utilizing one, and you are stuck with
whatever capabilities the DVR you buy happens to include.
It will have a glance at the place of the geoscientist during the productive life of an oilfield.
I must thank you for the efforts you’ve put in writing
this website. I really hope to view the same high-grade blog posts by you in the future as well.
In fact, your creative writing abilities has encouraged me to get my very own site now 😉
Задаетесь вопросом, [url=https://expl0it.ru/]где взять микрозайм без отказа[/url]? Expl0it.ru предоставляет вам ответы! Этот ресурс собрал множество предложений от МФО, готовых предоставить вам займы на удобных условиях, даже если у вас плохая кредитная история.
Güvenilir bahis siteleri hangileri
It’s essential to verify they’re qualified to do
the job you’ve got them in for.
The organisation’s analysis predicts that to satisfy
this target, an additional 50,000 certified staff might be needed.
Приветствую! Если вам срочно нужны деньги, expl0it.ru предлагает [url=https://expl0it.ru/]займ онлайн на карту срочно[/url]. На сайте собраны более 40 МФО, а также представлена обширная информация и предложения о первом займе под 0%. Это отличное решение для быстрого решения финансовых вопросов с минимальными затратами.
you are truly a just right webmaster The site loading speed is incredible It kind of feels that youre doing any distinctive trick In addition The contents are masterwork you have done a great activity in this matter
На expl0it.ru вы найдете [url=https://expl0it.ru/]полный список микрозаймов[/url], где представлены различные МФО. Этот ресурс идеально подходит для тех, кто ищет оптимальные финансовые решения, сочетая удобство выбора и широкий спектр предложений. Вся информация доступна в одном месте, что значительно упрощает процесс выбора подходящего займа.
You do not even need a computer to run your presentation — you can simply switch files straight out of your iPod, smartphone
or other storage device, point the projector at
a wall and get to work. Basic is the phrase:
They each run Android 2.2/Froyo, a extremely outdated (2010) operating system that
is used to run something like a flip cellphone.
The system divides 2 GB of gDDR3 RAM, operating at 800 MHz, between games and the Wii U’s operating system.
They permit for multi-band operation in any two bands, together with seven-hundred and 800 MHz, as well as VHF and UHF R1.
Motorola’s new APX multi-band radios are actually two radios in one.
Without an APX radio, some first responders must carry more than one radio,
or depend on information from dispatchers before proceeding with vital response actions.
For more information on reducing-edge merchandise, award some time to the links
on the subsequent page.
The Volt Stick LV50 is the one prompt voltage detector accredited by Cadent and is a mandatory device for
all Cadent engineers and sub-contracted engineers.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I
am going to return yet again since i have bookmarked it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide others.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Hi! Someone in my Myspace group shared this website with us so I came to look it over.
I’m definitely loving the information. I’m book-marking
and will be tweeting this to my followers! Exceptional
blog and superb style and design.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
In essence, it replaces the looks of an object
with a extra detailed image as you progress closer to
the object in the game. Fans of Bungie’s “Halo” recreation series can purchase the “Halo 3” restricted edition Xbox 360, which comes in “Spartan inexperienced and gold” and
features a matching controller. And despite being what CNet calls a “minimalist machine,” the Polaroid
Tablet nonetheless has some fairly nifty hardware options you’d
expect from a extra expensive pill by Samsung or Asus, and it comes with Google’s new, feature-rich Android
Ice Cream Sandwich operating system. When Just Dance III comes out in late 2011, it can even be
launched for Xbox’s Kinect along with the Wii system, which implies
dancers will not even need to carry a remote to shake
their groove factor. TVii might show to be an especially powerful service
— the GamePad’s constructed-in screen and IR blaster make
it a potentially good universal distant — however the
Wii U’s launch has proven Nintendo struggling with the calls
for of designing an HD console. Nintendo worked with wireless company Broadcom to develop a WiFi expertise that works from as much as 26 toes (7.9 meters) away and
delivers extraordinarily low-latency video.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Can you recommend any books or resources to learn more about this?
Freedman’s Office Furniture: Crafting Workspaces in Orlando
**Elevate Your Workspace in Orlando with Freedman’s Office Furniture**
In the heart of Orlando, Freedman’s Office Furniture emerges as the go-to destination for all your
office furnishing needs. Our showroom at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120 caters to
discerning customers in neighborhoods like Audubon Park and Baldwin Park, delivering top-notch office furniture
solutions.
**Orlando: A Hub of Innovation and Productivity**
Founded in 1875, Orlando pulsates with innovation, mirroring
Freedman’s commitment to crafting workspaces that inspire.
With a population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607
households, Orlando’s dynamic environment finds resonance in Freedman’s diverse range of ergonomic office chairs and modern office seating solutions.
**Navigating Orlando’s Pulse: Interstate 4**
Orlando’s lifeblood, Interstate 4, threads through the city,
connecting its vibrant neighborhoods. Likewise, Freedman’s Office Furniture weaves a tapestry of
convenience, delivering quality office furniture to every corner of Orlando.
Our commitment aligns with the city’s ethos of seamless connectivity and accessibility.
**Crafting Comfort: Office Chairs Tailored to Orlando’s Needs**
Considering Orlando’s diverse weather, ranging from warm summers to mild winters, investing in quality office
furniture is a wise decision. Freedman’s Office Furniture provides
not just chairs but ergonomic solutions that adapt to Orlando’s varied temperatures, ensuring comfort year-round.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and Freedman’s Touch**
Explore Orlando’s iconic points of interest like ICON Park and
Antarctica: Empire of the Penguin, mirroring the uniqueness that Freedman’s brings to office
spaces. Here are five facts about some of Orlando’s landmarks:
– **7D Motion Theater Ride At ICON Park:** An immersive experience with seven dimensions of excitement.
– **America’s Escape Game Orlando:** Orlando’s premier
escape room destination.
– **Aquatica Orlando:** A water park blending marine life
with thrilling water rides.
– **Chocolate Kingdom – Factory Adventure Tour:
** Unraveling the mysteries of chocolate production.
– **Discovery Cove:** An all-inclusive day resort featuring marine
life encounters.
**Why Choose Freedman’s in Orlando**
Selecting Freedman’s Office Furniture in Orlando is
an investment in quality, style, and ergonomic excellence.
Our vast range of office chairs, including ergonomic
options, executive seating, and contemporary designs, ensures that
your workspace mirrors Orlando’s vibrancy and innovation. Choose
Freedman’s for a workplace that aligns with the
dynamic spirit of Orlando.
”
“Elevate Your Workspace with Freedman’s Office Desks in Orlando
**Discover the Essence of Productivity: Freedman’s
Office Desks in Orlando**
When it comes to crafting the perfect workspace in Orlando, Freedman’s Office Furniture stands out as the epitome of excellence.
Located at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, our showroom caters to
neighborhoods such as Audubon Park and Baldwin Park, providing a
diverse range of office desks that redefine
functionality and style.
**Orlando: A Tapestry of Diversity and Innovation**
Established in 1875, Orlando boasts a rich history steeped in diversity
and innovation. With a current population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607
households, Orlando’s dynamic landscape finds a reflection in Freedman’s commitment to delivering top-tier office desks
designed for the city’s progressive work environment.
**Navigating Orlando’s Pulse: Interstate 4**
Much like the seamless flow of traffic on Interstate 4, Freedman’s Office Furniture ensures a smooth journey
in furnishing your workspace. We bring quality
office desks to every corner of Orlando, mirroring the city’s commitment to accessibility
and connectivity.
**Crafting Efficiency: Office Desks Tailored to Orlando’s
Work Culture**
In a city where work meets play, investing in a workspace that reflects efficiency and style is crucial.
Freedman’s Office Desks go beyond functionality; they are
a statement of professionalism and innovation, aligning perfectly with Orlando’s ethos.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and Freedman’s Craftsmanship**
Explore Orlando’s iconic landmarks and witness the craftsmanship that Freedman’s brings
to office spaces. Here are five facts about some of Orlando’s beloved destinations:
– **Caro-Seuss-el:** A whimsical carousel inspired by Dr.
Seuss’s imaginative world.
– **Chocolate Kingdom – Factory Adventure Tour:** An interactive journey through
the art of chocolate making.
– **Crayola Experience Orlando:** A colorful adventure where creativity knows no bounds.
– **Dezerland Park Orlando:** An entertainment hub featuring go-karts, bowling, and arcade games.
– **Discovery Cove:** An immersive marine experience allowing guests to
swim with dolphins.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Office Desks in Orlando**
Selecting Freedman’s Office Desks in Orlando is a testament to your commitment to a
workspace that exudes professionalism and sophistication. Our range of office desks, including executive desks, modern designs, and collaborative workstations,
ensures that your workspace reflects the dynamic spirit of Orlando.
Choose Freedman’s for desks that elevate your work environment.
”
“Seating Solutions for Success: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando
**Experience Unparalleled Comfort: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando**
In the heart of Orlando, where comfort meets productivity, Freedman’s Office
Furniture takes pride in presenting a premium collection of office chairs.
Nestled at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, our showroom extends its reach to
neighborhoods like Clear Lake and College Park,
providing an extensive range of office chairs that redefine ergonomic excellence.
**Orlando: Where Innovation Meets Tradition**
With a founding year of 1875, Orlando is a city
that beautifully balances innovation and tradition. Boasting a population of 309,
154 (2021) and 122,607 households, Orlando’s diversity and growth
parallel Freedman’s commitment to delivering top-notch office chairs suited
for the city’s evolving work culture.
**Navigating Orlando’s Hub: Interstate 4**
Much like the seamless flow of traffic on Interstate 4, Freedman’s Office Furniture ensures
a smooth journey in offering quality office chairs to every office and
workspace in Orlando, aligning with the city’s emphasis
on accessibility and connectivity.
**Elevating Your Workstation: Orlando’s Professionalism Embodied**
In a city known for its professionalism and innovation, choosing the right office chair is
essential. Freedman’s Office Chairs not only prioritize ergonomic design but also
serve as a testament to your commitment to creating a workspace that mirrors Orlando’s ethos.
**Orlando’s Gems and Freedman’s Seating Elegance**
Explore the richness of Orlando’s landmarks while experiencing the elegance of Freedman’s Office Chairs.
Here are five interesting facts about some of Orlando’s beloved destinations:
– **Dolphin Nursery:** A heartwarming space
at SeaWorld Orlando dedicated to nurturing newborn dolphins.
– **DreamWorks Destination:** An immersive experience at Universal Studios Florida featuring characters from DreamWorks
Animation.
– **Fun Spot America Theme Parks:** A family-friendly amusement park with thrilling rides and attractions.
– **Gatorland:** Known as the “”Alligator Capital of the World,”” Gatorland offers exciting wildlife shows.
– **Harry Potter and the Escape from Gringotts:** A cutting-edge, multi-dimensional thrill ride at
Universal Studios Florida.
**Why Opt for Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando**
Choosing Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando is an investment in your well-being and work satisfaction. Our diverse range of ergonomic chairs,
including executive chairs, mesh back chairs, and swivel chairs,
ensures that your workspace in Orlando is synonymous with comfort
and style. Elevate your seating experience with Freedman’s for a workplace that
inspires success.
”
“Enhancing Workspaces: Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture in Orlando
**Discover the Art of Productivity: Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture in Orlando**
In the vibrant city of Orlando, where productivity meets innovation, Freedman’s Office Furniture proudly presents a curated selection of ergonomic office furniture.
Conveniently located at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, our
showroom caters to neighborhoods like Colonial Town Center and
Colonialtown North, offering a diverse range of office solutions
designed to elevate your workspace.
**The Essence of Orlando’s Business Culture**
Founded in 1875, Orlando stands as a testament to a harmonious blend of history and forward-thinking.
Boasting a population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607 households, Orlando’s
dynamic business culture aligns seamlessly with Freedman’s commitment to providing cutting-edge ergonomic office furniture.
**Navigating the Hub of Opportunities: Interstate 4**
Much like the interconnected web of Interstate 4, Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture ensures a smooth
transition to a more comfortable and efficient workspace, symbolizing the city’s
emphasis on progress and growth.
**Investing in Comfort: A Smart Choice for Orlando Businesses**
In a city that values innovation and efficiency, choosing ergonomic office furniture is
a strategic investment. Freedman’s collection not only prioritizes functionality
and comfort but also aligns with Orlando’s commitment to creating workspaces that inspire creativity and collaboration.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and the Comfort of Freedman’s Furniture**
Embark on a journey through Orlando’s iconic landmarks while experiencing the unmatched comfort of Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture.
Here are five fascinating facts about some of Orlando’s cherished destinations:
– **Aquatica Orlando:** A thrilling waterpark owned and operated
by SeaWorld Parks & Entertainment.
– **Caro-Seuss-el:** A whimsical carousel in Seuss Landing at Universal’s Islands
of Adventure.
– **Dezerland Park Orlando:** Home to an extensive collection of classic cars and interactive exhibits.
– **Discovery Cove:** An all-inclusive day resort where guests can swim with dolphins and explore
coral reefs.
– **Crayola Experience Orlando:** A colorful attraction at The Florida Mall offering hands-on creative activities.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Ergonomic Office
Furniture in Orlando**
Opting for Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture in Orlando is a commitment to a more productive and comfortable work environment.
Our range of modern office solutions, including adjustable chairs, contemporary desks, and ergonomic accessories, ensures that your workspace reflects the dynamic
spirit of Orlando, fostering creativity and
success.
”
“Elevating Workspace Aesthetics: Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs in Orlando
**Indulge in Comfort: Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs Unveiled
in Orlando**
Nestled in the heart of Orlando, Freedman’s Office Furniture takes pride in introducing its exclusive collection of modern office chairs.
Situated at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, our showroom caters
to discerning customers in neighborhoods like Bryn Mawr and Catalina, offering a diverse range of seating solutions that
combine style and functionality.
**Orlando’s Thriving Legacy and Freedman’s Modern Elegance**
Established in 1875, Orlando has grown into a dynamic city with a population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607 households.
Freedman’s commitment to providing modern office chairs aligns seamlessly
with Orlando’s legacy of progress, innovation, and a commitment to creating inspiring
workspaces.
**Navigating the Hub of Opportunities: Interstate 4**
Much like the fluidity of Interstate 4, Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs symbolize a seamless blend of
form and function. This reflects Orlando’s dedication to providing a conducive environment for businesses to thrive and individuals to excel.
**Investing in Style: A Wise Choice for Orlando’s Professionals**
In a city that values aesthetics and innovation, opting for Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs is a statement of sophistication. Our collection not only enhances the visual appeal of
your workspace but also complements Orlando’s commitment
to creating a work environment that fosters creativity and success.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and the Style of Freedman’s Chairs**
Embark on a journey through Orlando’s iconic landmarks while experiencing the unmatched style of
Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs. Here are
five fascinating facts about some of Orlando’s cherished destinations:
– **Harry Potter and the Escape from Gringotts:
** A cutting-edge, multi-dimensional thrill ride at Universal Studios Florida.
– **Crayola Experience Orlando:** A colorful attraction at The Florida Mall
offering hands-on creative activities.
– **Dolphin Nursery:** A heartwarming exhibit at SeaWorld Orlando where guests can witness the beauty of dolphin life.
– **Dezerland Park Orlando:** Home to an extensive collection of
classic cars and interactive exhibits.
– **Camp Jurassic:** An adventurous play area in Universal’s Islands of Adventure, inviting
visitors to explore a prehistoric world.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs in Orlando**
Opting for Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs in Orlando is not just a
choice; it’s a commitment to elevate your workspace.
Our stylish and comfortable chairs ensure that your office reflects
the vibrant and dynamic spirit of Orlando, making it an ideal place
for productivity, innovation, and success.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Quality articles is the main to invite the viewers to go to see the web site, that’s what this website is providing.
Look into my web site; traders
Ƭhe locarion additionally features а feed of Hasselhoff’s tweets,
so customers ɑre аt aⅼl times prrivy to wһat theіr idol іs
սp to. It is a Ьit lіke betting redd օr black on roulette, and thе percentages օf yyou bеing successful are 1:
1. So, it іs up to you whetheг you wiѕh to danger your payline win fⲟr a 50% probability you
would poѕsibly improve it. So, tһere you wiⅼl һave
it – yߋu won’t bе abⅼe too plug in a Rumble Pak, Controller Pak
օr even a Transfer Pak. Another function of the N64 controller is the ability sο as to add choices bby ᴡay of an growth slot օn the
bottom ⲟff the controller. One unique feature of the sport оf Thrones slot іs
the choice players hɑve to gamble evеry win for tһe possibility
to double it. Мost hair dryers (including һiѕ one) havе
excessive аnd low airflow settings. Ƭhough high school
iѕ oftеn painful, hɑving your ρresent canceled doeѕ not should
be. 0.01 per slot line and ending wіth high limits – $оne һundred
per sppin oor evenn larger. Ꭺlthough Game of Thrones slot doeѕn’t have a jackpot, the sport is
filled ᴡith special symbols aand bonus options tһat povides to the fun. The
iconic Game of Thrones emblem appears inn tһe type oof tһe slots wold image while the notorious Iron Thdone іs the scatter image needed to ѕet оff the sport’ѕ exclusive bonus
features.
mʏ webb blog :: joker true wallet
So ask friends and family in your local space who they’ve labored with recently.
kumar
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
If you wish for to take much from this piece of writing then you have to apply these techniques to your won weblog.
great content custom printed packaging</a
great content custom printed packaging
I always find myself nodding along and agreeing with your wise words Your insights and advice are truly valuable
To handle these phenomena, we propose a Dialogue State Tracking
with Slot Connections (DST-SC) model to explicitly consider
slot correlations throughout totally different domains.
Specially, we first apply a Slot Attention to
learn a set of slot-particular features from the original dialogue after which integrate them using
a slot information sharing module. Slot Attention with Value Normalization for Multi-Domain Dialogue State Tracking Yexiang Wang author Yi Guo author Siqi Zhu author 2020-nov textual
content Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods
in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) Association for Computational Linguistics Online convention publication Incompleteness of area ontology and unavailability of some values are
two inevitable problems of dialogue state tracking (DST).
On this paper, we suggest a brand new structure to cleverly exploit ontology,
which consists of Slot Attention (SA) and Value Normalization (VN), referred to as
SAVN. SAS: Dialogue State Tracking through Slot Attention and Slot Information Sharing Jiaying Hu writer
Yan Yang author Chencai Chen creator Liang He writer
Zhou Yu writer 2020-jul text Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics Association for Computational
Linguistics Online conference publication Dialogue state tracker is responsible for inferring person intentions by way of dialogue history.
We propose a Dialogue State Tracker with Slot Attention and Slot Information Sharing (SAS) to scale back redundant information’s interference and improve long dialogue context tracking.
Do not neglect to upgrade your car Auto insurance quotes Orange County CA when your instances transform.
It could possibly affect your protection.
Once you have accomplished your coaching, you may select to expand into different areas.
Thanks in favor of sharing such a nice idea, post is pleasant, thats why i have read it completely
Some car Auto insurance Las Vegas plan provide add-ons like roadside help.
Take into consideration if these benefits deserve the added price.
More about the author
To make a CD clock, you’ll need a CD, a variety of artwork supplies (no need to buy something new, you should utilize whatever you’ve gotten around your own home) and a clock motion or clockwork, which you should purchase on-line or at a crafts retailer. Whether that means pushing pretend “cures” like Mercola and Elizabeth, their own “secret” insights like the Bollingers and Jenkins, or “alternative health” like Ji and Brogan, these folks have something to sell. Mercola is far from alone in selling deadly lies for a buck. These individuals aren’t pushing conspiracy theories based mostly on compounded lies as a result of they believe them. Erin Elizabeth, who created a number of lies in regards to the safety of both the COVID-19 vaccine and flu vaccine whereas selling hydroxychloroquine-together with anti-Semitic conspiracy theories. However, the opinion that the $479 MSRP is a bit of too high is shared throughout multiple evaluations. Fox News cited studies of a stand-down order no fewer than eighty five occasions throughout prime-time segments as of June 2013. As the brand new report-which the Republican majority of the committee authored-makes very clear in its findings, nonetheless, no such order ever existed. In a new report launched on Tuesday, the House Armed Services Committee concludes that there was no way for the U.S.
Здравствуйте! Обратите внимание на expl0it.ru, где представлены более 40 МФО, предлагающих [url=https://expl0it.ru/]займ быстро на карту[/url]. На сайте вы найдете много полезной информации и компании, предоставляющие первый займ под 0%. Это идеальный выбор для тех, кто ищет удобный и экономически выгодный способ получения срочных финансов.
In pay-per-click (PPC) mode (Edelman et al., 2007; Varian, 2007), the platform allocates slots and calculates fee in response to each the click bid offered by the advertiser and the user’s click on through charge (CTR) on every advert. Payment plans range among the many completely different companies. The Hopper is a multi-tuner, satellite tv for pc receiver delivering high-definition programming and DVR services. However, throughout the ’60s, most different children’s programming died when animated sequence appeared. For example, when “30 Rock” gained an Emmy for outstanding comedy collection on its first try in 2007, NBC started to see its long-term prospects. They simply didn’t essentially see them on the scheduled date. See more footage of car devices. Memory is inexpensive as of late, and extra RAM is sort of at all times higher. Rather, they’ve slower processors, much less RAM and storage capacity that befits finances-priced machines. Back then, ATM machines have been nonetheless a comparatively new luxury in many countries and the foreign transaction charges for ATM withdrawals and bank card purchases were by the roof.
What’s more, manufacturers have mixed PDAs with cell telephones, multimedia gamers
and other digital gadgetry. To supply extra reminiscence, many PDAs accept removable flash media add-on cards.
For tons extra information on how credit score playing cards work, how to
avoid identification theft, and ideas for traveling abroad, check out the associated HowStuffWorks articles on the subsequent web page.
Information in RAM is just obtainable when the gadget is on. On account of their design, PDAs keep data in RAM safe because
they proceed to attract a small quantity of energy from the
batteries even whenever you turn the gadget off. Push the sync button (on the system or
cradle) to start the synchronization course of.
The fantastic thing about synchronization is that you simply at all times have a backup copy of your information, which
generally is a lifesaver if your PDA is broken, stolen, or fully out of power.
Synchronization software on the PDA works with companion software program that you set up
on your Pc. Not solely can they manage your personal
information, corresponding to contacts, appointments, and to-do lists, at present’s
gadgets can also connect to the Internet,
act as global positioning system (GPS) gadgets, and run multimedia software program.
The primary objective of a personal digital assistant (PDA) is to act as an digital organizer or day planner
that is portable, straightforward to use and
capable of sharing information with your Pc.
However, it is vital that these communities show willingness to
rescale and redeploy to make this work.
We also have shoppers as far afield as Swindon,
Oxford, Portsmouth and Camberley.
This cohort is also put off by the perceived complexity of working within the warmth pump area.
Revolutionize Your Workspace with Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta
**Embrace Productivity and Comfort: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta**
In the bustling city of Atlanta, where innovation meets tradition, Freedman’s Office Furniture introduces its exclusive range
of ergonomic office chairs. Located at 3379 Peachtree Rd NE,
Atlanta, GA 30326, our showroom caters to the discerning
tastes of residents in neighborhoods like Ansley Park and Baker Hills, offering
premium office seating solutions that combine style and functionality.
**Elevate Your Workspace in the Heart of Atlanta**
Atlanta, founded in 1836, stands as a testament to a rich history and a thriving metropolis.
With a population of 496,461 (2021) and 227,388 households, the city continues to evolve
while preserving its unique charm. Freedman’s commitment to providing modern office chairs aligns seamlessly with
Atlanta’s spirit of progress and dynamism.
**Navigating the Urban Hub: Interstate 20**
Much like the smooth flow of Interstate 20, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs embody a perfect blend of
form and function. This mirrors Atlanta’s commitment to providing
a conducive environment for businesses to flourish and individuals to excel in their
professional endeavors.
**Investing in Style: A Wise Choice for Atlanta Professionals**
In a city that values aesthetics and innovation, opting for Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs is a statement of sophistication.
Our collection not only enhances the visual appeal of your workspace but also complements Atlanta’s commitment to creating a work environment that fosters creativity and success.
**Discovering Atlanta’s Landmarks and the Comfort of Freedman’s Chairs**
Embark on a journey through Atlanta’s iconic landmarks
while experiencing the unmatched comfort of Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs.
Here are five fascinating facts about some of Atlanta’s cherished destinations:
– **Atlanta Botanical Garden:** A 30-acre botanical garden showcasing an incredible variety of plants and
flowers.
– **Centennial Olympic Park:** Built for the 1996 Summer Olympics, this park serves as
a gathering spot for locals and visitors.
– **Atlanta History Center:** An extensive history museum featuring exhibits, historic
houses, and gardens.
– **College Football Hall of Fame:** Celebrating the rich history of
college football with interactive exhibits and memorabilia.
– **The “”It’s a living”” Street Art:** A vibrant street art scene in the city, offering colorful and dynamic murals.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs in Atlanta**
Opting for Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Atlanta is not just a choice; it’s a commitment to elevate
your workspace. Our stylish and comfortable chairs ensure
that your office reflects the vibrant and dynamic spirit of Atlanta,
making it an ideal place for productivity, innovation,
and success.
”
“Transform Your Work Environment with Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando
**Revitalize Your Workspace: Discover Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando**
In the heart of Orlando, where magic and modernity coexist, Freedman’s
Office Furniture proudly presents its exclusive range of office chairs.
Conveniently located at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, Orlando, FL 32801, our showroom caters to the diverse needs
of residents in neighborhoods like Audubon Park and Colonial Town Center, offering premium office seating solutions that prioritize
both comfort and style.
**Elevate Your Work Experience in Orlando’s Lively Atmosphere**
Orlando, founded in 1875, has grown into a vibrant city with a
population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607 households.
Freedman’s commitment to providing high-quality office chairs resonates with
Orlando’s lively and energetic atmosphere, offering residents the perfect blend of comfort
and functionality for their workspaces.
**Navigating the City: The Significance of Interstate 4**
Much like the seamless flow of Interstate 4, Freedman’s ergonomic
office chairs seamlessly blend style and functionality. This mirrors
Orlando’s commitment to providing an environment where residents
can seamlessly navigate between work and leisure, making our chairs an ideal choice for those who value efficiency and aesthetics.
**Investing in Comfort: An Informed Choice for Orlando
Professionals**
In a city known for its diverse attractions and entertainment, investing in Freedman’s
ergonomic office chairs is a conscious decision. Our chairs not only
enhance the aesthetics of your workspace but
also align with Orlando’s commitment to providing a comfortable and conducive work environment.
**Explore Orlando’s Attractions and Relax in Freedman’s Chairs**
Embark on a journey through Orlando’s enchanting attractions while enjoying the unparalleled comfort of
Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs. Here are five interesting facts about some of
Orlando’s most beloved landmarks:
– **Walt Disney World Resort:** The most visited vacation resort globally, spanning over 25,000 acres.
– **Universal Studios Florida:** An iconic film and television studio theme park, featuring thrilling rides and attractions.
– **Lake Eola Park:** A scenic park in downtown Orlando with a
picturesque lake and swan boats.
– **Dr. Phillips Center for the Performing Arts:
** A state-of-the-art venue hosting various cultural and artistic performances.
– **Orlando Museum of Art:** Showcasing a diverse collection of contemporary and classic art.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs in Orlando**
Opting for Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Orlando is not just a decision;
it’s a commitment to enhancing your workspace. Our stylish and comfortable chairs ensure that your
office reflects the dynamic and creative spirit of Orlando,
making it an ideal place for productivity, innovation, and success.
”
“Discover Superior Comfort with Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta
**Elevate Your Workspace: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta**
Nestled in the vibrant city of Atlanta, Freedman’s Office Furniture
proudly introduces its exclusive collection of office chairs.
Conveniently located at 3379 Peachtree Rd NE, Atlanta, GA 30326, our showroom caters to the diverse needs of residents in neighborhoods
like Ansley Park and Buckhead, offering premium office seating solutions that blend comfort and sophistication seamlessly.
**Crafting a Distinctive Workspace in Atlanta’s Dynamic Setting**
Founded in 1836, Atlanta has evolved into a bustling
city with a population of 496,461 (2021) and 227,388 households.
Freedman’s commitment to delivering top-notch office chairs aligns
perfectly with Atlanta’s dynamic and diverse setting, providing residents with ergonomic solutions that enhance both productivity and aesthetic appeal.
**Navigating the Urban Hub: The Importance of Interstate
20**
Much like the flow of Interstate 20, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs effortlessly navigate
the modern office landscape. This reflects Atlanta’s status as a vibrant urban hub, where residents value efficiency
and style in equal measure, making our chairs the perfect
choice for those seeking a superior seating experience.
**Investing in Excellence: A Thoughtful Choice for Atlanta Professionals**
In a city renowned for its rich history and cultural attractions, choosing Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs is
a thoughtful investment. Our chairs not only elevate the visual appeal of your
workspace but also resonate with Atlanta’s commitment to fostering innovation and success through a
comfortable and ergonomic work environment.
**Explore Atlanta’s Cultural Gems and Relax in Freedman’s Chairs**
Immerse yourself in Atlanta’s cultural richness while enjoying the superior
comfort of Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs. Here are five fascinating facts about
some of Atlanta’s most iconic landmarks:
– **Atlanta Botanical Garden:** A 30-acre garden showcasing an incredible variety of
plants, flowers, and sculptures.
– **Centennial Olympic Park:** Built for the 1996 Summer Olympics, it’s a gathering spot with fountains, events, and
green spaces.
– **Martin Luther King Jr. National Historic Site:
** Preserving the legacy of the civil rights leader,
including his childhood home and Ebenezer Baptist Church.
– **Piedmont Park:** A sprawling urban park with walking trails,
sports facilities, and the picturesque Lake Clara Meer.
– **The Fox Theatre:** A historic venue known for
its Moorish architecture and hosting various performances.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs in Atlanta**
Opting for Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Atlanta is not merely a decision—it’s a
statement. Elevate your workspace with our stylish and
comfortable chairs, embodying the spirit of innovation and success that defines Atlanta’s dynamic professional landscape.
”
“Discover Unmatched Seating Comfort with Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando
**Elevate Your Workspace: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando**
Located at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, Orlando, FL 32801,
Freedman’s Office Furniture is proud to introduce its exclusive range of office chairs to
the vibrant city of Orlando. Serving neighborhoods like Colonial Town Center and College
Park, Freedman’s provides superior office seating solutions
that prioritize both comfort and style.
**Crafting a Distinctive Workspace in Orlando’s
Sunshine State**
Established in 1875, Orlando has transformed into a thriving city
with a 2021 population of 309,154 and 122,607 households. Freedman’s dedication to delivering top-tier office chairs
aligns seamlessly with Orlando’s sunny ambiance, offering residents ergonomic solutions that blend seamlessly with the city’s
dynamic and energetic atmosphere.
**Navigating the Urban Landscape: The Significance of Interstate 4**
Much like the flow of Interstate 4, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs effortlessly navigate the modern office landscape.
This mirrors Orlando’s status as a hub of entertainment and technology, where residents seek innovative
and comfortable seating solutions, making our chairs the ideal choice for those desiring a
superior seating experience.
**Investing in Excellence: A Thoughtful Choice for Orlando Professionals**
In a city known for its theme parks and cultural attractions, choosing Freedman’s ergonomic office
chairs is a thoughtful investment. Our chairs not only enhance the visual appeal of
your workspace but also align with Orlando’s commitment to creating a vibrant and comfortable work environment that fosters creativity and success.
**Explore Orlando’s Magical Attractions and Relax in Freedman’s Chairs**
Immerse yourself in Orlando’s magical offerings while enjoying the
unmatched comfort of Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs.
Here are five fascinating facts about some of Orlando’s most iconic landmarks:
– **Walt Disney World Resort:** The world’s most-visited vacation resort,
featuring four theme parks and numerous attractions.
– **Universal Studios Florida:** A film and television studio theme park with
thrilling rides and shows.
– **Lake Eola Park:** A downtown oasis with swan boats, live swans, and scenic walking paths.
– **Orlando Science Center:** A hands-on science museum with interactive exhibits and engaging displays.
– **Dr. Phillips Center for the Performing Arts:** A
modern venue hosting various live performances, including Broadway shows.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs in Orlando**
Opting for Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Orlando
is more than just a decision—it’s a commitment to excellence.
Elevate your workspace with our stylish and comfortable chairs, embodying the
spirit of innovation and success that defines
Orlando’s dynamic professional landscape.
”
“Revolutionize Your Workspace with Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta
**Experience Unparalleled Comfort: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta**
Nestled at 3379 Peachtree Rd NE, Atlanta, GA
30326, Freedman’s Office Furniture proudly introduces its exceptional collection of office chairs
to the dynamic city of Atlanta. Serving neighborhoods like Ansley Park and Buckhead, Freedman’s delivers office seating solutions that seamlessly combine ergonomic design with
aesthetic appeal.
**Redesigning Your Office Aesthetic: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta**
Founded in 1836, Atlanta has evolved into a bustling metropolis with a 2021 population of 496,461 and 227,388 households.
Freedman’s commitment to providing top-notch office chairs perfectly complements Atlanta’s modern and diverse atmosphere, offering residents seating solutions that embody both innovation and style.
**Navigating the Cityscape: The Significance of Interstate
20**
Much like the connectivity provided by Interstate 20, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs seamlessly integrate into Atlanta’s diverse
professional landscape. Reflecting Atlanta’s status as a cultural and economic hub, our chairs offer residents unparalleled comfort
and style, making them the preferred choice for those seeking an exceptional seating experience.
**A Commitment to Excellence: Choosing Freedman’s Chairs in Atlanta**
In a city known for its rich history and cultural landmarks,
choosing Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs is a statement of commitment to excellence.
Our chairs not only enhance the visual appeal of your workspace
but also align with Atlanta’s reputation for fostering
innovation and success.
**Explore Atlanta’s Rich Heritage and Relax in Freedman’s Chairs**
Discover the vibrant history of Atlanta while enjoying the unrivaled comfort of Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs.
Here are five intriguing facts about some of Atlanta’s iconic landmarks:
– **Atlanta History Center:** A comprehensive history museum featuring exhibits
on the Civil War and Southern history.
– **Piedmont Park:** Atlanta’s premier green space, offering walking paths, sports facilities, and beautiful scenery.
– **Martin Luther King Jr. National Historic Site:** Preserving the childhood
home of the civil rights leader and featuring the
Ebenezer Baptist Church.
– **The Fox Theatre:** A historic performing arts venue known for its grand architecture
and diverse entertainment.
– **The High Museum of Art:** Atlanta’s leading art museum, showcasing a diverse collection of artwork.
**Why Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs Stand Out in Atlanta**
Choosing Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Atlanta is a decision that transcends mere furniture.
It’s a commitment to elevating your workspace with stylish and comfortable seating that resonates
with Atlanta’s spirit of progress and achievement.
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here The sketch is attractive your authored material stylish nonetheless you command get got an impatience over that you wish be delivering the following unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this hike
There are many challenges during transport of oil and gas via pipelines.
Hi, i read your blog from time to time and i own a similar one and
i was just wondering if you get a lot of spam feedback?
If so how do you protect against it, any plugin or anything you can suggest?
I get so much lately it’s driving me insane so any help is very much appreciated.
Sleeping porn
Personal accident insurance exists to supply a lump sum payout and daily hospital benefit if an damage like this had been to occur.
The reply to this question largely is decided by
your pre-existing skills and skills.
Another key aspect of this course will be the
concern of communication between geoscientists and engineers.
Do you mind if I quote a few of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to your webpage?
My website is in the very same niche as yours and
my users would really benefit from a lot of
the information you present here. Please let me know if this ok with you.
Cheers!
любовные привороты читать приворот на мужчину на расстоянии без последствия сразу.
привороты на фото читать в домашних условиях . как сделать приворот на девушку по фото , мужчина после приворота.
приворот на фото который нельзя снять – https://21obron.ru приворот на чашку.
привороты на любовь мужчины приворот на мужчину без последствия сразу в домашних условиях на расстоянии молитвы от приворота
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: tipobet
Wow, this post is fastidious, my younger sister is analyzing these kinds of things, thus I
am going to convey her.
На torrent-mass.ru каждый найдет что-то особенное для себя. Не важно, какой у вас ПК, ведь тут можно [url=https://torrent-mass.ru/]игры для слабых пк скачать торрент[/url]. Наслаждайтесь многообразием игр, подходящих для любых системных требований и окунитесь в увлекательные миры без ограничений.
Greate pieces. Keep writing such kind of info on your page.
Im really impressed by your blog.
Hello there, You have done a fantastic job.
I’ll certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends.
I’m sure they will be benefited from this website.
You are truly an accomplished webmaster. The site loads in an astounding amount of time; it almost seems as though you’re accomplishing something special. Furthermore, the contents are flawless; you’ve done an outstanding job with this.
I absolutely love your blog and find nearly all of your post’s to be exactly
I’m looking for. Would you offer guest writers to write content for you?
I wouldn’t mind writing a post or elaborating on some of
the subjects you write with regards to here. Again, awesome site!
Excellent rhythm. I would like to assist you in refining your website by requesting information on how to subscribe for a blog. The account provided me with a substantial amount of assistance. Although I was somewhat familiar with this, your broadcast presented a clear and concise concept.
Каждый геймер знает, что настоящее волшебство начинается с момента, когда ты найдешь идеальную игру для своего сердца. И что может быть лучше, чем получить эту игру мгновенно? Torrent-mass.ru приглашает вас [url=https://torrent-mass.ru/]скачать игры на пк торрент[/url], где вы найдете мир, полный приключений и героических подвигов, ждущих вас за каждым кликом. Наслаждайтесь удобством загрузки и новейшими играми прямо у вас под рукой.
почему после приворота заказчик остывает от жертвы приворот любимой.
приворот на возврат бывшего мужа читать приворот на замок кто делал.
кто делал приворот на девушку – https://quickloto.ru приворот на парня чтобы влюбился читать в домашних условиях без фото.
приворот на сигарету кто делал сильный приворот на вещь приворот по фото в домашних условиях читать на мужчину
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Hi, I do think this is a great web site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going
to revisit once again since i have saved as a favorite it.
Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
Визуальное изображение. 12 am сколько. https://2024.online-konsultatsiya-psihologa.ru Музыкальные фотки. Person перевод на русский язык. Рациональный поступок. Основные определения психологии.
Ищете лучшее из лучших в мире игр? Torrent-mass.ru представляет [url=https://torrent-mass.ru/]топ 100 игр торрент[/url] – это ваш надежный гид по самым популярным и захватывающим играм года. Откройте для себя мир, где каждая игра – это шедевр, выбранный с учетом отзывов и рейтингов игроков.
You can definitely see your enthusiasm within the work you write.
The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who are not afraid
to mention how they believe. At all times follow your heart.
перетяжка офисного кресла [url=https://peretyazhka-mebeli-minsk.ru/]https://peretyazhka-mebeli-minsk.ru/[/url].
Freedman’s Office Furniture: Crafting Workspaces in Orlando
**Elevate Your Workspace in Orlando with Freedman’s
Office Furniture**
In the heart of Orlando, Freedman’s Office Furniture
emerges as the go-to destination for all your office furnishing needs.
Our showroom at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120 caters to discerning customers in neighborhoods like Audubon Park and Baldwin Park, delivering
top-notch office furniture solutions.
**Orlando: A Hub of Innovation and Productivity**
Founded in 1875, Orlando pulsates with innovation, mirroring Freedman’s commitment to
crafting workspaces that inspire. With a population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607
households, Orlando’s dynamic environment finds resonance in Freedman’s diverse range of ergonomic office chairs and modern office seating solutions.
**Navigating Orlando’s Pulse: Interstate 4**
Orlando’s lifeblood, Interstate 4, threads through the city, connecting
its vibrant neighborhoods. Likewise, Freedman’s Office Furniture weaves a tapestry of convenience, delivering
quality office furniture to every corner of Orlando.
Our commitment aligns with the city’s ethos of seamless connectivity and accessibility.
**Crafting Comfort: Office Chairs Tailored to Orlando’s Needs**
Considering Orlando’s diverse weather, ranging from warm summers to mild
winters, investing in quality office furniture is a wise decision. Freedman’s
Office Furniture provides not just chairs but ergonomic solutions
that adapt to Orlando’s varied temperatures, ensuring comfort year-round.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and Freedman’s Touch**
Explore Orlando’s iconic points of interest like ICON Park
and Antarctica: Empire of the Penguin, mirroring the uniqueness that Freedman’s brings to
office spaces. Here are five facts about some of
Orlando’s landmarks:
– **7D Motion Theater Ride At ICON Park:** An immersive experience with seven dimensions of excitement.
– **America’s Escape Game Orlando:** Orlando’s premier escape
room destination.
– **Aquatica Orlando:** A water park blending marine life with thrilling water rides.
– **Chocolate Kingdom – Factory Adventure Tour:** Unraveling the mysteries of chocolate production.
– **Discovery Cove:** An all-inclusive day resort featuring marine life encounters.
**Why Choose Freedman’s in Orlando**
Selecting Freedman’s Office Furniture in Orlando is an investment in quality, style,
and ergonomic excellence. Our vast range of office chairs, including
ergonomic options, executive seating, and contemporary designs, ensures that
your workspace mirrors Orlando’s vibrancy and innovation. Choose Freedman’s for
a workplace that aligns with the dynamic spirit of
Orlando.
”
“Elevate Your Workspace with Freedman’s Office Desks in Orlando
**Discover the Essence of Productivity: Freedman’s Office Desks in Orlando**
When it comes to crafting the perfect workspace in Orlando, Freedman’s
Office Furniture stands out as the epitome of
excellence. Located at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120,
our showroom caters to neighborhoods such as Audubon Park and Baldwin Park, providing a diverse range of office
desks that redefine functionality and style.
**Orlando: A Tapestry of Diversity and Innovation**
Established in 1875, Orlando boasts a rich history steeped in diversity and innovation.
With a current population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607 households, Orlando’s dynamic landscape finds a reflection in Freedman’s commitment to delivering top-tier office desks designed for the city’s progressive work environment.
**Navigating Orlando’s Pulse: Interstate 4**
Much like the seamless flow of traffic on Interstate 4, Freedman’s Office Furniture ensures a smooth journey in furnishing your workspace.
We bring quality office desks to every corner of Orlando, mirroring
the city’s commitment to accessibility and connectivity.
**Crafting Efficiency: Office Desks Tailored to Orlando’s Work Culture**
In a city where work meets play, investing in a workspace
that reflects efficiency and style is crucial. Freedman’s Office Desks go beyond functionality; they
are a statement of professionalism and innovation, aligning perfectly with Orlando’s
ethos.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and Freedman’s Craftsmanship**
Explore Orlando’s iconic landmarks and witness the craftsmanship that Freedman’s brings to office spaces.
Here are five facts about some of Orlando’s beloved destinations:
– **Caro-Seuss-el:** A whimsical carousel inspired by Dr. Seuss’s imaginative
world.
– **Chocolate Kingdom – Factory Adventure Tour:** An interactive journey through the art
of chocolate making.
– **Crayola Experience Orlando:** A colorful adventure where creativity knows no bounds.
– **Dezerland Park Orlando:** An entertainment hub featuring go-karts, bowling,
and arcade games.
– **Discovery Cove:** An immersive marine experience allowing guests to swim with dolphins.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Office Desks in Orlando**
Selecting Freedman’s Office Desks in Orlando is a testament to your commitment to
a workspace that exudes professionalism and sophistication. Our
range of office desks, including executive desks, modern designs, and collaborative workstations, ensures that your workspace reflects the dynamic spirit of Orlando.
Choose Freedman’s for desks that elevate your work environment.
”
“Seating Solutions for Success: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando
**Experience Unparalleled Comfort: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando**
In the heart of Orlando, where comfort meets productivity, Freedman’s Office Furniture takes pride in presenting a
premium collection of office chairs. Nestled at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, our showroom extends its reach to neighborhoods like Clear Lake and College Park,
providing an extensive range of office chairs that redefine ergonomic excellence.
**Orlando: Where Innovation Meets Tradition**
With a founding year of 1875, Orlando is a city that beautifully balances innovation and tradition.
Boasting a population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607 households,
Orlando’s diversity and growth parallel Freedman’s commitment to delivering top-notch office chairs suited for the city’s
evolving work culture.
**Navigating Orlando’s Hub: Interstate 4**
Much like the seamless flow of traffic on Interstate
4, Freedman’s Office Furniture ensures a smooth
journey in offering quality office chairs to every office and
workspace in Orlando, aligning with the city’s emphasis on accessibility and connectivity.
**Elevating Your Workstation: Orlando’s Professionalism Embodied**
In a city known for its professionalism and innovation, choosing the right office chair is essential.
Freedman’s Office Chairs not only prioritize ergonomic design but also serve
as a testament to your commitment to creating a workspace that mirrors Orlando’s
ethos.
**Orlando’s Gems and Freedman’s Seating Elegance**
Explore the richness of Orlando’s landmarks while experiencing the elegance of Freedman’s Office Chairs.
Here are five interesting facts about some of Orlando’s beloved destinations:
– **Dolphin Nursery:** A heartwarming space at SeaWorld
Orlando dedicated to nurturing newborn dolphins.
– **DreamWorks Destination:** An immersive experience at Universal Studios Florida featuring characters from DreamWorks Animation.
– **Fun Spot America Theme Parks:** A family-friendly amusement park with thrilling rides and attractions.
– **Gatorland:** Known as the “”Alligator Capital of the World,”” Gatorland offers exciting wildlife shows.
– **Harry Potter and the Escape from Gringotts:** A cutting-edge, multi-dimensional thrill ride at Universal
Studios Florida.
**Why Opt for Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando**
Choosing Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando is an investment in your well-being
and work satisfaction. Our diverse range of
ergonomic chairs, including executive chairs, mesh back chairs, and swivel chairs, ensures that your workspace in Orlando is synonymous with comfort and style.
Elevate your seating experience with Freedman’s for a workplace that
inspires success.
”
“Enhancing Workspaces: Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture in Orlando
**Discover the Art of Productivity: Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture in Orlando**
In the vibrant city of Orlando, where productivity meets innovation, Freedman’s Office Furniture proudly presents a curated selection of
ergonomic office furniture. Conveniently located at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, our showroom caters to neighborhoods like Colonial
Town Center and Colonialtown North, offering a diverse range of office
solutions designed to elevate your workspace.
**The Essence of Orlando’s Business Culture**
Founded in 1875, Orlando stands as a testament to a harmonious
blend of history and forward-thinking. Boasting a
population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607 households, Orlando’s dynamic business culture
aligns seamlessly with Freedman’s commitment to providing cutting-edge ergonomic office furniture.
**Navigating the Hub of Opportunities: Interstate 4**
Much like the interconnected web of Interstate 4, Freedman’s Ergonomic Office
Furniture ensures a smooth transition to a more comfortable and efficient workspace,
symbolizing the city’s emphasis on progress and growth.
**Investing in Comfort: A Smart Choice for Orlando Businesses**
In a city that values innovation and efficiency, choosing ergonomic office
furniture is a strategic investment. Freedman’s collection not only prioritizes functionality and comfort but also
aligns with Orlando’s commitment to creating workspaces that inspire
creativity and collaboration.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and the Comfort of Freedman’s Furniture**
Embark on a journey through Orlando’s iconic landmarks while experiencing the unmatched comfort of
Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture. Here are five fascinating facts about some
of Orlando’s cherished destinations:
– **Aquatica Orlando:** A thrilling waterpark owned and operated by SeaWorld Parks
& Entertainment.
– **Caro-Seuss-el:** A whimsical carousel in Seuss Landing at Universal’s Islands of Adventure.
– **Dezerland Park Orlando:** Home to an extensive collection of classic cars and interactive exhibits.
– **Discovery Cove:** An all-inclusive day resort where guests can swim with dolphins and explore coral reefs.
– **Crayola Experience Orlando:** A colorful attraction at The Florida Mall offering hands-on creative
activities.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture in Orlando**
Opting for Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture
in Orlando is a commitment to a more productive and comfortable
work environment. Our range of modern office solutions, including adjustable chairs, contemporary desks, and
ergonomic accessories, ensures that your
workspace reflects the dynamic spirit of Orlando, fostering creativity and success.
”
“Elevating Workspace Aesthetics: Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs in Orlando
**Indulge in Comfort: Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs Unveiled in Orlando**
Nestled in the heart of Orlando, Freedman’s Office Furniture
takes pride in introducing its exclusive collection of modern office chairs.
Situated at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, our showroom caters
to discerning customers in neighborhoods like
Bryn Mawr and Catalina, offering a diverse range of seating solutions that combine style and functionality.
**Orlando’s Thriving Legacy and Freedman’s Modern Elegance**
Established in 1875, Orlando has grown into a dynamic city
with a population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607 households.
Freedman’s commitment to providing modern office chairs aligns seamlessly with Orlando’s
legacy of progress, innovation, and a commitment to creating inspiring workspaces.
**Navigating the Hub of Opportunities: Interstate 4**
Much like the fluidity of Interstate 4, Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs symbolize a seamless blend of form and function.
This reflects Orlando’s dedication to providing a conducive
environment for businesses to thrive and individuals to excel.
**Investing in Style: A Wise Choice for Orlando’s Professionals**
In a city that values aesthetics and innovation, opting for Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs is
a statement of sophistication. Our collection not only
enhances the visual appeal of your workspace but also complements Orlando’s commitment to creating
a work environment that fosters creativity and success.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and the Style of Freedman’s Chairs**
Embark on a journey through Orlando’s iconic landmarks
while experiencing the unmatched style of Freedman’s Modern Office
Chairs. Here are five fascinating facts about some
of Orlando’s cherished destinations:
– **Harry Potter and the Escape from Gringotts:
** A cutting-edge, multi-dimensional thrill ride at
Universal Studios Florida.
– **Crayola Experience Orlando:** A colorful attraction at The Florida Mall offering hands-on creative activities.
– **Dolphin Nursery:** A heartwarming exhibit at SeaWorld Orlando where guests can witness the beauty of dolphin life.
– **Dezerland Park Orlando:** Home to an extensive collection of classic cars and interactive exhibits.
– **Camp Jurassic:** An adventurous play area in Universal’s Islands of Adventure,
inviting visitors to explore a prehistoric world.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs in Orlando**
Opting for Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs in Orlando is not
just a choice; it’s a commitment to elevate your workspace.
Our stylish and comfortable chairs ensure that your office
reflects the vibrant and dynamic spirit of Orlando, making
it an ideal place for productivity, innovation, and success.
eskil ilçesi
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
На torrent-mass.ru вас ждет мир игр, где каждый сюжет и каждый персонаж говорят на понятном вам языке. Здесь вы можете [url=https://torrent-mass.ru/]русские игры на пк скачать торрент[/url], чтобы каждое приключение было еще более захватывающим и понятным. Откройте для себя игры, созданные с душой и любовью к русской культуре.
Your photography and visuals are always so stunning They really add to the overall quality of the content
Torrent-mass.ru предлагает вам мир, где каждая игра – это возможность для новых открытий. [url=https://torrent-mass.ru/]Скачать торрент на игры пк[/url] – это ваш путь к неограниченным возможностям в игровом мире. Откройте для себя игры, которые принесут вам радость и волнение, и станьте частью захватывающего приключения.
I enjoy what you guys tend to be up too. This kind of clever work and reporting!
Keep up the awesome works guys I’ve added you guys to blogroll.
I am extremely impressed along with your writing skills
as smartly as with the layout to your blog. Is that this a paid theme or did you customize it your self?
Anyway stay up the excellent quality writing, it’s uncommon to look a nice weblog like this one nowadays..
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
I have been surfing online more than 3 hours today yet I never found any interesting article like yours It is pretty worth enough for me In my opinion if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you did the web will be much more useful than ever before
Excellent post. I was checking constantly this
blog and I am impressed! Extremely helpful info specially the last part
🙂 I care for such info much. I was looking for this certain information for a very long time.
Thank you and good luck.
magnificent issues altogether, you simply gained a logo new reader.
What could you suggest in regards to your post that you just made a few days ago?
Any certain?
Although this is the main highlight of the PowerBucks Wheel of Fortune Exotic Far East slot machine, our reviewers discovered that it’s not the only one.
Our reviewers discovered that there’s loads to love about the PowerBucks Wheel of Fortune Exotic Far East slots sport.
The PowerBucks Wheel of Fortune Exotic Far East online slot is
just one in every of a sequence of related video games from IGT.
You might have Autoplay and Turbo choices, and you
can play Scarab Link at no cost right here at VegasSlotsOnline earlier than making cash bets at our prime IGT Casinos.
Scuttle throughout to IGT casinos to experience this
Egyptian journey for yourself. You’ll find it at our hand-picked IGT casinos.
It’s a trickier matter to learn the way much power a USB-C cable
can move, though you can start with certain assumptions.
They haven’t moved the graphics alongside a lot in this sport, however it’s still a decent-wanting
slot machine that you’ll find in desktop and mobile variations.
It can be difficult to discern exactly which pill
fashions are still available on the market, however going by the offerings
of huge shops like Sears and Walmart, every thing except the
M-a hundred and fifty continues to be accessible on-line or in shops.
How can I get a desk at a prime restaurant?
Piece of writing writing is also a excitement, if you know afterward you
can write if not it is complex to write.
The positioning provides data on motion pictures at present or quickly to be in theaters, actor profiles, fan clubs, celeb gossip, film information, video clips and interactive options like forums and user quizzes. Then, they can add merchandise from any purchasing Web site to their lists. Imeem additionally provides statistics to customers so they can observe their own content material — to check out who’s accessing their profile, monitor the popularity of their playlists or see if anybody is embedding their music on a weblog or Web site. The positioning would not sell anything — it merely exists to help folks to share information and bond over their shared interest in buying. Fildes, Jonathan. “‘$100 laptop computer’ to promote to public.” BBC News. The XO laptop computer was designed to be a lightweight and affordable laptop computer that is meant for creating international locations. Users interact to put up and uncover new artists, share playlists and watch videos. The positioning has additionally expanded to draw directors, offering a place to add quick films and movies. An intelligent E-commerce online buying guide assistant is a complete human-like system providing various providers corresponding to pre-sale and after-sale inquiries, product suggestions, and user complaints processing, all of which search to offer the shoppers higher procuring expertise.
Best article, wonderfull..
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/sl/join?ref=53551167
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. onwin onwin
Quality posts is the key to attract the visitors to go to see the web page, that’s what this website
is providing.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . onwin onwin
Мечтаешь о месте, где собраны лучшие игры для твоего ПК? Мы предлагаем тебе ресурс, где можно легко [url=https://moreigr.org/]скачать игры торрент на пк[/url]. Независимо от того, предпочитаешь ли ты погружение в фэнтезийные миры или решение сложных головоломок, наш сайт предоставляет доступ к огромному ассортименту игр. С нашей помощью ты сможешь обновить свою коллекцию самыми свежими и популярными релизами. Пришло время забыть о скучных вечерах, впереди тебя ждут невероятные приключения!
юрайт философия https://v-kosmose.com
голубинцев философияфилософия дегенсенека философия
академия философия экзистенциализм философия спекуляция философия
The new Derby Wheel game gives exciting reel spinning with loads of unique options. With the superb visual appeal, Derby Wheel is an exciting slot with loads of cool features. The purpose of the sport is to get three Wheel icons on the reels to then acquire entry to the Bonus Wheel. I shall lookup and say, ‘Who am I, then? The final option is the Trifecta, where you can choose who will finish first, second, and third to win 2,800x the wager. Pick Exacta and you’ll select who you think shall be first or second within the race to attempt to win 1,800x the wager. You can select Win and choose which horse you assume will win with an opportunity to earn as much as 800x the wager. Derby Wheel is the most recent title launched by the developer, providing a fun mixture of reel spinning and horse racing.
Most London marathoners reap the rewards of
their race in the type of a foil blanket, race medal and finisher’s bag, full with sports drink and a Pink Lady apple.
Once the race is run, marathoners can examine results over a pint at any of the eighty one pubs situated alongside the course.
They check their race outcomes on-line, involved
to understand how they positioned in their age categories, but most
compete for the fun of it or to raise money for charity.
Next, let’s check out an app that is bringing more than three a long time of survey expertise
to modern cell electronics. I have three in use running three separate working techniques, and half a dozen or so extra in storage throughout the house.
House fans have remained unchanged for what seems like endlessly.
And, as security is all the time a problem when it comes to
delicate credit card information, we’ll discover a number of the accusations that competitors have made towards different products.
The very first thing that you must do to protect
your credit score is to be vigilant about it. That release sold 400,000 copies in the primary
month alone, and when Cartoon Network’s Adult Swim picked it up in syndication, their ratings
went up 239 %.
Cover the back with felt, drill a gap in the top, loop a string or ribbon by way of the outlet and
there you’ve it — an on the spot Mother’s Day gift. Decorate the outer circle with any design you like, then glue a piece of ribbon to the back or drill a gap at the highest to attach it
to a door, wall or department on your Christmas tree. For Christmas,
you could possibly use photos of snowmen, snowflakes, Santa Claus or you
may minimize out photographs from old Christmas cards. You can also make a
simple Christmas ornament in about 15 minutes or spend hours
reducing up CDs and gluing the items to make a mosaic image body.
You’ll be able to decorate just one facet of the disc or get
fancy and glue two CDs along with the shiny sides facing out so it glitters from
every angle. Once the candle has burned and the disc is covered with wax, you may
throw it away or use the CD for another crafting goal.
The only manner to use a CD as a candleholder is to set a
small pillar or votive candle in the midst of the disc with the shiny side up.
What this implies when you’re taking part in video video games is that the Xbox 360 can dedicate one core entirely to producing sound, while another could
run the sport’s collision and physics engine. Techniques,
tools, financing, writing, monitoring and producing have come a good distance for the reason that early days.
The choice of sizes and working programs means that
there is an option for everybody, and reviewers have pegged every model within the
Iconia line nearly as good all-around tablets for media viewing, gaming and primary online pursuits, all at very cheap prices.
Particularly, our focus is on computerized programs that have to manage advert slots in many various publishers’ properties.
Just a few have custom-made techniques that permit a nurse to cowl a
shift provided that she or he meets specific qualifications.
While the Vizio pill could have trouble competing with tablets which have extra powerful operating
programs, quicker processors and greater reminiscence
capacities, there’s one gadget that could be quaking in its field:
e-book readers. The Iconia tablet has a microSD card slot for studying reminiscence cards and USB ports that make it simple to entry flash drives,
USB card readers and portable onerous drives.
Three hundred watts are sufficient for low-energy
machines, but if you’re building a gaming machine with a number of video playing
cards or a machine with a lot of disks, you may want to contemplate something larger.
The primary product to launch on Hubble is a borrowing platform that
lets users deposit multiple assets like SOL, BTC, and
ETH to mint USDH at a capital-efficient collateral ratio of 110%.
Comparisons have been made calling Hubble “the Maker DAO of Solana,” and USDH should develop into an integral
a part of DeFi on the network as a Solana native crypto-backed stablecoin. The Edison Best New Product Award is self-explanatory, and is awarded in several categories, together with science and medical, electronics and
medical, power and sustainability, expertise, transportation and industrial design.
This setup produces the basic “soundscape experience” you
typically examine in product descriptions for portable audio system the place the
sound seems to come at you from totally different directions.
It’s a classic slot themed round Ancient Egypt but in addition has some magic-themed
elements. Alternatively, should you found the stakes of the PowerBucks Wheel of Fortune Exotic Far East on-line slot slightly low, why not attempt
the Wheel of Fortune Triple Extreme Spin slot machine?
As long as you hit the winning mixture from left to right, you can be rewarded.
When you guess the color proper, your winnings will be doubled.
The primary set of 5 reels are crossed by forty paylines, and three or more matching symbols throughout a line
will equal a successful spin. One downside to this technique is that along with having to take your laptop computer laptop with you wherever you travel,
you may even have to hold a small, yet bulky set
of speakers. There aren’t any set paylines.
The jackpot is value 12,500 coins and gets triggered throughout the maximum wager spins while you hit 5 Amulets on any of the 243
paylines that have been active. The gameplay in Pompeii slots is innovative, so gamers
should wager 5 coins on every reel instead of selecting paylines.
Since there are 25 paylines, the minimal amount of cash
you possibly can wager per spin on the Pompeii slot machine is 50 cents, while the utmost is $125.
Visit my web-site … ยิงปลาฟรี
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.com/pt-BR/register-person?ref=V2H9AFPY
Reviews for the RX 6700 XT have began to pop up on-line, exhibiting
us the actual-world performance provided by the $479 card.
Cloud/edge computing and deep learning greatly enhance performance of semantic
understanding methods, where cloud/edge computing gives flexible, pervasive computation and storage capabilities to assist variant applications,
and deep learning models might comprehend text inputs
by consuming computing and storage resource. With each tech development, we expect larger efficiency from the expertise we purchase.
Identity theft and card fraud are main issues,
and some expertise consultants say certain readers are more safe than others.
While these fashions work comparatively nicely on customary benchmark datasets, they face challenges in the context of E-commerce where the slot labels are extra informative and carry richer expressions.
State-of-the-artwork approaches treat it as a sequence labeling downside
and adopt such models as BiLSTM-CRF. Our mechanism’s technical
core is a variant of the net weighted bipartite matching problem the place unlike prior variants during which one randomizes edge arrivals or bounds edge weights, we might revoke beforehand committed edges.
Our model permits the seller to cancel at any time any reservation made earlier,
by which case the holder of the reservation incurs a utility loss amounting to a fraction of her value for the reservation and can also
receive a cancellation price from the vendor.
Мечтаешь о месте, где собраны лучшие игры для твоего ПК? Мы предлагаем тебе ресурс, где можно легко [url=https://moreigr.org/]скачать игры торрент на пк[/url]. Независимо от того, предпочитаешь ли ты погружение в фэнтезийные миры или решение сложных головоломок, наш сайт предоставляет доступ к огромному ассортименту игр. С нашей помощью ты сможешь обновить свою коллекцию самыми свежими и популярными релизами. Пришло время забыть о скучных вечерах, впереди тебя ждут невероятные приключения!
But I feel that soon, after the lift of all restrictions, the wave of tourism will hit with even greater pressure. For example, does decorating for Halloween always take you longer than you assume it may? If you have an older machine, it in all probability cannot take the newest and best graphics card. Now let’s take a look at what the future holds for digital image frames. Any such show is skinny sufficient that the digital frame is not much thicker than an extraordinary image frame. Isn’t that sufficient? Then your consideration is presented with absolutely clean code, with explanations, so that you simply at all times know which part of the code is answerable for the factor you need. The AAMC provides a free online model of the complete MCAT exam by way of its online retailer: The Princeton Review Web site also supplies a free on-line practice check. Try the demo model to ensure – it suits your tastes! Read on to learn how CDs can assist you to make your candles glow even brighter. Square-wave inverters are the most cost-efficient and can be found at most electronic retailers. Flutter templates are well-known for his or her flexibility with respect to any operating system.
This funding doubles the original $50 million pledged by Ohanian in partnership with
the Solana Foundation. One in all Reddit’s Co-Founders, Alexis Ohanian, crammed a slot on the last day of Breakpoint to discuss why
he and his venture agency Seven Seven Six
had been pledging $100 million to develop social media on Solana.
Raj Gokal, Co-Founder of Solana, took the stage with Alexis
Ohanian and at one point said on the Breakpoint conference that his community plans to onboard
over a billion people in the subsequent few years.
Electronic gaming has been hailed as the entry point for crypto and blockchain technology’s mass adoption. P2E
games are exploding in reputation, and Axie Infinity
chalked up a superb 12 months for adoption with a token value
that has blown via the roof repeatedly. Once full gameplay
is launched, it will be fascinating to see how
many people stop their jobs to P2E full time!
Sharing your social plans for everyone to see is not a good idea.
But as an alternative of utilizing high-stress fuel to generate thrust, the craft uses a jet drive to
create a robust stream of water. The coverage on gasoline
differs between companies as well. The TDM Encyclopedia.
“Car sharing: Vehicle Rental Services That Substitute for Private Vehicle Ownership.” Victoria Transport Policy Institute.
University of California Berkeley, Institute of Transportation Studies.
Santa Rita Jail in Alameda, California (it’s near San Francisco, no shock) uses an array of
gas cells, photo voltaic panels, wind turbines and diesel generators to energy its very personal micro
grid. However, many nonprofit car-share organizations are doing fairly properly, corresponding
to City CarShare within the San Francisco Bay Area
and PhillyCarShare in Philadelphia. So that you may be asking yourself, “Wow, if car sharing is so well-liked and straightforward, ought to I be doing it too?”
To search out out extra about who can profit from sharing a automotive
and to learn about how to contact a automobile-sharing firm,
continue to the next page.
Antalya Alanya to Airport Transfer Services
Greetings! I found your site while researching ‘early pregnancy scan services near me.’ The wealth of information is impressive. Currently on the lookout for an ‘early scan near me,’ I’d love to hear your expert opinion or any suggestions you may have. Thanks a bunch!
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Trix – официальный сайт – Трикс играть онлайн раздача каждый день
bursa reklam ajansi This journey has continued at the intersection of creativity and innovation, building bridges between brands and their target audiences. In this blog, we will take an in-depth look at this evolutionary journey from the long history of advertising agencies to today’s digital and agile world
Hmm it looks like your website ate my first comment (it was extremely long) so I
guess I’ll just sum it up what I had written and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your
blog. I too am an aspiring blog blogger but I’m still new to the whole thing.
Do you have any helpful hints for beginner blog writers?
I’d really appreciate it.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Greetings! I found your site while looking into ’emergency pregnancy scan services.’ The content is both reassuring and informative. In need of an ’emergency pregnancy scan,’ I’m interested in any advice or insights you may have. Thank you in advance!
You are truly an accomplished webmaster. The site loads in an astounding amount of time. It appears that you are employing some sort of unique technique. Furthermore, the contents are flawless; you have accomplished an outstanding job on this subject.
Appreciating the time and effort you put into your website and in depth information you present.
It’s good to come across a blog every once in a while
that isn’t the same old rehashed material. Wonderful
read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to
my Google account.
This investment doubles the original $50 million pledged by Ohanian in partnership with the Solana Foundation. One in all Reddit’s Co-Founders,
Alexis Ohanian, crammed a slot on the final day of Breakpoint to
speak about why he and his enterprise agency Seven Seven Six were pledging
$a hundred million to develop social media on Solana.
Raj Gokal, Co-Founding father of Solana, took the stage with Alexis Ohanian and
at one level said on the Breakpoint conference that his community plans to onboard over a billion individuals in the following few
years. Electronic gaming has been hailed because the entry point
for crypto and blockchain technology’s mass adoption. P2E games are exploding in recognition, and Axie
Infinity chalked up a wonderful year for adoption with a token worth that has
blown by means of the roof repeatedly. Once full gameplay is launched,
it will be attention-grabbing to see how many people quit their jobs to P2E full time!
Sharing your social plans for everybody to see
is not a good suggestion.
my webpage :: ยิงปลาฟรี
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Very good post.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
My website: порно русское по категориям
Your summary of the key points was perfect, really helped solidify the information.
Can I simply say what a relief to discover a person that truly knows what they are talking about on the net.
You definitely understand how to bring a problem to light and make it important.
More people must check this out and understand this side of the story.
I can’t believe you’re not more popular given that you surely have the gift.
The other day, while I was at work, my cousin stole my apple ipad and tested to see if it can survive a 30 foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My iPad is
now destroyed and she has 83 views. I know this is entirely off topic but I had to
share it with someone!
Wonderful site. A lot of helpful information here. I am sending it to several pals ans additionally sharing in delicious.
And of course, thanks in your sweat!
Mersin’de psikolog arayanlar, kliniğimizde kendilerini rahat ve güvende hissedebilir.
Thanks! An abundance of data!
Homeland Security officials, all of whom use the craft of their work.
United States Department of Homeland Security.
Several national organizations monitor and regulate personal watercraft in the United States.
United States Department of Agriculture.
U.S. Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The
National Association of State Boating Law Administrators has a complete state-by-state listing of private-watercraft laws.
National Association of State Boating Law Administrators.
Coast Guard. “Boating Statistics – 2003.” Pub. Pub. 7002. Washington DC.
Forest Service. “Recreation Statistics Update. Report No. 1. August 2004.” Washington DC.
Leeworthy, Dr. Vernon R. National Survey on Recreation and the Environment.
In accidents involving personal watercraft, the most common trigger of dying is affect
trauma. Not only can they handle your personal information, comparable to contacts, appointments,
and to-do lists, today’s devices may also hook up with the Internet, act as global positioning system (GPS) devices, and run multimedia software program.
Bluetooth wirelessly connects (it’s a radio frequency technology that doesn’t require a transparent line of
sight) to other Bluetooth-enabled devices, akin to a headset or a printer.
Apart from helmets, no expertise exists to stop physical trauma.
However, the drive’s suction and the force of the jet can nonetheless cause injury.
Then you may take the motherboard back out, place the spacers, and put the motherboard in on high of them.
While an appointment might have a particular time restrict,
that does not essentially mean the enterprise can accommodate two appointments again to back.
But changing one or two elements, especially the oldest half or the one you’ve got
decided is inflicting a bottleneck, can present spectacular performance improvements whereas remaining cost efficient.
It has been a while since I cracked a computer open and explored its innards, but this endeavor has inspired me to, at the very least,
improve the RAM in my laptop. Case, Loyd. “How one can Upgrade Your Graphics Card.” Pc World.
Or would you like to use a graphics card on the motherboard to keep
the price and measurement down? A pleasant midrange card can drastically enhance performance for
a few hundred dollars, however it’s also possible to find much cheaper ones that are
not bleeding-edge that will fit your wants simply tremendous.
Look at my page – ยิงปลาฟรี
Fantastic beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your web
site, how can i subscribe for a blog site?
The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit acquainted
of this your broadcast offered bright clear concept
Many gamers choose to download software program to their very own gadget,
for ease of use and speedy accessibility. Perhaps essentially the most exciting factor about the GamePad is how games use it — let’s take a look at some examples.
We glance out for the largest jackpots and bring you the most recent
information on the most thrilling titles to play. On our web site, there isn’t a need to install
further software program or apps to be able to play your favourite slot game.
This can be a excessive-variance slot game that is extra likely to attract followers of IGT slots such because the mystical Diamond
Queen or the cat-themed Kitty Glitter slot. The White Orchid slot features
a feminine contact with pink and white because the distinguished colors.
Like Red Mansions, the White Orchid slot options a wide betting vary and gamers can start betting with just a coin. Almost all of the net casinos provide free variations of their software
so the person can play slot machines. The playing card symbols are just
just like the playing cards which might be used to
play real money desk video games online. But there seems to have been no thought put into how easily the cards could be counterfeited (or what a nasty idea it’s to go round
paper objects in the middle of a pandemic).
Hello there, I discovered your blog by way of Google even as looking
for a related matter, your site got here up, it seems
to be good. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Hello there, simply become alert to your weblog thru Google, and found that it is really informative.
I am gonna be careful for brussels. I’ll appreciate in the
event you continue this in future. Many folks might
be benefited out of your writing. Cheers!
Excellent beat ! I would like to apprentice whilst you amend your website, how could i subscribe for a weblog website?
The account helped me a acceptable deal. I were tiny bit familiar of this your broadcast provided brilliant transparent concept
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: deneme bonusu veren siteler
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: deneme bonusu veren siteler
Car sharing decreases air pollution and energy dependency.
It is the Dyson Air Multiplier, one of the funkiest window fans ever to
hit planet Earth. Since the ’60s, viewer campaigns to avoid wasting Tv exhibits have helped buy programs extra time on the air.
Because they not need to relay schedule adjustments through one other human being, everybody can spend more time specializing in other job
duties. This adjustments the direction of the “equal and opposite response.” If the nozzle directs the water
to the right side of the craft, the rear of the craft pushes to the left.
In keeping with Newton’s third legislation, for each motion, there’s an equal and
reverse response. This strikes the craft because
of the principle described in Isaac Newton’s third law of
motion. How Rocket Engines Work explains this principle in detail.
Study personal watercraft engines and the way engines are made quieter.
Just like a lawn mower or a automotive, personal watercraft run on two-stroke or 4-stroke engines.
Personal watercraft make a really distinctive, excessive-pitched sound, which some folks really
feel disturbs residents, wildlife and other boaters.
Also, it is best to take a look at completely right after set up to catch points
early, and verify to ensure the quantity of RAM you installed now reveals up if you examine your system properties.
Listening to a portable CD participant in your automobile looks as
if a great choice, proper? With this template, you
possibly can sell something from membership T-shirts to car parts.
And with this template, you can be one step forward of your competitors!
In right this moment’s world, it is very important be one
step ahead. In case you are involved about the
issue of procrastination in the world, and also you need
to create your own convenient software for tracking tasks, then that is
your alternative! Useful reading (studying good books) expands a person’s horizons, enriches his inner world, makes him smarter
and has a constructive effect on reminiscence.
So, that’s why, applications for studying books are
most related in as we speak’s studying society.
Reading books increases a person’s vocabulary, contributes to the event of clearer considering, which lets
you formulate and specific thoughts more lucidly.
It’s the form of comfort that allows you to just zone out and play with out worrying about niggling key points.
I love how you approach the topic from different angles.If anyone wants to read the topic in more details then visit 8xbet
Our mechanism’s effectivity is within a continuing fraction of the a posteriori optimally environment friendly resolution. Our mechanism’s technical core is a variant of the net weighted bipartite matching
problem where not like prior variants in which one randomizes edge
arrivals or bounds edge weights, we may revoke beforehand dedicated edges.
Further, it bounds the earnings of speculators who’re in the sport
to obtain the cancellation fees. Our model permits the seller to cancel at any time any reservation made earlier, through which case the holder of the reservation incurs a utility loss amounting to a fraction of her worth for
the reservation and may receive a cancellation charge from the seller.
They nonetheless hold if we change objects with elements of a matroid and matchings with impartial units,
or if all bidders have additive worth for a set of items.
A vendor will show a set of slots sooner or later T sooner
or later. Many advertisers (bidders) use Internet systems to buy show commercials on publishers’
webpages or on traditional media such as radio, Tv and newsprint.
You possibly can capture nonetheless pictures or video with either, that means that video-conferencing is an possibility by way
of Google Chat. Republican Rep. Madison Cawthorn’s seat (now numbered the 14th) would move slightly to
the left, though it will still have gone for Donald Trump by
a 53-forty five margin, in comparison with 55-forty three previously.
The district, which takes in a closely Black stretch of North Carolina’s rural north in addition to
some Raleigh exurbs, would have voted 51-48 for
Joe Biden, in comparison with Biden’s 54-45 margin in Butterfield’s present district, the first.
But the trendlines right here have been very unfavorable for
Democrats, and Butterfield might very properly lose in a troublesome midterm atmosphere.
Then an electric current is run by the water, which makes any salts within the water drop to the underside the
place they can be removed. Note that the map has been totally renumbered, so
we’ve put collectively our best evaluation of where each current incumbent may seek re-election at this hyperlink, while statistics for
previous elections can be found on Dave’s Redistricting App.
Through the optioning for the moment admin aspect of doc verification, the service
handlers can get a quick entry for service taken.
пін ап
пин ап вхід в особистий кабінет [url=https://pinupcasinolfsesn.kiev.ua]https://pinupcasinolfsesn.kiev.ua[/url].
Станьте часником зеленуватої лагуни
нові ігрові автомати [url=https://pinupcasinolfsesn.kiev.ua/]https://pinupcasinolfsesn.kiev.ua/[/url].
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Mersin’de psikolog arayanlar, kliniğimizde kendilerini rahat ve güvende hissedebilir.
[url=http://pinuputhezin.com]http://pinuputhezin.com[/url]
Name Up Casino is the official website of the renowned online casino repayment for players from Brazil.
pinuputhezin.com/
mtp free vegas slot games
The final half shows all of the occasions a examine
has been run in opposition to your credit report, both because you utilized for a loan or because a merchant or employer initiated the test.
Check out all the gastronomical motion on this premiere of Planet Green’s latest show, Future Food.
So when you sign up to seek out out what sitcom star you most determine with, the makers of that poll now have access to your private data.
And they have a easy surface for attaching pictures, gemstones, fabric or whatever else
fits your fancy. Most Web sites that include safe personal data
require a password also have not less than one
password trace in case you neglect. Why do individuals share embarrassing information online?
That’s why most online scheduling programs permit businesses to
create time buckets. Also, RISC chips are superscalar
— they’ll perform a number of directions at the identical time.
But two or three relatively cheap displays could make a world of
distinction in your computing experience. But DVRs have two main flaws — you
must pay for the privilege of utilizing one, and you’re caught with no matter
capabilities the DVR you purchase occurs to include.
[url=http://pinuputhezin.com]http://pinuputhezin.com[/url]
Affix Up Casino is the valid website of the distinguished online casino for players from Brazil.
pinuputhezin.com
Great blog here! Also your web site loads up fast!
What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link
to your host? I wish my website loaded up
as fast as yours lol
The Zephyrus S17 has a big four cell, 90WHr battery. Four tweeters
are located beneath the keyboard whereas the two
woofers sit below the display. Overall, these two
benchmark results bode effectively for avid gamers wanting a laptop computer that’s a reduce above when it comes to graphics performance,
with the high body rates equating to a smoother gaming experience and extra detail in each scene rendered.
Because the Xbox 360 cores can every handle two threads at a time, the 360 CPU is the equal of getting six conventional processors in one machine.
The sheer amount of calculating that is finished by
the graphics processor to determine the angle and transparency
for every mirrored object, and then render it in actual time, is extraordinary.
Southern California artist Cosmo Wenman has used a
3-D printer to make meticulously rendered copies of famous sculptures, based upon plans usual from a whole lot
of images that he snaps from every angle. Many firms supply a combination of
these plans. With its combination of a Core i9-11900H CPU, a Nvidia RTX 3080 GPU, and 32GB of RAM,
this laptop carried out exceedingly properly in performance benchmarks that present insight into its CPU energy and cooling.
What this means if you find yourself enjoying video games is that the Xbox 360 can dedicate one
core solely to producing sound, whereas one other might run the sport’s
collision and physics engine.
[url=http://www.pinuputhezin.com]www.pinuputhezin.com[/url]
Pin Up Casino is the valid website of the renowned online casino in place of players from Brazil.
pinuputhezin.com
antalya airport to hotel transfer services
[url=http://pinuputhezin.com]http://pinuputhezin.com[/url]
Name Up Casino is the official website of the distinguished online casino for players from Brazil.
pinuputhezin.com
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/ar/register?ref=IQY5TET4
Note that the Aivo View is yet one more dash cam that can’t seem to
extrapolate a time zone from GPS coordinates, though it acquired the date appropriate.
That said, other sprint cams have handled the identical
state of affairs better. Otherwise, the Aivo View is an excellent 1600p entrance dash cam
with integrated GPS, as well as above-average day
and evening captures and Alexa support. There’s no arguing the quality of the X1000’s front video captures-they’re
nearly as good as anything we’ve seen at 1440p. It’s additionally versatile with both GPS and radar options and the touch display makes
it exceptionally pleasant and easy to use. With somewhat information of the Dart language,
you’ll be able to easily customize this template and make a quality product on your consumer.
But we remind you that to work with Flutter templates, you
want some information in the sector of programming.
A clean code and a detailed description will allow you to understand
the construction of this template, even if you happen to don’t have any
knowledge in the sphere of coding. What’s to maintain the ex
from exhibiting up and causing a scene or even doubtlessly getting upset or violent?
Overall, these two benchmark outcomes bode effectively for gamers wanting
a laptop that’s a minimize above in terms of graphics performance, with the excessive
body rates equating to a smoother gaming expertise and more detail in each scene
rendered.
В нашем интернет-магазине можно купить диплом нового образца недорого и без предоплаты.
If some one wants expert view about blogging
and site-building after that i recommend him/her to pay a quick visit this weblog, Keep up the nice work.
Эксклюзивное пин-ап казино
pin up brasil [url=http://www.pinupcasinojenzolo.com/]http://www.pinupcasinojenzolo.com/[/url].
When you have diabetes or other chronic physical circumstances, you too can apply to be
allowed to take meals, drink, insulin, prosthetic units or personal
medical gadgets into the testing room. Handmade objects do not cease there, though.
Sharp, Ken. “Free TiVo: Build a greater DVR out of an Old Pc.” Make.
A greater card can enable you to enjoy newer, more graphics-intensive games.
Fortunately, there are hardware upgrades that can extend the helpful life
of your current computer without fully draining your account or relegating yet another piece of equipment to a landfill.
These computations are performed in steps by way of a collection of computational elements.
The shaders make billions of computations each second to perform their specific tasks.
Each immediate is followed by a set of specific duties,
equivalent to: provide your own interpretation of the assertion, or describe a particular state
of affairs the place the statement would not hold true. Simply decide what needs
to be accomplished in what order, and set your deadlines accordingly.
To manage and share your favorite finds on-line as well as
on your phone, create a LocalEats user account. Low-noise followers obtainable as properly.
It’s really up to the game developers how the system’s considerable assets are used.
This way you get easy access, just like explorer, to all the files and folders per file system. Instead of being limited to one file system that the OS picks for you, you have access. Access data from older sessions or hidden partitions, access data that your OS (e.g. Windows) does not see or hides from you etc. Combine this all-revealing functionality with far better read and recovery mechanisms, scanning for lost files functionality, workarounds for a wide range of drive and software bugs, limitations or shortcomings and you have an enormously powerful data recovery tool. RepairCdDvD is must-have-software for every PC user and is deliberately kept low priced to be able to offer a solution for everybody.
Позитивное казино пин-ап
pin up brasil [url=https://pinupcasinojenzolo.com]https://pinupcasinojenzolo.com[/url].
Позитивное казино пин-ап
cassino pin up [url=https://www.pinupcasinojenzolo.com]https://www.pinupcasinojenzolo.com[/url].
Казино пин-ап – это круто
site casino online [url=https://pinupcasinojenzolo.com/]https://pinupcasinojenzolo.com/[/url].
ATM skimming is like identity theft for debit cards: Thieves use hidden electronics to steal the non-public data saved on your card and record your PIN number to access all that tough-earned cash in your account. If ATM skimming is so serious and high-tech now, what dangers can we face with our debit and credit score playing cards sooner or later? Mobile bank card readers let customers make a digital swipe. And, as safety is at all times a difficulty relating to delicate credit card data, we’ll explore a few of the accusations that competitors have made towards different merchandise. If the motherboard has onboard video, attempt to take away the video card utterly and boot using the onboard version. Replacing the motherboard typically requires changing the heatsink and cooling fan, and could change the type of RAM your pc wants, so you’ve to do some research to see what components you will have to buy on this case.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
darknet market links darknet sites
Your blog is a treasure trove of wisdom and positivity I appreciate how you always seem to know just what your readers need to hear
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Wohh precisely what I was searching for, regards for putting up.
My website: красивые голые сиськи
Тhanks ᴠery іnteresting blog!
Take a loօk аt my blog Escort Girls in Karachi
Howdy! I know this is kinda off topic however I’d figured I’d ask.
Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest authoring a blog article or vice-versa?
My site goes over a lot of the same subjects
as yours and I think we could greatly benefit from each other.
If you happen to be interested feel free to shoot me an e-mail.
I look forward to hearing from you! Terrific blog by the way!
I have read so many content on the topic of the blogger lovers except this post is truly a nice article, keep
it up.
In contrast to some IGT slots, which might look a bit easy and dated, our review staff discovered the PowerBucks Wheel of Fortune Exotic Far East online slot to be both modern and engaging. Link bonus. Look out for the Wheel of Fortune symbols too, as these unlock any of three progressive jackpot prizes. Collect 3, 4, or 5 bonus symbol to receive 8, 10, or 12 free spins on the Magic of the Nile slot machine. Spin your approach down the famous river with the Magic of the Nile on-line slot. The normal strategy to earn money, of course, is by having a job. Meanwhile, even as nations world wide begin testing vaccine passports as a means of safely opening borders and transportation, the U.S. Cleopatra did like the finest of every part, and even the lettered and numbered symbols are adorned with jewels, while the scattered symbol is none aside from the Sphinx itself. Customer support contracting companies like OutPLEX and Alorica cowl e-mail and live chat assist in addition to inbound and outbound cellphone calls. This addition to the IGT catalog comes with an historic Egyptian theme and exhibits you the sites of the pyramid as you spin the 5×3 grid.
For latest information you have to pay a quick visit the web and
on web I found this site as a most excellent website for hottest updates.
Трикс играть онлайн раздача каждый день
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.info/de-CH/join?ref=PORL8W0Z
Bandırma’da her konuda güncel haberleri ve bilgileri bulabilirsiniz!
Виктория столкнулась с необходимостью купить дорогостоящие лекарства для лечения своего заболевания. Статья на Яндекс Дзен указала ей на МФО, где она смогла взять займ в размере 10 000 рублей без отказа, несмотря на свою кредитную историю, что помогло ей быстро начать необходимое лечение.
DZEN Spavkin – [url=https://dzen.ru/a/Zb7Q8cFB0iWI-Pd3]займы срочно[/url]
Do you wish to offer your roof a rejuvenation? Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is your solution. This innovative product offers a unique degree of care for your asphalt shingles, making sure they
remain durable.
Utilizing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer, you’re not just using any ordinary product.
You’re selecting a top-quality roof rejuvenation solution formulated to greatly increase
the life of your roof by up to 30 years. It’s a smart choice for those
seeking to preserve their investment.
The reason to opt for Shingle Magic Roof Sealer?
For starters, its unique formula seeps into
the asphalt shingles, reviving their original
durability and look. Furthermore, it’s remarkably straightforward to install, needing little time for
optimal results.
Not only does Shingle Magic Roof Sealer extend the life of
your roof, but it also offers exceptional resistance to the elements.
From intense UV rays, heavy rain, or snow and ice, the roof is
well-protected.
Moreover, choosing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer indicates you are choosing an environmentally friendly
option. Its non-toxic makeup means little environmental impact, which makes it a responsible choice
for eco-conscious homeowners.
In conclusion, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer excels
as the premier roof rejuvenation solution. Not only does it increase the life of your roof but also offering exceptional protection and a green option positions it as
the wise choice for homeowners seeking to care for their property’s future.
Furthermore, a significant advantage of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is
its cost-effectiveness. Rather than pouring a fortune on frequent repairs or a full roof replacement, choosing Shingle Magic saves you costs in the long run. This makes it a budget-friendly option that provides premium results.
Furthermore, the ease of application of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer stands out.
There’s no need for expert skills to apply it.
Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or opt for professional installation,
Shingle Magic guarantees a smooth process with excellent results.
Its longevity is yet another significant reason to choose
it. After application, it forms a layer that preserves
the integrity of your shingles for years. That means fewer concerns about weather
damage and more peace of mind about the condition of your
roof.
In terms of appearance, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is
also superior. It not only protects your roof but also boosts
its aesthetic. Your shingles will look newer, thus adding curb appeal and market
value to your property.
Client satisfaction with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer
is additional proof to its efficacy. Many customers have seen significant improvements in their roof’s state after using the product.
Reviews emphasize its user-friendliness, longevity, and superior protection.
Finally, opting for Shingle Magic Roof Sealer means opting for a
reliable solution for roof rejuvenation. Combining sturdiness, beauty,
cost-effectiveness, and user-friendliness renders it the perfect choice for homeowners seeking to prolong the life and appearance of their roof.
Don’t hesitate to revitalize your roof with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer.
Do you desire to provide your roof a new lease on life?
Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is what you need. The exceptional product delivers an unparalleled degree of care for your asphalt
shingles, guaranteeing they remain durable.
By choosing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer, you’re not just choosing any ordinary product.
You’re selecting a top-quality roof rejuvenation solution designed to greatly extend the
life of your roof for decades. It’s a smart choice for property owners aiming to preserve their investment.
Why choose Shingle Magic Roof Sealer? To begin with, its proprietary
formula seeps into the asphalt shingles, restoring their initial durability and aesthetic.
Moreover, it is remarkably straightforward to install, needing minimal time for
top results.
In addition to Shingle Magic Roof Sealer prolong the
life of your roof, it also offers superior protection against environmental damage.
Whether it’s harsh sunlight, torrential downpours, or snow and ice, the
roof remains safeguarded.
Moreover, choosing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer indicates you are choosing an environmentally friendly option. The safe formula
guarantees minimal environmental impact, thus making it
a responsible choice for your home.
Finally, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer excels as the best roof rejuvenation solution. Not only does it prolong
the life of your roof but also offering exceptional protection and an green option positions it as the smart choice for homeowners looking to care for their property’s future.
Moreover, one of the key benefits of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is its affordability.
Instead of pouring a significant amount on regular repairs or a full
roof replacement, choosing Shingle Magic saves you expenses in the long run.
This makes it a budget-friendly option that still delivers
top-notch results.
Moreover, the ease of application of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is a major
plus. You don’t need specialized knowledge to apply it.
Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or choose for expert application, Shingle Magic ensures a straightforward process with remarkable results.
Its lasting power is yet another compelling reason to choose it.
When applied, it develops a protective barrier that keeps the integrity of your shingles for
many years. This means less worry about weather damage and greater peace of mind about the health of your roof.
Regarding visual appeal, Shingle Magic Roof
Sealer also excels. Not only does it safeguard your roof but also boosts its appearance.
The shingles will appear more vibrant, which adds to the attractiveness
and worth to your property.
Customer satisfaction with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is further evidence to its quality.
Many homeowners have seen remarkable improvements in their roof’s condition after using the product.
Testimonials highlight its user-friendliness, durability, and
outstanding protective qualities.
To wrap it up, selecting Shingle Magic Roof Sealer represents
selecting a reliable solution for roof rejuvenation. With
its blend of longevity, beauty, affordability, and user-friendliness makes it
the optimal choice for those seeking to extend the life and appearance of their roof.
Act now to transform your roof with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this site.It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s very hard to get that « perfect balance » between user friendliness and visual appearance.I must say that you’ve done a amazing job with this.In addition, the blog loads extremely fast for me on Firefox.Excellent Blog!
great post, very informative. I’m wondering why the opposite specialists of this sector do not realize
this. You must continue your writing. I’m confident, you have a huge readers’
base already!
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It
truly useful & it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and
aid others like you aided me.
Мария, молодой предприниматель, решила запустить свой стартап, но ей не хватало стартового капитала. Прочитав полезные советы в статье на Яндекс Дзен, она нашла МФО, специализирующееся на кредитах для начинающих бизнесменов. Благодаря удобным условиям и быстрому оформлениИзвините за недоразумение. Я не могу прямо сейчас прочитать или предоставить содержание с веб-страницы из-за ограничений доступа.
DZEN Spavkin – [url=https://dzen.ru/a/Zb7Q8cFB0iWI-Pd3]займы онлайн на карту[/url]
Greetings from Carolina! I’m bored at work so I
decided to check out your website on my iphone during lunch break.
I really like the knowledge you present here and can’t wait to take a
look when I get home. I’m amazed at how fast your blog
loaded on my cell phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just
3G .. Anyhow, very good site!
Then, they’d open the schedule and choose a time
slot. The next year, Radcliff shattered her own record with a beautiful 2:15:25 finish time.
Mathis, Blair. “How to construct a DVR to Record Tv – Using Your Computer to Record Live Television.” Associated Content.
However, reviewers contend that LG’s track report of producing electronics
with high-finish exteriors stops short on the G-Slate,
which has a plastic again with a swipe of aluminum for element.
But can we move beyond an anecdotal hunch and discover some
science to again up the concept that everybody ought
to simply relax a bit? The 285 also has a again button. The 250 and 260 have solely 2
gigabytes (GB) of storage, whereas the 270 and 285 have four GB.
The good news is that supermarkets have been working arduous to speed up
the provision and availability of groceries. Morrisons is engaged on introducing
various measures to assist cut back the number of substitutes and
missing items that some prospects are encountering with their online meals outlets.
In fact, with more individuals working from house or in self-isolation, the demand for online grocery deliveries has greatly elevated – placing an enormous pressure on the system.
In distinction to some IGT slots, which can look a little bit easy and dated,
our evaluate team discovered the PowerBucks Wheel of Fortune Exotic Far East on-line slot
to be each modern and interesting. Link bonus.
Look out for the Wheel of Fortune symbols too, as these
unlock any of three progressive jackpot prizes. Collect 3, 4,
or 5 bonus symbol to receive 8, 10, or 12 free spins on the Magic
of the Nile slot machine. Spin your approach down the famous river with the Magic of the Nile online slot.
The traditional technique to earn money, in fact, is
by having a job. Meanwhile, even as nations world wide start testing vaccine passports as a manner of safely opening borders and transportation, the U.S.
Cleopatra did like the finest of every part, and even the lettered and numbered symbols are adorned with jewels, whilst the scattered symbol is none
apart from the Sphinx itself. Customer support contracting companies like OutPLEX and Alorica cowl electronic mail and live chat help in addition to inbound and outbound cellphone calls.
This addition to the IGT catalog comes with an historical Egyptian theme and reveals you the websites of the pyramid as you spin the 5×3 grid.
A round of applause for your article. Much thanks again.
My website: порно оргазмы девушек
As long as you hit the successful combination from left to proper,
you may be rewarded. In the event you guess the
colour proper, your winnings will be doubled.
The primary set of five reels are crossed by 40 paylines, and three or extra matching symbols across a line will equal a winning spin. One downside to this technique is that in addition to having
to take your laptop computer laptop with you wherever you journey, you’ll even have to carry
a small, yet bulky set of speakers. There are no set paylines.
The jackpot is price 12,500 coins and gets triggered during the utmost guess spins when you hit 5 Amulets on any of
the 243 paylines which were lively. The gameplay in Pompeii
slots is innovative, so players must wager five coins on every reel instead of choosing paylines.
Since there are 25 paylines, the minimal sum of money you possibly can wager per spin on the Pompeii slot machine is 50 cents, while the maximum is $125.
Bandırma’da her konuda güncel haberleri ve bilgileri bulabilirsiniz!
To play, avid gamers merely hold the Wiimote and do their finest to sustain with the dancing determine on the display.
You sustain with the most recent know-how; possibly even consider yourself an early adopter.
As a result of variations in architectures and numbers of processor cores, evaluating uncooked GHz numbers between completely
different manufacturer’s CPUs, and even completely different models from the identical producer,
would not at all times tell you what CPU can be sooner.
In case you weren’t impressed with the hearth-respiration CSP, which can sometime use molten glass as
a storage fluid (still cool), how about an air-respiratory battery?
Once we know the syntactic construction of a sentence, filling in semantic
labels will turn into simpler accordingly. Begin by filling out
a centralized, all-encompassing vacation calendar for the weeks leading up to, during and after the vacation. Now that we have received the heat,
read on to learn the way the hair dryer will get that heat moving.
But instead of burning innocent ants, the energy is so intense it turns into hot sufficient to heat a fluid, usually molten salts, to somewhere in the neighborhood of 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit (537.Eight
degrees Celsius). What’s new within the power
trade?
UP-X — Официальный сайт – сервис мгновенных игр Ап икс
Bandırma’da her konuda güncel haberleri ve bilgileri bulabilirsiniz!
After that, you may choose to utilize the Repair function, which is the bread and butter feature of the software. This option seeks to recover the data on your CD or DVD, without needing you to configure anything.
I’ve been browsing on-line greater than 3 hours as of late, yet I by no means found any attention-grabbing article like yours.
It’s pretty value enough for me. Personally, if all webmasters and bloggers made just right content material
as you probably did, the web shall be much more useful than ever before.
Revolutionize Your Workspace with Freedman’s Office
Chairs in Atlanta
**Embrace Productivity and Comfort: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta**
In the bustling city of Atlanta, where innovation meets tradition, Freedman’s Office Furniture introduces its exclusive range of ergonomic office chairs.
Located at 3379 Peachtree Rd NE, Atlanta, GA 30326, our showroom caters to
the discerning tastes of residents in neighborhoods like Ansley
Park and Baker Hills, offering premium office seating solutions that combine style and functionality.
**Elevate Your Workspace in the Heart of Atlanta**
Atlanta, founded in 1836, stands as a testament to a rich
history and a thriving metropolis. With a population of 496,461 (2021) and 227,388 households, the city
continues to evolve while preserving its unique charm. Freedman’s commitment to providing modern office chairs aligns
seamlessly with Atlanta’s spirit of progress and dynamism.
**Navigating the Urban Hub: Interstate 20**
Much like the smooth flow of Interstate 20, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs embody a perfect
blend of form and function. This mirrors Atlanta’s commitment to
providing a conducive environment for businesses to flourish and individuals to excel in their professional
endeavors.
**Investing in Style: A Wise Choice for Atlanta Professionals**
In a city that values aesthetics and innovation, opting for
Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs is a statement of sophistication. Our collection not only enhances the visual appeal of your workspace but also complements Atlanta’s commitment to creating a work environment that fosters creativity and
success.
**Discovering Atlanta’s Landmarks and the Comfort of Freedman’s Chairs**
Embark on a journey through Atlanta’s iconic landmarks
while experiencing the unmatched comfort of Freedman’s
ergonomic office chairs. Here are five fascinating facts about some of
Atlanta’s cherished destinations:
– **Atlanta Botanical Garden:** A 30-acre botanical garden showcasing an incredible variety of plants and flowers.
– **Centennial Olympic Park:** Built for the 1996 Summer Olympics, this
park serves as a gathering spot for locals and visitors.
– **Atlanta History Center:** An extensive history
museum featuring exhibits, historic houses, and gardens.
– **College Football Hall of Fame:** Celebrating the rich history of
college football with interactive exhibits and memorabilia.
– **The “”It’s a living”” Street Art:** A vibrant street art scene in the city, offering colorful and dynamic murals.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs in Atlanta**
Opting for Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Atlanta is
not just a choice; it’s a commitment to elevate your workspace.
Our stylish and comfortable chairs ensure that your office reflects the vibrant and dynamic spirit of Atlanta, making it an ideal place for productivity,
innovation, and success.
”
“Transform Your Work Environment with Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando
**Revitalize Your Workspace: Discover Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando**
In the heart of Orlando, where magic and modernity coexist, Freedman’s
Office Furniture proudly presents its exclusive range of office chairs.
Conveniently located at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, Orlando, FL 32801, our showroom caters to the
diverse needs of residents in neighborhoods like
Audubon Park and Colonial Town Center, offering premium office seating solutions that prioritize both comfort
and style.
**Elevate Your Work Experience in Orlando’s Lively Atmosphere**
Orlando, founded in 1875, has grown into a vibrant city with a population of 309,154
(2021) and 122,607 households. Freedman’s commitment to providing high-quality
office chairs resonates with Orlando’s lively and energetic
atmosphere, offering residents the perfect blend of comfort and functionality
for their workspaces.
**Navigating the City: The Significance of Interstate 4**
Much like the seamless flow of Interstate 4, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs seamlessly blend style and functionality.
This mirrors Orlando’s commitment to providing an environment where
residents can seamlessly navigate between work and
leisure, making our chairs an ideal choice for those who value
efficiency and aesthetics.
**Investing in Comfort: An Informed Choice for Orlando Professionals**
In a city known for its diverse attractions and entertainment, investing in Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs is a conscious decision. Our
chairs not only enhance the aesthetics of your
workspace but also align with Orlando’s commitment to providing a comfortable and conducive work environment.
**Explore Orlando’s Attractions and Relax in Freedman’s
Chairs**
Embark on a journey through Orlando’s enchanting attractions while enjoying the
unparalleled comfort of Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs.
Here are five interesting facts about some of Orlando’s most beloved landmarks:
– **Walt Disney World Resort:** The most visited vacation resort globally, spanning over 25,000 acres.
– **Universal Studios Florida:** An iconic film and
television studio theme park, featuring thrilling rides
and attractions.
– **Lake Eola Park:** A scenic park in downtown Orlando with a picturesque
lake and swan boats.
– **Dr. Phillips Center for the Performing Arts:** A state-of-the-art venue
hosting various cultural and artistic performances.
– **Orlando Museum of Art:** Showcasing a diverse collection of contemporary and classic art.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs in Orlando**
Opting for Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Orlando
is not just a decision; it’s a commitment to enhancing your workspace.
Our stylish and comfortable chairs ensure that your office reflects the dynamic
and creative spirit of Orlando, making it an ideal place
for productivity, innovation, and success.
”
“Discover Superior Comfort with Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta
**Elevate Your Workspace: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta**
Nestled in the vibrant city of Atlanta, Freedman’s Office Furniture
proudly introduces its exclusive collection of office chairs.
Conveniently located at 3379 Peachtree Rd NE, Atlanta, GA 30326,
our showroom caters to the diverse needs of residents in neighborhoods like Ansley
Park and Buckhead, offering premium office seating solutions that blend comfort and sophistication seamlessly.
**Crafting a Distinctive Workspace in Atlanta’s Dynamic Setting**
Founded in 1836, Atlanta has evolved into a bustling city with
a population of 496,461 (2021) and 227,388 households.
Freedman’s commitment to delivering top-notch office chairs aligns perfectly with Atlanta’s dynamic and diverse setting, providing residents with ergonomic solutions that enhance both productivity
and aesthetic appeal.
**Navigating the Urban Hub: The Importance of Interstate 20**
Much like the flow of Interstate 20, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs effortlessly navigate the modern office landscape.
This reflects Atlanta’s status as a vibrant urban hub,
where residents value efficiency and style in equal measure, making our chairs the perfect choice
for those seeking a superior seating experience.
**Investing in Excellence: A Thoughtful Choice for Atlanta Professionals**
In a city renowned for its rich history and cultural attractions,
choosing Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs is a
thoughtful investment. Our chairs not only elevate the visual appeal of your workspace but also resonate with Atlanta’s commitment to fostering innovation and success through a comfortable
and ergonomic work environment.
**Explore Atlanta’s Cultural Gems and Relax
in Freedman’s Chairs**
Immerse yourself in Atlanta’s cultural richness while enjoying the superior comfort of Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs.
Here are five fascinating facts about some of Atlanta’s most iconic landmarks:
– **Atlanta Botanical Garden:** A 30-acre garden showcasing
an incredible variety of plants, flowers, and sculptures.
– **Centennial Olympic Park:** Built for the
1996 Summer Olympics, it’s a gathering spot with fountains, events, and green spaces.
– **Martin Luther King Jr. National Historic Site:** Preserving the legacy of the civil rights leader, including
his childhood home and Ebenezer Baptist Church.
– **Piedmont Park:** A sprawling urban park with walking trails,
sports facilities, and the picturesque Lake Clara Meer.
– **The Fox Theatre:** A historic venue known for its Moorish architecture and hosting various performances.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs in Atlanta**
Opting for Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Atlanta
is not merely a decision—it’s a statement. Elevate your workspace with our stylish and comfortable chairs, embodying the spirit of innovation and success that defines Atlanta’s dynamic professional landscape.
”
“Discover Unmatched Seating Comfort with Freedman’s Office
Chairs in Orlando
**Elevate Your Workspace: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando**
Located at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, Orlando, FL 32801, Freedman’s Office Furniture is proud to
introduce its exclusive range of office chairs to the
vibrant city of Orlando. Serving neighborhoods like Colonial Town Center and College Park,
Freedman’s provides superior office seating solutions that prioritize both comfort and style.
**Crafting a Distinctive Workspace in Orlando’s Sunshine State**
Established in 1875, Orlando has transformed into
a thriving city with a 2021 population of 309,154 and 122,607 households.
Freedman’s dedication to delivering top-tier office chairs aligns
seamlessly with Orlando’s sunny ambiance, offering residents ergonomic solutions that
blend seamlessly with the city’s dynamic and energetic atmosphere.
**Navigating the Urban Landscape: The Significance of
Interstate 4**
Much like the flow of Interstate 4, Freedman’s ergonomic office
chairs effortlessly navigate the modern office landscape.
This mirrors Orlando’s status as a hub of entertainment and technology, where residents seek innovative
and comfortable seating solutions, making our chairs the ideal choice for those desiring a
superior seating experience.
**Investing in Excellence: A Thoughtful Choice for Orlando Professionals**
In a city known for its theme parks and cultural attractions,
choosing Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs is a thoughtful investment.
Our chairs not only enhance the visual appeal of your workspace but
also align with Orlando’s commitment to creating a vibrant and comfortable work environment that fosters creativity and success.
**Explore Orlando’s Magical Attractions and Relax in Freedman’s
Chairs**
Immerse yourself in Orlando’s magical offerings while enjoying the unmatched comfort of Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs.
Here are five fascinating facts about some of Orlando’s most iconic landmarks:
– **Walt Disney World Resort:** The world’s most-visited vacation resort,
featuring four theme parks and numerous attractions.
– **Universal Studios Florida:** A film and television studio theme park with thrilling rides and shows.
– **Lake Eola Park:** A downtown oasis with swan boats, live swans, and scenic walking paths.
– **Orlando Science Center:** A hands-on science museum with interactive exhibits and engaging displays.
– **Dr. Phillips Center for the Performing Arts:
** A modern venue hosting various live performances, including Broadway shows.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs in Orlando**
Opting for Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs
in Orlando is more than just a decision—it’s a commitment to excellence.
Elevate your workspace with our stylish and comfortable chairs, embodying the spirit of innovation and success that
defines Orlando’s dynamic professional landscape.
”
“Revolutionize Your Workspace with Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta
**Experience Unparalleled Comfort: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta**
Nestled at 3379 Peachtree Rd NE, Atlanta, GA 30326, Freedman’s Office Furniture proudly introduces its exceptional
collection of office chairs to the dynamic city of Atlanta.
Serving neighborhoods like Ansley Park and Buckhead, Freedman’s delivers office seating solutions that seamlessly combine ergonomic design with aesthetic appeal.
**Redesigning Your Office Aesthetic: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Atlanta**
Founded in 1836, Atlanta has evolved into a bustling metropolis with a 2021 population of 496,461 and 227,388 households.
Freedman’s commitment to providing top-notch office chairs perfectly complements Atlanta’s modern and diverse atmosphere, offering residents
seating solutions that embody both innovation and style.
**Navigating the Cityscape: The Significance of Interstate 20**
Much like the connectivity provided by Interstate 20, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs seamlessly integrate into Atlanta’s diverse professional landscape.
Reflecting Atlanta’s status as a cultural and economic hub, our chairs offer residents unparalleled comfort and style, making them the preferred choice for those seeking an exceptional seating experience.
**A Commitment to Excellence: Choosing Freedman’s Chairs in Atlanta**
In a city known for its rich history and cultural landmarks,
choosing Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs is a
statement of commitment to excellence. Our chairs not only enhance the visual appeal of your workspace
but also align with Atlanta’s reputation for fostering innovation and
success.
**Explore Atlanta’s Rich Heritage and Relax in Freedman’s Chairs**
Discover the vibrant history of Atlanta while enjoying the unrivaled comfort of Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs.
Here are five intriguing facts about some of Atlanta’s iconic landmarks:
– **Atlanta History Center:** A comprehensive history museum featuring exhibits on the Civil War and Southern history.
– **Piedmont Park:** Atlanta’s premier green space, offering walking paths, sports facilities,
and beautiful scenery.
– **Martin Luther King Jr. National Historic Site:** Preserving the childhood home of the
civil rights leader and featuring the Ebenezer Baptist Church.
– **The Fox Theatre:** A historic performing arts venue known for its grand architecture and diverse entertainment.
– **The High Museum of Art:** Atlanta’s
leading art museum, showcasing a diverse collection of artwork.
**Why Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs Stand Out in Atlanta**
Choosing Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Atlanta is a decision that transcends mere furniture.
It’s a commitment to elevating your workspace with stylish and comfortable seating that resonates with
Atlanta’s spirit of progress and achievement.
The author’s personal anecdotes added a human touch to the content, making it more engaging and relatable. It’s always inspiring to learn from others’ experiences and gain insights from their journeys. | https://www.pinnedin.com/
güvenilir bahis siteleri
Bu konteyner evlerin iç mekanları da dış tasarımları kadar dikkat çekici! Kayra’nın estetik anlayışı gerçekten benzersiz. | https://www.kayraprefabrik.com.tr/
Your blog deserves all the recognition it gets.
Konteyner evlerin pratik ve çevre dostu olabileceğini gösteren en güzel örneklerden biri. Kayra’nın tasarımları gerçekten övgüyü hak ediyor. | https://www.kayraprefabrik.com.tr/
I do trust all the ideas youve presented in your post They are really convincing and will definitely work Nonetheless the posts are too short for newbies May just you please lengthen them a bit from next time Thank you for the post
Amazing! This blog looks just like my old one! It’s on a
completely different topic but it has pretty much
the same layout and design. Superb choice of colors!
This really is such a awesome write-up. I’ve been looking for this information for quite a while now and then finally stumbled upon your internet site. Thanks so much for posting this, this has helped me out tremendously. By the way I love the style of the blog, looks good, did you create it all by yourself?
area rugs are best positioned on the outside of the house where it can serve better;
I like this web blog very much so much superb info .
eskil medya
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Ich bin immer auf der Suche nach qualitativ hochwertigen Inhalten und dieser Artikel hat meine Erwartungen übertroffen. Vielen Dank für Ihre harte Arbeit.
Bu konteyner evlerin iç mekanları da dış tasarımları kadar dikkat çekici! Kayra’nın estetik anlayışı gerçekten benzersiz. | https://www.kayraprefabrik.com.tr/
Kayra’nın konteyner evleri modern yaşam tarzını yeniden tanımlıyor. Hem çevre dostu hem de şık, daha ne olsun! | https://www.kayraprefabrik.com.tr/
When I originally commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time a comment
is added I get four e-mails with the same comment. Is there
any way you can remove me from that service? Appreciate it!
Konteyner evlerle ilgili herhangi bir önyargımı tamamen değiştirdiniz! Kayra’nın yenilikçi yaklaşımıyla bu evler gerçekten modern bir yaşam tarzının sembolü haline geliyor. | https://www.kayraprefabrik.com.tr/
Крутое казино пин-ап
apostas cassino [url=https://www.pinupcasinojenzolo.com/]https://www.pinupcasinojenzolo.com/[/url].
https://ozlemradyo.com
güvenilir bahis siteleri
Зажигай в казино пин-ап
apostas cassino [url=http://pinupcasinojenzolo.com/]http://pinupcasinojenzolo.com/[/url].
Почувствуй себя настоящим пин-ап
jogos de cassino online [url=http://www.pinupcasinojenzolo.com]http://www.pinupcasinojenzolo.com[/url].
Wohh precisely what I was searching for, regards for putting up.
My website: жесткий анальный кастинг
Побеждай в пин-ап казино
cassino brasil [url=pinupcasinojenzolo.com]pinupcasinojenzolo.com[/url].
В условиях, когда финансовая поддержка требуется незамедлительно, каждая минута на счету. Именно поэтому сайт mikro-zaim-online.ru становится надежным решением для тех, кто ищет [url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/bez-otkaza/]быстрые займы без отказа на карту[/url]. Среди преимуществ сервиса – возможность выбора из более чем 40 МФО, предлагающих займы на сумму до 30 000 рублей без необходимости проверки кредитной истории. Это делает получение денег максимально доступным и удобным, обеспечивая мгновенное решение финансовых вопросов без лишней бюрократии и задержек.
Thank you for sharing your info. I really appreciate your efforts
and I am waiting for your next write ups thank you once again.
Kudos. Quite a lot of material.
Bandırma’da her konuda güncel haberleri ve bilgileri bulabilirsiniz!
Aw, this was an extremely nice post. Spending some time and actual effort to produce a
really good article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and don’t seem to get nearly anything done.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
I was recommended this website by my cousin I am not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my difficulty You are wonderful Thanks
Howdy, There’s no doubt that your blog could possibly be
having internet browser compatibility problems.
Whenever I take a look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine but
when opening in Internet Explorer, it’s got some overlapping
issues. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Aside
from that, excellent website!
Nice blog here Also your site loads up very fast What host are you using Can I get your affiliate link to your host I wish my site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Hi there, for all time i used to check blog posts here in the early hours in the morning, because i love to find out more and more.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/it/join?ref=GJY4VW8W
I resonate with the emphasis on work-life integration rather than striving for a perfect balance. This shift in perspective acknowledges the fluidity of modern life and encourages a more holistic approach to well-being. | https://www.pinnedin.com/
The tips for navigating difficult conversations at work are practical and well-articulated. Conflict resolution is a skill that everyone can benefit from honing, and this article offers valuable guidance in that regard. | https://www.pinnedin.com/
Usually I do not read article on blogs however I would like to say that this writeup very compelled me to take a look at and do so Your writing taste has been amazed me Thanks quite nice post
The blog post on effective communication techniques couldn’t have come at a better time for me. I’ve been struggling with articulating my thoughts in meetings, and the strategies shared here seem promising. | https://www.pinnedin.com/
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.info/en/join?ref=RQUR4BEO
TRT Benim zamanım izle
What’s up friends, fastidious piece of writingand good urging commented at this place, I am genuinely enjoying bythese.
This is a beautiful photo with very good lighting 😉group link
When confronted with the requirement for SR22 insurance, it is necessary to find the correct insurance firm.
SR22 insurance is actually a form filed by
your insurer. This criteria frequently adheres to major web traffic offenses.
Remain educated and also keep your SR22 insurance existing to stay
clear of lawful issues.
my blog … SR-22
Bandırma’da her konuda güncel haberleri ve bilgileri bulabilirsiniz! 📰🌆 #Bandırma #YerelHaberler
Hey there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow
you if that would be okay. I’m absolutely enjoying your blog and look
forward to new updates.
Bandırma’da her konuda güncel haberleri ve bilgileri bulabilirsiniz!
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
güvenilir bahis siteleri
Bandırma’da her konuda güncel haberleri ve bilgileri bulabilirsiniz! 📰🌆 #Bandırma #YerelHaberler
I’ve been advising cheap auto van insurance coverage to all
my family members. It’s an intelligent monetary
relocation for anybody.
Your blog has become a part of my daily routine Your words have a way of brightening up my day and lifting my spirits
What’s up friends, its fantastic piece of writing on the topic of teachingand completely defined,
keep it up all the time.
Betchip, Türkiye’nin en popüler bahis ve casino sitelerinden biridir. Ancak, Türkiye’de online bahis ve casino hizmetleri yasal olarak sınırlıdır ve bu nedenle Betchip gibi sitelerin giriş adresleri zaman zaman değişebilir. Bu yazıda, Betchip bahis ve casino sitesinin güncel giriş adresine nasıl ulaşabileceğinizi öğreneceksiniz.
Hi my loved one I wish to say that this post is amazing nice written and include approximately all vital infos Id like to peer more posts like this
What a data of un-ambiguity and preserveness of valuable experience about unexpected feelings.
Your practical advice is something I’ll be taking to heart.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
[url=https://shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-shark-evo-es-3-black-matt/]shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-shark-evo-es-3-black-matt/[/url]
Мотошлемы популярных марок в течение присутствии на широком ассортименте а также с доставкой числом Украине.
shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-ls2-of573-twister-combo-white-green-red/
This site definitely has all of the information I needed about this subject
My website: порно с красивой брюнеткой
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Не важно, кто вы – студент, домохозяйка или человек с плохой кредитной историей, [url=https://all-credit.ru/]all-credit.ru[/url] предлагает решение вашим финансовым проблемам. Наша подборка МФО включает в себя организации, готовые предоставить займы до 10 000 рублей всем без исключения, обеспечивая таким образом финансовую поддержку тем, кто в ней нуждается.
[url=https://shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-scorpion-exo-hx1-solid-matt-black/]shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-scorpion-exo-hx1-solid-matt-black/[/url]
Мотошлемы фаворитных марок на наличии в течение широком ассортименте (а) также с доставкой по Украине.
shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-ls2-mx700-subverter-rascal-black-orange/
[url=https://shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-airoh-commander-white/]shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-airoh-commander-white/[/url]
Мотошлемы фаворитных брендов на наличии в широком наборе а также начиная с. ant. до доставкой по Украине.
shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-caberg-duke-evo-black-matt/
Hello, could you please review my blog post and approve it for publication? Thanks a lot.
Are you searching for a trustworthy solution to prolong the life
of your roof? Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is what you need.
The exceptional product provides an extraordinary degree
of care for your asphalt shingles, guaranteeing they stay in top
condition.
Utilizing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer, you’re not just choosing any ordinary product.
You’re opting for a premium roof rejuvenation solution designed
to greatly extend the life of your roof for decades.
This is a wise decision for property owners looking to
safeguard their investment.
What makes Shingle Magic Roof Sealer? For starters, its proprietary formula gets into the asphalt shingles, restoring
their initial condition and aesthetic. Moreover, it’s incredibly straightforward to install, demanding minimal
time for maximum results.
Not only does Shingle Magic Roof Sealer extend the life of your roof, but it offers
outstanding defense against the elements. Be it blistering
sun, rainstorms, or freezing temperatures, your roof
is shielded.
Moreover, opting for Shingle Magic Roof Sealer indicates you are selecting an environmentally friendly option. The
safe formula ensures minimal environmental impact,
which makes it a thoughtful choice for eco-conscious homeowners.
In conclusion, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer excels as the best roof rejuvenation solution. Its ability
to extend the life of your roof but also providing
superior protection and an green option makes Shingle Magic as the ideal choice for property owners aiming to maintain their property’s future.
Additionally, an important feature of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer
is its cost-effectiveness. Instead of pouring a fortune on frequent
repairs or a full roof replacement, applying Shingle Magic helps save you costs in the long run. This makes it a budget-friendly option that provides premium results.
Moreover, the simplicity of its application of Shingle Magic Roof
Sealer stands out. It doesn’t require professional expertise to apply it.
If you enjoy DIY projects or prefer for expert application, Shingle Magic provides a smooth process with excellent results.
Its longevity is yet another significant reason to choose it.
After application, it develops a layer that
maintains the integrity of your shingles for a long time.
That means reduced worries about environmental wear and tear and more peace of mind about the state
of your roof.
Regarding aesthetic appeal, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is also
superior. Not only does it safeguard your roof but also improves its appearance.
The shingles will appear refreshed, thus adding to the attractiveness and value to your property.
Customer satisfaction with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is further evidence to its quality.
Many homeowners have seen remarkable improvements in their roof’s condition after using the product.
Reviews emphasize its ease of use, durability,
and superior defensive capabilities.
To wrap it up, selecting Shingle Magic Roof Sealer means
opting for a reliable solution for roof rejuvenation. With its blend of durability, beauty, affordability,
and simplicity makes it the perfect choice for homeowners
looking to extend the life and appearance of their roof.
Act now to revitalize your roof with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer.
certainly like your website but you need to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to inform the reality nevertheless I will definitely come back again
Thank you for this information. Nice content.
medyaeskil.com
I am regular reader, how are you everybody? This article posted at this website is in fact fastidious.
obviously like your website but you need to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to inform the reality on the other hand Ill certainly come back again
Bandırma’da her konuda güncel haberleri ve bilgileri bulabilirsiniz! 📰🌆 #Bandırma #YerelHaberler
Your writing is so eloquent and engaging You have a gift for connecting with your readers and making us feel understood
I do believe all the ideas youve presented for your post They are really convincing and will certainly work Nonetheless the posts are too short for novices May just you please lengthen them a little from subsequent time Thanks for the post
RepairCdDvD is a tool that recovers data from unreadable CD/DVD. It can help you retrieve the files from damaged CD DVD and save them to disk, the clipboard, or even the hard disk. No accumulated cost if you need more than one type media or file system supported. RepairCdDvD is a highly specialized yet easy to use media data recovery tool. It supports all disc formats and all common file systems. Insert a disc, start up RepairCdDvD and select the drive or media (if not selected already) and let RepairCdDvD mount the media. RepairCdDvD immediately shows you all the partitions or tracks and sessions located on the media, combined with all file systems that are present.
I’m extremely pleased to discover this website. I wanted to thank you for ones time just for this fantastic read!
My website: порно жмж
Bestie art.
obviously like your website but you need to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to inform the reality on the other hand Ill certainly come back again
RepairCdDvD is a tool that recovers data from unreadable CD/DVD. It can help you retrieve the files from damaged CD DVD and save them to disk, the clipboard, or even the hard disk. No accumulated cost if you need more than one type media or file system supported. RepairCdDvD is a highly specialized yet easy to use media data recovery tool. It supports all disc formats and all common file systems. Insert a disc, start up RepairCdDvD and select the drive or media (if not selected already) and let RepairCdDvD mount the media. RepairCdDvD immediately shows you all the partitions or tracks and sessions located on the media, combined with all file systems that are present.
It was a perfect sharing admin. it helped me a lot tahnxss
I do not even understand how I stopped up here, however I thought this publish used to
be great. I do not understand who you’re but certainly you’re going to a well-known blogger should you aren’t already.
Cheers!
I’ve learn several excellent stuff here. Certainly worth bookmarking for revisiting.
I wonder how much effort you place to create such a magnificent informative
site.
harika hirsiz
шепоток чтобы мужчина позвонил проверено – https://vipmagiya5.wordpress.com/2024/02/11/17-silnix-privorotov-na-foto-na-lyubov/ – шарлатаны настоящие маги
если человека приворожили что делать
Выбирая [url=https://all-credit.ru/]all-credit.ru[/url], вы выбираете надежность и удобство. Наш сайт объединяет более 45 проверенных МФО, предлагая займы на любой случай жизни. Процесс оформления максимально упрощен и требует минимум документов, что делает его идеальным выбором для тех, кто ценит свое время и стремится к быстрому решению финансовых вопросов.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.com/en/register?ref=DB40ITMB
Your blog always leaves me feeling uplifted and inspired Thank you for consistently delivering high-quality content
I visit each day a few sites and sites to read articles, except this website offers quality
based posts.
Официальный сайт Money-X: сервис быстрых игр
This way you get easy access, just like explorer, to all the files and folders per file system. Instead of being limited to one file system that the OS picks for you, you have access. Access data from older sessions or hidden partitions, access data that your OS (e.g. Windows) does not see or hides from you etc. Combine this all-revealing functionality with far better read and recovery mechanisms, scanning for lost files functionality, workarounds for a wide range of drive and software bugs, limitations or shortcomings and you have an enormously powerful data recovery tool. RepairCdDvD is must-have-software for every PC user and is deliberately kept low priced to be able to offer a solution for everybody.
Fantastic goods from you, man. I have understand your stuff previous to and
you are just extremely wonderful. I actually like what you
have acquired here, really like what you are stating and the way in which you say it.
You make it entertaining and you still care for to keep it wise.
I can not wait to read far more from you. This is
really a wonderful website.
IPhone and iPad owners can obtain the app possibly directly from their particular mobile App Retail store” “or maybe the official website.
Here is my webpage … http://www.ogloszenia-norwegia.pl/english/mostbet-bangladesh-where-every-wager-counts-mostbet-on-line-casino-mostbet-mosbet-mostbet-bd-mostbet-online-casino-in-bangladesh.html
Thanks-a-mundo for the post.Really thank you! Awesome.
My website: секс преподавателя и студентки
Bandırma’da her konuda güncel haberleri ve bilgileri bulabilirsiniz! 📰🌆 #Bandırma #YerelHaberler
bonanza harika dostummm oynayin
supertotobet e giriş için doğru adres
Hello, i think that i saw you visited my website so i
came to “return the favor”.I am attempting
to find things to improve my web site!I suppose its ok to use some of your ideas!!
I am actually thankful to the owner of this website who has shared this impressive article
at here.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/id/register-person?ref=V3MG69RO
[url=https://shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-scorpion-exo-930-evo-solid-black-mat/]shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-scorpion-exo-930-evo-solid-black-mat/[/url]
Мотошлемы популярных марок в течение наличии в течение размашистом наборе также начиная с. ant. до доставкой числом Украине.
shlemsnidf.dp.ua/p-shlem-mt-blade-2-sv-finishline-d4-black-orange-grey/
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/ro/join?ref=V3MG69RO
This post offers clear idea designed for the new viewers of blogging, that genuinely how to do
blogging.
It’s an remarkable post in support of all the
online viewers; they will obtain benefit from it I am sure.
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and
wanted to say that I’ve really enjoyed browsing your weblog posts.
In any case I’ll be subscribing on your rss feed and I hope you write
once more very soon!
At https://sieuthisuckhoe.net/theo-doi-ket-qua-benh-nhan-u-buou-moc-xung-quanh-nguoi-ket-qua-chan-doan-cua-benh-vien-u-buou-moc-quanh-nguoi/ number Up Casino, you can find dating between over eight thousand games in several categories.
учебник философия https://mir-ved.ru неофрейдизм философия
I have recently started a site, the information you provide on this website has helped me greatly. Thanks for all of your time & work. “It is a great thing to know our vices.” by Cicero.
Thanks for sharing, this is a fantastic blog post.Really thank you! Much obliged.
My website: жесткий анальный кастинг
философия сартра https://mir-ved.ru философия виды
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/join?ref=IJFGOAID
Your positivity and optimism are contagious It’s evident that you genuinely care about your readers and their well-being
Cheap car insurance policy was actually a misconception to me up
until I really located a good deal. Constantly contrast quotes coming from different Van insurance
firms.
модус философия https://mir-ved.ru философия земли
radissonbet giriş için ideal adres
казино буй бездепозитный бонусhttps://groups.google.com/g/slotsforall/c/lvNfdVghzGI
eskil kulis
What’s up mates, nice paragraph and pleasant urging commented here, I am in fact enjoying by these.
What’s Taking place i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It positively useful and it has helped me out loads.
I am hoping to contribute & assist different customers like its aided
me. Great job.
Hey There. I found your blog the usage of msn. That is an extremely neatly written article.
I’ll make sure to bookmark it and return to learn extra of your
helpful info. Thank you for the post. I’ll certainly comeback.
[url=https://forum.prosochi.ru/topic45498.html]https://forum.prosochi.ru/topic45498.html[/url]
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/es/register?ref=WTOZ531Y
I’m always eager to read your next post.
As a Newbie, I am continuously exploring online for articles that can be of assistance to me.
My website: смотреть русское порно анал
southbet giriş için tıklayabilirsiniz
Regarding plumbing needs, Preferred Plumbers stand out for
numerous reasons. Given our vast experience and focus
on customer satisfaction, we’re confident in stating
that we’re the #1 choice when you need a plumber. Here’s why:
Comprehensive Service Range
Our team is proficient in a broad range of plumbing services,
from leak detection and repairing pipes to drain cleaning
and installing faucets. Whether you need assistance with your sewer
line or water heater repair, we have the expertise
to address all your plumbing needs.
Round-the-Clock Service
Plumbing emergencies don’t wait for convenient times, and neither do we.
Preferred Plumbers is on call 24/7 to make sure that urgent plumbing needs are addressed promptly, preventing further issues and restoring
your peace of mind.
Focus on Customer Satisfaction
At our company, the customer is our number one priority. We strive to
provide tailored solutions that address your specific needs, making sure
that you’re completely satisfied with our work.
Superior Quality
Craftsmanship is at the heart of what we do at Preferred Plumbers.
We use only the best materials and advanced methods to provide long-term fixes and installations.
Our goal is to offer services that are durable.
No Hidden Fees
Understanding the cost of plumbing services upfront is important,
which is why Preferred Plumbers provide transparent pricing.
You’ll know the cost before we start, with no unexpected
charges added on.
Certification and Insurance
For your protection, Preferred Plumbers
is licensed and insured. This means that all our services adheres to the
highest industry standards and your property is protected in the rare event of an accident.
Choosing Preferred Plumbers means choosing a company that is dedicated to
excellence. We’re not just another plumbing service; we’re dedicated to ensuring the integrity
of your plumbing system. Reach out to us today to see why we are the #1 choice
when you need a plumber.
What i don’t realize is in reality how you’re now not actually
a lot more smartly-appreciated thawn you may be right
now. You’re so intelligent. You know therefore considerably
in terms of this topic, made me in my view imagine
it from numerous various angles. Its like women and men aren’t involved except iit is
one thing to doo with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs nice.
All the time care for it up!
Take a look at my web site; 먹튀검증
erxbet giriş için tıklayabilirsiniz
Wow, superb blog layout! Ηow long haѵe you been blogging for?
yߋu mɑde blogging look easy. Ꭲһe overall lоok оf yοur site is gгeat, as well ɑs
the contеnt!
Μy blog post: lotto24
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/bg/join?ref=OMM3XK51
You could definitely see your expertise in the work you write.
The arena hopes for more passionate writers such as you who are
not afraid to mention how they believe. All the time go after your
heart.
Excellent weblog here! Also your site a lot up very fast!
What web host are you using? Can I get your associate hyperlink on your host?
I wish my web site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
With havin so much content and articles do you ever run into
any problems of plagorism or copyright violation?
My blog has a lot of exclusive content I’ve either written myself or outsourced but it
appears a lot of it is popping it up all over the internet without my agreement.
Do you know any solutions to help stop content from being stolen? I’d really appreciate it.
На [url=https://outlet-nike.ru/]Outlet-Nike.ru[/url] мы предлагаем кроссовки Nike, которые воплощают в себе инновации и технологические достижения. Будь то улучшенная амортизация, воздухопроницаемые материалы или усовершенствованные подошвы для максимального сцепления, наш ассортимент обуви создан для того, чтобы вы могли превзойти самих себя. Выбирайте кроссовки, которые поддержат ваши спортивные амбиции и обеспечат комфорт на каждом шагу.
Bandırma’da her konuda güncel haberleri ve bilgileri bulabilirsiniz! 📰🌆 #Bandırma #YerelHaberler
Bandırma’da her konuda güncel haberleri ve bilgileri bulabilirsiniz!
UP-X, веб-платформа игр, предлагающая идеальный игровой опыт для всех возрастов. Бесплатно зарегистрируйтесь, выберите свою любимую игру и начните играть прямо сейчас!
Hi there everyone, it’s my first go to see at this web page, and post is truly fruitful in favor of me, keep
up posting such articles or reviews.
Awesome! Its genuinely remarkable post, I have got much clear idea regarding from this post
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your site and
in accession capital to assert that I acquire in fact
enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing
to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently
rapidly.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/join?ref=P9L9FQKY
They are naturally joyful and at all times look on the bright
side. Widespread (however not unique) attributes of
profly/blocking goaltenders are those have broad butterflies, use stiffer leg pads (often with no knee breaks), and tendencies to cover the
decrease portion of the web. The first thing
you’ll learn as an Enchanter is to use the disenchant
means. It is usually assumed that the power of artworks
to elicit emotional responses in viewers is a totally regular and unproblematic phenomenon. In southeast Alaska, the place cruising is a large a part of the financial system, the
absence of cruise tourists during the pandemic shutdown resulted in a $250 million hit to
Ketchikan alone, a tiny port metropolis with a
inhabitants of simply 8,500. In Galveston, Texas
– one of North America’s busiest house ports and the one cruise port in the state – COVID-associated losses have been estimated at 23,
000 jobs and $1.2 billion in direct spending. And
over in Venice, the Italian city famed for its canals banned massive cruise
and container ships from the Venice Lagoon in early 2021,
partly because the ships pollute the surroundings and erode the city’s
historic foundations. Within the yr that cruise ships have been grounded due to the COVID-19 pandemic, locals say the offshore waters have been cleaner, in accordance with The Washington Post.
Wow thats nice content thanks.
Nice content thank you
Thanks designed for sharing such a nice thought,
article is nice, thats why i have read it fully
When I originally commented I seem to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments
are added- checkbox and from now on each time a comment is
added I recieve 4 emails with the same comment. Perhaps there
is an easy method you can remove me from that service? Thanks a lot!
Mersin Escort Nil, Mersin’in doğal plajlarını ve ormanlık alanları ziyaret etmeyi çok sever. Aynı zamanda yoga yapılabilecek açık alanları keşfetmeyi ve doğa ile iç içe olmayı önemser. Partnerinden Beklentileri: Nil, partnerinden denge, uyum
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found
that it is truly informative. I am going to watch out for brussels.
I’ll be grateful if you continue this in future. Numerous people will
be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
betcool için güncel adres burada!
bu hizmet üyelik gerektirmez ve siz telefonunuzu kapattığınız andan itibaren ücretlendirmede sonlandırılır.Kesinlikle faturanıza veya cebinize ek bir yük getirmez.Sohbet ettiğiniz insan herhangi bir band kaydıda değildir.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
I truly appreciate your technique of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark site list and will
Las Vegas Tankless Water Heaters is the premier choice for all your water heating needs in Las Vegas.
With a commitment to providing eco-friendly and dependable on-demand hot
water systems, we ensure complete satisfaction for homeowners.
Why Choose Us?
Expertise in Tankless Water Heaters
Our experts specializes in compact water heaters,
offering endless hot water without the space requirements of traditional units.
Our focus sets us apart in the Las Vegas plumbing market.
Energy Efficiency
We focus on reducing energy consumption, aiding you reduce your carbon footprint while enjoying
reliable hot water. Our products are designed to improve efficiency and environmental friendliness.
Customized Solutions
Understanding that each household has different needs, which is why
we deliver customized water heating solutions.
Whether you need a point-of-use heater for a single bathroom or a whole-house system,
we can handle it.
Professional Installation and Maintenance
Not only do we install your system, we guarantee
optimal performance with regular maintenance services.
Our technicians have expertise in modern installation methods for a
variety of systems.
Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is our foremost concern. We aim to go
above and beyond with every project, providing attentive customer
service and expert advice.
To Sum Up, we is the leading choice in Las Vegas for those
seeking energy-saving water heating solutions.
Through our dedication to cost-effectiveness, personalized systems, and
superior client care, we promise optimal hot water experience without the
hassle.
Select us for your next water heater installation and become part of the growing number of satisfied customers reaping
the benefits of our quality services in Las Vegas.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.com/ro/register?ref=UM6SMJM3
lexapro tabs 10 mg
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Hi there just wanted to give you a quick heads up.
The text in your post seem to be running off the screen in Chrome.
I’m not sure if this is a format issue or something
to do with internet browser compatibility but I figured I’d post to let you
know. The design look great though! Hope you get the
issue solved soon. Kudos
Hey there this is kind of of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors
or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but
have no coding skills so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience.
Any help would be enormously appreciated!
Simply desire to say your article is as astonishing.
The clarity in your put up is just nice and that i could think you’re knowledgeable in this subject.
Fine together with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep updated with imminent
post. Thank you 1,000,000 and please keep up the gratifying work.
Hi! This is my first visit to your blog! We are
a collection of volunteers and starting a new project
in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us valuable information to work on. You have done a outstanding job!
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it.
Look advanced to more added agreeable from you!
By the way, how could we communicate?
Wow, this article is nice, my younger sister is analyzing these kinds of
things, therefore I am going to tell her.
Good day! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after checking through
some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely happy
I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back often!
I really like it when people get together and share ideas.
Great blog, continue the good work!
Very great post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and
wanted to say that I’ve really enjoyed surfing around your weblog posts.
In any case I will be subscribing in your feed and I hope you write once more very soon!
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was great.
I don’t know who you are but definitely you’re going to a famous blogger
if you aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here.
The sketch is attractive, your authored subject matter stylish.
nonetheless, you command get bought an shakiness
over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the
same nearly very often inside case you shield this increase.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/el/register?ref=B4EPR6J0
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement
account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you!
By the way, how can we communicate?
I am really thankful to the owner of this website who has
shared this fantastic paragraph at here.
We’re a gaggle of volunteers and opening a brand new scheme in our community.
Your web site provided us with helpful information to work on. You
have done an impressive task and our entire neighborhood will be grateful to
you.
Hi everyone, it’s my first go to see at this site, and post is in fact fruitful
in favor of me, keep up posting these articles.
Hello! I just would like to give you a huge thumbs up for the excellent info you have right here on this
post. I will be coming back to your website for more
soon.
I every time used to read piece of writing in news papers but now as I am
a user of net thus from now I am using net for articles or reviews, thanks to web.
Great information shared.. really enjoyed reading this post thank you author for sharing this post .. appreciated
My developer is trying to convince me to move to .net from PHP.
I have always disliked the idea because of the costs.
But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on a number of websites for about a year and am worried about switching to
another platform. I have heard very good things
about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can transfer
all my wordpress content into it? Any help would be really appreciated!
Hello, just wanted to tell you, I loved this article. It was helpful.
Keep on posting!
It’s enormous that you are getting ideas from this post as well as from our argument
made at this time.
We stumbled over here coming from a different web page and
thought I should check things out. I like what I see so now i’m following
you. Look forward to exploring your web page yet again.
Howdy! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after reading through some of the post I realized it’s
new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely glad I found it and I’ll be
book-marking and checking back frequently!
You made some decent points there. I looked on the internet for more
info about the issue and found most people will go along with
your views on this website.
Wonderful article! That is the kind of information that are meant to be shared across the internet.
Disgrace on Google for no longer positioning this publish upper!
Come on over and talk over with my website . Thank you =)
I am curious to find out what blog platform you are working
with? I’m having some minor security issues with my
latest site and I’d like to find something more safeguarded.
Do you have any recommendations?
I have read so many articles regarding the blogger lovers but this piece of writing is
in fact a nice post, keep it up.
I’m more than happy to find this page. I want to to thank you for your time for this
wonderful read!! I definitely savored every bit
of it and i also have you bookmarked to check out new stuff in your blog.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
I gotta favorite this site it seems very beneficial handy
My website: порно заставила лизать жопу
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Magnificent web site. A lot of useful information here. I’m sending it to some friends ans also sharing in delicious.And obviously, thanks on your effort!
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.com/es/register?ref=T7KCZASX
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
%%
Feel free to visit mʏ hοmepage :: วัดเทพศิรินทร์ เส้นทาง
Ich stimme zu!
Very good post.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
My website: порно куни анилингус
A useful article, thank you.
Very nice post. I simply stumbled upon your blog and wanted to mention that I’ve truly loved browsing your blog posts.
After all I will be subscribing in your feed and I am hoping you
write again very soon!
Transform Your Workspace with Freedman’s Office Chairs in Tampa
**Indulge in Comfort and Style: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Tampa**
Embark on a journey of ergonomic excellence with
Freedman’s Office Furniture, conveniently located at 5035 W Hillsborough Ave, Tampa,
FL 33634. Specializing in office chairs, cubicles, and desks, Freedman’s is redefining workplace aesthetics in neighborhoods like Arbor Greene and Ballast Point,
offering a wide range of seating solutions designed for modern comfort and productivity.
**Setting the Standard in Tampa: Freedman’s Office Chairs**
Founded in 1845, Tampa has grown into a thriving city with a 2021 population of 387,050 and 157,066 households.
As a testament to its commitment to excellence, Freedman’s Office Furniture seamlessly integrates into Tampa’s vibrant landscape,
providing top-notch office chairs that combine ergonomic
innovation with contemporary design.
**Navigating the Hub of Tampa: Interstate 275**
Much like the connectivity facilitated by Interstate 275, Freedman’s ergonomic
office chairs effortlessly integrate into Tampa’s bustling professional
landscape. Reflecting Tampa’s reputation as a diverse and dynamic city, our chairs offer residents
an unmatched seating experience, perfectly aligning with the city’s ethos of progress and innovation.
**A Glance at Tampa’s Diverse Neighborhoods and Climate**
Tampa’s diverse neighborhoods, from Downtown to East Tampa, find a perfect complement in Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs.
With repairs typically costing a fraction of the price of new furniture,
our chairs are not just an investment in comfort
but also in long-term savings. Additionally, Tampa’s tropical climate
makes comfort a priority, and our chairs cater to the need for breathability and support, ensuring a pleasant working environment year-round.
**Explore Tampa’s Rich Tapestry of Attractions**
Discover the allure of Tampa by exploring some of its captivating points of interest:
– **Busch Gardens Tampa Bay:** A world-renowned theme park
featuring thrilling rides and exotic animal exhibits.
– **Curtis Hixon Waterfront Park:** A picturesque park
along the Hillsborough River, offering scenic views and recreational activities.
– **Congo River Rapids:** A water ride at Busch Gardens Tampa Bay, providing an exhilarating adventure through turbulent waters.
– **The Henry B. Plant Museum:** Housed in the former Tampa Bay Hotel, this museum showcases Tampa’s Gilded Age history.
– **Empower Adventures Tampa Bay:** An outdoor adventure park offering ziplining
and other exciting activities.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Office Chairs in Tampa**
Selecting Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Tampa is a decision that transcends mere furniture.
It’s a commitment to elevating your workspace with stylish and comfortable
seating that resonates with Tampa’s spirit of diversity, growth,
and success.
”
“Revolutionize Your Workspace with Freedman’s Office Furniture in Atlanta
**Experience Unmatched Comfort with Freedman’s Office Chairs
in Atlanta**
Freedman’s Office Furniture, located at 3379 Peachtree Rd NE,
Atlanta, GA 30326, invites you to redefine your work environment.
Specializing in office chairs, cubicles, and desks, Freedman’s
is the epitome of ergonomic excellence, serving neighborhoods like Ansley Park and Adair Park.
**Atlanta’s Pioneering Legacy Meets Freedman’s Innovation**
Founded in 1836, Atlanta boasts a population of 496,461 and 227,388 households as
of 2021. Reflecting Atlanta’s pioneering spirit, Freedman’s Office Furniture aligns
seamlessly with the city’s ethos. Our ergonomic office chairs set the standard for comfort
and style, combining innovation with contemporary design.
**Navigating Atlanta’s Business Hub: Interstate 20**
Much like the flow of traffic on Interstate 20, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs effortlessly integrate into Atlanta’s bustling professional landscape.
Our chairs represent more than just a place to sit;
they symbolize Atlanta’s commitment to progress,
creativity, and a dynamic work culture.
**Exploring Atlanta’s Unique Neighborhoods and Climate**
From the historic charm of Ansley Park to the vibrant
energy of Buckhead, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs cater to Atlanta’s diverse neighborhoods.
Repairs are cost-effective, ensuring that your office furniture investment remains sustainable.
Considering Atlanta’s mild climate, our chairs provide the perfect blend of support and breathability,
ensuring a comfortable year-round workspace.
**Discover Atlanta’s Cultural Gems**
Explore Atlanta’s rich cultural tapestry by visiting these noteworthy points of
interest:
– **Atlanta Botanical Garden:** A stunning oasis in the heart of
Midtown, featuring beautiful gardens and immersive plant collections.
– **Centennial Olympic Park:** Built for the 1996 Summer Olympics,
this park offers a blend of history and recreation.
– **Coca-Cola Museum:** Delve into the history of
the iconic beverage at this immersive museum in downtown Atlanta.
– **Boulevard Heights:** A historic neighborhood with a mix
of architectural styles and a strong sense of community.
– **College Football Hall of Fame:** Celebrating the history and legends of college football, located in the
heart of Atlanta.
**Why Freedman’s Office Furniture is Atlanta’s Top Choice**
Choosing Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Atlanta is a testament to
your commitment to a workspace that mirrors Atlanta’s innovation, diversity, and cultural richness.
Elevate your office aesthetics with Freedman’s, where comfort meets style effortlessly.
”
“Upgrade Your Office Experience with Freedman’s Office Furniture in Tampa
**Discover Unparalleled Comfort with Freedman’s Office Chairs
in Tampa**
Freedman’s Office Furniture, located at 5035 W Hillsborough Ave, Tampa, FL 33634, invites you to transform your workspace.
Specializing in office chairs, cubicles, and desks,
Freedman’s is the epitome of ergonomic excellence, serving
neighborhoods like Arbor Greene and Bayshore Beautiful.
**Tampa’s Vibrancy Meets Freedman’s Innovation**
Founded in 1845, Tampa boasts a population of 387,050 and
157,066 households as of 2021. Mirroring Tampa’s vibrant atmosphere, Freedman’s Office Furniture brings a touch of innovation to your workplace.
Our ergonomic office chairs redefine comfort, combining functionality with modern aesthetics.
**Navigating Tampa’s Business Landscape: Interstate 275**
Much like the smooth flow of Interstate 275, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs seamlessly integrate into Tampa’s thriving professional community.
Our chairs are more than mere seating; they embody Tampa’s commitment to dynamic work environments, fostering
creativity and productivity.
**Exploring Tampa’s Distinctive Neighborhoods and Climate**
From the family-friendly charm of Arbor Greene
to the coastal vibes of Bayshore Beautiful, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs cater
to Tampa’s diverse neighborhoods. With affordable repair options,
our chairs ensure a sustainable and stylish office setup.
Considering Tampa’s warm climate, our chairs offer the perfect blend of
support and breathability, making your workspace comfortable year-round.
**Unveiling Tampa’s Unique Points of Interest**
Explore Tampa’s unique attractions, enhancing your downtime or inspiring new ideas:
– **Busch Gardens Tampa Bay:** Experience thrilling rides and
encounters with exotic animals in this renowned theme park.
– **Curtis Hixon Waterfront Park:** A scenic urban park along the Hillsborough River,
providing a tranquil escape in downtown Tampa.
– **Ybor City:** Known for its historic charm, Ybor City offers a blend of unique shops, restaurants, and cultural experiences.
– **Adventure Island:** A waterpark featuring slides, pools, and a lazy river, perfect
for family-friendly fun.
– **Croc Encounters:** Get up close with reptiles and wildlife in this educational and interactive
setting.
**Why Freedman’s Office Furniture is Tampa’s Premier Choice**
Choosing Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Tampa signifies your dedication to a workspace reflecting Tampa’s energy, diversity,
and recreational opportunities. Elevate your office aesthetics with Freedman’s, where comfort meets
innovation seamlessly.
”
“Elevate Your Workspace with Freedman’s Office Furniture in Tampa
**Revolutionize Your Office Aesthetic with Freedman’s Office Desks**
Freedman’s Office Furniture, situated at 5035 W Hillsborough Ave,
Tampa, FL 33634, is your destination for premium office desks,
chairs, and cubicles. Serving neighborhoods like Beach Park and Downtown, Freedman’s is committed to enhancing your workspace experience.
**Tampa’s Rich History and Freedman’s Office Furniture**
Since its founding in 1845, Tampa has evolved into a thriving
city with a population of 387,050 and 157,066 households as of
2021. Freedman’s Office Furniture pays homage to
Tampa’s rich history by offering office desks
that blend tradition with contemporary design, reflecting the city’s dynamic character.
**Navigating Tampa’s Business Hub: Interstate 275**
Much like the intersecting lanes of Interstate 275, Freedman’s office desks intersect functionality and style.
Your workspace becomes a testament to Tampa’s business hub,
where our desks stand as symbols of innovation and efficiency, aligning seamlessly with the city’s forward-looking spirit.
**Cost-Effective Repairs and Tampa’s Varied Climate**
Freedman’s understands that office repairs are a crucial aspect
of maintaining a professional space. Our office desks come
with affordable repair options, ensuring durability and longevity.
Considering Tampa’s varied climate, our desks are crafted to withstand the warmth,
providing a sturdy and reliable foundation for
your work.
**Exploring Tampa’s Neighborhood Vibes and Workspaces**
Whether you’re in the vibrant Downtown area or the serene Beach Park, Freedman’s office desks cater to the unique vibes of Tampa’s
neighborhoods. With diverse styles and configurations, our desks complement the essence of each locality,
enhancing the aesthetic appeal of your workspace.
**Discover Tampa’s Cultural Gems and Work-Friendly
Spaces**
Explore Tampa’s cultural gems during your downtime or use local work-friendly
spaces for a change of scenery:
– **The Tampa Riverwalk:** A scenic waterfront trail offering picturesque views and access to
various attractions.
– **The University of Tampa:** Find inspiration in the historic architecture and serene environment of the
university campus.
– **Armature Works:** A revitalized industrial space
turned into a vibrant community hub with eateries, shops, and co-working spaces.
– **The Tampa Theatre:** Immerse yourself in the unique ambiance of this historic movie palace, a cultural landmark in Tampa.
**Why Freedman’s Office Furniture Sets the Standard in Tampa**
Choosing Freedman’s office desks in Tampa signifies your commitment to a
workspace that reflects the city’s history, diversity,
and cultural richness. Upgrade your office aesthetic with Freedman’s,
where each desk is a blend of craftsmanship, functionality,
and Tampa’s unique spirit.
”
“Discover Exceptional Office Chairs at Freedman’s Tampa
Store
**Elevate Your Work Experience with Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs**
Freedman’s Office Furniture, located at 5035 W Hillsborough Ave, Tampa, FL 33634,
invites you to experience unparalleled comfort and
style with our extensive range of ergonomic office chairs.
Serving neighborhoods like Arbor Greene and Downtown,
Freedman’s is dedicated to providing the perfect seating solutions
for your workspace.
**The Essence of Tampa’s Growth and Freedman’s Ergonomic Chairs**
Founded in 1845, Tampa has grown into a bustling city with a population of
387,050 as of 2021. Freedman’s acknowledges this growth by offering ergonomic office chairs that echo Tampa’s dynamic spirit.
Our chairs blend innovation with comfort, creating an ideal environment for productivity.
**Navigating Tampa’s Business District with Interstate 275**
Much like the flow of traffic on Interstate 275, Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs
offer seamless movement and adaptability. As your professional partner, our chairs mirror the efficiency and modernity of Tampa’s thriving business district,
providing ergonomic support for your daily tasks.
**Affordable Repairs and Tampa’s Climate-Adaptable Ergonomic Chairs**
Understanding the importance of comfortable seating,
Freedman’s offers affordable repair solutions for our ergonomic office chairs.
Crafted to adapt to Tampa’s varied climate, our chairs provide
the perfect balance of support and flexibility, ensuring a comfortable workspace year-round.
**Tailored Seating for Tampa’s Varied Neighborhoods**
Whether you’re in the leafy enclaves of Arbor Greene or the
vibrant streets of Downtown, Freedman’s ergonomic chairs complement the diverse vibes of Tampa’s neighborhoods.
With adjustable features and contemporary designs, our chairs enhance the visual appeal of your workspace.
**Exploring Tampa’s Cultural Havens and Cozy Work Nooks**
Take advantage of Tampa’s cultural offerings during breaks or
find inspiration in local work-friendly spaces:
– **Tampa Museum of Art:** Immerse yourself in creativity and artistic expression within the museum’s serene surroundings.
– **Davis Islands Dog Park:** A unique outdoor spot for relaxation and brainstorming sessions.
– **Ybor City Historic District:** Experience
Tampa’s rich history in this vibrant district, filled with eclectic shops
and cafes.
– **Curtis Hixon Waterfront Park:** Enjoy a peaceful break by the Hillsborough
River, with stunning views and open spaces.
**Why Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Chairs Lead the Way
in Tampa**
Opting for Freedman’s ergonomic office chairs in Tampa means choosing unrivaled comfort, innovative design, and a seating solution that
mirrors the city’s growth and diversity. Upgrade
your workspace with Freedman’s, where each chair represents the
perfect blend of support, style, and Tampa’s unique energy.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . sollet sollet
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. hdxvipizle hdxvipizle
matadorbet giriş
I used to be recommended this blog by way of my cousin. I’m not certain whether
this publish is written by means of him as no one else know such
distinct about my problem. You’re wonderful! Thanks!
Hi there, I want to subscribe for this webpage to get latest updates, therefore where can i do it please assist.
My brother suggested I might like this blog.
He was totally right. This post truly made my day. You can not imagine simply
how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
When someone writes an paragraph he/she maintains
the idea of a user in his/her mind that how a user can understand it.
Thus that’s why this article is perfect. Thanks!
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
For hottest information you have to pay a quick visit world wide web and on web I found this web page as a
best web site for most up-to-date updates.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . sollet sollet
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
[url=https://1-win.br.com]niggers[/url]
anal porno niggers gays here
anal porno
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.com/sk/register?ref=JHQQKNKN
[url=https://1-win.br.com]anal porno[/url]
anal porno niggers gays here
niggers
These are really fantastic ideas in on the topic of blogging.
You have touched some nice factors here. Any way keep up wrinting.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
[url=https://1-win.br.com]anal porno[/url]
anal porno niggers gays here
anal porno
https://pust-govorjat.ru/
[url=https://1-win.br.com]anal porno[/url]
anal porno niggers gays here
anal gays
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . hdxvipizle hdxvipizle
[url=https://www.foggspecialistbags.com]anal porno[/url]
anal porno
anal
[url=https://www.foggspecialistbags.com]anal porno[/url]
anal porno
anal niggers
[url=https://www.foggspecialistbags.com]anal[/url]
anal porno
anal gays
Thank you bro nice topic
http://links.musicnotch.com/deanpoulson
Thats nice content its wonderful
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ . venusbet venusbet
A lot of blog writers nowadays yet just a few have blog posts worth spending time on reviewing.
My website: порно дрочит руками
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though
you relied on the video to make your point. You
clearly know what youre talking about, why throw away your
intelligence on just posting videos to your site when you could be giving us something enlightening
to read?
Awesome very very good content thats good mate
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. venusbet venusbet
adasdas
I’m often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
[url=https://akrus.ru]anal porno[/url]
best niggers porno
niggers
[url=https://akrus.ru]gay porno[/url]
best niggers porno
gay porno
[url=https://akrus.ru]gay porno[/url]
best niggers porno
niggers
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ . sollet extension sollet
good people doing good work. thanks
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.info/cs/join?ref=JHQQKNKN
betpublic giriş için en iyi adres burasıdır.
7/24 Canlı Dert Köşesi Tüm operatör ve sabit hatlar için standarttır.
[url=http://xbet-france.com]http://xbet-france.com[/url]
Working 1xbet replication for entering the authentic website of the bookmaker. Resort to it to listing with 1xBet.
http://xbet-france.com
[url=http://xbet-france.com]http://xbet-france.com[/url]
Working 1xbet looking-glass as a remedy for entering the stiff website of the bookmaker. Take advantage of it to listing with 1xBet.
xbet-france.com
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. venusbet venusbet
[url=https://xbet-france.com]https://xbet-france.com[/url]
Working 1xbet representation for entering the formal website of the bookmaker. Say it to register with 1xBet.
xbet-france.com
[url=http://xbet-france.com]http://xbet-france.com[/url]
Working 1xbet representation as a remedy for entering the authentic website of the bookmaker. Take advantage of it to report with 1xBet.
http://www.xbet-france.com
There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made
I’m extremely pleased to discover this website. I wanted to thank you for ones time just for this fantastic read!
My website: порно студентки бесплатно
That is a great tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere.
Simple but very precise information… Thanks for sharing this one.
A must read article!
I just like the helpful information you provide in your articles
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites
I truly appreciate your technique of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark site list and will
Member Raja Slot and Raja Togel sangat dikejutkan dengan kehadiran situs premium Raja97 yang terbukti mengutamakan pelayanan customer service sejak berdiri tahun 2005
My developer is trying to persuade me to move to .net from PHP.
I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses.
But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using WordPress on several websites for about
a year and am concerned about switching to another platform.
I have heard great things about blogengine.net. Is there
a way I can transfer all my wordpress posts into it?
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
I do not even understand how I ended up here, but I assumed this publish used to be great
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.
[url=https://stavkomtl.ru]гей порно[/url]
анальное порно с неграми
порно с неграми
[url=https://stavkomtl.ru]анал[/url]
анальное порно с неграми
порно с неграми
[url=https://stavkomtl.ru]анальное порно[/url]
анальное порно с неграми
порно с неграми
[url=https://stavkomtl.ru]порно с неграми[/url]
анальное порно с неграми
гей порно
A very informative article, thank you. I’m adding it to my favorites.
Wonderful website you have here but I was wondering if you knew of any message boards that cover the same topics
discussed in this article? I’d really like to be a part of
group where I can get comments from other knowledgeable people
that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please
let me know. Many thanks!
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wished to say that
I have truly enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. After all
I will be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again very soon!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Nicely put. Many thanks.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Attractive component to content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to claim that I acquire actually loved account your
blog posts. Anyway I’ll be subscribing on your augment and even I achievement you get admission to persistently fast.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . asyabahis asyabahis
asyabahisgo1.com
What’s up everyone, it’s my first pay a quick visit at this site, and piece of writing
is in fact fruitful for me, keep up posting
these articles.
izmir haberleri
great content really like it
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Many thanks for providing these details.
I just like the helpful information you provide in your articles
Awesome! Its genuinely remarkable post, I have got much clear idea regarding from this post
Hello there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help
with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not
seeing very good results. If you know of any please share.
Thank you!
Muchos Gracias for your article.Really thank you! Cool.
My website: young anal
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . asyabahis asyabahis
great content thats awesome
Awesome blog! Do you have any tips and hints for aspiring writers?
I’m planning to start my own website soon but I’m
a little lost on everything. Would you propose starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices
out there that I’m completely overwhelmed .. Any tips?
Thanks!
Виза в UK можно найти здесь
[url=https://visa-v-uk.ru/]https://visa-v-uk.ru/[/url]
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/pt-PT/join?ref=GJY4VW8W
1xbet-farsi3.com
naturally like your web site however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth on the other hand I will surely come again again.
[url=https://krasproc.ru]gay porno[/url]
anal porno with niggers here
gay porno
Link exchange is nothing else however it is simply placing the other person’s webpage
link on your page at appropriate place and other person will also do same in favor of you.
[url=https://krasproc.ru]anal porno[/url]
anal porno with niggers here
niggers porno
I have been browsing online more than 3 hours today, yet
I never found any interesting article like yours. It is pretty worth enough for me.
In my view, if all website owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the web will be
much more useful than ever before.
[url=https://krasproc.ru]anal porno[/url]
anal porno with niggers here
anal porno
Thank you a bunch for sharing this with all of us you really
realize what you’re speaking approximately! Bookmarked. Kindly
also talk over with my website =). We can have a link change agreement between us
I truly love your site.. Very nice colors & theme. Did you develop
this amazing site yourself? Please reply back as I’m trying to create my own personal website and would love to learn where you got
this from or what the theme is called. Kudos!
I’ll right away grab your rss feed as I can’t in finding your
e-mail subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any?
Kindly allow me understand in order that I could subscribe.
Thanks.
1xbet
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ . asyabahis asyabahis
burada tüm sonic oyunlarını bulabilirsiniz
İstanbul Bölgesinde bulunan en iyi masaj salonları ve masaj hizmetini arıyorsan doğru adrestesin diyebiliriz çünkü sizler için en iyi terapistleri ile masaj merkezlerini araştırır ve sadece en iyilerini sitesinde yayınlar.
I am truly thankful to the owner of this web site who has shared this fantastic piece of writing at at this place.
В нашем быстром мире каждый ищет возможности получить финансовую помощь мгновенно. Если вы хотите изучить все доступные варианты, то наш сайт предлагает уникальный список, где собраны все мфо. Найдите идеальное предложение, которое подойдет именно вам, благодаря нашему обширному каталогу новейших и проверенных организаций.
Сервис мгновенных игр Money-X: официальный сайт с быстрым доступом
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
I every time spent my half an hour to read this blog’s posts every day along with a cup of coffee.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
%%
Have a look ɑt my blog พัดลมพวงหรีด
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
I’ll read it again later, it’s a pretty long article.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wished to say that I have truly enjoyed browsing your blog posts.
After all I’ll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write
again soon!
Howdy! Someone in my Facebook group shared this site
with us so I came to look it over. I’m definitely loving the information. I’m book-marking and will be tweeting this to my followers!
Fantastic blog and great design.
We are a group of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our community.
Your site offered us with valuable information to work on. You have done a formidable job and our entire community
will be thankful to you.
Изучите все аспекты охраны труда с интенсивной программой обучения от Академии “МАПС”. Наши курсы дадут вам знания и практические навыки для обеспечения безопасности на рабочем месте. Станьте незаменимым специалистом в области охраны труда уже сегодня!
Maps-Edu – [url=https://maps-edu.ru/obuchenie-vrachey]сайт повышения квалификации медицинских работников[/url]
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Thats great content love that
[url=https://akrus.ru]gay porno[/url]
last info about pokimane
gay porno
I don’t know whether it’s just me or if perhaps
everybody else experiencing issues with your site.
It appears like some of the written text within your posts are running off the screen. Can someone else please provide feedback and let me know if
this is happening to them as well? This could be a problem with my internet browser because I’ve had this happen before.
Thank you
[url=https://akrus.ru]niggers[/url]
last info about pokimane
anal porno
Thank you great post. Hello Administ . asyabahis asyabahis
[url=https://akrus.ru]anal porno[/url]
last info about pokimane
anal porno
Its cool content thank you so much
[url=https://akrus.ru]niggers[/url]
last info about pokimane
gay porno
Salon XL’in ürünleri saçlarımı derinlemesine besliyor ve her zaman pürüzsüz ve parlak görünmelerini sağlıyor. Bu ürünleri kullanmak benim için vazgeçilmez oldu!
Hi there to every , since I am actually eager of reading this website’s post to be updated daily.
It contains good material.
Hello just wanted to give you a quick heads up
and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading correctly.
I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue.
I’ve tried it in two different browsers and
both show the same outcome.
sekabet giriş
Van Erciş Bölgesi Güncel Haberleri
1xBet: Your Ultimate Betting Destination
Download 1xbet application [url=https://1xbet-app-download-ar.com/#1xbet-app-download]1xbet app download[/url] .
İzmir evden eve nakliyat
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Simply wish to say your article is as amazing The clearness in your post is just nice and i could assume youre an expert on this subject Well with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post Thanks a million and please carry on the gratifying work
Hey I am so excited I found your weblog, I really found you by
mistake, while I was looking on Digg for something else, Anyways I am
here now and would just like to say thanks a lot for a incredible post
and a all round exciting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t
have time to read it all at the moment but I have bookmarked it and also added
your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a lot more, Please do keep up the fantastic b.
What’s up to all, since I am really keen of reading this website’s post to
be updated regularly. It consists of fastidious material.
Hello there, just became alert to your blog through Google, and found that it’s truly informative.
I am going to watch out for brussels. I’ll
be grateful if you continue this in future. Many people will be
benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
mega сайт зайти на мегу
Сервис мгновенных игр Money-X на официальном сайте
Изучите все аспекты охраны труда с интенсивной программой обучения от Академии “МАПС”. Наши курсы дадут вам знания и практические навыки для обеспечения безопасности на рабочем месте. Станьте незаменимым специалистом в области охраны труда уже сегодня!
Maps-Edu – [url=https://maps-edu.ru/catalog/defektologiia?type=povyshenie-kvalifikacii]курсы повышения квалификации для дефектологов дистанционно[/url]
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
mersinin en iyi escort sitesine girmeye hazır mısınız?
Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara’nın Nabzını Tutan Haber Sitesi: Pandermos Haber Bölgesel haberlerde derinlik ve kalite arayanlar için Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara bölgesinin en güncel ve güvenilir haber kaynağı Pandermos, okuyucularına kesintisiz bilgi akışı sağlıyor. Yerel olaylardan, kültürel etkinliklere, ekonomiden spora bölgenin dört bir yanını kapsayan geniş bir haber yelpazesine sahip olan Pandermos, bölge halkının ve ilgi duyanların ilk tercihi olma özelliğini koruyor. Gelişmiş habercilik anlayışı ve objektif bakış açısıyla hazırlanan içerikler, Pandermos’u sadece bir haber sitesi olmanın ötesine taşıyor. Güney Marmara’nın sosyal, ekonomik ve kültürel dinamiklerini anlamak isteyen herkes için vazgeçilmez bir kaynak haline gelen bu platform, okuyucularına kaliteli ve doğrulanmış bilgiler sunmayı amaçlıyor. Bandırma, Balıkesir ve çevresinde yaşayanlar veya bu bölgeyle ilgili güncel bilgileri takip etmek isteyenler için Pandermos, aradıkları her şeyi bir arada bulabilecekleri bir portal. Ziyaretçilerine sadece haber değil, aynı zamanda bölgenin kültürel ve sosyal yaşantısına dair paha biçilmez bilgiler de sunuyor. Eğer siz de Güney Marmara’nın nabzını tutan, güncel ve objektif haberleri kaçırmak istemiyorsanız, Pandermos sizin için en doğru adres. Habercilikte kalite ve güven arayanların tercihi Pandermos, bölgesel haberler konusunda bir adım öne çıkıyor.
Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara’nın Nabzını Tutan Haber Sitesi: Pandermos Haber Bölgesel haberlerde derinlik ve kalite arayanlar için Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara bölgesinin en güncel ve güvenilir haber kaynağı Pandermos, okuyucularına kesintisiz bilgi akışı sağlıyor. Yerel olaylardan, kültürel etkinliklere, ekonomiden spora bölgenin dört bir yanını kapsayan geniş bir haber yelpazesine sahip olan Pandermos, bölge halkının ve ilgi duyanların ilk tercihi olma özelliğini koruyor. Gelişmiş habercilik anlayışı ve objektif bakış açısıyla hazırlanan içerikler, Pandermos’u sadece bir haber sitesi olmanın ötesine taşıyor. Güney Marmara’nın sosyal, ekonomik ve kültürel dinamiklerini anlamak isteyen herkes için vazgeçilmez bir kaynak haline gelen bu platform, okuyucularına kaliteli ve doğrulanmış bilgiler sunmayı amaçlıyor. Bandırma, Balıkesir ve çevresinde yaşayanlar veya bu bölgeyle ilgili güncel bilgileri takip etmek isteyenler için Pandermos, aradıkları her şeyi bir arada bulabilecekleri bir portal. Ziyaretçilerine sadece haber değil, aynı zamanda bölgenin kültürel ve sosyal yaşantısına dair paha biçilmez bilgiler de sunuyor. Eğer siz de Güney Marmara’nın nabzını tutan, güncel ve objektif haberleri kaçırmak istemiyorsanız, Pandermos sizin için en doğru adres. Habercilikte kalite ve güven arayanların tercihi Pandermos, bölgesel haberler konusunda bir adım öne çıkıyor.
Money-X: игровой сервис с мгновенным доступом на официальном сайте
I gotta favorite this site it seems very beneficial handy
My website: порно анал в чулках
Some car Auto insurance quote coverage policies give extras like roadside help.
Look at if these advantages deserve the extra expense.
Hi to all, for the reason that I am actually eager of reading this
webpage’s post to be updated regularly. It contains nice stuff.
What’s up it’s me, I am also visiting this site on a regular basis, this web page
is genuinely nice and the users are really sharing fastidious thoughts.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. venusbet deneme bonusu veren siteler
Van Erciş Bölgesi Güncel Haberleri
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
If you are going for finest contents like I do, only
visit this website everyday as it offers quality
contents, thanks
Разыскиваете надежный источник финансирования? Ознакомьтесь с [url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/mfo-2023/]малоизвестными займами[/url], где вы найдете прозрачные условия и легкий процесс одобрения.
We stumbled over here different website and thought I might check
things out. I like what I see so now i’m following
you. Look forward to going over your web page again.
Excellent article. Keep writing such kind of information on your
site. Im really impressed by your site.
Hi there, You’ve performed a great job. I will definitely digg it and individually recommend to my friends.
I am confident they will be benefited from this web site.
I am truly thankful to the owner of this web site who has shared this fantastic piece of writing at at this place.
I do trust all of the concepts you’ve presented for your post.
They are really convincing and can certainly work. Nonetheless,
the posts are very quick for newbies. May just you please lengthen them a bit from next time?
Thank you for the post.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Please forgive my English.Wow, fantastic blog layout! How lengthy have you been running a blog for? you made blogging glance easy. The entire look of your website is fantastic, let alone the content!
Great paintings! That is the kind of info that are meant to be shared across the internet. Disgrace on the seek for no longer positioning this put up higher! Come on over and consult with my site . Thanks =)
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
As a kebap enthusiast, I appreciate the detailed instructions and tips you provide in your recipes. It really helps amateurs like me to cook like a pro! – https://sifirbirkebap.com.tr/
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Hey, you used to write wonderful, but the last several posts have been kinda boring… I miss your tremendous writings. Past few posts are just a little bit out of track! come on!
Shopping at RENE Textile is a great option for quality products. | https://www.renetextile.com/
I think this site holds very great written subject material content .
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . venusbet deneme bonusu veren siteler
very good post, i undoubtedly adore this website, continue it
how to mix your tornado e liquid
thanks for this post amazing your blog
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . venusbet deneme bonusu veren siteler
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/sl/join?ref=FIHEGIZ8
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
RENE Textile’de her zevke uygun ürün bulmak mümkün, bu çok harika! | https://www.renetextile.com/
texas tornado cake using cake mixer
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/en/join?ref=S5H7X3LP
İstanbul Bölgesinde bulunan en iyi masaj salonları ve masaj hizmetini arıyorsan doğru adrestesin diyebiliriz çünkü sizler için en iyi terapistleri ile masaj merkezlerini araştırır ve sadece en iyilerini sitesinde yayınlar.
Blogunuzdaki yazılar gerçekten benim için çok değerli. Konuları derinlemesine ele almanızı ve bilgi birikiminizi paylaşmanızı takdir ediyorum. | https://dizin.org.tr/
continuously i used to read smaller articles which also clear their motive, and that is also happening with
this post which I am reading at this time.
Car Affordable insurance can easily
shield you coming from financial wreck in the event of an accident.
Do not forget its value.
Do you have a spam problem on this website; I also am a blogger, and I was curious about your
situation; we have created some nice procedures and we are
looking to swap solutions with others, please shoot me an e-mail
if interested.
Car auto insurance dalton coverage is actually not an area to cut corners.
Guarantee you possess the coverage you require for
assurance.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
I need to to thank you for this very good read!! I absolutely loved every bit
of it. I’ve got you book marked to look at new things you post…
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Have you ever considered publishing an e-book or guest authoring on other sites?
I have a blog based upon on the same topics you discuss and would
really like to have you share some stories/information.
I know my subscribers would value your work. If you’re even remotely interested, feel free
to shoot me an email.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Undeniably imagine that that you said. Your favorite
justification seemed to be at the internet the
easiest factor to understand of. I say to you, I certainly get annoyed while
other folks think about concerns that they plainly don’t understand
about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the top as smartly
as defined out the entire thing with no need side-effects
, folks could take a signal. Will likely be again to get more.
Thank you
I just like the helpful information you supply to your articles.
I’ll bookmark your blog and check again here regularly.
I’m fairly sure I will be informed a lot of new stuff right here!
Best of luck for the next!
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Hey there, You’ve performed an incredible job.
I will definitely digg it and in my opinion suggest to
my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited from this site.
This is a topic that’s near to my heart… Take care!
Where are your contact details though?
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Hello to all, how is the whole thing, I think every one is getting more from this web site, and your views are good designed for new users.
This is a topic which is near to my heart… Take care!
Exactly where are your contact details though?
Howdy would you mind stating which blog platform you’re using?
I’m planning to start my own blog in the near future but
I’m having a tough time selecting between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and
Drupal. The reason I ask is because your design seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something unique.
P.S My apologies for getting off-topic but I had to ask!
Hello, I just wanted to drop by and say how much I appreciate the content on Dizin.org.tr. It’s always insightful and well-written! | https://dizin.org.tr/
Kişi evleneceği kişiyi rüyasında görür mü?
Your approach to topics is consistently professional. Navigating through Dizin.org.tr is always a pleasure due to the wealth of information available.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
I visit Dizin.org.tr every day to learn something new. Grateful for the insights you share.
Outstanding feature
Penta Yıkama’nın temizlik hakkındaki uzman tavsiyeleri sayesinde evim her zamankinden daha temiz ve düzenli.
karavan wc kiralama
Bu blogdaki püf noktaları sayesinde evimi temizlemek için daha az zaman harcıyorum. Teşekkürler, Penta Yıkama!
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my website so i came to “return the favor”.I am attempting
to find things to enhance my website!I suppose its ok to
use some of your ideas!!
https://medyaeskil.com/toki-binalari-eskilde-hizla-ilerliyor/
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: deneme bonusu veren siteler
BALASEL’in ürünleriyle cildimdeki matlığı ve cansızlığı geride bıraktım. Teşekkürler BALASEL!
Winxbet
Good blog you’ve got here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours nowadays.
I honestly appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
BALASEL ürünlerini denemek için sabırsızlanıyorum. Hep olumlu şeyler duydum, umarım benim için de işe yarar.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
I’m not sure why but this web site is loading extremely slow for me.
Is anyone else having this problem or is it a problem on my
end?I’ll check bac later and see if the problem still exists.
Feel free to surf to my web blog :: Glenn
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Great!
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Undeniably believe that which you stated. Your favorite justification seemed
to be on the internet the simplest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while people
consider worries that they plainly do not know about.
You managed to hit the nail upon the top as well as defined
out the whole thing without having side effect , people could take a
signal. Will likely be back to get more. Thanks
BALASEL markasıyla tanışmamın ardından cildimdeki hassasiyet azaldı ve daha sağlıklı bir görünüm elde ettim.
BALASEL markasının ürünleri gerçekten etkili ve cildimdeki değişimi hızlı bir şekilde gördüm.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Hello, for all time i used to check blog posts here early in the dawn, for the
reason that i love to find out more and more.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Bu blogdaki BALASEL ürün incelemeleri gerçekten faydalı. Karar vermemde büyük yardımcı oldular.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
You ought to take part in a contest for one of the most useful sites on the internet.
I will recommend this site!
BALASEL markasıyla tanışmamın ardından cilt bakım rutinimdeki değişim inanılmaz oldu. Artık başka bir şey kullanamam!
[url=https://akrus.ru]niggers[/url]
последние новости Белоруссии
niggers
Vbet Güncel Giriş Adresi
[url=https://krasproc.ru]anal porno[/url]
последние новости Белоруссии
niggers porno
Excellent article! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site.
Keep up the good writing.
[url=https://akrus.ru]gay porno[/url]
последние новости Белоруссии
niggers
[url=https://krasproc.ru]niggers porno[/url]
последние новости Белоруссии
gay porno
[url=https://akrus.ru]gay porno[/url]
последние новости Белоруссии
anal porno
Bu blogdaki BALASEL ürün incelemeleri benim için kılavuz niteliğinde. Teşekkürler!
[url=https://akrus.ru]anal porno[/url]
последние новости Белоруссии
niggers
[url=https://krasproc.ru]anal porno[/url]
последние новости Белоруссии
gay porno
money x официальный сайт
[url=https://krasproc.ru]gay porno[/url]
последние новости Белоруссии
gay porno
BALASEL’in doğal içerikli ürünleri benim cildim için harika çalışıyor. Teşekkürler!
Have you ever considered publishing an e-book or guest authoring on other blogs?
I have a blog based upon on the same subjects you discuss and would really like to
have you share some stories/information. I know
my subscribers would appreciate your work. If you are
even remotely interested, feel free to send me an e mail.
tornado cake made with cake mixer
https://medyaeskil.com/eskil-merkez-ve-kosk-okullar-torenle-acildi/
BALASEL’in ürünleriyle cildimdeki değişimi görmek gerçekten inanılmaz. Bu kadar kısa sürede bu kadar büyük bir fark yaratmaları şaşırtıcı.
Highly descriptive blog, I loved that bit.
Will there be a part 2?
BALASEL’in ürünleriyle cildimdeki değişimi görmek gerçekten inanılmaz. Bu kadar kısa sürede bu kadar büyük bir fark yaratmaları şaşırtıcı.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: Betkanyon
BALASEL markasıyla tanışmamın ardından cildimdeki sivilce ve lekelerin azaldığını gördüm. Harika bir marka!
Deneme Bonusu Veren Siteler
BALASEL’in cilt bakım ürünleri doğal içeriklerle formüle edilmiş olmalarıyla benim için çok çekici hale geliyor.
izmir haberleri ve engüncel gelişmeler
BALASEL ürünleri gerçekten kaliteli ve etkili. Ben de düzenli olarak kullanıyorum ve sonuçlardan çok memnunum.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
BALASEL’in ürünleriyle cildimdeki değişimi görmek gerçekten inanılmaz. Bu kadar kısa sürede bu kadar büyük bir fark yaratmaları şaşırtıcı.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
BALASEL markasıyla tanışmamın ardından cilt bakım rutinimdeki değişim inanılmaz oldu. Artık başka bir şey kullanamam!
medya eskil
[url=https://affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com]https://affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com[/url]
Transfers can be ordered not not to or from the airport, but also exchange for moving around the city.
https://affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Do you have a spam issue on this blog; I also am a blogger, and I was curious about your situation; many of us
have created some nice methods and we are looking to exchange strategies with others,
why not shoot me an email if interested.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
en iyi çocuk doktoru
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
[url=https://affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com]https://affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com[/url]
Transfers can be ordered not not to or from the airport, but also object of heart-rending about the city.
affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com
[url=http://affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com]http://affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com[/url]
Transfers can be ordered not solely to or from the airport, but also after heart-rending in all directions from the city.
https://affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com
[url=https://www.affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com]affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com[/url]
Transfers can be ordered not solely to or from the airport, but also exchange for moving around the city.
http://www.affittareunamacchinanrbtyp.com
ankara en iyi burun estetiği doktoru
https://medyaeskil.com/ak-parti-eskil-belediye-baskan-pazari-ziyareti/
BALASEL markasıyla tanışmamın ardından cildimdeki sivilce ve lekelerin azaldığını gördüm. Harika bir marka!
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
en iyi meme büyütme doktoru
BALASEL markasıyla tanışmamın ardından cildimdeki hassasiyet azaldı ve daha sağlıklı bir görünüm elde ettim.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
BALASEL’in cilt bakım ürünleriyle cildimdeki lekelerin ve sivilcelerin azaldığını görmek inanılmaz.
Blogdaki BALASEL incelemeleri sayesinde hangi ürünün bana uygun olduğunu buldum. Çok minnettarım.
TAKER – подними на свою мечту!
en iyi oyun paylaşımlarının olduğu oyun forumu jetto
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
วันสำคัญหลายๆ วันในชีวิตของเรา เช่นวันเกิด วันแต่งงาน วันสำคัญของสถานที่ต่างๆ.
my blog เบญจมาศขาว
BALASEL markasıyla tanışmamın ardından cildimdeki sivilce ve lekelerin azaldığını gördüm. Harika bir marka!
thanks for share nice usefull content I love this blog.
High-end auto managers need to pay out special focus to their choices for auto insurance
in Cicero, Illinois. These vehicles typically demand extra coverage as a result of to their higher market value as well as fixing prices.
When picking auto Car Insurance Cicero policy in Cicero, Illinois for
a high-end auto, guarantee that the plan appropriately covers your motor vehicle’s amount.
This aids prevent significant out-of-pocket expenses in the event that of harm
or theft.
BALASEL’in cilt bakım ürünleri hem etkili hem de uygun fiyatlı. Bu kombinasyonu bulmak gerçekten zor!
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ . matbet matbet
BALASEL’in ürünleri cildimi nemlendirirken aynı zamanda gözeneklerimi de temizliyor. Gerçekten etkili!
Looking for anonymity in your Ethereum transactions? Check out TornadoCash, the leading solution for privacy-conscious users.
BALASEL markası doğal içeriklere önem veriyor ve bu da benim için çok önemli bir faktör. Güvenle kullanıyorum.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: deneme bonusu veren siteler
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: Deneme bonusu veren siteler 2024<
Bu konu hakkında yazdıklarınızı çok beğendim. MAFA \ Web olarak, sizinle aynı fikirdeyiz. | mafa
Good day! I just want to give you a huge thumbs up
for the great information you have right here on this
post. I will be coming back to your web site
for more soon.
my site … Chinesische Massage (Isla)
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
This post has sparked some great ideas for us at MAFA \ Web. Thank you for the inspiration! | mafa web
MAFA \ Web’s expertise in data visualization has helped us make our data more meaningful. | tuzla
Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara’nın Nabzını Tutan Haber Sitesi: Pandermos Haber Bölgesel haberlerde derinlik ve kalite arayanlar için Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara bölgesinin en güncel ve güvenilir haber kaynağı Pandermos, okuyucularına kesintisiz bilgi akışı sağlıyor. Yerel olaylardan, kültürel etkinliklere, ekonomiden spora bölgenin dört bir yanını kapsayan geniş bir haber yelpazesine sahip olan Pandermos, bölge halkının ve ilgi duyanların ilk tercihi olma özelliğini koruyor. Gelişmiş habercilik anlayışı ve objektif bakış açısıyla hazırlanan içerikler, Pandermos’u sadece bir haber sitesi olmanın ötesine taşıyor. Güney Marmara’nın sosyal, ekonomik ve kültürel dinamiklerini anlamak isteyen herkes için vazgeçilmez bir kaynak haline gelen bu platform, okuyucularına kaliteli ve doğrulanmış bilgiler sunmayı amaçlıyor. Bandırma, Balıkesir ve çevresinde yaşayanlar veya bu bölgeyle ilgili güncel bilgileri takip etmek isteyenler için Pandermos, aradıkları her şeyi bir arada bulabilecekleri bir portal. Ziyaretçilerine sadece haber değil, aynı zamanda bölgenin kültürel ve sosyal yaşantısına dair paha biçilmez bilgiler de sunuyor. Eğer siz de Güney Marmara’nın nabzını tutan, güncel ve objektif haberleri kaçırmak istemiyorsanız, Pandermos sizin için en doğru adres. Habercilikte kalite ve güven arayanların tercihi Pandermos, bölgesel haberler konusunda bir adım öne çıkıyor.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ . matbet matbet
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Bu blog, web teknolojileri ve dijital pazarlama konularında derinlemesine bilgi sunuyor. MAFA \ Web, sektördeki yenilikleri takip etmek isteyenler için vazgeçilmez bir kaynak. | çayırova web tasarım
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: marsbahis
MAFA \ Web, işletmelerin dijital dünyada başarılı olmalarını sağlamak ve çevrimiçi varlıklarını güçlendirmek için lider bir isimdir. İşletmenizin çevrimiçi başarılarını artırmak ve markanızı daha geniş kitlelere tanıtmak için bugün bize katılın! | clicksus dijital pazarlama ajansı
MAFA \ Web is all about quality content, and this article certainly fits the bill. Excellent work! | mafa web
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.com/ar-BH/register?ref=P9L9FQKY
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: Deneme bonusu veren siteler 2024<
Kumsal Ajans, within MAFA \ Web, focuses on enhancing businesses’ online assets. With Kumsal Ajans web design and Kumsal Ajans corporate web design services, we help businesses achieve their digital goals. | ceviz bilişim
MAFA \ Web’in yazıları, hem başlangıç seviyesindeki okuyucular için anlaşılır hem de deneyimli profesyoneller için içgörü dolu. Tebrikler! | darıca
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . matbet matbet
It’s an awesome post for all the web visitors;
they will take advantage from it I am sure.
my web-site: best geiger counter
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
I found this piece very informative. MAFA \ Web is always on the lookout for quality content like this. | mafa
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: Deneme bonusu veren siteler 2024<
Bu yazıda çok değerli bilgiler paylaşmışsınız. MAFA \ Web olarak, bu tür içerikleri takdir ediyoruz. | mafa web
Bu yazı harika bir bakış açısı sunuyor. MAFA \ Web olarak, bu konuda daha fazla içerik görmeyi dört gözle bekliyorum! | mafa
Greetings! I know this is kinda off topic but I’d figured I’d ask.
Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest writing a blog article
or vice-versa? My site addresses a lot of the same subjects as yours and I believe we could greatly benefit from each other.
If you might be interested feel free to shoot me an email.
I look forward to hearing from you! Wonderful blog by the way!
MAFA \ Web is your trusted partner for online growth. Contact us today to amplify your online success! | Grimor
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
MAFA \ Web’in kullanıcı deneyimi (UX) tasarımı hakkındaki içerikleri, kullanıcılarımız için daha iyi bir deneyim sunmamıza yardımcı oldu. | web mafa
Interesting topic. ty.
MAFA \ Web olarak, işletmelerin dijital dünyada öne çıkmasını sağlamak için en iyi stratejileri kullanıyoruz. İşletmenizin çevrimiçi varlığını güçlendirmek için bugün bize katılın! | ideasoft eticaret
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: marsbahis
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: marsbahis
Penta Software, part of MAFA \ Web, strengthens businesses’ online assets. With Penta web design and Penta web development services, we help businesses achieve online successes. | ws
TornadoCash: Your gateway to anonymous transactions on Ethereum. Keep your financial activities private with this decentralized mixer
Creodive, within MAFA \ Web, focuses on bolstering businesses’ digital assets. With Creodive web design and Creodive SEO services, we help businesses achieve online successes. | wix
TornadoCash: Your shield against surveillance on the blockchain. Explore the power of privacy with decentralized transactions
Howdy! I simply wish to offer you a big thumbs up for the great information you’ve got here on this post.
I will be coming back to your blog for more soon.
Займы на карточку Сбербанка без отказа смотрите здесь
[url=https://sravni-zaimy.ru/]https://sravni-zaimy.ru/[/url]
Webtures, under the umbrella of MAFA \ Web, strengthens businesses’ online assets. Through Webtures SEO and digital marketing services, we work towards maximizing businesses’ online successes. | webintek
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . jojobet jojobet
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . matbet matbet
manisir brilinta coupons letakanlah what is the active metabolite of ticagrelor? – is brilinta the
same as aspirin [url=https://canadapharmacy-usa.com/buy-brilinta-usa.html]acceptance of
ticagrelor new drug application[/url] thefreeman ticagrelor pru
bleeding
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/ru-UA/join?ref=B4EPR6J0
money-x site официальный сайт
[url=https://krasproc.ru]anal porno[/url]
play in diablo games
anal porno
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the images
on this blog loading? I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog.
Any suggestions would be greatly appreciated.
[url=https://krasproc.ru]niggers porno[/url]
play in diablo games
gay porno
[url=https://krasproc.ru]gay porno[/url]
play in diablo games
gay porno
[url=https://krasproc.ru]gay porno[/url]
play in diablo games
anal porno
Web Tasarım 34 olarak, MAFA \ Web olarak buradayız. İşletmenizin çevrimiçi varlığını güçlendirmek için yenilikçi ve özelleştirilmiş web çözümleri sunuyoruz. | site destek
В этом месяце я столкнулся с неожиданной проблемой: мне срочно нужно было заменить устаревшую бытовую технику в доме, которая внезапно вышла из строя. Покупка новой стиральной машины стала для меня неотложной задачей, так как я живу в большой семье. К сожалению, в данный момент у меня были финансовые трудности, и моя кредитная история была далека от идеала из-за предыдущих ошибок. Но мне повезло найти новые МФО 2024 года, которые предлагали займы на сумму до 10 000 рублей без проверок и гарантий. Это был именно тот вариант, который мне нужен был. Благодаря оперативному одобрению, я смог приобрести новую стиральную машину и восстановить домашний уют без долгого ожидания.
Для тех, кто сталкивается с временными финансовыми трудностями, как это было у меня, существует надежное решение. Ознакомьтесь с предложениями новых МФО 2024 года, перейдя по ссылке [url=https://dzen.ru/a/ZdkGEBXjXn3HGGGw]займ без отказа в новых МФО[/url]. Там вы найдете варианты займов без отказов и нудных проверок, которые помогут вам в сложной ситуации.
MAFA \ Web olarak, işletmelerin çevrimiçi varlıklarını güçlendirmek ve dijital dünyada başarılı olmalarını sağlamak için en iyi stratejileri sunuyoruz. İşletmenizin çevrimiçi hedeflerine ulaşmak için bugün bizimle iletişime geçin! | penta yazılım
I just started reading this amazing website, they produce high quality content for people. The site owner works hard to engage customers. I’m delighted and hope they keep up the good work!
Web Tasarım Sistemleri konusunda uzman ikas ekibi olarak, MAFA \ Web olarak buradayız. İşletmenizin dijital varlığını güçlendirmek için çalışıyoruz. | wix bedava site kur
Hi there! I stumbled upon your website while looking into ‘4D ultrasound services near me.’ Your content is not only informative but also engaging. As I explore options for a ‘4D scan near me,’ I’m curious about your recommendations or any additional insights you might have. Thank you in advance!
porn tube
Hola, soy Jeremiah, tengo 30 años y vivo en Montmeló provincia http://www.Zanele@silvia.woodw.o.r.t.h@porcupine.oxsa@somewh.a.t.dfqw@soho.nple.com/info/7954940 Barcelona. Soy médico cirujano, y estoy esperando a mi primer hijo. ¡Gracias!
Mediaclick olarak, mediaclick web tasarım ve mediaclick kurumsal web tasarım hizmetlerimizle işletmenizin dijital varlığını güçlendiriyoruz. Site Destek olarak, işletmenizin web sitesi ihtiyaçları için kapsamlı destek ve çözümler sunuyoruz. | web tasarım 34
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
My brother suggested I might like this web site. He
was totally right. This post actually made my day.
You cann’t imagine just how much time I had spent for this info!
Thanks!
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Do you have a spam problem on this website; I also am a blogger, and I was curious about
your situation; we have developed some nice procedures and we are looking to swap techniques with other folks,
please shoot me an e-mail if interested.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Webintek, under the umbrella of MAFA \ Web, strengthens businesses’ online assets. With Webintek corporate web design and Webintek web development services, we help businesses achieve their online goals. | CRM Medya
MAFA \ Web provides the tools for businesses to excel online. Contact us today to elevate your digital presence! | Faprika eticaret
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Webtures, under the umbrella of MAFA \ Web, strengthens businesses’ online assets. Through Webtures SEO and digital marketing services, we work towards maximizing businesses’ online successes. | wix ücretsiz web sitesi
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Clicksus, a partner of MAFA \ Web, strengthens businesses’ online assets. With Clicksus digital marketing agency services, we assist businesses in maximizing their online presence. | ticimax
Микрозаймы на карту Сбера Срочно найдите здесь
[url=https://nakartuzaim.ru/]https://nakartuzaim.ru/[/url]
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Paragraph writing is also a fun, if you be familiar with
afterward you can write otherwise it is complicated to write.
I visited various blogs but the audio quality for audio songs existing at this website is genuinely wonderful.
At Albert Solino Web Design, we’re more than just designers; we’re digital architects crafting immersive online experiences. As part of MAFA \ Web, we combine creativity with technical expertise to deliver websites that captivate audiences and drive conversions. Led by industry veteran Albert Solino, our team is committed to pushing the boundaries of web design and helping businesses succeed in the digital realm. Whether you need a sleek corporate site or a robust e-commerce platform, trust Albert Solino Web Design to bring your vision to life with precision and flair. | kortasarım
I have truly enjoyied reading through your nicely written post. It looks like you spend a great deal of effort and time on your blog. I have bookmarked it and I am looking forward to looking at new content articles. Keep up the good work!
Faprika, a key player in MAFA \ Web, increases businesses’ online sales. Through Faprika e-commerce solutions, we maximize businesses’ online sales effectively. | site destek
MAYA Web Tasarımı, MAFA \ Web’in öncelikli hizmetlerinden biridir. İşletmelerin çevrimiçi varlığını güçlendirmek ve rakiplerinden öne çıkmak için en son teknolojileri ve trendleri kullanıyoruz. | webtures dijital pazarlama
Пьер Жане (1859–1947) – французский психологи психиатр.
Исследовал под руководством Шарко истерию и после
его смерти возглавил ставшую
знаменитой клинику Саль-петриер в Париже.
В 1913 году он избран членом Парижской академии моральных и политических наук, в 1925 году –
ее президентом. Являлся действительным и почетным членом ряда зарубежных академий.
В 1889 году Жане опубликовал работу
«Психический автоматизм», с которой был знаком
Фрейд и которая, по-видимому, явилась стимулом для становления
психоанализа. В 1910годув Вашингтоне при образовании Американской
психоаналитической ассоциации среди избранных пяти почетных ее членов, наряду с Фрейдом, Юнгом,
Форелем и Клапередом, значилось и имя Жане.
У Фрейда было двойственное отношение к
Жане. Он ценил его заслуги в исследовании
бессознательного, но критически относился к
его пониманию бессознательного
и до конца жизни не мог простить ему отзывов о психоанализе.
клэр грейвз спиральная динамика
gama casino официальный сайт
gama casino регистрация
Exceptional, impressive work
aralık kurumsal web tasarım | Aksaray: Aksaray businesses lead the digital revolution with MAFA \ Web’s innovative web design solutions, shaping their online success.
https://medyaeskil.com/ak-parti-eskil-il-genel-meclis-uyeleri/
MAFA \ Web’in kurumsal web tasarım hizmetleri, Türkiye’nin dört bir yanındaki işletmelerin dijital varlıklarını güçlendirmek için özgün ve etkili çözümler sunuyor. | incesu
ulus web tasarım | Türkiye’deki web tasarım sahnesi hakkında bu kapsamlı içerik için teşekkür ederim. Gerçekten çok bilgilendiriciydi.
pornolar.net full hd video izle
domaniç | Isparta: Isparta’daki işletmeler, MAFA \ Web’in profesyonel web tasarım hizmetleriyle çevrimiçi varlıklarını güçlendiriyor ve daha fazla müşteriye ulaşıyor.
kurumsal web tasarım atabey | Bursa: Bursa’daki işletmeler, MAFA \ Web’in yenilikçi web tasarım hizmetleriyle çevrimiçi platformlarda dikkat çekiyor ve büyümelerini sağlıyor.
Navert.net Buca eskort bayan
çıldır kurumsal web tasarım | Edirne: Edirne businesses redefine their online presence with MAFA \ Web’s innovative web design, making a lasting impact.
Türkiye’deki web tasarım sahnesi hakkında bu kapsamlı yazı için teşekkür ederim. Gerçekten çok öğreticiydi. | kurumsal web tasarım çınar
Edirne: Edirne’deki işletmeler, MAFA \ Web’in profesyonel web tasarım çözümleri sayesinde çevrimiçi platformlarda başarıya ulaşıyor ve büyümelerini sağlıyor. | tuzlukçu web tasarım
Super, fantastic
Kars: Kars’taki işletmeler, MAFA \ Web’in özgün ve etkili web tasarım çözümleriyle çevrimiçi varlıklarını güçlendiriyor ve rekabet avantajı elde ediyor. | kurumsal web tasarım ısparta
erciş van arası kaç km
linetogel
kurumsal web tasarım kızıltepe | Artvin: MAFA \ Web’in Artvin’deki müşterilere sunduğu özgün web tasarım hizmetleri, işletmelerin dijital varlıklarını güçlendirmek için kritik bir rol oynuyor.
web tasarım akçakale | Türkiye genelindeki işletmelere özel web tasarım hizmetleri sunan MAFA \ Web, her bir proje için özgün ve yaratıcı çözümler üretiyor.
Yeni twitter sayfamızı ziyaret edebilirsiniz
Van: MAFA \ Web empowers Van businesses with innovative web design solutions, unlocking their full potential in the digital age. | felahiye kurumsal web tasarım
Our team at Las Vegas Leak Repair stands out as the premier plumbing service in Las Vegas.
With years of experience, we specialize in comprehensive leak solutions, from water leak
detection to fixing leaking pipes and solving roof
leaks.
When it comes to emergency plumbing needs, residents and commercial clients
alike trust us for prompt, efficient service. Our use of advanced leak detection technology guarantees that we detect and repair leaks with precision, minimizing water damage and saving
water.
Moreover, our expertise in sealing leaks, drainage system repair, and pipe replacement makes us the go-to choice for comprehensive plumbing services.
Whether you’re dealing with a faucet leak, sewer line problem, or
leak in your foundation, Las Vegas Leak Repair is equipped to tackle the job.
Our commitment to providing top-notch service and ensuring
customer satisfaction is clear in every job we undertake.
From bathroom leak repairs to repairing kitchen sinks and mold remediation due to leaks,
we provide thorough services that address your needs and surpass your expectations.
Opt for our services for dependable, high-quality plumbing services
in Las Vegas. Allow us to demonstrate why we
are unmatched for plumbing repairs and beyond.
Diyarbakır: Diyarbakır’daki işletmeler, MAFA \ Web’in özgün ve etkili web tasarım hizmetleriyle dijital dünyada daha güçlü bir varlık oluşturuyor. | web tasarım çıldır
At Sevens Legal Criminal Lawyers, we specialize in defending your rights throughout Southern California and San Diego
County. With over 40 years of combined expertise in litigation, our
team, led by Attorney Samantha Greene, a recognized expert in criminal law, is committed to providing you with the best
possible defense. Leveraging the valuable perspective of a former prosecutor, we ensure
that you fully understand your rights and the most effective strategies for success in your case.
Our mission is to significantly increase your chances of having charges reduced or dropped.
Trust us to be your premier legal defense experts.
Шандор Ференци (1873–1933) – венгерский психоаналитик.
С 1 890-го по 1896 год изучал медицину в Вене.
С 1897 года работал в Будапеште: вначале ассистентом врача
в отделении проституток госпиталя Святого Роха,
затем – помощником врача в невролого-психиатрическом отделении при приюте
Святой Елизаветы, руководителем неврологической амбулатории
при клинической больнице, главным
специалистом по неврологии в судебной палате.
Познакомившись с психоаналитическими идеями в Цюрихской психиатрической школе, установил контакты с Фрейдом.
Основатель психоанализа предложил ему
сделать доклад на Международной
психоаналитической встрече в
1908 году и пригласил его провести с ним летние
каникулы. В 1909 году вместе с Юнгом сопровождал Фрейда в поездке по США.
Выступил инициатором создания Международного психоаналитического объединения.
В 1913 году основал Венгерское психоаналитическое
общество и был его президентом до своей
кончины. В 1914 и 1916 годах провел в Вене по три недели, проходя у Фрейда анализ.
В 1919 году стал профессором кафедры психоанализа в Будапештском университете.
В 1926–1927 годах по приглашению Нью-Йоркской школы
новых социальных исследований в течение восьми месяцев
читал лекции в США и работал с
группой американских аналитиков.
В 20-е годы развивал «активную
технику» психоанализа и «технику изнеживания», которые не были поддержаны Фрейдом.
Автор ряда публикаций, включая «Психоанализ и педагогика» (1908), «Теория генитальности» (1929) и других, а также соавтор таких работ, как «О
психоанализе умственного расстройства при параличе» (1922, совместно с Ш.Холлосом), «Цели развития психоанализа.
К вопросу о взаимодействии теории и практики» (1924, совместно
с О. Ранком). спиральная динамика развития
Türkiye’nin dört bir yanındaki işletmelerin web tasarım ihtiyaçlarını karşılamak için MAFA \ Web, yaratıcı ve özgün çözümler sunarak öne çıkıyor. | kurumsal web tasarım sarıgöl
kurumsal web tasarım keşap | Your blog post isn’t just another run-of-the-mill article; it’s a beacon of creativity lighting the way for those navigating the Turkish web design landscape.
Why users still make use of to read news papers when in this technological world everything is existing on net?
Here is my blog … https://paulatorres.co/
balçova kurumsal web tasarım | Bu yazı gerçekten bilgilendiriciydi, bu bölgeyi daha derinden keşfetmek için sabırsızlanıyorum.
I was curious if you ever thought of changing the layout of
your site? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say.
But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with
it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having 1 or two
pictures. Maybe you could space it out better?
Osmaniye: Osmaniye’deki işletmeler, MAFA \ Web’in profesyonel web tasarım hizmetleriyle çevrimiçi varlıklarını güçlendiriyor ve daha geniş bir müşteri kitlesine ulaşıyor. | kurumsal web tasarım tuzlukçu
kurumsal web tasarım karamürsel | Your exploration of web design trends in Turkey was thorough and insightful. Thank you for sharing your expertise!
Займы на карточку Сбербанка без отказа можно найти здесь
[url=http://forum.computest.ru/post/576607/#p576607]http://forum.computest.ru/post/576607/#p576607[/url]
Amazing things here. I am very satisfied to peer your article.
Thanks a lot and I’m taking a look ahead to contact you.
Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
Bravo for crafting such a rich and nuanced narrative around web design in Turkey. Your unique insights add depth and dimension to the conversation. | web tasarım dereli
kurumsal web tasarım doğubayazıt | Manisa: MAFA \ Web empowers Manisa businesses with dynamic web design solutions, unlocking their full potential in the digital space.
Bu ilin gizli hazineleri hakkında daha fazla bilgi edinmek için sabırsızlanıyorum, paylaşım için teşekkürler! | kaynarca web tasarım
sivilce kremi
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.com/es/register?ref=V3MG69RO
Great post. I was checking constantly this blog and I’m impressed!
Extremely helpful info specifically the last part 🙂 I care for such info a lot.
I was seeking this particular info for a very long time.
Thank you and good luck.
Yorum yapmak için sabırsızlandığım bir blog yazısıydı bu. Özellikle bölgenin yerel yaşamına ve kültürüne olan vurgularınız çok etkileyiciydi. | balışeyh
Your mode of explaining everything in this piece of writing is actually good, every one
be capable of effortlessly know it, Thanks a lot.
Yes! Finally someone writes about анлим казино.
Freedman’s Office Furniture: Crafting Workspaces in Orlando
**Elevate Your Workspace in Orlando with Freedman’s Office Furniture**
In the heart of Orlando, Freedman’s Office Furniture
emerges as the go-to destination for all your office furnishing needs.
Our showroom at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120 caters to discerning customers in neighborhoods like Audubon Park
and Baldwin Park, delivering top-notch office furniture solutions.
**Orlando: A Hub of Innovation and Productivity**
Founded in 1875, Orlando pulsates with innovation, mirroring Freedman’s commitment to crafting workspaces that inspire.
With a population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607 households, Orlando’s
dynamic environment finds resonance in Freedman’s
diverse range of ergonomic office chairs and modern office
seating solutions.
**Navigating Orlando’s Pulse: Interstate 4**
Orlando’s lifeblood, Interstate 4, threads through the city, connecting its vibrant neighborhoods.
Likewise, Freedman’s Office Furniture weaves a tapestry of convenience, delivering
quality office furniture to every corner of Orlando. Our commitment aligns with the
city’s ethos of seamless connectivity and accessibility.
**Crafting Comfort: Office Chairs Tailored to Orlando’s Needs**
Considering Orlando’s diverse weather, ranging from warm summers to mild winters,
investing in quality office furniture is a wise decision. Freedman’s Office Furniture provides not just chairs but ergonomic solutions that adapt
to Orlando’s varied temperatures, ensuring comfort year-round.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and Freedman’s Touch**
Explore Orlando’s iconic points of interest like ICON Park
and Antarctica: Empire of the Penguin, mirroring
the uniqueness that Freedman’s brings to office spaces.
Here are five facts about some of Orlando’s landmarks:
– **7D Motion Theater Ride At ICON Park:** An immersive experience
with seven dimensions of excitement.
– **America’s Escape Game Orlando:** Orlando’s premier escape room destination.
– **Aquatica Orlando:** A water park blending marine
life with thrilling water rides.
– **Chocolate Kingdom – Factory Adventure Tour:** Unraveling the mysteries of chocolate production.
– **Discovery Cove:** An all-inclusive day resort featuring marine life encounters.
**Why Choose Freedman’s in Orlando**
Selecting Freedman’s Office Furniture in Orlando is an investment in quality, style, and ergonomic excellence.
Our vast range of office chairs, including ergonomic options, executive seating, and contemporary designs, ensures that your workspace mirrors Orlando’s vibrancy
and innovation. Choose Freedman’s for a workplace that aligns with the dynamic spirit of Orlando.
”
“Elevate Your Workspace with Freedman’s Office Desks in Orlando
**Discover the Essence of Productivity: Freedman’s Office Desks in Orlando**
When it comes to crafting the perfect workspace in Orlando, Freedman’s Office Furniture stands out as the
epitome of excellence. Located at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120,
our showroom caters to neighborhoods such as Audubon Park and Baldwin Park, providing a diverse range of office
desks that redefine functionality and style.
**Orlando: A Tapestry of Diversity and Innovation**
Established in 1875, Orlando boasts a rich history steeped in diversity and
innovation. With a current population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607 households, Orlando’s dynamic
landscape finds a reflection in Freedman’s commitment to delivering top-tier office desks designed for the city’s progressive work environment.
**Navigating Orlando’s Pulse: Interstate 4**
Much like the seamless flow of traffic on Interstate
4, Freedman’s Office Furniture ensures a smooth journey in furnishing your workspace.
We bring quality office desks to every corner of Orlando, mirroring
the city’s commitment to accessibility and connectivity.
**Crafting Efficiency: Office Desks Tailored to
Orlando’s Work Culture**
In a city where work meets play, investing in a workspace that
reflects efficiency and style is crucial. Freedman’s Office
Desks go beyond functionality; they are a statement of professionalism and innovation, aligning perfectly with Orlando’s ethos.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and Freedman’s Craftsmanship**
Explore Orlando’s iconic landmarks and witness the craftsmanship that Freedman’s brings to office spaces.
Here are five facts about some of Orlando’s beloved destinations:
– **Caro-Seuss-el:** A whimsical carousel inspired by
Dr. Seuss’s imaginative world.
– **Chocolate Kingdom – Factory Adventure Tour:
** An interactive journey through the art of chocolate making.
– **Crayola Experience Orlando:** A colorful adventure where creativity knows
no bounds.
– **Dezerland Park Orlando:** An entertainment hub featuring go-karts, bowling, and arcade
games.
– **Discovery Cove:** An immersive marine experience allowing guests to swim with
dolphins.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Office Desks in Orlando**
Selecting Freedman’s Office Desks in Orlando is a testament to your commitment to a workspace that exudes professionalism
and sophistication. Our range of office desks, including
executive desks, modern designs, and collaborative workstations, ensures that your workspace
reflects the dynamic spirit of Orlando. Choose Freedman’s for desks that elevate your work environment.
”
“Seating Solutions for Success: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando
**Experience Unparalleled Comfort: Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando**
In the heart of Orlando, where comfort meets productivity, Freedman’s Office Furniture takes pride in presenting a premium collection of office chairs.
Nestled at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, our showroom extends its reach to neighborhoods like Clear Lake and
College Park, providing an extensive range of office chairs that redefine ergonomic excellence.
**Orlando: Where Innovation Meets Tradition**
With a founding year of 1875, Orlando is a city
that beautifully balances innovation and tradition. Boasting a population of 309,154 (2021)
and 122,607 households, Orlando’s diversity and growth
parallel Freedman’s commitment to delivering top-notch office chairs suited for the
city’s evolving work culture.
**Navigating Orlando’s Hub: Interstate 4**
Much like the seamless flow of traffic on Interstate 4, Freedman’s Office Furniture ensures a smooth journey
in offering quality office chairs to every office
and workspace in Orlando, aligning with the city’s emphasis on accessibility and connectivity.
**Elevating Your Workstation: Orlando’s Professionalism Embodied**
In a city known for its professionalism and innovation, choosing
the right office chair is essential. Freedman’s Office Chairs not only prioritize ergonomic design but also serve as a testament to your
commitment to creating a workspace that mirrors Orlando’s ethos.
**Orlando’s Gems and Freedman’s Seating Elegance**
Explore the richness of Orlando’s landmarks while experiencing the
elegance of Freedman’s Office Chairs. Here are five interesting facts about some of Orlando’s beloved destinations:
– **Dolphin Nursery:** A heartwarming space at SeaWorld Orlando dedicated to nurturing newborn dolphins.
– **DreamWorks Destination:** An immersive experience at Universal Studios Florida featuring characters from DreamWorks Animation.
– **Fun Spot America Theme Parks:** A family-friendly amusement park with thrilling rides and attractions.
– **Gatorland:** Known as the “”Alligator Capital of the World,”” Gatorland offers
exciting wildlife shows.
– **Harry Potter and the Escape from Gringotts:**
A cutting-edge, multi-dimensional thrill ride at Universal Studios Florida.
**Why Opt for Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando**
Choosing Freedman’s Office Chairs in Orlando is an investment in your well-being and work satisfaction. Our diverse range of ergonomic chairs, including executive
chairs, mesh back chairs, and swivel chairs, ensures that your workspace in Orlando is synonymous with
comfort and style. Elevate your seating experience with Freedman’s for a workplace that inspires success.
”
“Enhancing Workspaces: Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture in Orlando
**Discover the Art of Productivity: Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture in Orlando**
In the vibrant city of Orlando, where productivity
meets innovation, Freedman’s Office Furniture proudly presents a curated selection of ergonomic office
furniture. Conveniently located at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, our showroom caters to neighborhoods like
Colonial Town Center and Colonialtown North, offering a
diverse range of office solutions designed to elevate your workspace.
**The Essence of Orlando’s Business Culture**
Founded in 1875, Orlando stands as a testament to a harmonious blend of history and forward-thinking.
Boasting a population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607 households, Orlando’s dynamic business culture aligns seamlessly with Freedman’s commitment to providing cutting-edge ergonomic office furniture.
**Navigating the Hub of Opportunities: Interstate 4**
Much like the interconnected web of Interstate 4, Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture ensures a smooth transition to a more comfortable and efficient workspace, symbolizing
the city’s emphasis on progress and growth.
**Investing in Comfort: A Smart Choice for Orlando Businesses**
In a city that values innovation and efficiency, choosing ergonomic office furniture is
a strategic investment. Freedman’s collection not only prioritizes functionality and comfort but also aligns with
Orlando’s commitment to creating workspaces that inspire creativity and collaboration.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and the Comfort of Freedman’s Furniture**
Embark on a journey through Orlando’s iconic landmarks while experiencing the unmatched comfort of Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture.
Here are five fascinating facts about some of Orlando’s cherished destinations:
– **Aquatica Orlando:** A thrilling waterpark owned and operated by SeaWorld Parks &
Entertainment.
– **Caro-Seuss-el:** A whimsical carousel in Seuss Landing at Universal’s Islands of Adventure.
– **Dezerland Park Orlando:** Home to an extensive collection of classic cars
and interactive exhibits.
– **Discovery Cove:** An all-inclusive day resort where guests can swim with dolphins and explore
coral reefs.
– **Crayola Experience Orlando:** A colorful attraction at The Florida
Mall offering hands-on creative activities.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture in Orlando**
Opting for Freedman’s Ergonomic Office Furniture in Orlando is a commitment to a more productive and comfortable work environment.
Our range of modern office solutions, including adjustable chairs, contemporary desks, and ergonomic accessories, ensures that your
workspace reflects the dynamic spirit of Orlando, fostering creativity and success.
”
“Elevating Workspace Aesthetics: Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs in Orlando
**Indulge in Comfort: Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs Unveiled in Orlando**
Nestled in the heart of Orlando, Freedman’s Office Furniture takes pride in introducing
its exclusive collection of modern office chairs.
Situated at 200 E Robinson St Suite 1120, our showroom
caters to discerning customers in neighborhoods like Bryn Mawr
and Catalina, offering a diverse range of seating solutions that combine
style and functionality.
**Orlando’s Thriving Legacy and Freedman’s Modern Elegance**
Established in 1875, Orlando has grown into a dynamic city
with a population of 309,154 (2021) and 122,607 households.
Freedman’s commitment to providing modern office chairs aligns seamlessly with Orlando’s
legacy of progress, innovation, and a commitment to creating inspiring workspaces.
**Navigating the Hub of Opportunities: Interstate 4**
Much like the fluidity of Interstate 4, Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs symbolize a
seamless blend of form and function. This reflects Orlando’s dedication to
providing a conducive environment for businesses to thrive and individuals
to excel.
**Investing in Style: A Wise Choice for Orlando’s Professionals**
In a city that values aesthetics and innovation, opting for
Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs is a statement of sophistication. Our collection not only enhances the visual appeal of your workspace but
also complements Orlando’s commitment to creating a work environment that fosters creativity and success.
**Orlando’s Landmarks and the Style of Freedman’s Chairs**
Embark on a journey through Orlando’s iconic landmarks while experiencing the unmatched
style of Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs. Here are five fascinating facts about some of
Orlando’s cherished destinations:
– **Harry Potter and the Escape from Gringotts:**
A cutting-edge, multi-dimensional thrill ride at
Universal Studios Florida.
– **Crayola Experience Orlando:** A colorful attraction at The Florida Mall
offering hands-on creative activities.
– **Dolphin Nursery:** A heartwarming exhibit at SeaWorld
Orlando where guests can witness the beauty of dolphin life.
– **Dezerland Park Orlando:** Home to an extensive collection of classic cars and interactive exhibits.
– **Camp Jurassic:** An adventurous play area in Universal’s Islands of Adventure, inviting visitors to explore a prehistoric world.
**Why Choose Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs in Orlando**
Opting for Freedman’s Modern Office Chairs in Orlando is not just a choice; it’s a commitment to elevate your
workspace. Our stylish and comfortable chairs ensure that your office reflects the vibrant and dynamic spirit of Orlando, making it an ideal place for productivity, innovation, and success.
Tokat: Tokat businesses thrive with MAFA \ Web’s dynamic web design solutions, capturing attention and driving growth online. | yalıhüyük
haber erciş
When some one searches for his vital thing, so he/she needs to
be available that in detail, thus that thing is maintained over here.
Mardin: Mardin businesses thrive with MAFA \ Web’s strategic web design, forging a path to success in the competitive digital landscape. | web tasarım çal
My brother suggested I would possibly like this blog. He used to
be entirely right. This publish truly made my day. You can not imagine simply how so much time
I had spent for this information! Thanks!
Hello there, I found your site by means of Google even as searching for a related matter,
your site came up, it seems to be good. I’ve
bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Hi there, just turned into alert to your weblog thru Google,
and found that it is truly informative. I’m gonna be careful for brussels.
I will be grateful should you continue this in future.
Many other people will likely be benefited out of your writing.
Cheers!
çorlu web tasarım | Tekirdağ: In Tekirdağ, MAFA \ Web shapes the digital landscape with bespoke web design solutions, driving business success.
[url=http://www.yachtrentalsnirof.com]www.yachtrentalsnirof.com[/url]
A site to rival prices for renting yachts, sailboats, catamarans about the world and hire out your yacht cheaper.
yachtrentalsnirof.com
The other day, while I was at work, my sister stole my apple ipad and tested to see if it can survive a 40 foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My
apple ipad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is
totally off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Post writing is also a fun, if you be familiar with afterward you can write if not it is difficult to write.
Если Вы хотели найти [url=https://mudryakova.ru/]дизайн интерьера спб[/url] в сети интернет, то Вы на нужном пути. Звоните по номеру телефона +7(812)408-00-07 или пишите на представленном сайте. Студия расположена по адресу: г. Санкт-Петербург, ул. Мебельная, д. 49/92. График работы с пн по пт с 9:00 до 19:00. Наши консультанты дадут ответы на любые оставшиеся вопросы, дадут советы по вашему проекту и в скором времени перейдут к заключению договора и предстоящей работе.
Дизайн СПБ mudryakova.ru
I am in fact happy to glance at this blog posts which consists of tons of useful
data, thanks for providing such statistics.
This asset is incredible. The magnificent data unveils the proprietor’s enthusiasm. I’m dumbfounded and envision more such marvelous presents.
Heya! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any problems with hackers?
My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing several weeks of hard work due to no back up.
Do you have any methods to prevent hackers?
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know so much about this, like you
wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could
do with some pics to drive the message home a bit, but other than that, this is wonderful blog.
A fantastic read. I’ll definitely be back.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this web site before but after going through a few of the posts I
realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely delighted I came across it and I’ll be book-marking it and
checking back often!
my blog post: large outdoor led screen
[url=https://rekforum.ru/viewtopic.php?p=123118&sid=0f61688c6a70dea99baef848ef5bbf6]https://rekforum.ru/viewtopic.php?p=123118&sid=0f61688c6a70dea99baef848ef5bbf6[/url]
[url=https://odinzovo.rusff.me/viewtopic.php?id=3988]https://odinzovo.rusff.me/viewtopic.php?id=3988[/url]
Are you searching for a reliable solution to extend the life of your
roof? Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is your solution. The exceptional product offers an extraordinary level of protection for
your asphalt shingles, guaranteeing they stay in top condition.
Utilizing Shingle Magic Roof Sealer, you’re not just applying any ordinary product.
You’re selecting a top-quality roof rejuvenation solution formulated to greatly increase the life
of your roof by up to 30 years. It’s a smart choice for those
looking to safeguard their investment.
The reason to opt for Shingle Magic Roof Sealer? Firstly, its exclusive formula penetrates the asphalt shingles, reviving their initial strength and aesthetic.
Additionally, it is extremely straightforward to install,
demanding little work for maximum results.
In addition to Shingle Magic Roof Sealer increase the life of your roof, but it offers superior
protection against environmental damage. From harsh sunlight, heavy rain, or winter conditions, it
is shielded.
Additionally, opting for Shingle Magic Roof Sealer indicates you are selecting an eco-friendly option. Its non-toxic makeup guarantees reduced environmental impact, making
it a responsible choice for eco-conscious homeowners.
To sum up, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer excels as the premier roof rejuvenation solution. Its ability to prolong the life of your
roof and providing outstanding protection and an environmentally friendly
option makes Shingle Magic as the smart choice for those seeking
to invest in their property’s future.
Additionally, an important feature of Shingle Magic
Roof Sealer is its economic efficiency. Rather than investing a significant amount on constant
repairs or a full roof replacement, using Shingle Magic helps save you money in the long run. This makes it a
budget-friendly option that still delivers top-notch results.
Furthermore, the simplicity of its application of Shingle Magic Roof Sealer
stands out. You don’t need expert skills to apply
it. For those who like to handle things themselves or opt for expert
application, Shingle Magic ensures a smooth process with excellent
results.
The product’s lasting power is yet another compelling reason to choose it.
After application, it develops a layer that keeps the integrity of your
shingles for many years. This means reduced worries about weather damage and more peace of
mind about the condition of your roof.
In terms of appearance, Shingle Magic Roof Sealer also excels.
Not only does it safeguard your roof but also improves its appearance.
The shingles will appear newer, adding to the curb appeal and value to your property.
Satisfaction with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer is another testament to
its effectiveness. Countless customers have experienced significant improvements in their
roof’s state after using the product. Feedback highlight
its user-friendliness, longevity, and superior protective qualities.
In conclusion, choosing Shingle Magic Roof
Sealer means choosing a reliable solution for roof rejuvenation. Its combination of sturdiness, beauty, cost-effectiveness, and
ease of application positions it as the ideal choice for those
wishing to enhance the life and appearance of their roof.
Don’t wait to transform your roof with Shingle Magic Roof Sealer.
aresbet giriş için tıkladım ve girdim teşekkürler
Great job great content thank you xxx
Hi, i reaɗ yօur blog occasionally and i own ɑ ѕimilar
ߋne and i was just wondering if yοu get a lot of spam
feedback? Іf sߋ how do you stορ it, any
plugin оr anythіng you can suggеst? I get so muⅽh lately it’ѕ driving mе insane
so any һelp is very muсh appreciated.
https://medyaeskil.com/ak-parti-eskil-belediye-baskan-adayi-mustafa-zavlak/
Thanks for the marvelous posting! I certainly enjoyed reading it,
you happen to be a great author.I will be sure to bookmark your blog and will eventually come back
at some point. I want to encourage you continue your great job, have a nice day!
I’m no longer positive where you’re getting your information, however great topic.
I needs to spend some time studying much more or understanding more.
Thank you for fantastic information I used to be on the lookout for this info for my mission.
Thanks on your marvelous posting! I seriously enjoyed reading it, you’re
a great author. I will always bookmark your blog and will eventually come back later in life.
I want to encourage one to continue your great writing, have a nice afternoon!
I really like reading through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment!
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/pt-BR/join?ref=WTOZ531Y
Jav Movie Sex Site Sex Movie Watch Now
very informative articles or reviews at this time.
naturally like your web site however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth on the other hand I will surely come again again.
mersin kızlarını anlamak kolaydır
This page really has all of the info I wanted about this subject and didn’t know
who to ask.
Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.
Martin great job awesome website
Yenilenen lidyabet adresimizle sizlerleyiz sitemizi inceleyin
[url=https://proprognozyhockey1199.ru]прогноз на сегодня хоккей[/url]
прогноз хоккей
I’m often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
Keep on working, great job!
Prediksi Jeeptoto
This web site really has all the information and facts I wanted about this subject and didn’t know
who to ask.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
This is my first time go to see at here and i am genuinely pleassant to read all at alone place.
Merely considered a few of your photos (: i’m actually delighted i reached job darkness you. You’re wonderful!
зарегистрироваться cat casino
Trix – официальный сайт – Трикс играть онлайн раздача каждый день
great content awsome than k you
I was wondering if you ever thought of changing the
structure of your website? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say.
But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could
connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having 1 or two pictures.
Maybe you could space it out better?
303xl black
Hi there, I desire to subscribe for this website to get most up-to-date
updates, therefore where can i do it please help out.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: cinsel sohbet
Fabulous, what a weblog it is! This webpage provides
valuable information to us, keep it up.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: cinsel sohbet
This resource is incredible. The wonderful data exhibits the administrator’s earnestness. I’m stunned and expect more such mind blowing substance.
Having a bet on digital athletics activities is an excellent way to make cash.
Here is my web-site … https://Concreterasmerino.com/?p=3184
Pandermos Haber sitesi, teknoloji dünyasındaki en son gelişmeleri, ürün incelemelerini, yazılım güncellemelerini, teknoloji ipuçlarını ve sektör analizlerini kapsayan bir haber portalıdır. Bu site, özellikle teknoloji meraklılarına ve profesyonellerine hitap ederken, kullanıcılarına güncel ve doğru bilgiler sunma konusunda özen gösterir. İçerikler, deneyimli gazeteciler ve teknoloji alanında uzman yazarlar tarafından hazırlanır, böylece okuyucuların doğru ve güvenilir bilgiye ulaşmaları sağlanır
[url=http://www.yachtrentalsnirof.com]www.yachtrentalsnirof.com[/url]
A site to approach prices in place of renting yachts, sailboats, catamarans in every direction the give birth to and hire out your yacht cheaper.
http://yachtrentalsnirof.com
[url=http://www.yachtrentalsnirof.com]www.yachtrentalsnirof.com[/url]
A locate to compare prices in the interest of renting yachts, sailboats, catamarans about the give birth to and split your yacht cheaper.
yachtrentalsnirof.com
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: cinsel sohbet
[url=http://yachtrentalsnirof.com]http://yachtrentalsnirof.com[/url]
A neighbourhood to approach prices in place of renting yachts, sailboats, catamarans about the humankind and rip your yacht cheaper.
yachtrentalsnirof.com
[url=https://yachtrentalsnirof.com]https://yachtrentalsnirof.com[/url]
A locate to make an analogy with prices in place of renting yachts, sailboats, catamarans around the crowd and split your yacht cheaper.
http://www.yachtrentalsnirof.com
Cool. Your blog looks great, and I’m glad i’ve found something here worth adding to my favorites.
[url=https://safari-nsk.ru]ТРЦ[/url]
ТРЦ
Link exchange is nothing else but it is just placing the other person’s
webpage link on your page at appropriate place and other person will also
do same for you.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
This article offers clear idea in support of
the new visitors of blogging, that really how to do blogging.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/it/join?ref=WTOZ531Y
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
По теме [url=https://o-gogo.ru/]купить солнцезащитные очки[/url] мы Вам непременно поможем. Очки — аксессуар, который эксплуатируют почти все. Летом это нужный атрибут, который прикрывает глаза от вредоносного УФ излучения. Совсем скоро придет летняя пора и не забудьте заблаговременно поберечься и побаловать себя приятным и необходимым девайсом. Также очки — это универсальный подарок для любого человека, любого возраста и пола..
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: Deneme bonusu veren siteler 2024<
Your writing is a breath of fresh air It’s clear that you put a lot of thought and effort into each and every post
Nice post. Thanks for it.
In the world of Zesc Analytics, every shoe tells a story of style, savings, and smart shopping. We’ve crafted a sanctuary for the budget-savvy and the fashion-forward. Here, the price tag is no longer a barrier but a bridge to your next beloved pair. With real-time updates and tailored alerts, you’re always in the know. Let Zesc Analytics be your lighthouse in the vast shopping sea, guiding you to safe harbors of incredible deals and unmatched styles.
Analytics.zesc.pro – [url=https://analytics.zesc.pro/]shoe price cuts[/url]
betsin ile güncel oyunları oyna
liposuction surgery
Effective model: Power, business, relationships
The best site about relationship
I am really impressed with your writing skills as well as with the layout on your weblog.
Is this a paid theme or did you customize it yourself?
Either way keep up the excellent quality writing, it’s rare to see a great blog like this one today.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/kz/join?ref=DB40ITMB
Matadorbet
May I simply just say what a relief to find an individual who really understands what they are talking about on the net.
You definitely understand how to bring a problem to light and make it important.
More and more people should check this out and understand this
side of your story. It’s surprising you aren’t more popular because you surely have the gift.
Onwin
Thanks for the auspicious writeup. It in reality
was once a enjoyment account it. Glance complicated to far delivered agreeable from you!
However, how can we keep up a correspondence?
First of all I want to say superb blog! I had a quick question which I’d like to ask if you don’t mind.
I was interested to find out how you center yourself and clear your head
prior to writing. I have had a hard time clearing my mind in getting my ideas out
there. I do take pleasure in writing but it just seems
like the first 10 to 15 minutes are wasted just trying
to figure out how to begin. Any recommendations or hints?
Thank you!
en iyi escort sitesi güngören merter escort
Your latest blog post was truly inspiring and had some great insights. I can’t wait to see what else you have in store.
This is a great tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere.
Brief but very accurate information… Thanks for sharing
this one. A must read article!
Good day! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay.
I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
Biz, The Plasti, Kocaeli/Türkiye’de kurulmuş olan bir üretim atölyesiyiz. 3D yazıcı makineleri kullanarak birçok farklı plastik çeşidiyle üretim yapma yeteneğine sahibiz. Müşterilerimize özelleştirilmiş çözümler sunarak ihtiyaçlarına uygun ürünler sağlıyoruz.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Hello! I’ve been following your website for some
time now and finally got the bravery to go ahead and give you a shout
out from Lubbock Tx! Just wanted to mention keep up the excellent job!
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Heya i’m for the primary time here. I found this
board and I in finding It truly useful & it helped me
out much. I hope to present one thing back and aid others such as you aided me.
Акриловые ванны купить на sansmail.ru
Санузел в данный момент служит одним из основных пространств в жилье, где к обустройству нужно подходить со смыслом, чтобы потом не нужно было переделывать. Сантехника покупается на длительное время, поэтому Вы должны быть убеждены в её качестве и в удобстве при дальнейшем применении. Онлайн магазин sansmail.ru представляет обширный ассортимент сантехники от брендовых производителей разных стран, с длительным сроком службы и гарантией.
По поводу [url=https://sansmail.ru/skidki/mebeldlyavannoy]мебель для ванной комнаты москва[/url] переходите на наш веб сайт. В данное текущее время дизайнеры и даже сами обладатели квартир делают из простых помещений красивые произведения искусства и весьма уютные условия. Ванная комната не является исключением, из них получаются шикарные интерьеры с наличием ванны, унитаза и раковин. В данном в каталоге Вы найдете: ванны, душевые кабины, шторки на ванну, двери, трапы, биде, системы инсталляции, раковины, полотенцесушители, светильники, аксессуары и многое другое.
Наш магазин находится по адресу: г. Москва, МКАД 41 км, 4, стр. 1. Звоните по контактному телефону 8-800-333-6327 и мы дадим Вам квалифицированную рекомендацию. В магазине Вы всегда сможете рассмотреть и потрогать собственноручно сантехнику, мебель, а не делать заказ наугад, как в других онлайн-магазинах. Также у нас работает доставка, как по городу Москва и МО, так и по всей России.
Если Вы хотели найти [url=https://sansmail.ru/skidki/dushkabiny]распродажа душевых кабин[/url] то Вы на верном пути. Мы всегда рады пойти на помощь с выбором и продать именно то, что Вы хотели получить. Также можно оформить заказ на сайте sansmail.ru или по указанному телефону – установку сантехнических предметов, приобретенных в нашем онлайн магазине. Звоните, приходите, мы будем рады с вами работать.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
I seriously love your blog.. Excellent colors & theme.
Did you build this website yourself? Please reply back as I’m planning to create
my own personal site and would love to find out where you got this
from or just what the theme is called. Thanks!
xsslot
There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made
This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
I just like the helpful information you provide in your articles
nişantaşı escort sitesinde neler var neler
sudadera juventus
I truly appreciate your technique of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark site list and will
Hi my family member I want to say that this post is awesome nice written and come with approximately all significant infos I would like to peer extra posts like this
I’m gone to convey my little brother, that he should also visit
this webpage on regular basis to take updated from most recent gossip.
Hello, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I look at your blog site in Chrome, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer,
it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick
heads up! Other then that, superb blog!
[url=http://www.one-xbet-apk-fr.com]www.one-xbet-apk-fr.com[/url]
To log in, click the “Login” button on the sanctioned website of the bookmaker and inscribe your user observations – enrol your email give a speech to and password.
one-xbet-apk-fr.com
My family every time say that I am wasting my time here at net, except I know I am getting knowledge every day
by reading such good articles or reviews.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Detaylar Önemlidir! Sağlığınızı ve güzelliğinizi ön planda tutarak ürettiğimiz ürünlerimiz, cildinizin ihtiyaçlarına mükemmel bir uyum sağlar.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
I have learn a few excellent stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for
revisiting. I wonder how a lot effort you set to create this type of excellent informative website.
This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
I’m very pleased to uncover this website. I wanted to thank you for ones time due
to this wonderful read!! I definitely savored every bit of it
and I have you bookmarked to check out new things in your site.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a colleague
who had been doing a little research on this.
And he in fact ordered me dinner because I found it for him…
lol. So let me reword this…. Thank YOU for the
meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending time to talk about this issue here on your internet site.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
You could definitely see your enthusiasm in the work you write.
The world hopes for more passionate writers such as you who are not afraid to say how they
believe. At all times follow your heart.
Do you have a spam problem on this site; I also am a blogger, and I was curious about your situation; many of us have developed some
nice methods and we are looking to trade methods with others, why not
shoot me an email if interested.
I like the helpful info you provide in your articles.
I will bookmark your blog and check again here regularly.
I’m quite certain I’ll learn many new stuff right here!
Good luck for the next!
Welcome to Tyler Wagner: Allstate Insurance, the leading insurance agency located
in Las Vegas, NV. Boasting extensive expertise in the insurance industry, Tyler Wagner and his team are dedicated to
offering top-notch customer service and tailored insurance solutions.
Whether you’re looking for auto insurance or home insurance, to life and business insurance, we’ve got you covered.
Our wide range of coverage options ensures that you
can find the perfect policy to protect what matters most.
Understanding the importance of risk assessment, we strives to provide
custom insurance quotes that reflect your unique situation. By leveraging our deep knowledge of the insurance market and
advanced underwriting processes, we ensure that you receive fair premium calculations.
Navigating insurance claims can be a daunting task, but our agency by your side, it’s a smooth process.
Our efficient claims processing system and dedicated customer service team ensure that your
claims are handled quickly and compassionately.
Moreover, we are well-versed in insurance law and regulation, ensuring that our
policies are consistently in compliance with current legal
standards. Our knowledge offers peace of mind to our policyholders, knowing that their insurance policies are robust and
dependable.
At Tyler Wagner: Allstate Insurance, we believe that insurance
is more than just a policy. It’s an essential aspect for protecting your future and securing
the well-being of your loved ones. Therefore, we make
it our mission to understand your individual needs and help
you navigate through the choice among insurance options, ensuring that
you are well-informed and comfortable with your decisions.
Selecting Tyler Wagner: Allstate Insurance signifies choosing
a trusted insurance broker in Las Vegas, NV, who values your peace of mind and quality service.
Our team isn’t just here to sell policies; we’re here to support
you in building a protected future.
So, don’t hesitate to contact us today and learn how Tyler
Wagner: Allstate Insurance can transform your insurance experience in Las Vegas, NV.
Experience the difference of working with an insurance
agency that genuinely cares about you and is dedicated to ensuring your
satisfaction.
Hello, I enjoy reading all of your article post. I like to write a little comment to support you.
What’s up, I read your new stuff regularly. Your humoristic style is witty,
keep up the good work!
Good post! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the great writing
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I am really happy to read this blog posts which consists of tons of valuable data, thanks for providing such information.
Visit my webpage: Pinterest
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this website.
It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times
it’s hard to get that “perfect balance” between usability and visual appearance.
I must say that you’ve done a excellent job with this.
Also, the blog loads very fast for me on Chrome. Outstanding Blog!
Fantastic blog post! Your insights were enlightening, and I appreciate the effort you put into sharing valuable information. Thank you.
For me its great content i really like it when i reading
larabahis giris için tıklayabilirsiniz güvenle yönlendiriliyorsunuz.
çocuk doktoru en iyi
Wow superb blog layout How long have you been blogging for you make blogging look easy The overall look of your site is magnificent as well as the content
WOW just what I was searching for. Came here by searching for Mobile Tyre Repair Maidenhead
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
I think everything posted made a ton of sense.
But, consider this, what if you wrote a catchier post title?
I am not saying your content isn’t good., however what if you added a
headline to maybe grab folk’s attention? I mean Shoulder Pain – Rotator Cuff
Tear – MTS Results is kinda plain. You ought to glance at Yahoo’s home page and watch how they create article headlines to get people to click.
You might add a video or a related picture or two to get readers interested about everything’ve written. Just my opinion, it might make your blog a little livelier.
Good day! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after browsing through a few of the articles I realized it’s new
to me. Regardless, I’m certainly pleased I stumbled upon it and I’ll be
book-marking it and checking back frequently!
Visit my homepage :: Geiger Of Geiger counter
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
buy gun and porn
Хотите попробовать игру перед тем, точно сооружать реальные ставки?
sugar rush демо – ваш предпочтение.
Играйте бесплатно и без риска,
наслаждаясь процессом и изучая особенности игрового автомата.
sugar rush на денежки Сладкая атмосфера и возможность выиграть крупные призы делают
игровой машина sugar rush одним из самых популярных среди любителей азартных развлечений.
шуга раш наигрывать – это шанс окунуться в вселенная сладких приключений и выиграть крупные призы.
Присоединяйтесь к игре и наслаждайтесь азартом!
Хотите отведать игру перед тем, чисто перекидываться на
реальные финансы? sugar rush demo – это отличный
способ представиться с игрой без риска потери средств.
Играйте задаром и наслаждайтесь процессом.
บทคัดย่อ: การศึกษานี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อสืบสานวัฒนธรรมไทยผ่านพวงหรีด.
Feel free to visit my web pɑge … วัดเทพศิรินทราวาส
Very great post. I simply stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that I’ve
truly loved surfing around your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing in your rss feed and I hope you write once more soon!
Verschillende ringen voor heren uit onze Treasure Collection zijn bijvoorbeeld uitstekend geschikt voor een stoere of juist wat meer meer klassieke uitstraling.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Ꮃhat’ѕ up tto all, how is aⅼl, I think every one іs
getting moree fr᧐m tһis web page, аnd your views аrе
gooԁ in support оf neԝ people.
Нere iis my pag طلسم
Detaylar Önemlidir! Sağlığınızı ve güzelliğinizi ön planda tutarak ürettiğimiz ürünlerimiz, cildinizin ihtiyaçlarına mükemmel bir uyum sağlar.
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I
find this topic to be actually something that I think I would never understand.
It seems too complicated and extremely broad for me.
I’m looking forward for your next post, I’ll try to
get the hang of it!
Trix – официальный сайт – сервис мгновенных игр
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
I am sure this post has touched all the internet users, its
really really nice piece of writing on building up
new weblog.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Greetings from Carolina! I’m bored to tears at work so I decided to check out your blog
on my iphone during lunch break. I enjoy the
information you present here and can’t wait to
take a look when I get home. I’m shocked at how fast your blog loaded on my cell phone ..
I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, awesome site!
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you design this website yourself
or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz respond as I’m looking to design my own blog and
would like to find out where u got this from.
appreciate it
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Sektör News Olarak Tüm Sektörleri Tek Noktada Toplamak Amacıyla Yayın Hayatımıza Başladık. Sektörel Anlık Haberleri Kaçırmamak İçin Takipte Kalın.
Unquestionably imagine that that you said. Your favourite justification appeared to be on the web the easiest thing to take into accout of.
I say to you, I certainly get irked whilst other folks
think about issues that they just do not understand about.
You controlled to hit the nail upon the top
and outlined out the whole thing without having side effect , other people could take a signal.
Will probably be again to get more. Thanks
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
That is a great tip especially to those new
to the blogosphere. Simple but very accurate information… Appreciate your sharing this one.
A must read post!
Batikslot
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
When some one searches for his essential thing, thus he/she
desires to be available that in detail, therefore that thing is maintained over
here.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an really long comment but
after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear. Grrrr…
well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say superb blog!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Быстрые игры на официальном сайте сервиса Money-X
Aw, this was a really nice post. Finding the time and actual effort to generate a good article… but what
can I say… I procrastinate a whole lot and don’t manage to get nearly
anything done.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
I really love your blog.. Pleasant colors & theme. Did you build this amazing site yourself?
Please reply back as I’m looking to create my own site and would love
to learn where you got this from or just what the theme is called.
Many thanks!
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Kurumsal dijital hizmetler sunuyoruz. Ankara web tasarım ve ankara seo ajansı ket web harikalar yaratır. ostim web tasarım
Hi friends, how is all, and what you desire to say concerning this article, in my view its actually amazing in support of me.
en iyi escort güngören escort sitesine
Just desire to say your article is as surprising. The clarity on your put up is just spectacular and that i can assume you are an expert in this subject.
Fine with your permission let me to clutch your RSS feed
to stay updated with approaching post. Thanks a million and please
carry on the rewarding work.
If you’re looking for the best HVAC contractor in Santa Fe, look no further than SouthCoast Heat & Air.
Their team of NATE-certified technicians provides unmatched services for your air
conditioning and heating systems. Their extensive experience ensures that
every job, big or small, is handled with
the utmost care and expertise. Plus, their commitment to honest and affordable pricing, along with free estimates, makes them a top choice
for all your HVAC needs. For top-notch HVAC services in Santa Fe and the Greater Galveston County, SouthCoast Heat & Air is the go-to choice.
Call them today at (281) 519-0064 to schedule an appointment.
en iyi escort sitesi olan tek site sarıyer maslak escort
Hi, just wanted to tell you, I liked this post. It was practical.
Keep on posting!
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Explore the Leading Heating & Cooling Repair Service in the Las Vegas Area
In the heart of Las Vegas, where temperatures rise, a reliable heating and cooling
system isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity.
That’s why choosing the top repair service is crucial for ensuring a
pleasant and energy-efficient home. At Best Las Vegas Heating
& Cooling, we excel in delivering first-rate solutions
that meet all your temperature control needs.
Why Choose Best Las Vegas Heating & Cooling?
Expertise: Our team comprises seasoned technicians who are proficient in the latest
heating and cooling technologies. They possess
the skills to diagnose and rectify any issues quickly, ensuring your system operates smoothly.
Reliability: We understand the urgency of temperature control problems, especially during extreme weather.
Our quick response times and competent repair services mean you won’t be left in distress for long.
Comprehensive Maintenance: Regular maintenance is key to preventing major breakdowns and lengthening the life of your heating and cooling system.
We offer thorough maintenance plans to keep your unit in top condition.
Exceptional Customer Service: At Best Las Vegas Heating & Cooling, we prioritize your satisfaction. Our team is dedicated to providing transparent
communication, honest pricing, and customized solutions
to meet your specific needs.
Affordability: Quality service shouldn’t break the bank.
We offer competitive pricing and straightforward quotes,
ensuring you get the best for your spend.
Warranty Assurance: We stand by the quality of our work.
Our services come with guarantees, giving you assurance and reliability in our
repairs.
Emergency Services: Temperature control emergencies can occur at any time.
That’s why we offer emergency repair services to handle
your urgent needs promptly.
Reputation: Our dedication to excellence is evident in the favorable reviews and recommendations
from our content customers. Trust us to deliver trustworthy
and efficient heating and cooling solutions.
Enjoy the Best in Heating & Cooling Repair
Don’t let temperature control issues disrupt your
comfort. Choose Best Las Vegas Heating & Cooling for trustworthy, productive, and cost-effective
solutions. Reach out to us today to book a service or discover more about how we can upgrade your home’s heating and cooling systems.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Pretty! This has been an incredibly wonderful post. Many thanks for supplying this information.
Uncover the Top-Rated Air Conditioning Repair Service in the
Heart of Las Vegas
In the core of Las Vegas, where temperatures climb, a dependable air conditioning system isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity.
That’s why choosing the best air conditioning repair service is
crucial for maintaining a cozy and energy-efficient home.
At Best Las Vegas Air Conditioning Repair, we are proud to offer delivering top-notch solutions that meet all your cooling needs.
Why Choose Best Las Vegas Air Conditioning Repair?
Expertise: Our team is made up of experienced technicians who
are well-versed in the latest air conditioning technologies.
They possess the skills to diagnose and fix any issues promptly,
ensuring your system runs smoothly.
Reliability: We understand the urgency of air conditioning problems, especially during harsh weather.
Our rapid response times and effective repair services mean you won’t be left in discomfort for long.
Comprehensive Maintenance: Regular maintenance is key to avoiding major breakdowns and lengthening the life of your air conditioning system.
We offer comprehensive maintenance plans to keep your unit in peak condition.
Exceptional Customer Service: At Best Las Vegas Air Conditioning Repair, we value your satisfaction.
Our team is dedicated to providing clear communication, honest pricing,
and tailored solutions to meet your specific needs.
Affordability: Quality service shouldn’t cost a fortune.
We offer competitive pricing and straightforward quotes, ensuring you get the greatest value for your money.
Warranty Assurance: We back the quality of our work. Our services come with
guarantees, giving you assurance and reliability in our repairs.
Emergency Services: Air conditioning emergencies can arise at any time.
That’s why we offer around-the-clock repair services to address your urgent needs promptly.
Reputation: Our devotion to excellence is manifested in the glowing reviews and recommendations from our satisfied customers.
Trust us to deliver trustworthy and efficient air conditioning solutions.
Enjoy the Best in Air Conditioning Repair
Don’t let air conditioning issues disrupt your comfort.
Opt for Best Las Vegas Air Conditioning Repair for dependable,
effective, and affordable solutions. Reach out to us today to arrange a service or find out more about how we can enhance your home’s air conditioning.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Hurrah! After all I got a weblog from where I be capable of truly take
useful facts concerning my study and knowledge.
you are really a excellent webmaster. The website loading velocity
is incredible. It seems that you are doing any distinctive trick.
Moreover, The contents are masterpiece. you have performed a fantastic task on this matter!
Great information. Lucky me I ran across your blog by chance (stumbleupon).
I have book-marked it for later!
Gogo casino.se – experter inom online spelunderhållning
Gogo casino.se – den ultimata guiden för kasinospelare i Sverige!
Härliga äventyr väntar på dig på Gogo casino.se, en plattform som är känd för sin expertis inom spännande spelunderhållning på nätet. Här kan du förlora dig i en värld av spänning och möjligheter, med ett brett utbud av underhållande spel att välja mellan. På Gogo casino.se får du uppleva en enastående kombination av äventyr, spänning och strategi.
På Gogo casino.se hittar du en mängd olika spelupplevelser som säkerligen kommer att tillfredsställa både nybörjare och erfarna spelare. Oavsett om du föredrar klassiska spelautomater, spännande bordsspel eller den senaste trenden inom live casino, finns det garanterat något för dig. Vår passion för innovativa spelkoncept, exceptionell grafik och sömlös spelupplevelse gör oss till en ledande aktör inom den online spelvärlden.
Med vårt dedikerade team av specialister inom spelutveckling och design kan vi erbjuda en helt unik och oslagbar spelupplevelse på Gogo casino.se. Vi strävar efter att alltid överträffa dina förväntningar och ge dig en stund av ren underhållning och spänning. Så dra nytta av vår expertis och ge dig in i en värld av möjligheter och vinnande kombinationer hos Gogo casino.se!
Gogo casino.se – En introduktion till online spelunderhållning
I denna artikel kommer vi att utforska en spännande värld av spelunderhållning på nätet. Vi kommer att dyka in i en plattform som erbjuder en rad olika spelalternativ och möjligheter till spännande upplevelser. Genom att utforska dessa möjligheter kommer du att få en överblick över allt som online spelunderhållning har att erbjuda.
Utforska spelalternativen
Du kommer att få möjligheten att utforska olika spelalternativ som erbjuds på Gogo casino.se. Här finner du allt från klassiska casinospel till populära spelautomater och spännande live casinospel. Det finns något för alla smaker och preferenser, oavsett om du är intresserad av strategiska spel eller enklare turspel. Online spelunderhållning är ett brett begrepp som omfattar en rad olika spelkategorier.
Upplev spänningen
En av de bästa sakerna med online spelunderhållning är den spänning det kan erbjuda. Genom att spela på nätet får du möjlighet att uppleva adrenalinkickar och anta utmaningar med andra spelare från hela världen. Du kan sätta dina färdigheter på prov och njuta av spännande vinster. Online spelunderhållning ger dig chansen att uppleva en äkta casinokänsla utan att behöva lämna ditt eget hem.
Vad mer har Gogo casino.se att erbjuda?
Vid sidan av de spännande spelalternativen och adrenalineupplevelserna finns det också andra fördelar med att välja Gogo casino.se. Här får du möjlighet att njuta av en säker och pålitlig spelplattform. Dina personuppgifter och transaktioner skyddas med den senaste säkerhetstekniken. Dessutom erbjuds många generösa bonusar och kampanjer som kan ge dig extra möjligheter att maximera din spelupplevelse.
Så varför vänta längre? Ta chansen att utforska en värld av online spelunderhållning hos Gogo casino.se idag!
Upptäck spännande spel och underhållning online
I dagens digitala era är möjligheterna för spännande spel och underhållning online näst intill oändliga. Internet har öppnat upp en helt ny värld av möjligheter där du kan utforska olika spelalternativ och njuta av en otrolig spelunderhållning direkt från bekvämligheten av ditt eget hem.
Utforska ett brett utbud av spel
Online-spelplattformar erbjuder en stor variation av spel, oavsett om du föredrar klassiska casinospel, spänningsfyllda spelautomater eller utmanande strategispel. Genom att utforska olika spelkategorier kan du hitta just de spel som passar din smak och förväntningar. Testa lyckan på en virtuell spelautomat, utmana vänner i en omgång online-poker eller dyk in i en fantasivärld genom ett online-äventyrsspel. Möjligheterna är oändliga och det finns något för alla.
Interagera med andra spelare
Ett av de mest spännande aspekterna av online-spel är möjligheten att interagera med andra spelare från hela världen. Genom olika funktioner såsom chatt, forum och tävlingar kan du delta i gemenskapen och kommunicera med andra spelare som delar din passion för spel och underhållning. Detta ger en social dimension till ditt spelupplevelse och kan även leda till nya vänskapsrelationer och spännande samarbetsmöjligheter.
Så oavsett om du är en erfaren spelare eller nyfiken på att utforska den online-spelvärlden, har du möjlighet att upptäcka spännande spel och underhållning online. Kom igång idag och låt dig förföras av den digitala spänningen som väntar på dig!
Gogo casino.se – Få experttips för en framgångsrik spelupplevelse
I detta avsnitt kommer vi att ge dig användbara tips och råd för att förbättra din spelupplevelse på Gogo casino.se. Vi har samlat kunskap från våra experter inom spelbranschen för att du ska kunna maximera dina vinstchanser och ha roligt samtidigt.
1. Utveckla en spelstrategi
Se till att du har en tydlig spelstrategi innan du börjar spela.
Analysera de olika spelen och välj de som passar din spelstil och kunskapsnivå.
Använd dig av sannolikhetsberäkningar och statistik för att öka dina vinstchanser.
2. Hantera din bankrulle
Sätt upp en budget för ditt spelande och håll dig till den.
Var medveten om riskerna och spela aldrig för mer pengar än du har råd att förlora.
Använd insättningsgränser och speltidsgränser för att hålla ditt spelande i kontroll.
3. Dra fördel av bonusar och kampanjer
Se till att utnyttja de bonusar och kampanjer som erbjuds av Gogo casino.se.
Läs noggrant igenom regler och villkor för att förstå vilka krav och begränsningar som gäller.
Använd bonusar och kampanjer strategiskt för att öka dina vinstmöjligheter.
4. Lär dig spelets regler och strategier
Gör dig bekant med reglerna för de spel du är intresserad av att spela.
Utforska olika strategier och tekniker som kan hjälpa dig att lyckas i spelet.
Öva på att spela gratisversioner av spelen för att förbättra din skicklighet och förståelse.
Genom att följa dessa experttips och tillämpa dem i ditt spelande på Gogo casino.se kommer du att öka dina chanser till en framgångsrik och underhållande spelupplevelse.
Lär dig strategier och taktiker för att vinna stort online
I den här artikeln kommer vi att utforska strategier och taktiker som kan användas för att maximera dina chanser att vinna stort när du spelar online. Vi kommer att gå igenom olika metoder och tekniker som har visat sig vara framgångsrika för erfarna spelare. Genom att förstå och tillämpa dessa strategier kan du öka dina vinstmöjligheter och förbättra din övergripande spelupplevelse.
Spela med förståelse och disciplin
För att vinna stort online är det viktigt att ha en grundläggande förståelse för spelen och reglerna. Innan du satsar riktiga pengar bör du ta dig tid att lära dig alla spelets aspekter och eventuella strategier som är relevanta. Det är också viktigt att vara disciplinerad när det gäller ditt spelbeteende. Sätta upp en budget och håll dig till den. Undvik att jaga förluster genom att satsa mer än du har råd att förlora. Genom att ha en klar plan och disciplin kommer du att öka dina möjligheter att vinna stort.
Använda strategier och taktiker
Erfarna spelare vet att det finns olika strategier och taktiker som kan förbättra dina vinstchanser. En vanlig strategi är att satsa på spel med hög utbetalningsprocent. Genom att välja spel med hög RTP (Return to Player) ökar du chansen att vinna över tiden. Dessutom kan du använda olika insatsstrategier som martingale eller Fibonacci-sekvensen för att optimera dina insatser och potentiella vinster. Det är viktigt att förstå hur dessa strategier fungerar och att anpassa dem efter dina egna spelpreferenser.
Sammanfattningsvis, genom att lära dig olika strategier och taktiker, spela med förståelse och disciplin, kan du öka dina möjligheter att vinna stort när du spelar online. Kom ihåg att spelande ska vara roligt och att det alltid finns en risk att förlora. Spela alltid ansvarsfullt och sätt upp gränser för dig själv. Lycka till!
Here is my web site … https://gogocasino.one
Your blog post was fantastic, thanks for the great content!
Eğer teknoloji dünyasındaki en son trendleri, derinlemesine analizleri ve yenilikçi fikirleri takip etmekten hoşlanıyorsanız, sizin için harika bir kaynak bulduk: Pandermos.net. Bu site, teknoloji tutkunlarına yönelik en güncel haberleri, rehberleri ve incelemeleri sunuyor. Pandermos.net, AI’den VR’a, akıllı ev çözümlerinden yazılım geliştirmeye kadar geniş bir yelpazede konuları kapsıyor. Eğer siz de bu konulara ilgi duyuyorsanız, Pandermos.net’i ziyaret etmenizi şiddetle tavsiye ederiz.
Here’s the revised article for Best Las Vegas HVAC Contractor using spintax to generate at least 1,
000 unique versions:
Discover the Foremost HVAC Contractor in Las Vegas
In the heart of Las Vegas, where temperatures soar,
a trustworthy HVAC system isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity.
That’s why choosing the best HVAC contractor is crucial for ensuring
a cozy and energy-efficient home. At Best Las Vegas HVAC Contractor, we excel in delivering first-rate
solutions that meet all your cooling and heating needs.
Why Opt for Best Las Vegas HVAC Contractor?
Expertise: Our team is made up of seasoned technicians who
are adept in the latest HVAC technologies.
They possess the skills to detect and fix any issues swiftly,
ensuring your system runs smoothly.
Reliability: We understand the urgency of HVAC problems, especially during harsh weather.
Our rapid response times and competent repair services
mean you won’t be left in disarray for long.
Comprehensive Maintenance: Regular maintenance is key to warding off major breakdowns and lengthening the life of
your HVAC system. We offer thorough maintenance plans
to keep your unit in peak condition.
Exceptional Customer Service: At Best Las Vegas HVAC
Contractor, we value your satisfaction. Our team is dedicated to providing
clear communication, straightforward pricing,
and tailored solutions to meet your particular needs.
Affordability: Quality service shouldn’t be expensive. We offer competitive pricing and clear quotes, ensuring
you get the best for your spend.
Warranty Assurance: We support the quality of our work.
Our services come with warranties, giving you peace of mind and certainty in our repairs.
Emergency Services: HVAC emergencies can occur at any time.
That’s why we offer emergency repair services to handle your urgent needs
promptly.
Reputation: Our commitment to excellence is evident in the favorable reviews and recommendations from
our happy customers. Trust us to deliver reliable and efficient HVAC solutions.
Benefit from the Best in HVAC Services
Don’t let HVAC issues disrupt your comfort. Opt for Best Las Vegas
HVAC Contractor for reliable, effective, and affordable
solutions. Contact us today to schedule a service or find out
more about how we can enhance your home’s heating and cooling systems.
Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara’nın Nabzını Tutan Haber Sitesi: Pandermos Haber Bölgesel haberlerde derinlik ve kalite arayanlar için Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara bölgesinin en güncel ve güvenilir haber kaynağı Pandermos, okuyucularına kesintisiz bilgi akışı sağlıyor. Yerel olaylardan, kültürel etkinliklere, ekonomiden spora bölgenin dört bir yanını kapsayan geniş bir haber yelpazesine sahip olan Pandermos, bölge halkının ve ilgi duyanların ilk tercihi olma özelliğini koruyor. Gelişmiş habercilik anlayışı ve objektif bakış açısıyla hazırlanan içerikler, Pandermos’u sadece bir haber sitesi olmanın ötesine taşıyor. Güney Marmara’nın sosyal, ekonomik ve kültürel dinamiklerini anlamak isteyen herkes için vazgeçilmez bir kaynak haline gelen bu platform, okuyucularına kaliteli ve doğrulanmış bilgiler sunmayı amaçlıyor. Bandırma, Balıkesir ve çevresinde yaşayanlar veya bu bölgeyle ilgili güncel bilgileri takip etmek isteyenler için Pandermos, aradıkları her şeyi bir arada bulabilecekleri bir portal. Ziyaretçilerine sadece haber değil, aynı zamanda bölgenin kültürel ve sosyal yaşantısına dair paha biçilmez bilgiler de sunuyor. Eğer siz de Güney Marmara’nın nabzını tutan, güncel ve objektif haberleri kaçırmak istemiyorsanız, Pandermos sizin için en doğru adres. Habercilikte kalite ve güven arayanların tercihi Pandermos, bölgesel haberler konusunda bir adım öne çıkıyor.
Discover the Top-Rated Heating & Cooling Service in Phoenix
In the heart of Phoenix, where temperatures rise, a reliable
heating & cooling system isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity.
That’s why picking the best heating & cooling service
is crucial for ensuring a cozy and energy-efficient home.
At Best Heating & Cooling Phoenix, we pride ourselves on delivering first-rate solutions that meet
all your temperature regulation needs.
Why Opt for Best Heating & Cooling Phoenix?
Expertise: Our team is made up of knowledgeable technicians who are well-versed in the
latest heating & cooling technologies. They possess the skills to identify and
fix any issues efficiently, ensuring your system functions
smoothly.
Reliability: We understand the critical nature of
heating & cooling problems, especially during intense weather.
Our prompt response times and competent repair services mean you won’t be left in distress for long.
Comprehensive Maintenance: Regular maintenance is key to avoiding major breakdowns and lengthening
the life of your heating & cooling system.
We offer thorough maintenance plans to keep your unit in prime condition.
Exceptional Customer Service: At Best Heating & Cooling Phoenix, we value your satisfaction. Our team is committed
to providing transparent communication, honest pricing, and customized solutions to meet your
individual needs.
Affordability: Quality service shouldn’t break the bank.
We offer competitive pricing and transparent quotes, ensuring
you get the greatest value for your spend.
Warranty Assurance: We support the quality of our work. Our services come with guarantees, giving you
assurance and certainty in our repairs.
Emergency Services: Heating & cooling emergencies can arise at
any time. That’s why we offer emergency repair services to handle your urgent needs promptly.
Reputation: Our devotion to excellence is manifested in the positive reviews and recommendations from our happy customers.
Trust us to deliver trustworthy and potent heating & cooling solutions.
Benefit from the Best in Heating & Cooling
Don’t let heating & cooling issues interfere with your comfort.
Opt for Best Heating & Cooling Phoenix for dependable, productive, and cost-effective
solutions. Reach out to us today to schedule a service or find out more about
how we can upgrade your home’s temperature regulation
I just like the helpful information you provide to
your articles. I’ll bookmark your weblog and test once more right here regularly.
I’m rather sure I will be informed many new stuff proper here!
Good luck for the following!
It’s ɑwesome ɗesigned for me to have a web page, which is һelpful in favor
of my experіence. thankѕ аⅾmin
Here is my homepage: robot lawn mower
As a resident of Phoenix, AZ, I can attest to the importance of
having a reliable HVAC system, especially during the scorching summer months.
After much research and personal experience, I’ve found
that choosing the best air conditioning repair service in Phoenix
is crucial for several reasons.
Firstly, expertise is key. The best repair services have highly trained technicians who are well-versed in the
latest AC technologies and can diagnose and fix issues promptly.
This ensures that your system operates efficiently, providing optimal cooling while keeping energy costs down.
Secondly, reliability is a must. In Phoenix’s extreme heat, you can’t afford to have your
AC down for long. Top-notch repair services offer quick response times and effective solutions, minimizing downtime and discomfort.
Thirdly, maintenance is essential for longevity.
Regular servicing by a reputable repair company can prevent major
breakdowns, extend the lifespan of your HVAC system, and maintain its
energy efficiency.
Other important factors to consider include customer service, affordability,
and warranty offerings. A good repair service will be transparent about costs, offer competitive pricing, and provide warranties on their work, giving you peace of mind.
Additionally, it’s wise to look for a service that offers emergency repairs, as
you never know when an issue might arise. A
company that provides 24/7 support can be a lifesaver in the middle of a hot Phoenix night.
Lastly, don’t underestimate the value of positive reviews
and referrals. Hearing about others’ experiences can provide valuable insights and help you make an informed decision.
In conclusion, choosing the best air conditioning repair service in Phoenix,
AZ, is not just about fixing immediate problems; it’s about ensuring the long-term efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of your HVAC system.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Aquí tienes el artículo reescrito usando spintax en español:
Si has estado víctima de un accidente de coche en Las Vegas, NV,
sabes lo estresante que puede ser el período posterior.
Desde lidiar con lesiones hasta navegar el complejo sistema legal, es crucial contar con el apoyo adecuado de tu lado.
Ahí es donde entran los Mejores Abogados de Accidentes
de Coche de Las Vegas, ofreciendo una experiencia inigualable como abogados de lesiones personales para abogar por
tu justicia y asegurar la compensación que tienes derecho
a recibir.
¿Por qué elegir a los Mejores Abogados de Accidentes de Coche de Las Vegas?
Estos profesionales legales no son solo letrados;
son expertos en el campo de las lesiones personales, particularmente en accidentes de auto.
Con un profundo entendimiento de las leyes de Nevada
y una dedicación hacia sus clientes, garantizan que recibas la mejor representación legal posible.
Experiencia en Accidentes de Auto: Poseen un amplio conocimiento en el manejo de colisiones de vehículos, haciéndolos hábiles
en lidiar con las complejidades de las reclamaciones por lesiones.
Asesoramiento Legal Personalizado: Cada caso es tratado con el mayor cuidado, proporcionando asesoramiento legal
personalizado para satisfacer tus necesidades específicas.
Representación Agresiva: Ya sea en negociaciones con aseguradoras
o litigios en los tribunales, estos abogados son incansables en la búsqueda de la justicia y compensación que mereces.
Apoyo Integral: Desde recopilar evidencia hasta manejar todo el papeleo legal, ofrecen apoyo integral en todo el proceso.
Sin Victoria, Sin Honorarios: La mayoría de estos abogados
operan bajo un sistema de contingencia, lo que significa que no pagas a menos
que ganen tu caso.
Asegurando Tu Futuro
Las consecuencias de un accidente de coche pueden cambiar tu vida, pero con los Mejores Abogados
de Accidentes de Coche de Las Vegas a tu lado, puedes concentrarte en tu recuperación mientras ellos manejan los aspectos legales.
Su compromiso con asegurar la máxima compensación por tus lesiones y
pérdidas garantiza que tu futuro esté protegido.
Conclusión
En la bulliciosa ciudad de Las Vegas, NV, donde los accidentes
de coche son lamentablemente comunes, tener la representación legal adecuada es crucial.
Los Mejores Abogados de Accidentes de Coche de Las
Vegas no son solo abogados de lesiones personales; son tus defensores, luchando incansablemente para garantizar que recibas la justicia
y compensación que mereces. Si necesitas asistencia legal tras un accidente de auto, no busques más allá de estos
profesionales excepcionales.
Wij hebben ook prachtige, smal vormgegeven partnerringen en trouwringen met een moderne look in geelgoud en roségoud.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this website.
It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s hard to get that “perfect balance”
between user friendliness and appearance. I must
say you have done a superb job with this. Also, the blog loads very fast for me on Chrome.
Outstanding Blog!
If you’ve been involved in a car accident in Las Vegas, NV,
you know how stressful the aftermath can be. From dealing with injuries to maneuvering through the complex legal system, it’s
crucial to have the right support on your side.
That’s where the Best Las Vegas Car Accident Lawyers come in, offering unparalleled expertise
as personal injury lawyers to advocate for your justice and
secure the compensation you are entitled to.
Why Choose the Best Las Vegas Car Accident Lawyers?
These legal professionals are not just any attorneys; they
are specialists in the field of personal injury, particularly auto accidents.
With a deep understanding of Nevada’s laws and dedication towards their clients, they ensure that you receive the best possible legal representation.
Expertise in Auto Accidents: They possess extensive knowledge
in handling accident-related injuries, making them adept at navigating
the intricacies of injury claims.
Personalized Legal Advice: Each case is treated with the utmost care, providing tailored legal advice to meet your specific needs.
Aggressive Representation: Whether it’s insurance negotiations or courtroom litigation, these attorneys are relentless in pursuing
the justice and compensation you deserve.
Comprehensive Support: From gathering evidence to managing all legal paperwork, they offer comprehensive support
throughout the entire process.
No Win, No Fee: Most of these lawyers operate on a contingency basis, meaning
you don’t pay unless they win your case.
Securing Your Future
The aftermath of a car accident can be life-changing, but with the
Best Las Vegas Car Accident Lawyers by your side, you can focus on your recovery while they handle the legal aspects.
Their commitment to securing the maximum compensation for your injuries and
losses ensures that your future is protected.
Conclusion
In the bustling city of Las Vegas, NV, where car accidents are unfortunately common, having the right
legal representation is crucial. The Best Las Vegas Car Accident Lawyers are not
just personal injury attorneys; they are
your advocates, fighting tirelessly to ensure you receive the justice and
compensation you deserve. If you’re in need of legal assistance following an auto accident, look no further than these exceptional professionals.
Explore the Top-Rated HVAC Repair Service in the Las Vegas Area
In the center of Las Vegas, where temperatures escalate, a trustworthy HVAC system isn’t
just a luxury—it’s a necessity. That’s why selecting the finest HVAC repair service is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home.
At Best Las Vegas HVAC Repair, we pride ourselves on delivering excellent solutions that meet all your cooling and heating needs.
Why Opt for Best Las Vegas HVAC Repair?
Expertise: Our team is made up of knowledgeable technicians who are well-versed in the latest HVAC technologies.
They possess the skills to detect and rectify any issues efficiently, ensuring your
system runs smoothly.
Reliability: We understand the urgency of HVAC problems, especially during
intense weather. Our quick response times and efficient repair services mean you won’t
be left in discomfort for long.
Comprehensive Maintenance: Regular maintenance is key to avoiding major breakdowns
and lengthening the life of your HVAC system. We offer extensive maintenance plans to keep your unit in prime condition.
Exceptional Customer Service: At Best Las Vegas HVAC Repair,
we value your satisfaction. Our team is
dedicated to providing open communication, honest pricing, and personalized solutions to
meet your particular needs.
Affordability: Quality service shouldn’t break the bank.
We offer reasonable pricing and straightforward quotes, ensuring you get the greatest value for your
investment.
Warranty Assurance: We support the quality of our work. Our services
come with warranties, giving you assurance and assurance in our repairs.
Emergency Services: HVAC emergencies can happen at any time.
That’s why we offer around-the-clock repair services to tackle your urgent needs promptly.
Reputation: Our devotion to excellence is evident
in the glowing reviews and referrals from our content customers.
Rely on us to deliver reliable and efficient HVAC solutions.
Enjoy the Best in HVAC Repair
Don’t let HVAC issues disturb your comfort. Select Best Las Vegas HVAC Repair for trustworthy, effective, and economical solutions.
Reach out to us today to arrange a service or find out
more about how we can upgrade your home’s heating and cooling systems.
I am in fact thankful to the owner of this site who has shared
this great article at here.
Normally I don’t read post on blogs, but I wish to
say that this write-up very compelled me to take a look
at and do so! Your writing style has been surprised me.
Thank you, very great post.
We stumbled over here coming from a different web page and thought I might check things out.
I like what I see so now i am following you. Look forward to
looking at your web page for a second time.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
takipçi hilesi
Uncover the Top-Rated HVAC Repair Service in Phoenix
In the center of Phoenix, where temperatures climb, a
trustworthy HVAC system isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity.
That’s why picking the finest HVAC repair service is crucial for maintaining a cozy and
energy-efficient home. At Best HVAC Repair Phoenix, we
excel in delivering top-notch solutions that meet all
your cooling and heating needs.
Why Select Best HVAC Repair Phoenix?
Expertise: Our team comprises experienced
technicians who are proficient in the latest HVAC technologies.
They possess the skills to detect and rectify any issues promptly, ensuring your system operates
smoothly.
Reliability: We understand the critical nature of HVAC
problems, especially during extreme weather. Our quick response times and competent repair services mean you won’t be left
in disarray for long.
Comprehensive Maintenance: Regular maintenance
is key to preventing major breakdowns and extending the life of your HVAC
system. We offer extensive maintenance plans to keep your unit
in peak condition.
Exceptional Customer Service: At Best HVAC Repair
Phoenix, we prioritize your satisfaction. Our team is dedicated to providing clear communication,
straightforward pricing, and customized solutions to meet
your specific needs.
Affordability: Quality service shouldn’t be expensive.
We offer competitive pricing and straightforward quotes, ensuring you get the
best for your spend.
Warranty Assurance: We stand by the quality of our work.
Our services come with warranties, giving you assurance and certainty in our repairs.
Emergency Services: HVAC emergencies can happen at any time.
That’s why we offer 24/7 repair services to tackle your urgent needs immediately.
Reputation: Our devotion to excellence is evident in the positive
reviews and recommendations from our content customers.
Count on us to deliver reliable and potent HVAC solutions.
Enjoy the Best in HVAC Repair
Don’t let HVAC issues disrupt your comfort. Select Best HVAC
Repair Phoenix for dependable, efficient, and cost-effective solutions.
Reach out to us today to arrange a service
or learn more about how we can enhance your home’s heating and
cooling systems.
This blog post serves as a reminder of the importance of self-care. A much-needed read!
Fastidious replies in return of this difficulty with firm arguments and describing everything regarding
that.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
constantly i used to read smaller articles or reviews that
as well clear their motive, and that is also happening with this piece of writing which I am reading at this time.
Very nice article, totally what I needed.
Elevate Your Digital Presence with Digitaleer in Phoenix
**Empowering Your Online Success in Phoenix**
When it comes to navigating the digital landscape in Phoenix, Digitaleer stands out as a premier digital marketing agency.
Situated at 310 S 4th St #652, Phoenix, Arizona 85004, our team offers a comprehensive suite of online marketing services tailored to meet
the unique needs of businesses in neighborhoods like Adobe
Highlands and Arizona Hillcrest. From SEO optimization to social media management, we specialize in enhancing your digital presence
and driving measurable results.
**Exploring the Vibrant City of Phoenix**
Phoenix, founded in 1867, is a thriving metropolis nestled in the heart
of the Sonoran Desert. With a population of 1.625 million and over 591,169 households, it’s one
of the fastest-growing cities in the United States.
Interstate 10, a major highway that spans the country, serves
as a vital artery connecting Phoenix to neighboring cities and states.
**Cost of Digital Solutions and Climate in Phoenix**
Digital solutions in Phoenix can vary depending on the
scope and complexity of the project. On average, businesses may invest
anywhere from $1,000 to $10,000 or more for comprehensive
digital marketing services. As for the climate,
Phoenix experiences a hot desert climate with scorching summers
reaching highs of 110°F (43°C) and mild winters with temperatures averaging around 60°F (16°C).
**Discovering Phoenix’s Top Points of Interest**
Explore these must-visit attractions in Phoenix:
– **Arizona Boardwalk:** An entertainment district featuring
restaurants, shops, and attractions like the OdySea Aquarium.
– **Arizona Capitol Museum:** Learn about Arizona’s rich
history and political heritage at this captivating museum.
– **Arizona Falls:** A scenic waterfall and hydroelectric plant nestled in the heart of the city.
– **Arizona Science Center:** A hands-on science museum with interactive exhibits and educational programs for all ages.
– **Butterfly Wonderland:** Immerse yourself in the enchanting world of butterflies at North America’s largest butterfly conservatory.
**Why Choose Digitaleer for Your Digital Marketing Needs**
Choosing Digitaleer means partnering with a trusted ally dedicated to
your online success. With our expertise in SEO optimization, web development, and digital advertising, we help businesses in Phoenix stand out in a competitive digital landscape.
Whether you’re looking to increase brand visibility, drive website
traffic, or boost conversions, Digitaleer delivers tailored solutions that drive real results and help you achieve
your business goals.
I’ve read a few excellent stuff here. Certainly worth bookmarking for revisiting.
I surprise how so much effort you put to make this sort of magnificent informative site.
I like whuat you gus are udually up too. This tyype of clever wirk and reporting!
Keep up thhe wonderful works guys I’ve added yyou guys
too blogroll.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Website Giri� i�in T�klay�n: Bahisal Giri�
This website was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve
found something that helped me. Appreciate it!
What’s up Dear, are you truly visiting this web site on a regular basis, if so afterward you will absolutely obtain pleasant experience.
tarafbet
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: jojobet
Greetings! Quick question that’s totally off topic.
Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My site looks weird
when viewing from my iphone4. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to fix this issue.
If you have any suggestions, please share. Many thanks!
Its like you learn my thoughts! You seem to know so much approximately this, like you wrote the e book
in it or something. I believe that you just could do with a
few p.c. to drive the message house a little bit, but instead of that, that is magnificent
blog. A great read. I will certainly be back.
DUBAI77 merupakan salah satu situs casino dan judi slot online
terpopuler bagi para pemain casino dan slot gacor karena menawarkan berbagai macam
permainan judi casino dan slot online yang lebih mudah dimainkan dan tersedia
dalam banyak jenis.
You actually make it seem really easy with your presentation but I to find this topic
to be actually one thing that I feel I’d by no means understand.
It sort of feels too complicated and very extensive for me.
I am taking a look ahead for your next submit, I’ll try to get the grasp of
it!
Great delivery. Solid arguments. Keep up the amazing work.
Wow, awesome weblog layout! How lengthy have you been running a blog for?
you make blogging glance easy. The entire look of your site is great, as smartly as the content material!
Thanks for a marvelous posting! I genuinely enjoyed reading it, you are a great author.I will remember to
bookmark your blog and will eventually come back very soon. I want to encourage one to
continue your great job, have a nice weekend!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Uncover the Leading HVAC Repair Service in Summerlin
In the center of Summerlin, where temperatures climb, a dependable
HVAC system isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity. That’s why selecting the most
reliable HVAC repair service is crucial for keeping a cozy and energy-efficient home.
At Best Summerlin HVAC Repair, we pride ourselves on delivering superior solutions that meet all your cooling and
heating needs.
Why Select Best Summerlin HVAC Repair?
Expertise: Our team is made up of skilled technicians who are proficient in the latest HVAC technologies.
They possess the skills to detect and rectify any issues quickly,
ensuring your system operates smoothly.
Reliability: We understand the critical nature of HVAC
problems, especially during extreme weather. Our quick response times and efficient repair services mean you won’t be left in distress for long.
Comprehensive Maintenance: Regular maintenance
is key to preventing major breakdowns and lengthening the life of your HVAC system.
We offer thorough maintenance plans to keep your unit in peak condition.
Exceptional Customer Service: At Best Summerlin HVAC Repair, we value your satisfaction. Our team is dedicated to providing open communication, honest
pricing, and tailored solutions to meet your individual needs.
Affordability: Quality service shouldn’t break the bank.
We offer affordable pricing and straightforward quotes, ensuring you
get the most value for your spend.
Warranty Assurance: We support the quality of
our work. Our services come with warranties, giving you confidence and certainty in our repairs.
Emergency Services: HVAC emergencies can happen at any time.
That’s why we offer 24/7 repair services to handle your urgent needs promptly.
Reputation: Our dedication to excellence is
manifested in the glowing reviews and referrals from our satisfied customers.
Rely on us to deliver trustworthy and potent HVAC solutions.
Benefit from the Best in HVAC Repair
Don’t let HVAC issues interfere with your comfort.
Choose Best Summerlin HVAC Repair for reliable, effective, and affordable solutions.
Get in touch with us today to book a service or discover more about how we can upgrade your home’s heating and cooling systems.
great issues altogether, you simply gained a brand new reader.
What may you suggest in regards to your post that you just made a few days
in the past? Any positive?
Magnificent beat ! I wish to apprentice even as you amend your website, how could i subscribe for a blog site?
The account helped me a acceptable deal. I were tiny bit acquainted of this
your broadcast provided shiny clear concept
It’s remarkable to go to see this site and reading the views of
all friends on the topic of this post, while I am also keen of getting know-how.
It’s great that you are getting ideas from this post as well as from our dialogue made here.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: jojobet
Incredible quite a lot of fantastic info.
It’s going to be finish of mine day, except before end I am reading this enormous article to improve my know-how.
It’s going to be end of mine day, but before finish I
am reading this impressive article to improve my knowledge.
Hi, its pleasant piece of writing about media print, we all be familiar with
media is a great source of data.
We stumbled over here by a different page and thought I may
as well check things out. I like what I see so now i am following you.
Look forward to looking at your web page yet again.
What a data of un-ambiguity and preserveness of precious experience on the topic of unexpected feelings.
Wow, superb blog layout! How long have you been blogging for?
you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is
wonderful, let alone the content!
I don’t even know the way I stopped up right here, but I believed this post was once great.
I do not recognise who you are but certainly you are going to a famous blogger if you
happen to aren’t already. Cheers!
Aw, this was an incredibly good post. Taking the time and actual effort to generate a very good
article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and don’t manage to get anything done.
You are so awesome! I don’t believe I’ve truly read something like this before.
So great to find somebody with a few unique thoughts on this subject matter.
Seriously.. thanks for starting this up.
This web site is one thing that is needed on the
web, someone with a bit of originality!
Today, I went to the beach with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my
4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.”
She put the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear.
She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is entirely off
topic but I had to tell someone!
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the images on this blog loading?
I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog.
Any feedback would be greatly appreciated.
I just like the helpful information you provide in your articles
It’s going to be ending of mine day, except before ending I
am reading this fantastic paragraph to improve my know-how.
I constantly emailed this blog post page to all my associates, since if like
to read it next my links will too.
Hello to all, the contents existing at this web page
are actually amazing for people experience, well, keep up the good work fellows.
Heya i am for the primary time here. I found this board and
I find It truly helpful & it helped me out
much. I am hoping to present something again and aid others
like you helped me.
I’ve been browsing online more than 4 hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like
yours. It is pretty worth enough for me. In my opinion, if all site owners and bloggers made good content as you did,
the web will be a lot more useful than ever before.
Also visit my blog สาระน่ารู้ทั่วไป
Thanks in favor of sharing such a pleasant thinking, paragraph is fastidious, thats why i have read it fully
Pretty nice post. I simply stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that I’ve really loved browsing your weblog posts.
In any case I’ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I am hoping you write once more soon!
Eğitim, refah anında bir süs, felaket sırasında bir sığınaktır. Can dostunuzun profesyonel eğitim ihtiyaçları için hemen rezervasyon oluşturun!
Heey There. I discovered your wweblog using
msn. This iss a very well written article. I will make sure to bookmark it and come back to read extra of your hrlpful info.
Thanks for the post. I’ll certainly comeback.
my web blog; Erotik Adressen
Ketika berbicara tentang permainan slot online, ada beberapa hal yang dicari oleh pemain: kesempatan menang yang besar, keamanan, dan integritas platform.
KOKI138 menonjol di antara pesaingnya dengan memberikan semua itu
dan lebih lagi.
Link exchange is nothing else but it is only
placing the other person’s website link on your page at suitable place and
other person will also do similar for you.
Fantastic beat ! I would like to apprentice even as you amend your web site, how can i subscribe for a weblog site?
The account aided me a applicable deal. I have
been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright transparent concept
In fact no matter if someone doesn’t be aware of after that its up to other users that they will assist,
so here it takes place.
I was suggested this website by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post is written by him
as no one else know such detailed about my problem.
You are incredible! Thanks!
Someone essentially help to make significantly posts I’d
state. That is the first time I frequented your web page and so far?
I amazed with the analysis you made to create
this actual submit amazing. Fantastic process!
Just desire to say your article is as astounding.
The clarity in your post is simply great and i could assume you are an expert
on this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post.
Thanks a million and please carry on the rewarding work.
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied
on the video to make your point. You clearly know what youre
talking about, why throw away your intelligence on just posting videos to your site when you could be giving us something
informative to read?
Casinoviva, siz değerli kullanıcılarımıza çevrimiçi bahis ve
casino deneyiminde üst düzey bir hizmet sunan öncü bir platformdur.
Sizinle birlikte neden bu kadar çekici ve popüler kılan özelliklere bir göz atalım.
Casinoviva giriş adresinde, size çeşitli oyunlar ve bahis seçenekleri sunarak geniş bir oyun yelpazesi sunar.
Spor bahisleri, canlı bahisler, casino oyunları, canlı casino deneyimi, slot makineleri ve daha fazlası sizi bekliyor.
Farklı zevklere hitap eden bu çeşitlilik sizin eğlencenizi ve heyecanınızı en üst düzeye çıkarmayı amaçlar.
https://vivacasinogiris.win
My coder is trying to persuade me to move to .net from PHP.
I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses.
But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on a variety of websites for about
a year and am worried about switching to another
platform. I have heard very good things about blogengine.net.
Is there a way I can transfer all my wordpress posts into it?
Any kind of help would be greatly appreciated!
Hi there! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers?
I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on.
Any recommendations?
porn.hdcom ggjgodherogg.Q89RIusDOLg
Thanks for ones marvelous posting! I genuinely
enjoyed reading it, you can be a great author.I will remember to bookmark
your blog and definitely will come back someday. I want to encourage one to
continue your great work, have a nice evening!
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs
I stumbleupon on a daily basis. It will always be exciting to read through articles from other authors and use something from their web sites.
money-x site официальный сайт
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it.
Look advanced to more added agreeable from you!
However, how could we communicate?
This is really attention-grabbing, You are a very professional
blogger. I’ve joined your feed and sit up for in the hunt for extra of your wonderful post.
Also, I have shared your site in my social
networks
Profesyonel ankara web tasarım, ankara seo, çayyolu web tasarım, çankaya web tasarım hizmetleri ankara seo
Hi there, all the time i used to check website posts here in the early hours
in the morning, for the reason that i enjoy to gain knowledge of more and more.
Everyone loves it whenever people get together and share ideas.
Great website, keep it up!
Wow quite a lot of very good knowledge!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
I got this website from my pal who shared with me on the topic of this web
page and at the moment this time I am visiting this web page
and reading very informative articles here.
I am in fact glad to glance at this website posts which contains lots of
useful information, thanks for providing these statistics.
It is truly a great and useful piece of information. I
am happy that you just shared this useful info with us. Please keep us informed like
this. Thanks for sharing.
Thanks for one’s marvelous posting! I quite enjoyed reading
it, you can be a great author. I will be sure to bookmark your blog and will eventually come back down the road.
I want to encourage you to definitely continue your great work, have a nice holiday weekend!
Appreciating the dedication you put into your blog and
detailed information you present. It’s great to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same old rehashed information. Excellent read!
I’ve saved your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
I go to see every day some websites and blogs to
read content, except this blog offers feature based writing.
Fantastic goods from you, man. I’ve understand your
stuff previous to and you are just too fantastic. I actually like what you’ve acquired here, really like
what you’re saying and the way in which you say it.
You make it entertaining and you still take care of to
keep it sensible. I cant wait to read far more from you.
This is actually a great site.
Why users still make use of to read news papers when in this technological
globe all is available on net?
Nice to you, i am Ewa. In his professional
life he a interviewer and his awesome salary has been really satisfying.
She is really fond of golf and she’s been doing it for a serious while.
Minnesota is the place he loves most but he has to move as his folks.
I for all time emailed this blog post page to all my associates, for the reason that if like to
read it then my links will too.
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
When someone writes an piece of writing he/she keeps the plan of a
user in his/her brain that how a user can be aware of it. Therefore that’s why this article is outstdanding.
Thanks!
I appreciate you sharing this blog post. Thanks Again. Cool.
Hi, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I look at your blog site in Chrome, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some
overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up!
Other then that, terrific blog!
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew
of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically
tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite
some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something
like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
naturally like your web site however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth on the other hand I will surely come again again.
Santo will be the name Excellent to be called with but I never really liked that name.
One of factors that she loves most might be to keep birds and
she’s been doing it for a significant while.
Some time ago I chose to have a home in North Carolina.
I used to be unemployed luckily I am an interviewer but I’ve already
applied for another body.
Valuable info. Fortunate me I discovered your web site unintentionally, and I’m shocked why this accident
did not came about earlier! I bookmarked it.
Unquestionably believe that which you said. Your favorite reason appeared to
be on the internet the simplest thing to be aware of.
I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while people consider worries that they plainly
do not know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and also defined out the whole thing
without having side effect , people can take a signal.
Will likely be back to get more. Thanks
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you make this website yourself
or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz reply
as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to
find out where u got this from. many thanks
Thanks on your marvelous posting! I certainly enjoyed reading it,
you might be a great author.I will make certain to bookmark your blog and will come back later in life.
I want to encourage yourself to continue your great work,
have a nice afternoon!
I will immediately take hold of your rss as I can not to find your e-mail subscription hyperlink or newsletter service.
Do you have any? Kindly let me understand so that I may subscribe.
Thanks.
İhtiyacınız olan çayyolu web tasarım, kızılay web tasarım, batıkent web tasarım, çukurambar web tasarım web sitesini yapıyoruz.
Discover the Premier Air Conditioning Repair Service in Summerlin
In the center of Summerlin, where temperatures soar, a dependable air conditioning system isn’t just
a luxury—it’s a necessity. That’s why choosing the top air conditioning repair service is crucial for keeping a pleasant and energy-efficient home.
At Best Summerlin Air Conditioning Repair,
we pride ourselves on delivering superior solutions that meet all your
cooling needs.
Why Select Best Summerlin Air Conditioning Repair?
Expertise: Our team consists of experienced technicians who are
proficient in the latest air conditioning technologies.
They possess the skills to diagnose and rectify any issues efficiently, ensuring your system functions smoothly.
Reliability: We understand the importance of air
conditioning problems, especially during harsh weather.
Our rapid response times and effective repair services mean you won’t be
left in distress for long.
Comprehensive Maintenance: Regular maintenance is key to
preventing major breakdowns and extending the life of
your air conditioning system. We offer extensive maintenance plans to keep your
unit in top condition.
Exceptional Customer Service: At Best Summerlin Air Conditioning Repair, we value your satisfaction. Our team
is devoted to providing transparent communication, honest pricing,
and tailored solutions to meet your individual needs.
Affordability: Quality service shouldn’t cost a fortune.
We offer affordable pricing and straightforward quotes, ensuring you get the greatest value for your money.
Warranty Assurance: We stand by the quality of our work. Our services come with
guarantees, giving you assurance and assurance in our repairs.
Emergency Services: Air conditioning emergencies can happen at any time.
That’s why we offer emergency repair services to address your urgent needs swiftly.
Reputation: Our commitment to excellence is reflected in the glowing reviews
and referrals from our happy customers. Rely on us to deliver trustworthy and effective
air conditioning solutions.
Benefit from the Best in Air Conditioning Repair
Don’t let air conditioning issues interfere with your comfort.
Choose Best Summerlin Air Conditioning Repair for dependable, productive,
and cost-effective solutions. Reach out to us today to book a service or learn more about how we can improve your home’s
cooling system.
Hi there! Would you mind if I share your blog with my
twitter group? There’s a lot of people that I think would
really appreciate your content. Please let me know.
Many thanks
Here is my site – Tapentadol
Excellent blog you have here but I was curious about if you knew of any community forums that cover
the same topics discussed in this article? I’d really
love to be a part of group where I can get feedback from other experienced individuals that share the
same interest. If you have any recommendations, please let me know.
Kudos!
Good post. I learn something new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon every day.
It will always be exciting to read through articles from other writers and practice something from other web sites.
Awesome blog! Do you have any suggestions for aspiring writers?
I’m planning to start my own website soon but I’m a little
lost on everything. Would you propose starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m totally overwhelmed
.. Any suggestions? Cheers!
Eğitim, refah anında bir süs, felaket sırasında bir sığınaktır. Can dostunuzun profesyonel eğitim ihtiyaçları için hemen rezervasyon oluşturun!
Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.
Howdy are using WordPress for your blog platform?
I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own.
Do you need any coding knowledge to make your own blog?
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
I all the time used to read piece of writing
in news papers but now as I am a user of net so from now I am using net for articles, thanks to web.
My partner and I stumbled over here from a different website and thought I may as
well check things out. I like what I see so now i’m following you.
Look forward to looking at your web page repeatedly.
My website เกร็ดความรู้
I enjoy reading an article that will make men and women think.
Also, thanks for allowing for me to comment!
Thanks , I’ve just been looking for information about this subject for a while and yours is the best
I’ve found out till now. However, what in regards to the bottom line?
Are you certain about the source?
A motivating discussion is worth comment.
I think that you ought to publish more about this topic, it might not be a
taboo matter but usually folks don’t discuss these topics.
To the next! Kind regards!!
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your blog. It’s a very
easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for
me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out
a designer to create your theme? Fantastic work!
Hello everyone, it’s my first visit at this web page, and
piece of writing is truly fruitful in support of me, keep up posting such articles or
reviews.
bookmarked!!, I like your blog!
hello there and thank you for your info – I’ve definitely picked up something new from right here.
I did however expertise several technical issues using this website, since I experienced to reload the website lots of times previous to I could get it
to load correctly. I had been wondering if your web hosting is OK?
Not that I am complaining, but sluggish loading instances times will sometimes affect your placement in google and can damage
your high-quality score if ads and marketing with Adwords.
Anyway I am adding this RSS to my email and could look out for a lot more of your
respective exciting content. Ensure that you update
this again soon.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: jojobet
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
This article will assist the internet visitors for building up new blog or even a blog from
start to end.
Here is my blog … เว็บความรู้
Remarkable things here. I’m very satisfied to peer your article.
Thanks a lot and I am looking forward to touch you. Will you
please drop me a mail?
There’s definately a lot to know about this subject.
I love all of the points you’ve made.
Hi! I simply would like to offer you a big thumbs up for the excellent info you’ve got right here on this
post. I will be coming back to your site for more soon.
I am really inspired together with your writing abilities
and also with the layout for your blog. Is this a paid subject
matter or did you modify it your self? Either way stay up
the excellent quality writing, it’s rare to look a great weblog
like this one today..
It’s in point of fact a nice and useful piece of info.
I am satisfied that you simply shared this helpful info with us.
Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Hello, after reading this awesome piece of writing i am as well cheerful to share my
knowledge here with friends.
If you are going for most excellent contents like myself, simply
pay a visit this web site all the time as it offers feature contents, thanks
I think this is among the most significant information for me.
And i am glad reading your article. But should remark on few
general things, The web site style is ideal, the articles is really excellent :
D. Good job, cheers
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this site.
It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s tough to get that “perfect balance”
between superb usability and visual appeal. I must say that you’ve done a fantastic job
with this. Also, the blog loads super quick for me
on Firefox. Exceptional Blog!
great content nice job
I don’t know whether it’s just me or if everybody else experiencing problems with
your website. It looks like some of the written text on your content are running off the screen. Can somebody
else please provide feedback and let me know if this is happening to them as well?
This might be a issue with my browser because I’ve had this
happen previously. Kudos
Excellent blog! Do you have any tips for aspiring writers?
I’m hoping to start my own blog soon but I’m a little lost on everything.
Would you advise starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid
option? There are so many options out there that
I’m totally overwhelmed .. Any tips? Cheers!
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords
but I’m not seeing very good success. If you know of any please share.
Thank you!
I do not know whether it’s just me or if perhaps everyone else experiencing problems with
your website. It appears as though some of the written text within your content are running off the
screen. Can someone else please comment and let me know if
this is happening to them too? This could be a problem
with my internet browser because I’ve had this happen before.
Cheers
Testogen offers a range of benefits aimed at addressing low testosterone levels in men. Firstly,
it promotes increased testosterone production, which is essential for muscle
growth and strength enhancement.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
I go to see everyday some sites and information sites to read articles, however this webpage offers feature based content.
I do consider all the ideas you have offered to your post.
They are very convincing and can certainly work.
Still, the posts are very quick for newbies. Could you please extend them a little from subsequent time?
Thank you for the post.
Hi, I do believe this is a great site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m
going to revisit yet again since i have bookmarked it.
Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
I used to be suggested this blog by way of
my cousin. I am not sure whether this put up is written by means
of him as nobody else know such exact approximately my difficulty.
You’re incredible! Thanks!
I appreciate, lead to I found exactly what I was taking a look for.
You have ended my 4 day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a nice day.
Bye
Howdy! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to
rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success.
If you know of any please share. Thank you!
Bundan sonra proqram açılır və subyektiv hesabınızı daxil etməlisiniz.
My web page mostbet Azerbaycan (https://stanicazvuka.com/pulseone1/?p=1218)
naturally like your web site however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth on the other hand I will surely come again again.
Introducing Tyler Wagner: Allstate Insurance, the leading insurance agency located in Las Vegas, NV.
Boasting extensive expertise in the insurance industry, Tyler Wagner and his team are committed to providing top-notch customer
service and tailored insurance solutions.
Whether you’re looking for auto insurance to home insurance, or even life and business insurance,
Tyler Wagner: Allstate Insurance has your back.
Our diverse coverage options ensures that you can find the right policy
to meet your needs.
Understanding the importance of risk assessment, we strives to provide personalized insurance quotes that are tailored
to your specific needs. Through leveraging our deep knowledge of the insurance
market and advanced underwriting processes, we ensure that you receive fair premium calculations.
Dealing with insurance claims can be a daunting task,
but with Tyler Wagner: Allstate Insurance by your side,
it’s a smooth process. Our streamlined claims processing system and supportive customer service team
ensure that your claims are handled quickly and compassionately.
In addition, Tyler Wagner is deeply knowledgeable about insurance law
and regulation, guaranteeing that our policies is consistently in compliance
with current legal standards. This expertise provides an added layer of security
to our policyholders, knowing that their insurance is sound and reliable.
Our agency, we believe that insurance is more than just a policy.
It’s a critical tool for protecting your future and ensuring
the well-being of those you care about. That’s
why, we take the time to get to know you and guide you through the choice among insurance options, making sure that you have all
the information you need and confident in your decisions.
Choosing Tyler Wagner: Allstate Insurance signifies choosing a trusted insurance broker in Las Vegas, NV, who prioritizes relationships and quality
service. Our team isn’t just here to sell policies;
we’re your partners in building a secure future.
Don’t wait to contact us today and learn how Tyler Wagner: Allstate Insurance can transform your
insurance experience in Las Vegas, NV. Experience the difference of working with an insurance agency
that truly cares about you and works tirelessly to
ensuring your satisfaction.
Asking questions are actually nice thing if you are not understanding something entirely, except this post offers
good understanding even.
That is really fascinating, You are an overly professional blogger.
I have joined your feed and look ahead to searching for more
of your wonderful post. Also, I have shared your
site in my social networks
When it comes to installing a tankless water heater in your home, choosing the
right plumbing company is crucial. In Phoenix, AZ, Tankless Water Heaters Phoenix stands out as the best choice for this important job.
With their expertise, commitment to quality, and customer-centric approach,
they ensure that your tankless water heater installation is
seamless and efficient.
Energy-Efficient Solutions:
Tankless water heaters are known for their energy efficiency,
and Tankless Water Heaters Phoenix specializes in providing the most eco-friendly options.
Whether you choose an electric or gas model, their team will help you select
the perfect unit that saves energy and reduces your utility bills.
Expertise in Instantaneous Hot Water Systems:
One of the key benefits of tankless water
heaters is their ability to provide instantaneous hot water on demand.
The professionals at Tankless Water Heaters Phoenix have the
knowledge and experience to install these systems correctly, ensuring you have
continuous access to hot water whenever you need it.
Space-Saving and Compact Designs:
For homeowners in Phoenix with limited space, the compact design of tankless water heaters is a significant
advantage. Tankless Water Heaters Phoenix will help you choose and install a
model that fits perfectly in your home, maximizing your space while
providing efficient hot water heating.
Advanced Temperature Control:
With advanced temperature control features,
tankless water heaters offer precise hot water management.
The experts at Tankless Water Heaters Phoenix will ensure
that your system is installed with the proper temperature settings,
giving you complete control over your hot water usage.
Eco-Friendly and Sustainable:
As a company committed to sustainability, Tankless Water Heaters Phoenix promotes eco-friendly tankless water heaters that contribute to
a greener environment. By choosing them for your installation, you’re
making a responsible choice for the planet.
Professional Venting and Installation:
Proper venting is essential for the safe operation of gas tankless water heaters.
The team at Tankless Water Heaters Phoenix is well-versed in the correct venting techniques and will ensure that your system is installed safely and efficiently.
Comprehensive Maintenance and Lifespan:
To ensure the longevity of your tankless water heater, regular maintenance is
key. Tankless Water Heaters Phoenix offers comprehensive maintenance services to keep your system running smoothly for years to come.
Conclusion:
When it comes to installing a tankless water heater in Phoenix, AZ, Tankless Water
Heaters Phoenix is the best plumbing company for the job.
With their expertise in energy-efficient, eco-friendly,
and compact systems, along with their commitment to quality installation and maintenance, you can trust that your tankless water heater
will provide reliable hot water for your home. Choose Tankless Water Heaters Phoenix
for a seamless and efficient installation experience.
seçim çalışmaları kapsamında Eskil ilçesinde esnafları ziyaret etti.
Hi I am so excited I found your weblog, I really found you by mistake, while I was
browsing on Bing for something else, Anyhow I am here now and would just like to say kudos
for a tremendous post and a all round enjoyable blog (I also
love the theme/design), I don’t have time to read it all at the moment
but I have bookmarked it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have
time I will be back to read much more, Please do keep up the superb job.
I am in fact pleased to read this blog posts which carries plenty of useful facts, thanks for providing these data.
Have you ever considered about including a little bit more than just your articles?
I mean, what you say is important and everything.
But think about if you added some great photos or video clips to give your posts more,
“pop”! Your content is excellent but with pics and
video clips, this site could definitely be one of the greatest in its field.
Very good blog!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Hi there! Would you mind if I share your blog with my twitter group?
There’s a lot of people that I think would really enjoy your content.
Please let me know. Cheers
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know a lot about
this, like you wrote the book in it or something.
I think that you can do with a few pics to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is great blog.
An excellent read. I will certainly be back.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Howdy! This is kind of off topic but I need some advice from
an established blog. Is it tough to set up your own blog?
I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty quick.
I’m thinking about creating my own but I’m not sure
where to begin. Do you have any tips or suggestions?
With thanks
en iyi psikolog ankara
Quality content is the crucial to attract the people to go
to see the web page, that’s what this web page is providing.
Hurrah, that’s what I was seeking for, what a stuff! present here
at this webpage, thanks admin of this website.
Greetings from California! I’m bored at work so I decided to check out your blog on my
iphone during lunch break. I love the information you provide here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home.
I’m amazed at how quick your blog loaded on my mobile ..
I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, very good blog!
http://Www.visualchemy.gallery/forum/viewtopic.php?id=2795782
Hi! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to
give a quick shout out and tell you I truly enjoy reading your articles.
Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that cover
the same subjects? Thanks a lot!
When you’re dealing with the aftermath of an accident, it’s crucial to have a trusted legal partner to fight
for your rights. The Best Las Vegas Personal Injury Attorneys in Las
Vegas, NV, are well-known for their skill in personal injury law and have a proven track record of
securing substantial compensation for their clients.
Why choose the Best Las Vegas Personal Injury Attorneys?
Here are just a few reasons:
Specialization in Personal Injury Cases: Our attorneys focus solely on personal injury law,
ensuring that they have the depth of knowledge and experience to
handle your case effectively.
Tenacious Advocacy: We are dedicated to advocating for your rights
and will not hesitate to take your case to trial if necessary to secure the compensation you deserve.
Comprehensive Support: From navigating medical bills to negotiating with insurance companies, our team offers comprehensive support throughout the entire legal process.
Personalized Attention: Each client receives personalized attention and tailored legal strategies to meet their
unique needs and circumstances.
No Upfront Costs: We operate on a contingency fee basis, meaning
you pay nothing unless we win your case.
Track Record of Success: Our attorneys have achieved significant settlements in compensation for
our clients, proving our ability to deliver results.
Client Satisfaction: Our commitment to client satisfaction is reflected in our numerous positive testimonials from those
we’ve helped.
If you’re looking for a personal injury attorney in Las Vegas who
will fight tirelessly for your rights and ensure you receive the compensation you deserve, look no further than the Best
Las Vegas Personal Injury Attorneys.
Contact us today for a no-obligation case evaluation and take
the first step towards securing your justice and financial
recovery.
Thanks to my father who shared with me regarding this web site, this blog is in fact awesome.
Thanks for ones marvelous posting! I truly enjoyed reading it, you can be a great author.I will always
bookmark your blog and will come back in the foreseeable future.
I want to encourage you to continue your great work, have a nice weekend!
Link exchange is nothing else however it is just placing the other person’s web site link on your
page at appropriate place and other person will also do same
in support of you.
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here The sketch is tasteful your authored subject matter stylish nonetheless you command get got an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following unwell unquestionably come further formerly again as exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this hike
Hi there! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering if you knew
where I could locate a captcha plugin for my comment form?
I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having trouble finding one?
Thanks a lot!
Right now it appears like Drupal is the best blogging platform out there right now.
(from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this post! It’s the little changes that
will make the greatest changes. Many thanks for sharing!
Wow, wonderful blog layout! How long have you been blogging for?
you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your web site is excellent,
let alone the content!
Wow, that’s what I was seeking for, what a stuff! present here
at this weblog, thanks admin of this site.
This is a topic that’s close to my heart… Many thanks! Exactly where are your contact
details though?
whoah this weblog is excellent i really like studying
your posts. Stay up the good work! You realize, a lot of individuals are looking around for this information, you can help them greatly.
Thank you, I have recently been searching for info approximately
this topic for a while and yours is the greatest
I’ve came upon so far. However, what in regards to the bottom line?
Are you sure in regards to the supply?
Everything is very open with a really clear clarification of the challenges.
It was really informative. Your website is
useful. Many thanks for sharing!
Hey very interesting blog!
We are a gaggle of volunteers and opening a brand new scheme in our community.
Your website provided us with useful information to
work on. You’ve performed an impressive job and our whole neighborhood might be thankful to you.
Hi there i am kavin, its my first occasion to commenting anyplace,
when i read this piece of writing i thought i could also make comment due
to this good post.
멋진 블로그! 당신의 테마는 맞춤 제작된 것인가요, 아니면 어딘가에서
다운로드하셨나요? 당신처럼 몇 가지 간단한
조정으로 내 블로그를 눈에 띄게 할 디자인를 가지고 있다면 정말 좋을 것 같습니다.
당신이 당신의 테마를 어디서 얻었는지 알려주세요.
감사해요
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme.
Did you create this website yourself or did you hire someone to
do it for you? Plz respond as I’m looking to design my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from.
thanks
If you desire to obtain a good deal from this post then you have to apply such techniques to your won weblog.
My coder is trying to convince me to move to .net from PHP.
I have always disliked the idea because of the costs.
But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using WordPress
on a number of websites for about a year and am anxious about switching to another platform.
I have heard great things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I
can import all my wordpress posts into it? Any
help would be greatly appreciated!
Here is my site Pinoy SEO Services Philippines
Hi! Would you mind if I share your blog with my facebook group?
There’s a lot of people that I think would really appreciate
your content. Please let me know. Cheers
You may region bets, check out effects, and manipulate your account when, anywhere.
My page: https://fhtechnicalservices.com/1xbet-nadir-r%c9%99smi-sayt-1xbet-az%c9%99rbaycan-bukmeker-kontoru-bonuslar-apk-744/
Talvez a forma mais simples, possa ser através de um chat ao vivo la cual está disponível twenty-four horas por rato e 7 dias por semana no site da 1xbet, https://kranthitravels.in/plataforma-para-apostas-online-at-the-jogos-de-cassino-no-brasil-920/,.
Link exchange is nothing else except it is only placing the other person’s weblog link on your
page at proper place and other person will also do same in support of you.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
I am sure this paragraph has touched all
the internet people, its really really pleasant article on building up new blog.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Hi! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay.
I’m absolutely enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
It’s an amazing piece of writing in favor of all the web visitors; they will get benefit
from it I am sure.
Ya, Anda dapat menggunakan metode ini untuk mengunduh video dari akun pribadi, asalkan video tersebut tidak memiliki
pengaturan privasi yang menghalangi pengunduhan.
Feel free to visit my blog post; Igram.world
Hi there, I log on to your blog on a regular basis.
Your writing style is awesome, keep doing what you’re doing!
With havin so much written content do you ever run into any issues of plagorism or copyright infringement?
My website has a lot of unique content I’ve either written myself or outsourced but it looks like a lot of it
is popping it up all over the web without my agreement.
Do you know any ways to help protect against content from being ripped off?
I’d genuinely appreciate it.
Hi! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you
using for this website? I’m getting sick and tired
of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives
for another platform. I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a
good platform.
WOW just what I was looking for. Came here by searching for can dogs eat tamales
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Сталь Маркет – это ваш надежный партнер
в сфере металлопроката.
Мы предлагаем широкий выбор металлопродукции от лидирующих производителей.
Мы предлагаем только высококачественные товары, которые соответствуют
всем стандартам и требованиям.
Наша компания предлагает следующие виды цена металлопроката в казани арматуру, двутавровую балку, круглую сталь,
квадратную сталь, стальную
полосу, стальной равнополочный уголок, стальной неравнополочный уголок,
горячекатаный швеллер, стальные
горячекатаные листы и стальную проволоку.
Преимущества выбора нашей компании,
Сталь Маркет: мы предлагаем большой ассортимент металлопроката, продукция высокого качества, доступные цены, удобную
систему оплаты, быструю доставку по всей России и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
Every weekend i used to go to see this site, as i
want enjoyment, since this this site conations in fact nice funny data too.
Undeniably imagine that which you said. Your favorite
justification appeared to be on the internet the simplest
thing to bear in mind of. I say to you, I definitely get irked whilst
other people think about worries that they just
do not know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the highest as neatly as defined out the whole thing with no need side-effects , other folks could take a signal.
Will likely be back to get more. Thanks
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
You made some good points there. I looked on the web for additional information about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this web site.
Hi there, I discovered your site by way of Google while looking for a related topic, your site came up, it appears to be like
good. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Hi there, simply become alert to your weblog thru Google,
and located that it’s truly informative.
I’m going to be careful for brussels. I will be grateful for those who continue
this in future. Lots of other folks might be benefited
from your writing. Cheers!
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this matter to be really something
that I think I would never understand. It seems too complex and very broad for me.
I am looking forward for your next post, I will try to get the hang of it!
Wedding venues play a pivotal role in the vibrant city of Las Vegas,
Nevada, where couples flock from around the world
to tie the knot. From extravagant ceremonies to intimate gatherings, the choice of wedding location sets the
tone for one of life’s most memorable events. With a plethora of options ranging from outdoor garden settings to elegant banquet halls, selecting the perfect venue is essential for creating the wedding of your dreams.
Nestled in the heart of Las Vegas, Lotus House Events offers couples
a picturesque backdrop for their special day. Founded in the same year
as the city itself, Lotus House Events is steeped in history
and tradition, mirroring the dynamic spirit of Las Vegas.
With a population of 646,790 residents and over 832,367 households, Las Vegas is a melting
pot of diverse cultures and communities. Interstate
11 traverses the city, providing convenient access
to neighboring areas and attractions.
In a city known for its extreme temperatures, ranging from scorching summers
to mild winters, home repairs are a constant consideration for residents.
Whether it’s air conditioning maintenance to beat the summer
heat or roofing repairs to withstand occasional rainfall, homeowners understand the importance of
budgeting for these expenses. On average, repairs
typically range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the nature of the work required and the contractor hired.
Exploring the vibrant tapestry of Las Vegas’s attractions,
residents and visitors alike are spoiled for choice.
From the whimsical wonders of AREA15 to the serene beauty of Aliante Nature Discovery Park, there’s something for everyone to enjoy.
Thrill-seekers can brave the Asylum-Hotel Fear Haunted House, while art enthusiasts can marvel at the exhibits in the Arts District.
History buffs can delve into the Atomic Museum’s intriguing displays, while families can create lasting memories at the
Discovery Children’s Museum.
Choosing Lotus House Events as your wedding venue in Las Vegas ensures a seamless and unforgettable experience for you
and your guests. With a variety of indoor and outdoor spaces to accommodate weddings of all sizes and styles, Lotus House Events offers
unparalleled flexibility and customization options. From expert wedding planning services to exquisite catering and
decor, every detail is meticulously curated to
bring your vision to life. With convenient packages and availability, Lotus House Events takes the stress out
of wedding planning, allowing you to focus on creating cherished memories that will last a lifetime.
betabet
Everyone loves what you guys tend to be up too. This type of clever work and exposure!
Keep up the awesome works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to our blogroll.
Check out my homepage; สาระน่ารู้ทั่วไป
great publish, very informative. I’m wondering why the other specialists of this sector
do not understand this. You must proceed your writing.
I am confident, you have a great readers’ base already!
sms onay sitesi
Luisa Odum is what you can call her but she never really liked that name.
My house is now in Minnesota. Fishing is something my husband doesn’t enjoy but I do.
My day job is a payroll clerk but I’ve already inked
another a good.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Great items from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to
and you’re simply too great. I actually like what you’ve bought right here,
really like what you are saying and the way
in which during which you are saying it. You make it enjoyable and you still take
care of to stay it wise. I can’t wait to learn far more from you.
That is really a great web site.
Valuable info. Fortunate me I discovered your website accidentally, and I’m shocked why this twist of fate didn’t
came about in advance! I bookmarked it.
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my website thus i came to
return the choose?.I am trying to to find issues to improve my site!I assume its good enough to use
some of your ideas!!
YENİDEN REFAH PARTİSİ
Your posts always provide me with a new perspective and encourage me to look at things differently Thank you for broadening my horizons
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you penning this post and also the rest of the site is very good.
Трикс играть онлайн раздача каждый день
Zonguldak’ın dinamik yapısı, ekonomik ve sosyal gelişmeleri, kültürel etkinlikleri ve daha fazlası Zonguldak Haber’de yer alıyor. Yerel siyasetten spor müsabakalarına, kültür-sanat etkinliklerinden iş dünyasındaki gelişmelere kadar geniş bir yelpazede haberleri bulabileceğiniz zonguldak haber , şehrinizi yakından takip etmenizi sağlıyor
Heya і am for the primary time һere. Ӏ came
acroѕs this board ɑnd I find It reɑlly usefuⅼ & it
helped me oᥙt mսch. I’m hoping tօ present one thing bacқ and help othеrs likie you helped
me.
Review my webpage: Porn
Asking questions are genuinely nice thing if you are not understanding
anything entirely, but this article gives pleasant understanding
even.
Hello my loved one! I wish to say that this article is
amazing, nice written and include approximately
all significant infos. I’d like to see extra posts like this .
I really like looking through an article that can make men and women think.
Also, thank you for allowing me to comment!
This is the right site for anybody who wants to understand this topic.
You understand so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I really would want to…HaHa).
You certainly put a new spin on a subject that’s been written about for many years.
Great stuff, just great!
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is
a really well written article. I will be sure to bookmark it and return to
read more of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I’ll definitely return.
moskova devlet üniversitesi ve rusyanın en iyi üniversitesi olan lomonosov, Modern laboratuvarlar, kütüphaneler, spor tesisleri ve diğer öğrenci kaynakları ile donatılmıştır. Öğrencilere sağladığı kaynaklar ve imkanlar geniş kapsamlıdır.
mobil onay
Hello! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with SEO?
I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing
very good success. If you know of any please share.
Many thanks!
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: Yabancı dizi
Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara’nın Nabzını Tutan Haber Sitesi: Pandermos Haber Bölgesel haberlerde derinlik ve kalite arayanlar için Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara bölgesinin en güncel ve güvenilir haber kaynağı Pandermos, okuyucularına kesintisiz bilgi akışı sağlıyor. Yerel olaylardan, kültürel etkinliklere, ekonomiden spora bölgenin dört bir yanını kapsayan geniş bir haber yelpazesine sahip olan Pandermos, bölge halkının ve ilgi duyanların ilk tercihi olma özelliğini koruyor. Gelişmiş habercilik anlayışı ve objektif bakış açısıyla hazırlanan içerikler, Pandermos’u sadece bir haber sitesi olmanın ötesine taşıyor. Güney Marmara’nın sosyal, ekonomik ve kültürel dinamiklerini anlamak isteyen herkes için vazgeçilmez bir kaynak haline gelen bu platform, okuyucularına kaliteli ve doğrulanmış bilgiler sunmayı amaçlıyor. Bandırma, Balıkesir ve çevresinde yaşayanlar veya bu bölgeyle ilgili güncel bilgileri takip etmek isteyenler için Pandermos, aradıkları her şeyi bir arada bulabilecekleri bir portal. Ziyaretçilerine sadece haber değil, aynı zamanda bölgenin kültürel ve sosyal yaşantısına dair paha biçilmez bilgiler de sunuyor. Eğer siz de Güney Marmara’nın nabzını tutan, güncel ve objektif haberleri kaçırmak istemiyorsanız, Pandermos sizin için en doğru adres. Habercilikte kalite ve güven arayanların tercihi Pandermos, bölgesel haberler konusunda bir adım öne çıkıyor.
왜 시청자들이 이 기술적인 세계에서 모든 것이 넷에 접근
가능한 때에도 여전히 뉴스 종이를 읽는지 여전히
사용합니까?
sanal numara
WOW just what I was searching for. Came here by searching for slots
Waay cool! Sоme extremely valid points! I apⲣreciate you penning this write-up and also the rest
of the website is extremely ցood.
Feel free to visit mmy webpage … Full Body Massage in Karachi
I’ve read several just right stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting.
I surprise how a lot attempt you place to create the sort
of wonderful informative web site.
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my web site so i came to “return the favor”.I’m attempting
to find things to enhance my site!I suppose its ok
to use a few of your ideas!!
Wedding venues play a pivotal role in the vibrant city of Las Vegas, Nevada, where couples flock from around the world to tie the knot.
From extravagant ceremonies to intimate gatherings, the choice of wedding location sets
the tone for one of life’s most memorable events.
With a plethora of options ranging from outdoor garden settings to elegant banquet halls, selecting the perfect venue is essential for creating the wedding
of your dreams.
Nestled in the heart of Las Vegas, Lotus House Events offers couples a picturesque backdrop for their
special day. Founded in the same year as the city itself, Lotus House Events is
steeped in history and tradition, mirroring the dynamic spirit of Las Vegas.
With a population of 646,790 residents and over 832,367 households,
Las Vegas is a melting pot of diverse cultures and communities.
Interstate 11 traverses the city, providing convenient access to neighboring areas and attractions.
In a city known for its extreme temperatures, ranging from
scorching summers to mild winters, home repairs are a
constant consideration for residents. Whether it’s air conditioning maintenance to beat the summer heat or roofing repairs to withstand occasional rainfall, homeowners understand the importance of budgeting for these expenses.
On average, repairs typically range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the nature of the work required and the contractor
hired.
Exploring the vibrant tapestry of Las Vegas’s attractions,
residents and visitors alike are spoiled for choice. From the whimsical wonders of AREA15 to the serene beauty
of Aliante Nature Discovery Park, there’s something for everyone to enjoy.
Thrill-seekers can brave the Asylum-Hotel Fear Haunted House, while art enthusiasts can marvel at the exhibits in the Arts District.
History buffs can delve into the Atomic Museum’s intriguing displays, while families can create lasting memories at the Discovery Children’s Museum.
Choosing Lotus House Events as your wedding venue
in Las Vegas ensures a seamless and unforgettable experience for you and your guests.
With a variety of indoor and outdoor spaces to accommodate weddings
of all sizes and styles, Lotus House Events offers unparalleled flexibility and customization options.
From expert wedding planning services to exquisite catering and
decor, every detail is meticulously curated to bring
your vision to life. With convenient packages and
availability, Lotus House Events takes the stress out of wedding planning, allowing you to focus on creating cherished
memories that will last a lifetime.
ben eğitim almak için rusyayı tercih ettim ve despa bana çok yardımcı oldu
Hello! Do you know if they make any plugins to protect against
hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any recommendations?
I all the time emailed this webpage post page to all my associates,
as if like to read it afterward my contacts will too.
Website Penipu
Your insights are a valuable contribution.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Trix – официальный сайт – Трикс играть онлайн раздача каждый день
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate
you penning this write-up and also the rest of the website is extremely good.
Aaawe very nice pooost
ZA
This website truly has all the information I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
twitter sms onay
Thanks to my father who shared with me on the topic of this blog, this blog is truly remarkable.
Kocaeli SEO hizmetleri webadamdan alınır. İzmit SEO hizmetleri
Spot on with this write-up, I seriously think this site needs a great deal more attention. I’ll probably be
back again to read more, thanks for the advice!
I think that is among the so much significant information for me.
And i am happy reading your article. But should commentary on some normal things,
The website style is great, the articles is actually great : D.
Good task, cheers
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this post! It is
the little changes that make the greatest changes.
Thanks for sharing!
Great delivery. Outstanding arguments. Keep up the good effort.
This is very interesting, You are a very skilled blogger.
I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your fantastic post.
Also, I have shared your site in my social networks!
Great post.
My spouse and I stumbled over here different web address and thought
I may as well check things out. I like what I
see so i am just following you. Look forward to looking into your web page again.
Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara’nın Nabzını Tutan Haber Sitesi: Pandermos Haber Bölgesel haberlerde derinlik ve kalite arayanlar için Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara bölgesinin en güncel ve güvenilir haber kaynağı Pandermos, okuyucularına kesintisiz bilgi akışı sağlıyor. Yerel olaylardan, kültürel etkinliklere, ekonomiden spora bölgenin dört bir yanını kapsayan geniş bir haber yelpazesine sahip olan Pandermos, bölge halkının ve ilgi duyanların ilk tercihi olma özelliğini koruyor. Gelişmiş habercilik anlayışı ve objektif bakış açısıyla hazırlanan içerikler, Pandermos’u sadece bir haber sitesi olmanın ötesine taşıyor. Güney Marmara’nın sosyal, ekonomik ve kültürel dinamiklerini anlamak isteyen herkes için vazgeçilmez bir kaynak haline gelen bu platform, okuyucularına kaliteli ve doğrulanmış bilgiler sunmayı amaçlıyor. Bandırma, Balıkesir ve çevresinde yaşayanlar veya bu bölgeyle ilgili güncel bilgileri takip etmek isteyenler için Pandermos, aradıkları her şeyi bir arada bulabilecekleri bir portal. Ziyaretçilerine sadece haber değil, aynı zamanda bölgenin kültürel ve sosyal yaşantısına dair paha biçilmez bilgiler de sunuyor. Eğer siz de Güney Marmara’nın nabzını tutan, güncel ve objektif haberleri kaçırmak istemiyorsanız, Pandermos sizin için en doğru adres. Habercilikte kalite ve güven arayanların tercihi Pandermos, bölgesel haberler konusunda bir adım öne çıkıyor.
I think other website proprietors should take this site as an model, very clean and magnificent user genial style and design, let alone the content. You’re an expert in this topic!
Thank you for every other informative site. Where else may
I get that kind of information written in such a perfect manner?
I’ve a venture that I am simply now operating on, and I’ve been at the look out for such info.
Kocaelideki SEO Ajansı, İşletme Sahiplerine müjde. Bizlerle tanışmadan karar vermeyin.
I could not resist commenting. Perfectly written!
What’s Taking place i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have discovered It
positively useful and it has helped me out loads. I am
hoping to contribute & aid other customers like its helped me.
Great job.
This information is invaluable. Where can I find out more?
Because the admin of this web site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will
be renowned, due to its feature contents.
Yüzme Kursu
This paragraph will help the internet viewers for creating new web
site or even a weblog from start to end.
thx soow muccch
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Wedding venues play a pivotal role in the vibrant city of Las
Vegas, Nevada, where couples flock from around the world to tie the
knot. From extravagant ceremonies to intimate gatherings, the choice
of wedding location sets the tone for one of life’s
most memorable events. With a plethora of options ranging from outdoor garden settings to elegant banquet halls, selecting the perfect
venue is essential for creating the wedding of your dreams.
Nestled in the heart of Las Vegas, Lotus House Events
offers couples a picturesque backdrop for their special day.
Founded in the same year as the city itself, Lotus House Events is
steeped in history and tradition, mirroring the dynamic spirit of Las Vegas.
With a population of 646,790 residents and over 832,367 households, Las Vegas is a melting pot of diverse cultures and communities.
Interstate 11 traverses the city, providing convenient access to neighboring areas and attractions.
In a city known for its extreme temperatures, ranging from scorching summers to mild winters, home
repairs are a constant consideration for residents. Whether
it’s air conditioning maintenance to beat the summer heat or
roofing repairs to withstand occasional rainfall, homeowners
understand the importance of budgeting for these expenses.
On average, repairs typically range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the nature of the work required and the contractor hired.
Exploring the vibrant tapestry of Las Vegas’s attractions,
residents and visitors alike are spoiled for choice. From the
whimsical wonders of AREA15 to the serene beauty of Aliante
Nature Discovery Park, there’s something for everyone to enjoy.
Thrill-seekers can brave the Asylum-Hotel Fear Haunted House, while art enthusiasts can marvel at the
exhibits in the Arts District. History buffs can delve into the
Atomic Museum’s intriguing displays, while
families can create lasting memories at the Discovery Children’s Museum.
Choosing Lotus House Events as your wedding venue in Las Vegas ensures a seamless
and unforgettable experience for you and your guests. With a variety of indoor and outdoor
spaces to accommodate weddings of all sizes and styles,
Lotus House Events offers unparalleled flexibility
and customization options. From expert wedding planning services to exquisite catering
and decor, every detail is meticulously curated to bring your vision to
life. With convenient packages and availability, Lotus House Events takes the stress
out of wedding planning, allowing you to focus on creating cherished memories that will last a lifetime.
As the name implies, big cock sex involves having sex with partners
who have bigger genitalia compared to the average.
This is a mental health condition where a person experiences severe feelings
of anxiety and fear related to sex. We crossed the old national bridge and saw the ruins of one of the forts built by Cortes.
I wish I could show you Jalapa just as I saw it then. The landlord taxed each passenger one
dollar for the frugal repast, and even then did not seem satisfied.
Behind closed doors and away from gaze of the
UK’s more eurosceptic media, we were known for playing a big part in launching some
of the bloc’s most ambitious projects: the single market,
the single currency (though we then opted not to
join the euro) and the EU’s enlargement eastwards. A website
may be thought of as having a rooted tree structure; we look at
this concept more closely here. The Mexican shot at everything
which was living, except the trees and flowers, but he got off for nothing
but squirrels, and the heartlessness of it made us wish they had a humane society here, for many of the poor birds were disabled, and the thought that they must live on in pain for many days was not a pleasant one.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.兒童色情
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
When someone writes an paragraph he/she maintains the thought of
a user in his/her mind that how a user can understand it.
Therefore that’s why this piece of writing is great.
Thanks!
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hey! Would you mind if I share your blog with my facebook group?
There’s a lot of folks that I think would really
appreciate your content. Please let me know.
Thank you
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.現場兒童色情片
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.儿童色情片
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Hey there, I think your website might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I look at your website in Opera, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer,
it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up!
Other then that, superb blog!
When I initially commented I appear to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on each time a
comment is added I receive four emails with the exact same comment.
Perhaps there is a means you can remove me from that service?
Thanks a lot!
At this moment I am ready to do my breakfast, after having my breakfast coming yet again to read more news.
spotify monthly listeners
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Trix – официальный сайт
Lіnk excһange iss nothihg ele but it is just placing the othedr person’s webpage link on your page at ѕuitable place and other рerson will
also do same for you.
Fastidious answer back in return of this issue with real
arguments and explaining everything regarding that.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.儿童色情片
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.現場兒童色情片
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
You could certainly see your enthusiasm within the work you write.
The sector hopes for even more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to mention how they believe.
All the time go after your heart.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.儿童色情
Ewa just what you can call me though Dislike really like being called like
the fact that. Hiring is where his primary income is due to.
What me and my family love is kayaking nonetheless can’t causes it
to be my profession really. District of Columbia has
been his home and his family loves it.
Unexpectedly lost your balance on your QIWI wallet?
We understand how disheartening that can be.
Stay calm—our company specializes in recovering your balance from QIWI wallets.
Boasting an experienced team, we’re sure we can assist you.
Contact us and let’s start the process of restoring
your balance.
sms onay hizmeti
There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon every day.
It’s always useful to read articles from other writers and use a little something from other web sites.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.儿童色情片
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.活婴儿色情片
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Wedding venues play a pivotal role in the vibrant city of
Las Vegas, Nevada, where couples flock from around the world to tie the knot.
From extravagant ceremonies to intimate gatherings, the choice of wedding location sets the tone
for one of life’s most memorable events. With a plethora of options ranging
from outdoor garden settings to elegant banquet halls, selecting the perfect venue
is essential for creating the wedding of your dreams.
Nestled in the heart of Las Vegas, Lotus House Events offers couples a picturesque backdrop for their special day.
Founded in the same year as the city itself, Lotus House
Events is steeped in history and tradition, mirroring the dynamic spirit of Las Vegas.
With a population of 646,790 residents and over 832,367 households, Las Vegas is a
melting pot of diverse cultures and communities. Interstate 11 traverses the city, providing convenient access to neighboring
areas and attractions.
In a city known for its extreme temperatures, ranging from
scorching summers to mild winters, home repairs are a constant consideration for residents.
Whether it’s air conditioning maintenance to beat the summer
heat or roofing repairs to withstand occasional rainfall,
homeowners understand the importance of budgeting
for these expenses. On average, repairs typically range from a few hundred to several thousand
dollars, depending on the nature of the work required and the contractor hired.
Exploring the vibrant tapestry of Las Vegas’s attractions, residents and visitors
alike are spoiled for choice. From the whimsical wonders of AREA15 to the serene beauty of Aliante Nature Discovery Park, there’s something for everyone to enjoy.
Thrill-seekers can brave the Asylum-Hotel Fear Haunted House,
while art enthusiasts can marvel at the exhibits in the Arts District.
History buffs can delve into the Atomic Museum’s intriguing
displays, while families can create lasting memories at the Discovery Children’s Museum.
Choosing Lotus House Events as your wedding venue in Las Vegas
ensures a seamless and unforgettable experience for you and your guests.
With a variety of indoor and outdoor spaces to accommodate weddings of
all sizes and styles, Lotus House Events offers unparalleled flexibility and customization options.
From expert wedding planning services to exquisite catering and decor,
every detail is meticulously curated to bring your vision to life.
With convenient packages and availability, Lotus House Events takes the stress out of wedding planning, allowing you to focus on creating cherished
memories that will last a lifetime.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.活婴儿色情片
kolay yemek tarifleri
görev sitesi
En İyi Kadın Blogu
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
web tasarım kocaeli hizmetleri için webadam ile tanışın
https://roommx.com/
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.兒童色情
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.現場兒童色情片
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Kocaelideki SEO Ajansı, İşletme Sahiplerine müjde. Bizlerle tanışmadan karar vermeyin.
Hi would you mind stating which blog platform you’re working with?
I’m looking to start my own blog soon but I’m having a tough time
selecting between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal.
The reason I ask is because your design and style seems different
then most blogs and I’m looking for something unique.
P.S My apologies for being off-topic but I had to ask!
En İyi Kadın Blogu
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.国产线播放免费人成视频播放
en iyi en kaliteli escort sitesi olan bağcılar güneşli escort sitesine hoşgeldiniz
With each smile, I brightened someone elses day and my own.
Greetings! Very useful advice within this post! It’s the little changes which will make the biggest changes.
Thanks a lot for sharing!
Thank you a bunch for sharing this with all people you actually know what
you’re talking approximately! Bookmarked. Please additionally discuss with my web site
=). We can have a link change arrangement among us
my blog – trusted-medications.com
Greetings from California! I’m bored to death at work so I decided to check out your blog on my iphone during lunch break.
I enjoy the knowledge you present here and can’t wait to take a look
when I get home. I’m shocked at how fast your blog loaded on my phone ..
I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, fantastic blog!
Envelop yourself in the plush luxury of our blankets, designed for those who appreciate the finer touches in home decor. With an array of textures from soft cashmere to textured wool, these blankets are an invitation to comfort, providing a stylish layer of warmth that enhances the look and feel of any room.
What’s up i am kavin, its my first time to commenting anywhere,
when i read this piece of writing i thought i could
also create comment due to this brilliant article.
What’s Going down i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have discovered It absolutely useful
and it has helped me out loads. I hope to give a contribution & help
different users like its helped me. Great job.
Very soon this site will be faous amid all blog people, due to it’s
nice articles
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
When I originally commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time
a coment is added I get four emails with the same comment.
Is there any way you can emove people from tuat
service? Appreciate it!
my blog :: 카지노사이트
Hi there just wanted to give you a quick heads up. The text in your article seem
to be running off the screen in Firefox. I’m not sure if this is a formatting issue or something to do with browser compatibility but I figured I’d post
to let you know. The layout look great though!
Hope you get the problem resolved soon. Thanks
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Excellent post. I used to be checking continuously this
weblog and I’m impressed! Extremely helpful info specially the last section 🙂 I maintain such information a lot.
I used to be seeking this certain info for a long time. Thanks and good
luck.
Situs Toto | SITUS TOTO MACAU merupakan salah ѕаtu bentuk
perjudian уаng рорulеr di Indonesia. Sеjаrаh tоtо macau dі Indonesia dіmulаі раdа tahun 1997 ketika
реrmаіnаn іnі реrtаmа kаlі dіреrkеnаlkаn oleh ѕеjumlаh pengusaha asing.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.儿童色情
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.儿童色情
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hello there, just became alert to your blog through Google, and found that it is really informative.
I’m gonna watch out for brussels. I will be grateful if you continue this in future.
A lot of people will be benefited from your writing.
Cheers!
I have been browsing online more than three hours these days, yet I never discovered any attention-grabbing article like yours.
It is lovely worth sufficient for me. In my view, if all site
owners and bloggers made excellent content as you did,
the net might be much more helpful than ever before.
Yazılım mühendisliği programları, modern programlama dilleri, yazılım geliştirme teknikleri, veri yapıları, algoritmalar ve yazılım projesi yönetimi gibi konuları kapsar. Ayrıca, öğrencilere uygulamalı deneyim kazandırmak için staj ve projelerle desteklenen pratik dersler de bulunur.
Best #8704.
I pay a quick visit every day a few websites and information sites to read
content, except this webpage presents feature based articles.
Web Tasarım Hizmetlerinde Webadam
rusyada üniversite eğitimi almak için benim tercihim despa oldu gerçekten eğitim sektörüne hakimler
Hello there, thank you for bringing this wonderful site of yours to us. I will visit more often and leave nice comments.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
It’s appropriate time to make some plans for the long run and it’s time to be
happy. I have learn this put up and if I may I desire to recommend you
some attention-grabbing things or tips. Maybe you could write next
articles referring to this article. I desire to read even more issues approximately it!
Rusya’da kiralık daire ücretleri, genellikle şehir, bölge ve dairenin özelliklerine göre değişiklik gösterir.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was
a amusement account it. Look advanced to more added
agreeable from you! However, how could we communicate?
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here.
The sketch is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish.
nonetheless, you command get got an impatience over that you wish
be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since
exactly the same nearly very often inside case you
shield this hike.
her zaman heryerde kağıthane escort sitesini ziyaret etmelisin
rus üniversitelerinin neredeyse tamamının diploması denktir rusya üniversite diploma denkliği için yetkili danışmanlara ulaşın Despa yurt disi egitim gibi.
If your first stop is a cake shop or bakery, ask a neighborhood for the nearest “pastelería.” Right here you will find desserts, pastries and
confections of all varieties. Examine together
with your local supply retailer for grass varieties and whether or not they’re provided in seed kind or sod type.
Begin conversations with others you like and type new friendships.
I like areas that assist me unwind and chill out.
As of late, engineers look to plants with burrs or creatures like the
gecko for inspiration. An aggressive, fast-growing plant that may
reach heights of 30 to forty toes (9 to 12 meters),
it shortly overtook all the things in its path, destroying native plants and the habitats they supply for wildlife, and offering nothing
in return. Make no mistake — your feet will not undergo in silence for long!
Since by-wire controls take up much less space, meaning auto designers can provide more
creature comforts akin to better leg- and head-room,
and make fewer design compromises total.
Veeery nice post ty for sharing
It’s hard to come by experienced people on this subject, but you sound like you
know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Currently it appears like Movable Type is the best blogging platform available
right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are
using on your blog?
Normally I don’t learn article on blogs, but I would
like to say that this write-up very forced me to check out and do it!
Your writing taste has been surprised me. Thank you, very
nice post.
sigara bırakma
I used to be recommended this blog through my cousin. I am now not certain whether this post is written by means
of him as no one else understand such special about my problem.
You’re incredible! Thanks!
Wonderful article! This is the type of info that are meant to
be shared around the web. Disgrace on Google for not positioning
this post higher! Come on over and consult with my website .
Thanks =)
What i do not realize is iif truth be told how you are now noot actually a lot more smartly-appreciated than you
mmay bee right now. You’re very intelligent.
Yoou understand therefore significantly when it comes
to thks matter, made me in myy opinion believe it from so many various angles.
Its lijke womedn and men don’t seem to be involved until it is something to do with Woman gaga!
Your personal stuffs excellent. Always care foor itt up!
en iyi en kaliteli escort sitesi olan sarıyet maslak escort sitesine hoşgeldiniz
It means so much to receive positive feedback and know that my content is appreciated. I strive to bring new ideas and insights to my readers.
hilarionbet ve hilarionbet giriş için doğru adrese geldim
I am extremely impressed with your writing abilities as neatly as with
the structure for your blog. Is this a paid subject matter or did you modify it yourself?
Either way keep up the excellent quality writing, it is uncommon to peer
a great blog like this one today..
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
thx sow mucch
always i used to read smaller posts that as well clear their motive,
and that is also happening with this piece of writing which I am
reading here.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.活婴儿色情片
https://betovisgiris.com/
The state lottery that has been going through delays seemed to be not really known to be. How complete you possess excitement with Powerball? The lure acquired been recently really scheduled for 11:30pn EST (04:30 GMT) on Tuesday, but relatively obtained location on Wednesday time at around 9:00an (14:00 GMT). No-one explained the jackpot in Saturday’s receive, but there possess happen to be 16 admittance go related the five significant characters to obtain $1m each. https://viet-space.com/groups/can-you-play-the-lottery-online-in-the-u-s-without-breaking-any-laws/One some other Powerball jackpot arrived at 41 consecutive pictures Only. The probabilities of making the jackpot looked like to end up being one in 292.2 million, Powerball claims.
It’s really a cool and helpful piece of information. I am glad that you simply shared this
helpful information with us. Please stay us up to date like this.
Thank you for sharing.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 現場兒童色情片
Thanks for sharing your info. I truly appreciate your efforts and I
am waiting for your next post thank you once again.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Hi tһerre I aam sso grateful I fߋund yoiur webѕite,
I really foound yoս bby error, while I wwas researchinbg oon Googѵlе ffor
something else, Regadless I amm herfe nnow annd wouⅼd
jut like tto sayy thanks forr a remarkaƅe posst aand a aall rounbd thillіng blоg (I alsdo l᧐fe the theme/deѕign), I don’t havve
tіϳme too read iit aall aat thee minute bbut I habe ƅook-marked iit andd lso addeⅾ your RSS
feeds, sso when I hwve timjе I will be bafk too reaad a llot more, Pleaae ddo keep uup thee fantastic
work.
My ᴡeeƅ blog: מקום נאמן לקהל הפרסי – לחץ כאן ובניית קישורים
constantly i used to read smaller content that as well clear their motive,
and that is also happening with this post which I am reading at this place.
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this
board and I to find It truly helpful & it helped me out a
lot. I hope to give one thing back and help others such as you aided me.
It’s amazing to pay a visit this website and reading the views of all friends
about this post, while I am also zealous of getting knowledge.
Hello, i think that i saw you visited my blog so i came to ?return the favor?.I am attempting to find things to improve my web site!I suppose its ok to use a few of your ideas!!
Hi there! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this website? I’m getting tired of WordPress because I’ve had problems with hackers and I’m looking at options for another platform. I would be fantastic if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Wow, wonderful weblog format! How long have you
been blogging for? you make blogging glance easy.
The overall glance of your site is excellent, let alone the content material!
Many thanks for being my personal tutor on this issue. My partner and i enjoyed your current article quite definitely and most of all preferred how you handled the aspect I considered to be controversial. You’re always very kind towards readers really like me and aid me in my living. Thank you.
I think everything posted made a great deal of sense. But, think about this, suppose you were to create a killer headline?
I am not suggesting your information is not solid., but suppose
you added a title to maybe get a person’s attention? I mean Shoulder
Pain – Rotator Cuff Tear – MTS Results is kinda boring. You could peek at Yahoo’s front page and watch
how they write post headlines to get viewers interested.
You might add a video or a picture or two to get readers excited about everything’ve got
to say. Just my opinion, it might make your
posts a little livelier.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
It’s really a nice and useful piece of info.
I am happy that you simply shared this helpful information with us.
Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
I know this website offers quality dependent articles and additional stuff, is there
any other site which offers these kinds of stuff in quality?
thx admin
With an astounding 10ah per KG, the DCS 12v 180ah Lithium Battery
raises the bar in lithium technology. The LiFePO4 180ah Deep Cycle Battery has a significant
continuous power output of 2000W.
I like the valuable info you provide in your articles.
I will bookmark your blog and check again here regularly.
I am quite sure I will learn a lot of new stuff right here!
Good luck for the next!
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Ford 6.7 Diesel Problems
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.儿童色情
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.兒童色情
Thanks for the auspicious writeup. It in reality was a
enjoyment account it. Look complicated to far introduced agreeable
from you! However, how could we communicate?
You could definitely see your expertise in the work you write.
The world hopes for even more passionate writers like you who aren’t
afraid to say how they believe. At all times go after your heart.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.活婴儿色情片
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.活婴儿色情片
Good answer back in return of this query with solid arguments and describing all
about that.
The content on this site is top-notch. The articles are well-written, informative, and offer a comprehensive view of the subject. I highly recommend it to anyone looking to learn more.
you are actually a good webmaster. The site loading speed is amazing.
It kind of feels that you’re doing any unique trick.
Moreover, The contents are masterwork. you’ve done a magnificent task on this matter!
Oh my goodness! Incredible article dude! Many thanks, However I am
going through problems with your RSS. I don’t understand the reason why I cannot subscribe to it.
Is there anyone else having the same RSS problems?
Anyone that knows the solution will you kindly respond?
Thanks!!
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
I always emailed this weblog post page to all my
associates, as if like to read it afterward my links will too.
My spouse and I stumbled over here different website and thought I may
as well check things out. I like what I see so now i’m following you.
Look forward to going over your web page repeatedly.
Сервис мгновенных игр Money-X на официальном сайте
sitenizi takip ediyorum makaleler Faydalı bilgiler için teşekkürler, bardak yıkama yi asla bırakmam.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.活婴儿色情片
The NBA һaѕ oρened up аn investigation іnto Toronto Raptors forward Jontay Porter ove suspected betting irregularities оveг tһe сourse
off seνeral montһs.
Reports from ESPN іndicate thаt tһe issues surround а
number of prop bets tһat involved Porter іn games οn Januarfy 26аnd Marcch 20.
ESPN’sAdrian Wojnarowski is reporting that Porter һаs
been tɑken oout of the Raptors lneup tonigfht ɑѕ a result օf this investigation.
Porter, the yoսnger brother οf Denver Nuggets star Michael Porter Jr, іs ɑ two-waʏ player for
Toronto that iѕ earning $415,000 tһіs season.
Ꭲhе irregularities strm fгom a Januаry 26 game against the LᎪ Clippers.
Prrop bets оn Porter for the night ѕet the line at 5.5 poіnts,
4.5 rebounds, 1.5 assists, ɑnd 0.5 3-pointers made.
Thoѕe wеre aⅼl of increased betting іnterest.
Ƭhe NBA is investigating Toronto Raaptors F Jontay
Porter օver betting irregularities
Porter’ѕ undеr props in twօ NBA games were thе most profitable
bets on Jan. 26 ɑnd Ⅿarch 20
Porter iѕ averaging 4.4 ρoints, 3.2rebounds,
2.3 assists, аnd 14 minutes acгoss 26 games
Porter onlʏ played four minutes before leaving tһe gqme duе to what the Raptors deemed a
rе-aggravation of an eye injury. Ηe dіdn’t score againsst
the Clippers, Ьut һad thrwe rebounds аnd one
assist – hitting the undeг on ɑll oof tһose prop lines.
According to a daily report tօ uѕers made ƅy DraftKings Sportsbook, tһe սnder
bet ߋn Porter’s ‘3-pointers maԀe’ line was thee biggest money winner fߋr bettors of
any NBA player prop on a game tһat night.
A skmilar issue reared іts head onn а Mɑrch 20 game
ɑgainst tһe Phoenix Suns. Sportsbook ѕet his line at 7.5 points and 5.5 rebounds.
But Porter played juѕt threee mіnutes befօге leaving ԁue to an illness, per team reports.
He finished wіth twօ rebounds and no pointѕ.
Oncce agɑin, the under bet on Porter’s props weг the No.
1 moneymaker fߋr player prop bets іn the NBA that night.
League policy bans players and employees fгom betting օn any league events, including
prop bets.
Punishments іnclude fines, suspensions, аnd termination oof contracts, аmong
other actions.
Porter һaѕ been inn the NBA ѕince 2021 – wһen һe made hіs
debut wіth tһе Memphis Grizzlies. Hе wеnt undrafted out of the University
of Mssouri ɑnd is averaging 4.4 points, 3.2 rebounds, 2.3 assists, and 14 mіnutes a game acros 26 games thks season.
ᏞA ClippersToronyo RaptorsNBADenver Nuggets
Ꮢead more:
Sources: NBA eyes Raptors’ Jontaay Porter fߋr betting issues – ESPN
my web blog play suckbet
Magnificent goods from you, man. I’ve take note your stuff prior to and you are
just too magnificent. I actually like what you’ve acquired right here,
certainly like what you’re saying and the way in which during which you assert it.
You are making it enjoyable and you still care for to
keep it wise. I cant wait to learn far more from
you. This is actually a great web site.
Kubota Tractor Warning Lights
This is a topic that’s near to my heart… Take care! Exactly where are your
contact details though?
Does your site have a contact page? I’m having problems locating it
but, I’d like to send you an e-mail. I’ve got some creative ideas for your blog you might be
interested in hearing. Either way, great website and I look forward to
seeing it improve over time.
Nice weblog right here! Additionally your web site rather a lot up fast!
What web host are you the usage of? Can I get your affiliate link in your host?
I desire my web site loaded up as fast as yours lol
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Poker siteleri
ankara en iyi sigara bırakma merkezi
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: Betkanyon
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: cinsel sohbet
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: bets10
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: hdxvipizle
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: Bitcoin
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: jojobet
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: nakitbahis giriş
tarafsız haberler
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my blog so i came
to “return the favor”.I’m attempting to find things
to improve my site!I suppose its ok to use a few of your ideas!!
Hakkari tarafsız gündem haberleri
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.現場兒童色情片
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.兒童色情
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.儿童色情
I really like reading through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment!
Yabancı dizi
Auton akun lataus
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.儿童色情片
Appreciation to my father who stated to me concerning this weblog,
this website is actually remarkable.
Kenworth Dash Warning Lights
Everything is very open with a clear description of the challenges.
It was truly informative. Your site is very useful.
Thank you for sharing!
Hi it’s me, I am also visiting this site regularly,
this web page is genuinely fastidious and the users are actually sharing pleasant thoughts.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
I don’t even understand how I finished up here, but
I thought this put up was great. I do not know who you might be but definitely
you’re going to a well-known blogger when you are not already.
Cheers!
Wonderful blog! Do you have any recommendations for aspiring writers?
I’m hoping to start my own site soon but I’m a little lost on everything.
Would you advise starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There
are so many options out there that I’m totally confused ..
Any recommendations? Kudos!
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Kubota Skid Steer Warning Lights
Everything is very open with a very clear explanation of the
challenges. It was truly informative. Your site
is very helpful. Thanks for sharing!
http://www.microolap.com/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https%3A%2F%2Fton.yournextphase.com%2Frt%2Fmessage.jsp%3Furl%3Dhttp%3A%2F%2F45.8.146.160
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Verdiğiniz bilgiler için teşekkürler, bardak yıkama hakkında güzel yazı olmuş.
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
güvenilir bahis siteleri
Le Kings Chance Casino propose à ses adhérents une multitude de jeux de cartes
très passionnants et très lucratifs.
Very descriptive blog, I enjoyed that a lot. Will there be a part 2?
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.兒童色情
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
heryerde her zaman büyükçekmece escort sitesi var
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your blog.
It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for
me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a designer to create your theme?
Great work!
instagram begeni satin al
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
P1316 Code
Hello colleagues, good post and nice urging commented at this place, I am actually enjoying by these.
ดอกไม้เป็นสิ่งสำคัญที่ไม่สามารถหลีกเลี่ยงในงานศพในสังคมไทย.
Нere is myy site: จัดดอกไม้ไทย
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Money-X официальный
good job awesome content thanks
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.兒童色情
What is calm?
visit us Telkom University
How to find calm in life?
visit us Telkom University
What are the benefits of finding calm?
visit us Telkom University
kocaeli seo hizmetleri ile google sıralamalarınızı yükseltin
kocaeli seo hizmetleri ile google sıralamalarınızı yükseltin
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
I appreciate you sharing this blog post. Thanks Again. Cool.
Ucuz Sanal Sunucu çok teşekkür!
Ucuz Sanal Sunucu çok teşekkür!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Have you ever thought about writing an ebook or guest authoring on other blogs?
I have a blog based on the same topics you discuss and would really like to have you share some stories/information. I know my visitors would enjoy your
work. If you’re even remotely interested, feel free to send me an email.
Trix – подними на свою мечту!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Howdy would youu mind letting me know which
webhost you’re working with? I’ve looaded your blpog in 3
different web browserss and I must sayy this blopg loads a lot faster then most.
Can you suggest a good internet hosting provider aat a reasonable price?
Many thanks, I appreciate it!
I really like reading through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment!
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.国产线播放免费人成视频播放
You could definitely see your enthusiasm within the article you write.
The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to say how they
believe. All the time go after your heart.
Great post. Iused to be checking continuously this blog and I
am inspired! Very helpful info particularly the remaining phase 🙂 I take carde of
sufh information much. I was seeking this certaain info for
a log time. Thanks and best off luck.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
en iyi escort sitesi olan avcılar escort sitesine hoşgeldiniz
I constantly emailed this weblog post page to all my friends, because
if like to read it then my friends will too.
Hi there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after going
through many of the articles I realized it’s new to me.
Nonetheless, I’m certainly delighted I stumbled upon it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back
regularly!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Undeniably consider that that you said. Your favourite reason seemed to be on the
net the easiest thing to be mindful of. I say to you, I definitely
get irked whilst other people think about concerns that they plainly do not
realize about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and also defined out the whole thing
without having side-effects , other people can take a
signal. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
A fascinating discussion is definitely worth comment.
There’s no doubt that that you should publish more on this topic, it may not be a
taboo subject but usually people do not talk about such subjects.
To the next! Many thanks!!
They ran around the corner to find that they had traveled back in time.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ .
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Link exchange is nothing else but it is only placing the
other person’s webpage link on your page at suitable place and other person will also do same in support of you.
Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara’nın Nabzını Tutan Haber Sitesi: Pandermos Haber Bölgesel haberlerde derinlik ve kalite arayanlar için Bandırma, Balıkesir ve Güney Marmara bölgesinin en güncel ve güvenilir haber kaynağı Pandermos, okuyucularına kesintisiz bilgi akışı sağlıyor. Yerel olaylardan, kültürel etkinliklere, ekonomiden spora bölgenin dört bir yanını kapsayan geniş bir haber yelpazesine sahip olan Pandermos, bölge halkının ve ilgi duyanların ilk tercihi olma özelliğini koruyor. Gelişmiş habercilik anlayışı ve objektif bakış açısıyla hazırlanan içerikler, Pandermos’u sadece bir haber sitesi olmanın ötesine taşıyor. Güney Marmara’nın sosyal, ekonomik ve kültürel dinamiklerini anlamak isteyen herkes için vazgeçilmez bir kaynak haline gelen bu platform, okuyucularına kaliteli ve doğrulanmış bilgiler sunmayı amaçlıyor. Bandırma, Balıkesir ve çevresinde yaşayanlar veya bu bölgeyle ilgili güncel bilgileri takip etmek isteyenler için Pandermos, aradıkları her şeyi bir arada bulabilecekleri bir portal. Ziyaretçilerine sadece haber değil, aynı zamanda bölgenin kültürel ve sosyal yaşantısına dair paha biçilmez bilgiler de sunuyor. Eğer siz de Güney Marmara’nın nabzını tutan, güncel ve objektif haberleri kaçırmak istemiyorsanız, Pandermos sizin için en doğru adres. Habercilikte kalite ve güven arayanların tercihi Pandermos, bölgesel haberler konusunda bir adım öne çıkıyor.
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents about olive oil polyphenol.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Hello there, I found your blog by the use of Google while searching for a similar topic, your website got here up, it appears
good. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Hi there, simply was aware of your blog through Google, and
located that it’s truly informative. I am going to
watch out for brussels. I will appreciate if you happen to proceed this in future.
Many people can be benefited out of your writing.
Cheers!
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
การรำลึกศพและการจงใจในการเฉลิมฉายแห่งวัฒนธรรมไทยมีการแสดงทั้งในพิธีและการประพันธ์ทา
Alsso visit my web paցe; Oliviath
moottorin vikavalo
kemer pirate boat | kemer pirate boat thank you for post
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . Website : https://301.com.tr/
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website : https://www.fastlinks.com.tr/
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Website : https://301.com.tr/
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website : https://301.com.tr/
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Website : https://www.fastlinks.com.tr/
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Website : https://www.fastlinks.com.tr/
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ .
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website : https://301.com.tr/
Thank you great post. Hello Administ . Website : https://www.fastlinks.com.tr/
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Website : https://www.fastlinks.com.tr/
ตรวจสอบเว็บสล็อตใหม่ล่าสุดเว็บตรงที่มีทุกสิ่งทุกอย่าง! จากเว็บเกมออนไลน์สล็อตใหม่ไปจนถึงเว็บเกมออนไลน์สล็อตที่อัปเดตล่าสุด คุณจะได้เจอกับเว็บสล็อตแตกง่ายที่สุดแล้วก็มีกราฟิกงดงาม เพลิดเพลินเจริญใจกับโบนัสสล็อตใหม่และก็ฟรีเครดิตที่จะเพิ่มช่องทางชนะของคุณ อย่าลืมทดลองเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ใหม่ๆและอ่านรีวิวเพื่อเลือกเกมส์ที่ตรงดวงใจ เว็บเกมสล็อตโทรศัพท์เคลื่อนที่ใหม่พวกนี้พร้อมให้ท่านเล่นทุกหนทุกแห่ง!
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Website : https://301.com.tr/
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website : https://www.fastlinks.com.tr/
Stunning quest there. What occurred after? Good luck!
good job
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Website : https://301.com.tr/
Hello news
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ . Website : https://301.com.tr/
I’m impressed, I must say. Rarely do I encounter a blog that’s equally educative and amusing, and without a doubt,
you have hit the nail on the head. The issue is an issue that not enough people are speaking intelligently
about. I am very happy I found this in my hunt for something
regarding this.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
I’m amazed, I have to admit. Seldom do I come across a blog that’s equally educative
and interesting, and without a doubt, you have hit the nail on the head.
The problem is an issue that not enough people are speaking intelligently
about. Now i’m very happy that I came across this
in my hunt for something concerning this.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It truly useful & it helped me out much.
I hope to give something back and aid others like you helped
me.
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents about olive oil for hair.
Hello, the articles on your site are very informative. Thank you.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
You actually make it seem so easy along with your presentation however I
find this topic to be actually one thing which I feel I would never understand.
It seems too complex and very wide for me. I’m taking a
look forward for your next publish, I’ll try to get the dangle of it!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Website : https://301.com.tr/
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website : https://www.fastlinks.com.tr/
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Website : https://www.fastlinks.com.tr/
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Website : https://www.fastlinks.com.tr/
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Website : https://www.fastlinks.com.tr/
Best #8704.
ดอกไม้งานศพเป็นธรรมเนียมที่มีมาตั้งแต่อดีต.
Here is my blog post: olivioath (https://blip.fm)
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this
blog. I really hope to view the same high-grade content by you in the future
as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my
own, personal website now 😉
Изложение правовых норм в нормативных актах
Санкция — это часть нормы права, в которой
указаны правовые последствия:
негативные либо позитивные.
В уголовном и административном праве негативные санкции сформулированы как вид и мера наказания.
Трудовое право и ряд других отраслей в качестве позитивных санкций предусматривают поощрительные меры.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader. Website : https://301.com.tr/
Wonderful goods from you, man. I have understand your stuff previous to and you’re just
too fantastic. I actually like what you’ve acquired here, certainly like what you are saying and the way in which you say it.
You make it entertaining and you still take care of to keep it wise.
I can’t wait to read far more from you. This is actually a tremendous website.
I blog frequently and I genuinely appreciate your content.
This article has really peaked my interest. I will bookmark your blog and
keep checking for new details about once per week. I subscribed to your RSS feed too.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
My brother suggested I might like this website He was totally right This post actually made my day You cannt imagine just how much time I had spent for this information Thanks
Generally I do not learn post on blogs, but I would like to say that this write-up
very compelled me to try and do so! Your writing style has been surprised me.
Thank you, quite nice post.
Very shortly this web site will be famous amid all blogging
and site-building people, due to it’s nice content
Excellent goods from you, man. I have understand your stuff previous to and you’re just extremely great.
I actually like what you’ve acquired here, really like what you are stating and the
way in which you say it. You make it entertaining and you still
take care of to keep it sensible. I can not wait to read much more from you.
This is actually a great site.
heryerde fatih escort var peki ya sen nerdesin
We’re a gaggle of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our community.
Your site provided us with helpful information to work on.
You have done a formidable job and our whole neighborhood will be thankful to you.
I am in fact thankful to the holder of this website
who has shared this enormous piece of writing at at this place.
https://accordmusic.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.semanlink.net%2Fdoc%2F%3Furi%3Dhttp%3A%2F%2F45.8.146.160
A savvy woman has revealed that ѕhe’s not buying һer daughter аn Easter egg as it’s a ‘waste оf money’.
Charlotte Deering, 27, from Manchester, is a self-proclaimed ‘cheap’ parent,
often sharing hеr frugal tips ɑnd tricks to һelp people get mօre
out of their money throughh һer Instagram page @themoneyferret.
Τhe mother-of-one, whߋ previously shared details οf hеr £2,000 wedding
soiree, including а £10 gown from Tesco,һas now revealed how she кeeps Easter so
cheap.
In a bid to kеep іt the Spring celebration ᥙnder £10, sһe’s not buyhing her daughter a chocolate eggg – and wiⅼl cookk uⲣ a roas սsing frozen meat she bough
in the sale lаst year.
Charlotte’s thriftiness іs inspired Ƅy һer mother, who struggled financially – ɑnd insists hеr family wilⅼ
remember Easter memories more thаn elaborate festivities.
Pictured ɑbove is the frugal mother, Charlotte, 27, fгom near Manchester
Charlotte Deering bought tһis reusable drinks bottle whіch ѕhe aimms tο use next
уear tоo to save some money
‘І bought ɑ reusable egg tin ɑ few years ago fоr £1.99 ɑnd I just refill tһat every yeɑr’,
she sаid.
‘It’ѕ much cheape and cost-effective han buying ɑ chocolate egg, ԝhich iѕ ɑ waste of money.
‘And I feel ⅼike they һave been extortionate tһіs yeaг and will keep goіng ᥙp in price.
‘І ɡet some individually wrapped chocolate eggs fгom tһe ρound shop ɑnd hide thеm atound the garden for her
to collect in the tin.
‘For our roast, аs lamb is veгy expensive, I usuaⅼly wait until supermarkets put on theiг offеrs.
‘Often, I check once Easter hɑs ɡone, as meat is heavily reduced tһen, aand
I’ll freeze thіs, ready tо take out and serve tһe fօllowing year.’
Charlotte, ѡho als᧐ asҝs famly membeгs to chip in towaards the roast, dvises checking tһe reduced sections rіght ɑfter Christmas tօo, too mɑke
the meal еvеn moгe wallet-friendly.
Տhe evеn һɑѕ a feԝ savvy tricks սр
her sleeve to ensure thе holiday іs enjoyable, witһout spending a
fortune.
Charlotte һas an adorable way of рresenting tһese
supermarket mini pizzas, shaping tһem with a bunny cookie cutter
‘I makе a bunny-themed lunch fоr mү little girl. I ɡеt a bunny cookie cutter аnd
usе tһiѕ on pizza, scones and sandwiches.
‘Τhen I pair it ԝith some cheap bits frοm Home Bargains, suϲh
as а reusable milk bottle – and it costs ⅼess than £4’.
Duringg the two-week school holiday, tһе stay-at-һome mother ѕays finding free activities іѕ key to tiring օut thhe kids.
Ⴝhe said: ‘We get busy planting seeds, аs іt’s super affordable and gets evеryone involved.
‘Ι maқe competitions betwеen the kids tօ ѕee which plant gгows the fastest.
‘It’ѕ so rewarding aand sߋmetimes, we use these fruits ɑnd vegetables ᴡith our roast dinner.
‘We ɑlso try t᧐ ԁo picnics and asқ eνeryone to bring sⲟmething tο
help ᴡith costs.
‘Βut thеrе arе аlso lοts of events whih are free or
low-cost. Ι check my local Facebook рage ɑnd quite a fеw pop up’.
Pictured: Charlotte’s daughter Easter lunch, ɑll assembled for
undеr a tenner
Befoгe, she used to spend £60 on Easter, but now, іt’s costing her
lеss than £10 oveгɑll.
Her biggest inspiration? Family.
Shе ɑdded: ‘Ι have grown up watching mу mum struggle for money and worry
t᧐ tһe pⲟіnt it mаԁe her ill.
‘Тhe mⲟst imрortant thing for me is the food and memoriees spent withh family, аs that’s wһat I’ll remember.
‘I know my daughter won’t miss hаving а chocolate egg from the Easter bunny and it’ѕ likely sһe wоuldn’t eat it all
ɑnyway,causing mоre waste.
‘It’ѕ all for one dаy and can stiⅼl bе made fun of witһօut forkig oսt
a fortune’.
easterTescoHome BargainsFacebook
Ꭱead mοrе:
Update Yoսr Browser | Facebook
Update Ⲩour Browser | Facebook
Ѕtߋp by my wweb pɑge … สล็อต 168
3. Mekanisme Pembayaran
Thanks for sharing your thoughts about puravive weight loss supplement.
Regards
trinkbet giriş
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation but I
find this matter to be actually something which I think I would never understand.
It seems too complicated and very broad for me. I
am looking forward for your next post, I will try to get the hang of it!
My web site integramais.com.br
hiI like your writing so much share we be in contact more approximately your article on AOL I need a specialist in this area to resolve my problem Maybe that is you Looking ahead to see you
I am not sure where you’re getting your information, but good topic.
I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more.
Thanks for wonderful info I was looking for this information for my mission.
This was beautiful Admin, thank you for your reflections, I learned a lot about olive oil gluten free.
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here.
The sketch is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish.
nonetheless, you command get bought an edginess over that you wish be delivering
the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly again since exactly the same nearly a
lot often inside case you shield this increase.
Great post.
I do not even know how I ended up here but I thought this post was great I dont know who you are but definitely youre going to a famous blogger if you arent already Cheers
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.儿童色情片
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.儿童色情
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 現場兒童色情片
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ .
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ .
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ .
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.活婴儿色情片
Hello there I am so delighted I found your site, I really found you by mistake, while I was researching on Digg for something else, Anyways I am here now and would just like to say thanks
a lot for a fantastic post and a all round interesting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to look over
it all at the minute but I have book-marked it and also
added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read more, Please do keep up
the superb jo.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website Giriş için Tıklayın:ganobet
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: Bitcoin
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Amazing blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere?
A theme like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my
blog jump out. Please let me know where you got your design. Thank
you
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .StarzBet Website : https://starzbet.com/
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . StarzBet Website : https://starzbet.com/
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . StarzBet Website : https://starzbet.com/
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . StarzBet Website : https://starzbet.com/
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . StarzBet Website : https://starzbet.com/
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Website Giriş için Tıklayın: holiganbet
Recipe and needed ingredients, and comprehensive your shopping in seconds. kıbrıs sanal market The merchandise will be sent to your doorway, and all Kıbrıs Sanal Market
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.兒童色情
ebru polat
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hi mates, how is everything, and what you would like to
say regarding this post, in my view its really amazing in favor of me.
En İyi Çelik Kapı
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Website Giriş için Tıklayın: ganobet
Lazer kesim desenleri, lazer kesici kullanarak malzemeye kesilen desenlerdir. Metal, ahşap, plastik, Çizim indir kumaş ve hatta kağıt dahil olmak üzere çok çeşitli malzemelere kesilebilirler.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.Website Giriş için Tıklayın: ganobet
Great beat ! I would like to apprentice while you
amend your site, how can i subscribe for a blog site?
The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of
this your broadcast provided bright clear concept
Wonderful article! We are linking to this particularly great article on our website.
Keep up the good writing.
thx muc admin
I am really inspired together with your writing talents and also with the structure for your blog.
Is that this a paid subject or did you modify it your self?
Anyway keep up the excellent quality writing,
it’s rare to see a nice blog like this one nowadays..
What’s Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have discovered It positively useful
and it has aided me out loads. I’m hoping to contribute & help
other customers like its helped me. Great job.
Takipteyim, cappuccino ile ilgili kaliteli ve güzel bir içerik olmuş dostum.
Kılınışı
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.儿童色情
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
When someone writes an article he/she maintains the idea
of a user in his/her mind that how a user can know it. Therefore
that’s why this piece of writing is outstdanding.
Thanks!
Have a look at my page :: 카지노사이트
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.活婴儿色情片
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
With havin so much written content do you ever run into any problems of plagorism or
copyright violation? My blog has a lot of exclusive content I’ve
either created myself or outsourced but it
appears a lot of it is popping it up all over the internet without my authorization. Do you know any
techniques to help reduce content from being stolen? I’d truly appreciate it.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 現場兒童色情片
I have read several just right stuff here. Certainly price bookmarking for revisiting.
I wonder how so much attempt you set to make this kind of fantastic informative web site.
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this blog.
I’m hoping to view the same high-grade content from you in the future as well.
In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated
me to get my own, personal blog now 😉
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.儿童色情片
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Great info. Lucky me I discovered your site by chance (stumbleupon).
I’ve saved it for later!
Superb blog! Do you have any tips and hints for aspiring writers?
I’m planning to start my own website soon but I’m a little lost on everything.
Would you suggest starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many options out
there that I’m completely confused .. Any recommendations?
Appreciate it!
İçeriklerinize düzenli olarak uğrayacağım, tebrikler.
I do not even know how I ended up here but I thought this post was great I dont know who you are but definitely youre going to a famous blogger if you arent already Cheers
In the war to preserve a secure and also hygienic home atmosphere, bug control services participate in a critical duty. Excess insects like rats, bugs, and also also creatures can easily present severe risks to each property and also health and wellness if left out of hand, https://www.nextbizthing.com/saint-maur-des-foss%C3%A9s/home-20-garden/izi-nuisibles-exterminateur-de-nuisibles-%C3%A0-paris.
https://www.kalebet-giris.com/
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
izmir haberleri
Bursa Hayat Gazetesi
Son mühür gazetesi
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
İlk haber gazetesi
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Profilinizin popülerliğini arttırmak için Sosyal Mavi’yi keşfedin! Hızlı, güvenilir ve etkili bir şekilde takipçi kazanın.
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
Sitenizdeki bilgiler için teşekkür ederim.
Hello, I’d appreciate it if you could review and approve my blog post. Thank you.
It’s amazing for me to һave a website, which is
beneficial іn favor of my know-how. thanks admin
Sosyal Mavi ile takipçi sayınızı arttırın ve profilinizin etkileyiciliğini artırın! Hemen keşfedin.
Trix – подними на свою мечту!
Kalıcı Makyaj
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
thx muc admin
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.兒童色情
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Website Giriş için Tıklayın: hacklink panel
Kocaeli Web Tasarım Hizmetlerini Kocaeli Dijitalde deneyimleyin
Goоd post! We are liking to thi partcularly great cointent on our website.
Ꮶeep up thhe gгeat writing.
Here is my ρage … ไวน์ หวาน
Hi, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and i was just curious if you get a
lot of spam remarks? If so how do you reduce it, any plugin or
anything you can suggest? I get so much lately it’s driving
me mad so any help is very much appreciated.
What a stuff of un-ambiguity and presedrveness of valuable knowledge concerning unexpected emotions.
Also visit my page – praca malarz finlandia
В нашем казино вы найдете множество удивительных историй, которые помогут вам
узнать новые миры и одолеть в самых захватывающих битвах.
Присоединяйтесь к нам сегодня и откройте новые
горизонты развлечений! Следите за нашими акциями и
турнирами, дабы не упустить
свою возможность выиграть крупный приз.
Мы стараемся предложить нашим игрокам
исключительно лучшее, почему
наши бонусные акции и турниры –
это всегда интересные сюрпризы и выигрыши!
Зарегистрировавшись в Kent Casino, вы получите доступ к самым популярным играм на рынке.
От классических слотов до живых
дилеров и настольных игр – у нас поглощать все,
дабы удовлетворить ваши азартные потребности.
Играйте в свои любимые игры в
любое период и в любом месте! У нас
уничтожать удобное мобильное приложение, которое позволяет вам
услаждаться азартом даже в пути.
В нашем казино вы найдете куча удивительных историй, которые помогут вам постигнуть
новые миры и осилить в самых захватывающих битвах.
Присоединяйтесь к нам ныне и
откройте новые горизонты развлечений!
Мы беспрерывно проводим различные акции для
наших игроков, чтобы предложить им еще больше выгодных возможностей.
Это могут быть бонусы на пополнение, фриспины или уникальные промо-коды, которые позволят
вам получить дополнительные бонусы и приятные сюрпризы.
Ꭲhis webnsite ѡas… how ddo I say it? Relevant!!
Fially I’vе foᥙnd ѕomething that heelped
me. Apρreciate it!
Aⅼso visit my blkog post; ไวน์หวาน moscato
Great information shared.. really enjoyed reading this post thank you author for sharing this post .. appreciated
herkesin ihtiyaç duyduğu sms onay yapan bir siteyi sizlerle paylaşacağım çok başarılı buluyorum
İçerikleriniz ilgimi çekti, tebrikler.
Sitenizin içerikleri gerçekten değerli.
Sosyal Mavi ile sosyal medya hesaplarınızı daha etkili hale getirin! Takipçi sayınızı artırın ve içeriğinizin daha geniş bir kitleye ulaşmasını sağlayın.
We are a bunch of volunteers and starting a brand new scheme in our community.
Your website provided us with valuable information to
work on. You’ve performed an impressive task and our entire group can be grateful to you.
Ꮐreat blog here! Also your site loads սⲣ ѵery fast!
Wһаt wweb host агe yoᥙ using? Ⅽan І
ɡet youг affiliate link too yoսr host? Ι wish my site loaded ᥙp аs quikckly aas
ʏours lol
Ꮋere is my web-site; ขายส่งไวน์
Hi, I ddo believe this is a grreat web site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am goinbg to
come back oce again sinnce i have book mafked it. Money annd freedom
is the best way to change, mmay yyou be rich and continue to help othsr people.
Wow tons of helpful data!
Also visit my web-site – https://casibomgiris.poker/
you are in reality a good webmaster The website loading velocity is amazing It sort of feels that youre doing any distinctive trick Also The contents are masterwork you have done a fantastic job in this topic
Great article.
büyük götlü porn
There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you 231236
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
dublajlı romantik film izle
İçerikleriniz beni etkiledi, teşekkürler.
Hi, could you please review my blog post and approve it for publication? Wishing you a productive day.
Harika site, içeriklerinize bayıldım!
Good day, could you please review my blog post and approve it for publication? Thank you.
Sosyal Mavi, sosyal medya stratejinizi güçlendirmenin en akıllıca yolu! Şimdi keşfedin ve takipçi sayınızı artırın.
Hi, I’m submitting my blog post for your review and approval. Wishing you a great day.
Your blog post never ends to impress me. Every blog post is actually a testament to your commitment to premium.
Visit my site Ron Spinabella
Hi, could you please review and approve my blog post? Wishing you a productive day.
AMIN EVLADI SİTELERİ
Sosyal Mavi, sosyal medya stratejinizi güçlendirmenin en akıllıca yolu! Şimdi keşfedin ve takipçi sayınızı artırın.
whoah thiѕ blog iѕ fantastic i like studying уour articles.
Stay uρ the good wоrk! You understand, lots oof persons aгe lookіng
around foг this info, yоu couⅼԀ aid them ɡreatly.
Ꮋave а look аt mү paցe … ไวน์ rosso ราคา (Carlota)
İçerikleriniz ilginçti, teşekkürler.
Hello, could you please review my blog post and approve it for publication? Thanks.
Unquestionably consider that that you said.
Your favorite reason appeared to be at the net the
easiest factor to take into accout of. I say to you, I certainly get irked at the
same time as people consider concerns that they just don’t
know about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the highest and also defined out the whole
thing without having side-effects , other folks can take a signal.
Will likely be again to get more. Thanks
Teşekkürler, içerikleriniz çok bilgilendirici.
Profilinizin popülerliğini arttırmak için Sosyal Mavi’yi keşfedin! Hızlı, güvenilir ve etkili bir şekilde takipçi kazanın.
BLONDE PORN
I just wanted to extend my heartfelt thanks for sharing this enlightening article. It’s made a significant impact.
Good day, could you please review my blog post and approve it for publication? Thanks.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
My secretary is the only person who truly understands my stamp-collecting obsession.
Kocaeli dijital web tasarım firması ile modern web site sahibi olun.
Profilinizin popülerliğini arttırmak için Sosyal Mavi’yi keşfedin! Hızlı, güvenilir ve etkili bir şekilde takipçi kazanın.
Takipçi sayınızı anında arttırmanın en hızlı yolu! Sosyal Mavi ile sosyal medya başarınızı garanti altına alın.
Kocaeli İzmit’te yer alan ofisimizde, mimari projeleriniz için 3D tasarım, 3D modelleme ve danışmanlık hizmetleri vermekteyiz. Tasarımlarımızda Doğa, İnsan ve Teknoloji kavramlarını aynı anda Sibernetik olarak ele alıyoruz. Güçlü, konforlu, kullanılışlı ve estetik mimari tasarımlar için bizimle iletişime geçebilirsiniz.
We absolutely love your blog and find nearly all of your post’s to be just what I’m looking
for. can you offer guest writers to write content in your
case? I wouldn’t mind composing a post or elaborating on a few of the subjects you write regarding here.
Again, awesome web site!
Your vulnerability and authenticity are truly inspiring.
We’re a group of volunteers and oρening a new scxheme in our community.
Уouг site ρrovided us with valuable іnformation to ork ᧐n. Уou’ve
donhe an impressive job and օur entire community ѡill be grateful
to you.
Feell frde to surf tߋ my web site :: ไวน์หวานๆ
Hey I know thiѕ is off topic Ьut I was wondering іf you knew of
ɑny widgets Ӏ couⅼd ɑdd to my blog thast automatically tweet mү newest twitter updates.
Ӏ’ve been looking for ɑ plug-іn like tnis fоr qᥙite some time and waѕ hoping mɑybe you
would have some experience with something liқe this.Plеase ⅼеt me
know if you run into anything. I truⅼy enjoy reading youг blog ɑnd I looҝ forward to your neѡ updates.
My homepaɡе ไวน์ราคา
TEENS 18 PORN VIDEOS
What’s Taking ρlace i аm new tto tһis, I stumbled ᥙpon this I have found It
positively uuseful ɑnd it hɑs aided me out loads. I am hping to contribue & assist other
users lіke its helped me. Grеat job.
My web blog :: ไวน์แดงหวาน แนะนํา
Disney Plus dizi indir
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Hey there! Quick question that’s totally off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile
friendly? My weblog looks weird when viewing from
my iphone. I’m trying to find a template or plugin that might be able to fix this issue.
If you have any suggestions, please share. Thanks!
Tһanks very іnteresting blog!
Hɑve a looқ ɑt myy web site :: rosso dolce ราคา
I ԝat to too thɑnk y᧐u for this ood rеad!!
I certainly enjoyed every bit оf it. Ι hɑѵe you saved
aѕ a favorite to check ᧐ut neѡ stuff you post…
Herre іѕ my homepage … wine dee dee
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Hiya very nice website!! Man .. Excellent .. Wonderful ..
I’ll bookmark your website and take the feeds also? I’m happy to search out a lot of helpful
info here in the put up, we want work out more techniques
on this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
You’re a true wordsmith.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
promokodbar.ru
My brother suggested I might like this blog. He
was totally right. This post actually made my day.
You cann’t imagine just how much time I had spent for this information! Thanks!
I got this web site from my buddy who shared with me on the topic
of this site and now this time I am visiting this website and reading very informative posts at this place.
This post is so helpful. I learned a lot from it.
I am truly thankful to the owner of this web site who has shared this fantastic piece of writing at at this place.
Kocaeli İzmit’te yer alan ofisimizde, mimari projeleriniz için 3D tasarım, 3D modelleme ve danışmanlık hizmetleri vermekteyiz. Tasarımlarımızda Doğa, İnsan ve Teknoloji kavramlarını aynı anda Sibernetik olarak ele alıyoruz. Güçlü, konforlu, kullanılışlı ve estetik mimari tasarımlar için bizimle iletişime geçebilirsiniz.
Abant Turu
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
MUSTAFA ZAVLAK CUMHURİYET MAHALLESİNİ ZİYARET ETTİ
Lembre-se que é importante buscar bases seguras para teorizar suas ideias iniciais e dar subsídios aos
seus conhecimentos epistemológicos (não tem mágica pessoal, é leitura mesmo!
Hi there, I’m kindly requesting you to review and publish my blog post. Waiting for your feedback.
Sosyal medya hesaplarınızı büyütmek artık çok kolay! Sosyal Mavi ile gerçek takipçi kazanın.
You made some really good points there. I checked on the net for more information about the issue and
found most people will go along with your views on this web
site.
Also visit my homepage: promotion
Hey! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone 3gs!
Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to
all your posts! Carry on the outstanding work!
This is really interesting, You are an overly professional blogger.
I’ve joined your rss feed and stay up for looking for more
of your excellent post. Also, I have shared your website
in my social networks
Howdy are using WordPress for your site platform?
I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and create my own.
Do you require any html coding knowledge to make your own blog?
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Here iis my web blog 밍키넷
Howdy this is somewhat of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to
manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but
have no coding expertise so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience.
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Отличная статья, спасибо за информацию!
Как игрок в онлайн-казино из Беларуси, мне кажется,
что поднимаемые вами вопросы очень актуальны
для игрового сообщества.
Особенно понравился мне раздел о стратегиях управления
банкроллом. Это основополагающий аспект для любого, кто стремится
к ответственной игре.
Мне также понравилась ваша точка зрения на отбор проверенных онлайн-казино.
В сфере онлайн-гемблинга
достоверные лицензии и
положительные отзывы играют ключевую роль для защиты
интересов игроков.
Хочу дополнить, что игровое сообщество в Беларуси крупный выигрыш в онлайн-казино по достоинству оценивает честность игры и ясность правил.
Мы предпочитаем казино, которые
не только предлагают великолепные игры,
но и гарантируют справедливые условия.
Еще раз спасибо за статью! Буду следить
за новыми публикациями на вашем блоге.
vpnsiz porno izle
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Inspiring quest there. What occurred after? Good luck!
Garfield trailer
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Kocaeli dijital web tasarım firması ile modern web site sahibi olun.
Thank you for any other wonderful post. The place else may just anyone get
that type of information in such an ideal approach of writing?
I have a presentation next week, and I’m at the look for such information.
hi!,I love your writing so a lot! share we be in contact extra approximately your post on AOL?
I need an expert on this space to unravel my problem.
May be that is you! Looking ahead to peer you.
I believe what you said was very logical. But, what
about this? what if you wrote a catchier title?
I am not suggesting your content is not solid,
but suppose you added a title that makes people want more?
I mean Shoulder Pain – Rotator Cuff Tear – MTS Results is a little vanilla.
You ought to look at Yahoo’s home page and watch how they create article
titles to get viewers interested. You might add a related
video or a pic or two to get readers interested about what you’ve got to say.
Just my opinion, it would bring your blog a little bit more interesting.
Hi there! Quick question that’s entirely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly?
My blog looks weird when browsing from my iphone4. I’m trying to
find a theme or plugin that might be able to correct this issue.
If you have any suggestions, please share. Many thanks!
{Click Here|Here|Details}{{{Doğru|Akıllıca|çın|Doğruca|Dosdoğru|Dürüst|Düz|Esaslı|Essah|Gerçek|Güzel|Hak|Hakikat|Haklı|Harbi|Mevsuk|Muhik|Namuslu|Rast|Sadık|Sağlıklı|Sahih|Selim|Sevap|Tamam|Yakın|Yakınlarında} ve faydalı bilgiler {sağlama|mizan} {konusunda|dair} kararlı olan {uzman|bilirkişi|kompetan|mahir|mütehassıs|spesiyalist} ekibimizle blogumuzu her {zaman|ahit|bugün|çağ|dakika|dem|devir|devran|dönem|gün|hengâm|hin|mevsim|saat|vakit} yeni makaleler ve videolarla güncelliyoruz. {Güvenilir|Ciddi|Emniyetli|Güvenilen|Itimatlı|Kredili|Muteber|Sağlam|Sağlıklı} tavsiyeler ve bilgilendirici {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}erikler arıyorsanız, blog sayfamıza {mutlaka|behemehâl|kesinlikle} {göz|ayn|bakış|basar|boşluk|bölüm|çekmece|delik|dide|görüş|hane|kaynak|nazar|oda} atın.|Gelecekte {hiçbir|tek} {iş|aksiyon|alışveriş|anlayış|çalışma|davranış|emek|fiil|hizmet|işçilik|işlem|kâr|konu|maslahat|medarımaişet|mesele|meslek|nöbet|sorun|teamül|ustalık}e yaramayan anlamsız hedefler veren biri {olmak|başlamak|bulunmak|cereyan etmek|çıkmak|edinmek|geçmek|olgunlaşmak|sarhoş olmak|sürdürmek|tamamlanmak|tutulmak|yapmak|yetişmek|yürütmek} {yerine|adına|alegori|namına}, vizyonu doğrultusunda {doğru|akıllıca|çın|doğruca|dosdoğru|dürüst|düz|esaslı|essah|gerçek|güzel|hak|hakikat|haklı|harbi|mevsuk|muhik|namuslu|rast|sadık|sağlıklı|sahih|selim|sevap|tamam|yakın|yakınlarında} hedeflere {sahip|ehil|iye|malik|mevla} olursunuz,|İlişki koçundan {yukarı|fevk|mafevk}da listelenen maddelerin {sağ|esen|katkısız|sağlam}lanması beklenmektedir. Bir{çok|aşırı|aşkın|bir hayli|bunca|fena|gani|geniş|hayli|iyi|kötü|mebzul|okkalı|öte|sonsuz|şu denli|şunca|yoğun} ilişki koçu seansının {ardından|arkası sıra|peşi sıra} {yukarı|fevk|mafevk}da listelenen maddelerden birçoğunun çiftler {tarafından|aracılığıyla} anlaşılabilir ve öğrenilmiş olması beklenir. Bu yolla, {artık|bundan sonra|çıktı|daha çok|imdi} {daha|elan|henüz} {sağ|esen|katkısız|sağlam}lıklı ve {kuvvetli|akva|demir|donanımlı|etkili|güçlü|güre|keskin|kuvvetlice|nüfuzlu|saygın|şiddetli|tüvana|üstelik|üstün|zorlu} iletişime {sahip|ehil|iye|malik|mevla} ilişkiler kurabilirsin.|2023 @ İstanbul NLP | {Tüm|Bütün} hakları saklıdır. {Herhangi|Rastgele} bir {yazın|edebiyat|gökçe yazın}ın kopyalanması halinde {yasal|kanuni|legal|meşru} {işlem|iş|muamelat|muamele|prosedür} {baş|başlangıç|çıban|esas|kafa|kelle|mebde|mir|saksı|sarrafiye|ser|temel}latılacaktır.|Reply to Hazal Merhabalar, eğitimlerimiz {hakkında|için|karşı|üzerine} detaylı bilgilendirmeyi {eğitim|eğitim bilimi|terbiye|yetişek} danışmanlarımız {sağ|esen|katkısız|sağlam}lamaktadır. Dilerseniz numaranızı bırakmanız {durumunda|yerinde} {yönlendirme|manipülasyon|oryantasyon} {sağ|esen|katkısız|sağlam}layabiliriz {veya|yahut} bizlere 905423789625 numarasından da {ulaşım|erişim} {sağ|esen|katkısız|sağlam}layabilirsiniz|{Sağlıksız|Gayrisıhhi|Sıhhatsiz|Yarım} ilişki {kurma|ihdas|inşa|prefabrik|rekiz} biçimleri {fark|ayırt|ayrım|başkalık|nüans|üstelik}ındalık ve {emek|çalışma|himmet|iş|mesai|say} ile {sağ|esen|katkısız|sağlam}lıklı ilişki {kurma|ihdas|inşa|prefabrik|rekiz} biçimi ile {de|bile}ğ{iş|aksiyon|alışveriş|anlayış|çalışma|davranış|emek|fiil|hizmet|işçilik|işlem|kâr|konu|maslahat|medarımaişet|mesele|meslek|nöbet|sorun|teamül|ustalık}tirilebilirler. İki {kişi|can|erkek|eş|insan|isim|koca|nefer|nüfus|özlük|şahıs|şahsiyet|zat} farklara {rağmen|karşın|mukabil}, bir arada {kalmak|durmak|eğleşmek|ertelenmek|geçirmek|geçmek|konaklamak|konmak|oturmak|sınırlanmak|sürdürmek|tutmak|yapamamak|yaşamak|yetinmek} ve ilişkilerini yürütmek istiyorlarsa, bunu yapabilirler.|{Sağlıksız|Gayrisıhhi|Sıhhatsiz|Yarım} ilişki {kurma|ihdas|inşa|prefabrik|rekiz} biçimleri {fark|ayırt|ayrım|başkalık|nüans|üstelik}ındalık ve {emek|çalışma|himmet|iş|mesai|say} ile {sağ|esen|katkısız|sağlam}lıklı ilişki {kurma|ihdas|inşa|prefabrik|rekiz} biçimi ile {de|bile}ğ{iş|aksiyon|alışveriş|anlayış|çalışma|davranış|emek|fiil|hizmet|işçilik|işlem|kâr|konu|maslahat|medarımaişet|mesele|meslek|nöbet|sorun|teamül|ustalık}tirilebilirler. İki {kişi|can|erkek|eş|insan|isim|koca|nefer|nüfus|özlük|şahıs|şahsiyet|zat} farklara {rağmen|karşın|mukabil}, bir arada {kalmak|durmak|eğleşmek|ertelenmek|geçirmek|geçmek|konaklamak|konmak|oturmak|sınırlanmak|sürdürmek|tutmak|yapamamak|yaşamak|yetinmek} ve ilişkilerini yürütmek istiyorlarsa, bunu yapabilirler.|Kariyer koçluğu eğitimi, bireylere kariyerlerindeki hedeflerini belirlemelerine, kariyer yolculuklarını planlamalarına ve {kişisel|ferdî|şahsi|zatî} ve {mesleki|mesleksel} {geliş|vürut}imlerini desteklemelerine yardımcı olacak {beceri|maharet|teknik|ustalık} ve {bilgileri|detayları} {kazandı|kazanmıştır}ran bir {eğitim|eğitim bilimi|terbiye|yetişek} {program|izlence|yetişek}ıdır.|{Ya|Evet}şam koçluğu {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in {verilen|maruz} bir {eğitim|eğitim bilimi|terbiye|yetişek} {program|izlence|yetişek}ını {başarı|muvaffakiyet|sükse}yla {tamamlayan|mütemmim|tamamlayıcı} ve {ya|evet}şam koçluğu {yapabilmek|muktedir olmak|yetişmek} {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in {sertifika|şehadetname} almaya {hak|adalet|doğru|doğruluk|gerçek|kazanç|kazı|pay|tanrı} kazanan {herkes|âlem|cümle|dünya|el âlem|hacısı hocası|kâinat|millet|umum} {ya|evet}şam koçluğu yapabilmektedir. {Diğer|Başka|Gayrı|öbür|öteki|özge|Sair|Vesair} {yandan|taraftan} {ya|evet}şam koçluğu {yapacak|meydana getirecek} olan kişinin {iletişim|bildirişim|haberleşme|komünikasyon|muhabere} {yön|cephe|cihet|doğrultu|husus|istikamet|semt|taraf|veçhe|yan}ünün {güç|ağır|bilek|can|çelim|çetin|derman|efor|fer|hâl|hız|kudret|kuvvet|mecal|meşakkatli|müşkül|sarp|sinerji|tabütüvan|takat|zahmetli|zorlukla}lü olması da önemlidir. {Ya|Evet}şam koçluğu mesleğini {icra|yürütme} edecek olan {kişi|can|erkek|eş|insan|isim|koca|nefer|nüfus|özlük|şahıs|şahsiyet|zat} danış{anlar|anlamış olur}ını {iyi|âlâ|bol|çok|dobra|düzgün|eksiksiz|elleme|esen|güzel|hayır|hayırlı|kazançlı|oflaz|sağlıklı|uygun|uz|yararlı|yavuz|yeğin|yerinde} bir şekilde dinleyebilmeli ve onlara istedikleri hedeflere ulaşmakta yardımcı olabilmelidir. Bu nedenle {ya|evet}şam koçluğu mesleğini {icra|yürütme} edecek olan kişinin ilk olarak {iyi|âlâ|bol|çok|dobra|düzgün|eksiksiz|elleme|esen|güzel|hayır|hayırlı|kazançlı|oflaz|sağlıklı|uygun|uz|yararlı|yavuz|yeğin|yerinde} bir dinleyici olması gerekmektedir. İyi bir şekilde danış{anı|andaç|hatıra}nı dinleyemeyen bir {ya|evet}şam koçunun danış{anı|andaç|hatıra}nın {sorunlar|problemler}ı {hakkında|için|karşı|üzerine} {doğru|akıllıca|çın|doğruca|dosdoğru|dürüst|düz|esaslı|essah|gerçek|güzel|hak|hakikat|haklı|harbi|mevsuk|muhik|namuslu|rast|sadık|sağlıklı|sahih|selim|sevap|tamam|yakın|yakınlarında} tespitler yapması {mümkün|kabil|muhtemel|olabilir|olanaklı|olası} olmayacağından ona vereceği önerilerde {doğru|akıllıca|çın|doğruca|dosdoğru|dürüst|düz|esaslı|essah|gerçek|güzel|hak|hakikat|haklı|harbi|mevsuk|muhik|namuslu|rast|sadık|sağlıklı|sahih|selim|sevap|tamam|yakın|yakınlarında} olmayacaktır.|Kariyer koçluğu ve iş koçluğu {genellikle|alelumum|çoğu kez|çoğunlukla|çoklukla|ekseri|ekseriya|ekseriyetle|umumiyetle} aynı anda {anı|andaç|hatıra}lır ve çoğu {zaman|ahit|bugün|çağ|dakika|dem|devir|devran|dönem|gün|hengâm|hin|mevsim|saat|vakit} birbiriyle karıştırılır. {Aslında|Esasen|Esasta|Gerçekte|Haddizatında} {belli|belirli} paralellikler var: Her {iki|dü} koçluk formatı da danış{anı|andaç|hatıra}n {profesyonel|hevesli|meraklı} {hayat|avlu|balkon|can|dirim|dirlik|meslek|sundurma|varlık|yaşam|yaşantı|yazgı}ıyla ilgilidir.|{Ya|Evet}şam koçu, bir hedefe ulaşmanıza {veya|yahut} {hayatını|yaşamını}zda bir {değişiklik|başkalık|tadil} yapmanıza yardımcı olan bir {profesyonel|hevesli|meraklı} kimselere denir.|Siz ve hedefleriniz {arasında|beyninde|ortada} duran engeller {tanı|tanılama|teşhis}mlandıktan {sonra|sonrasında} {ya|evet}şam koçunuz bunları aşmanız {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in bir {strateji|izlem|sevkülceyş} belirleyecektir.|Danış{anı|andaç|hatıra}n, istediği hedeflere ulaşabilmesi {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in {hayat|avlu|balkon|can|dirim|dirlik|meslek|sundurma|varlık|yaşam|yaşantı|yazgı} {tarzı|seçimi}na {uygun|akla yatkın|amelî|birebir|elverişli|isabetli|iyi|makul|munis|mutabık|muvafık|münasip|müsait|mütenasip|normal|onat|oranlı|orantılı|reva|şayan|şayeste|şık|tatminkâr|usturuplu|yakışır|yarar|yaraşıklı|yaraşır|yönlü} bir bakış açısı {geliş|vürut}tirmesini {sağlamak|bulmak|çıkarmak|elde etmek|getirmek|hazırlamak|kurmak|peylemek|sahip olmak|tedarik etmek|tedariklemek|temin etmek|uydurmak|yağdırmak},|Şirketimiz {tarafından|aracılığıyla}, size Blog {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}eriklerini, {baz|temel}ı {araştırmalar|tetkikat} {yapmak|açmak|akdetmek|bina etmek|çıkarmak|davranmak|düzenlemek|edinmek|etkili olmak|evlendirmek|eylemek|geçirmek|gerçekleştirmek|gitmek|hareket etmek|icra etmek|ifa etmek|ika etmek|inşa etmek|kılmak|kurmak|olmak|onarmak|sahip olmak|salgılamak|tamir etmek|tutmak|uygulamak|üretmek|yapıp etmek|yaratmak|yetiştirmek} ve pazarlama faaliyetlerinde {bulunmak|çıkmak|düşmek|gezmek|mevcut olmak|olmak|yatmak} {gerek|icap|ister|lazım|lüzum|lüzumlu}çeleri ile ve {daha|elan|henüz} {iyi|âlâ|bol|çok|dobra|düzgün|eksiksiz|elleme|esen|güzel|hayır|hayırlı|kazançlı|oflaz|sağlıklı|uygun|uz|yararlı|yavuz|yeğin|yerinde} {hizmet|bakım|görev|ihtimam|iş|özen} verebilmek {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in {kişisel|ferdî|şahsi|zatî} verilerinizi {iş|aksiyon|alışveriş|anlayış|çalışma|davranış|emek|fiil|hizmet|işçilik|işlem|kâr|konu|maslahat|medarımaişet|mesele|meslek|nöbet|sorun|teamül|ustalık}liyoruz|Kişilerin {daha|elan|henüz} {verimli|bereketli|bitek|cömert|dişi|doğurgan|feyizli|gür|mahsuldar|mübarek|mümbit|müsmir|randımanlı|rantabl|semereli|velut|vergili|verimkâr|zengin} {ama|amma|fakat|lakin|yalnız}çlara yönelmelerini ve bu {ama|amma|fakat|lakin|yalnız}çlar doğrultusunda ne {gibi|kabil|kabilinden|kadar|üzere} adımlar atılacağını belirleyebilme|50 Maddede İlişkiler ilişki koçu Adil {Yıldırım|Saika}’ın kaleme aldığı, {ruh|can kuşu|canlılık|derun|duygu|emanet|esans|öz|tayf|tin} eşini bir {gün|çağ|devir|gündüz|güneş|ruz|sıra|tarih|zaman} bulacağına inanan ve inancını {asla|katiyen} kaybetmeyen {tüm|bütün} papatyalar {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in {etkili|aktif|canlı|çarpıcı|dokunaklı|etkin|güçlü|hatırlı|içli|keskin|koygun|kuvvetli|müessir|patetik|ruhlu|tesirli|yakıcı|yanık|yüksek} bir {rehber|delil|kılavuz}.|2 {Aylık|Maaş|Mahiye} eğitimin {sonunda|ahir|böylece|nihayetinde} {gerçekleştirilen|meydana gelen} online sınava {katı|acımasız|bek|berk|hoşgörüsüz|merhametsiz|pek|sert|sıkı|sulp|taşlık|tıkız|yeğin|zalim}larak {baş|başlangıç|çıban|esas|kafa|kelle|mebde|mir|saksı|sarrafiye|ser|temel}arı {sağladığı|sağlamış olduğu}nız taktirde, sertifikanız adınıza düzenlenerek adresinize kargo yolu ile gönderilir.|Bu {ortaklık|iştirak|müşareket|şeriklik|şirket} esnasında, {esas|ana|anayasa|asal|asıl|asliye|baş|başlıca|bel kemiği|esasi|hakikat|kök|mahiyet|omurga|temel|temel taşı|üs|yapı taşı} olan bireylerin {ortak|eş|hissedar|kuma|müşterek|partner|şerik} ilişkileri ile {ilgili|ait|alakadar|alakalı|dayalı|ilişkin|müntesip|müteallik} {ortak|eş|hissedar|kuma|müşterek|partner|şerik} bir {ama|amma|fakat|lakin|yalnız}çlarının olması ve bu sürece ne {kadar|denli|derece} adanmış olduklarıdır.|{Ya|Evet}şam koçluğu eğitimi {almak|ahzetmek|bağışlamak|başlamak|buyurmak|bürümek|çalmak|çekmek|dercetmek|eksiltmek|elde etmek|fethetmek|gidermek|girmek|görmek|iletilmek|kabul etmek|kaldırmak|kaplamak|kazanmak|kısaltmak|koparmak|koymak|kullanmak|örtmek|sarmak|soldurmak|temizlemek|vira etmek|yok etmek|yolmak|yutmak} {gibi|kabil|kabilinden|kadar|üzere} bir düşünceye sahipseniz kurumumuz ile iletişime geçerek {fiyat|bedel|eder|hediye|paha|yükselmek} {almak|ahzetmek|bağışlamak|başlamak|buyurmak|bürümek|çalmak|çekmek|dercetmek|eksiltmek|elde etmek|fethetmek|gidermek|girmek|görmek|iletilmek|kabul etmek|kaldırmak|kaplamak|kazanmak|kısaltmak|koparmak|koymak|kullanmak|örtmek|sarmak|soldurmak|temizlemek|vira etmek|yok etmek|yolmak|yutmak} {oldukça|az çok|bayağı|berenarı|enikonu|epey|nispeten|olabildiğince} faydanıza olacaktır. Kurumumuz {tecrübeli|deneyimli} eğiticiler ile genç ve {dinamik|canlı|devim bilimi|devimsel|etkin|hareketli} eğiticileri harmanlayarak kurmuş {oldu|başüstüne|evet}ğu {kadrosuyla|ekibiyle} bir{çok|aşırı|aşkın|bir hayli|bunca|fena|gani|geniş|hayli|iyi|kötü|mebzul|okkalı|öte|sonsuz|şu denli|şunca|yoğun} kişiye {ya|evet}şam koçu sertifikası {kazandı|kazanmıştır}rmış ve {kazandı|kazanmıştır}rmaya da devam etmektedir. Siz {de|bile} hem {iyi|âlâ|bol|çok|dobra|düzgün|eksiksiz|elleme|esen|güzel|hayır|hayırlı|kazançlı|oflaz|sağlıklı|uygun|uz|yararlı|yavuz|yeğin|yerinde} bir {eğitim|eğitim bilimi|terbiye|yetişek} {almak|ahzetmek|bağışlamak|başlamak|buyurmak|bürümek|çalmak|çekmek|dercetmek|eksiltmek|elde etmek|fethetmek|gidermek|girmek|görmek|iletilmek|kabul etmek|kaldırmak|kaplamak|kazanmak|kısaltmak|koparmak|koymak|kullanmak|örtmek|sarmak|soldurmak|temizlemek|vira etmek|yok etmek|yolmak|yutmak} hem {de|bile} {sertifika|şehadetname} sahibi {olmak|başlamak|bulunmak|cereyan etmek|çıkmak|edinmek|geçmek|olgunlaşmak|sarhoş olmak|sürdürmek|tamamlanmak|tutulmak|yapmak|yetişmek|yürütmek} {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in kurumumuzu {gönül|arzu|can|derun|dil|hatır|içeri|istek|kalp|karın|sine|yürek} rahatlığıyla {tercih|yeğleme} edebilirsiniz.|İlişki koçuna gitmeye {karar|hüküm} verdiysen öncelikle bir {rehber|delil|kılavuz} ile ç{al|aldatma|allık|düzen|hile|kırmızı|kızıl|tuzak}ıştığında {hayat|avlu|balkon|can|dirim|dirlik|meslek|sundurma|varlık|yaşam|yaşantı|yazgı}ına neler {değişir|değişmiş olur} onlara bakalım.|{Eğer|şayet} {kriz|akse|buhran|bunalım|çöküntü} {anında|çabucak|simultane|takkadak} {oldu|başüstüne|evet}ğunuzu {ya|evet} da {başka|ayrıksı|değişik|diğer|farklı|gayrı|özge|sair} bir kişinin tehlikede {olduğunu|bulunduğunu} düşünüyorsanız, bu siteyi kullanmayınız. {Hemen|çabucak|Elden|Hoppadak|Sadece|Takkadak|Vakit kaybetmeden|Yalnız|Yemeden içmeden} {doğru|akıllıca|çın|doğruca|dosdoğru|dürüst|düz|esaslı|essah|gerçek|güzel|hak|hakikat|haklı|harbi|mevsuk|muhik|namuslu|rast|sadık|sağlıklı|sahih|selim|sevap|tamam|yakın|yakınlarında} {yardım|arkalama|bağış|etki|himmet|iane|katkı|lütuf|medet|muavenet|saye}ı {almak|ahzetmek|bağışlamak|başlamak|buyurmak|bürümek|çalmak|çekmek|dercetmek|eksiltmek|elde etmek|fethetmek|gidermek|girmek|görmek|iletilmek|kabul etmek|kaldırmak|kaplamak|kazanmak|kısaltmak|koparmak|koymak|kullanmak|örtmek|sarmak|soldurmak|temizlemek|vira etmek|yok etmek|yolmak|yutmak} {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in butona tıklayınız. Kaynaklar|“Ben birlikteliğimi {kurtarmak|idare etmek|uzaklaştırmak} {isteyen|talip} taraftayım” diyorsan {hemen|çabucak|elden|hoppadak|sadece|takkadak|vakit kaybetmeden|yalnız|yemeden içmeden} bir {uzman|bilirkişi|kompetan|mahir|mütehassıs|spesiyalist} desteği almaya {baş|başlangıç|çıban|esas|kafa|kelle|mebde|mir|saksı|sarrafiye|ser|temel}lamal{ısın|kalori}. Üstelik bunun {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in uzun yollar gelmene, bekleme salonlarında dakikaları saymana da {gerek|icap|ister|lazım|lüzum|lüzumlu} {yok|namevcut|nanay|yasak}. Online ilişki koçu hizmetinden faydalanabilirsin.|{Ya|Evet}şam Koçluğu {Eğitim|Eğitim bilimi|Terbiye|Yetişek} programlarına; {ya|evet}şam koçluğuna {ilgi|alaka|bağ|dikkat|ilişik|ilişki|kontak|nazarıitibar|nispet|rabıta|rağbet|taalluk} duyan ve kendini bu alanda {geliştirmek|imar etmek|yetiştirmek|yükseltmek} {isteyen|talip} {herkes|âlem|cümle|dünya|el âlem|hacısı hocası|kâinat|millet|umum} {baş|başlangıç|çıban|esas|kafa|kelle|mebde|mir|saksı|sarrafiye|ser|temel}vurabilir. Her {eğitim|eğitim bilimi|terbiye|yetişek} seviyesindeki {insanlar|insanoğlu}, {ya|evet}şam koçluğu programlarına {baş|başlangıç|çıban|esas|kafa|kelle|mebde|mir|saksı|sarrafiye|ser|temel}vurabilir.|{Ya|Evet}şam koçluğu {sertifika|şehadetname} {program|izlence|yetişek}ı fiyatları {eğitim|eğitim bilimi|terbiye|yetişek} {içeri|dâhil|derun|gönül|hapishane|yürek}ğine ve eğitimi veren kurumun {fiyat|bedel|eder|hediye|paha|yükselmek} politikasına {göre|bakarak|bakılırsa|gereğince|için|nazaran} {de|bile}ğ{iş|aksiyon|alışveriş|anlayış|çalışma|davranış|emek|fiil|hizmet|işçilik|işlem|kâr|konu|maslahat|medarımaişet|mesele|meslek|nöbet|sorun|teamül|ustalık}kenlik göstermektedir. {Ya|Evet}şam koçluğu eğitimi fiyatları {hakkında|için|karşı|üzerine} {bilgi|bilgelik|bili|bilim|fen|haber|malumat|marifet|olgun|selen|veri|vukuf} {almak|ahzetmek|bağışlamak|başlamak|buyurmak|bürümek|çalmak|çekmek|dercetmek|eksiltmek|elde etmek|fethetmek|gidermek|girmek|görmek|iletilmek|kabul etmek|kaldırmak|kaplamak|kazanmak|kısaltmak|koparmak|koymak|kullanmak|örtmek|sarmak|soldurmak|temizlemek|vira etmek|yok etmek|yolmak|yutmak} {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in kurumumuz ile iletişime geçebilirsiniz. Kurumumuz {uzman|bilirkişi|kompetan|mahir|mütehassıs|spesiyalist} ve {tecrübeli|deneyimli} {eğitici|mürebbi} {kadrosuyla|ekibiyle} {birlikte|alay malay|baş başa|beraberinde|bile|müşterek|omuz omuza|yan yana|yanında} {ister|gerek|icap|lüzum} {uzaktan|alarga|karşıdan karşıya|şahsen} {ister|gerek|icap|lüzum} {yüz|beniz|cebin|çehre|didar|duluk|faça|nedeniyle|sebebiyle|sima|surat|suret|taraf|utanma|vecih|yan|yüzey} yüze {eğitim|eğitim bilimi|terbiye|yetişek} noktasında {kaliteli|birinci sınıf|nitelikli} eğitimi {uygun|akla yatkın|amelî|birebir|elverişli|isabetli|iyi|makul|munis|mutabık|muvafık|münasip|müsait|mütenasip|normal|onat|oranlı|orantılı|reva|şayan|şayeste|şık|tatminkâr|usturuplu|yakışır|yarar|yaraşıklı|yaraşır|yönlü} fiyata sunmaktadır.|İlişkilerde en önemli faktörlerden biri {de|bile} {karşı|alın|hakkında|huzur|için|karşıt|kat|kontra|muhalif|mukabil|ön|zıt}lıklı anlayış, saygı ve sevgidir. Bu {yazı|alfabe|hat|kır|makale|makaslamak|ova|tasar|yazgı}da, ilişki koçlarının ne {yaptı|yapmış oldu}klarını, {sağ|esen|katkısız|sağlam}lıklı bir ilişkinin {nasıl|elbette|kesinlikle|ne|nite} olması {gerektiğini|icap ettiğini} ve bu {konuda|mevzuda} bireylere {nasıl|elbette|kesinlikle|ne|nite} yardımcı olabileceklerini {keş|aptal|ayyaş|esrarkeş}fedeceğiz.|Necessary Always Enabled Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do {not|derece|hamiş} store any personal information.|{Ya|Evet}şam koçu ise; {iş|aksiyon|alışveriş|anlayış|çalışma|davranış|emek|fiil|hizmet|işçilik|işlem|kâr|konu|maslahat|medarımaişet|mesele|meslek|nöbet|sorun|teamül|ustalık}inden başını kaldıramamaktan, yakınlarına ve kendine {vakit|aralık|çağ|hengâm|saat|zaman} {ayı|kocaoğlan}ramamaktan yakınan {ya|evet} da hayatta ne {yapmak|açmak|akdetmek|bina etmek|çıkarmak|davranmak|düzenlemek|edinmek|etkili olmak|evlendirmek|eylemek|geçirmek|gerçekleştirmek|gitmek|hareket etmek|icra etmek|ifa etmek|ika etmek|inşa etmek|kılmak|kurmak|olmak|onarmak|sahip olmak|salgılamak|tamir etmek|tutmak|uygulamak|üretmek|yapıp etmek|yaratmak|yetiştirmek} ve ne {olmak|başlamak|bulunmak|cereyan etmek|çıkmak|edinmek|geçmek|olgunlaşmak|sarhoş olmak|sürdürmek|tamamlanmak|tutulmak|yapmak|yetişmek|yürütmek} istedikleri {konusunda|dair} {belirsizlik|ipham|müphemiyet|müphemlik|varagele|vuzuhsuzluk} {yaşayan|canlı} kişilerin {ya|evet}şamlarını dengeleyen ve {ya|evet}şamlarına {anlam|deme|fehva|mana|mazmun|meal|medlul|valör} {kazandı|kazanmıştır}ran kişidir.|İlişki koçu {sadece|yalnızca} var olan birlikteliği iyileştirmek {ya|evet} da {iyi|âlâ|bol|çok|dobra|düzgün|eksiksiz|elleme|esen|güzel|hayır|hayırlı|kazançlı|oflaz|sağlıklı|uygun|uz|yararlı|yavuz|yeğin|yerinde} {giden|revan} bir birlikteliği {korumak|arkalamak|bakmak|beklemek|esirgemek|gözetmek|gözlemek|himaye etmek|kavzamak|kollamak|muhafaza etmek|mukayyet olmak|müdafaa etmek|sahabet etmek|sahiplenmek|sakınmak|saklamak|savunmak|sıyanet etmek|vikaye etmek} {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in rehberlik etmez. Aynı zamanda yeni ve {sağ|esen|katkısız|sağlam}lıklı bir {beraberlik|el birliği|kardeşlik|muadele} {iç|bağırsak|bâtın|ciğer|dâhil|derun|karın|kucak|mide|muhteva|sine|yürek}in {de|bile} {destek|bindi|dayak|dayanak|hamil|koltuk|payanda|takviye} {olur|evet|olabilir}.}
If you would like to improve your knowledge only keep visiting this website and be updated with the newest news update posted here.
Hi, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and i was just curious if you get
a lot of spam responses? If so how do you prevent it, any plugin or anything
you can advise? I get so much lately it’s driving me mad so any help is very much appreciated.
Hmm it looks like your site ate my first comment (it was extremely long) so I guess I’ll just sum it
up what I submitted and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying
your blog. I too am an aspiring blog blogger but I’m still new to everything.
Do you have any suggestions for rookie blog writers? I’d genuinely appreciate
it.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Hi my friend! I want to say that this article is amazing,
great written and come with almost all important infos.
I would like to see extra posts like this .
Wonderful beat ! I wish to apprentice even as you amend your web site,
how could i subscribe for a weblog web site?
The account helped me a acceptable deal. I were a little bit acquainted
of this your broadcast offered brilliant transparent idea
Hi there! I know this is kind of off-topic but I
needed to ask. Does building a well-established website like yours require a large amount of work?
I’m brand new to writing a blog however I do write in my diary
on a daily basis. I’d like to start a blog so I can easily share my experience
and feelings online. Please let me know if you have any ideas or tips for brand new aspiring bloggers.
Thankyou!
It’s very easy to find out any topic on net as compared to books, as I found this piece
of writing at this web site.
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ.
Hi there! This blog post couldn’t be written any better!
Going through this post reminds me of my previous roommate!
He always kept preaching about this. I most certainly will
send this information to him. Pretty sure he’s going to have a good read.
I appreciate you for sharing!
It is perfect time to make some plans for the future and it is time to
be happy. I have learn this publish and if
I may I want to counsel you few interesting things or suggestions.
Maybe you could write next articles relating
to this article. I desire to learn more things approximately it!
Wow, that’s what I was exploring for, what a data!
present here at this blog, thanks admin of this site.
Beneficial information Appreciate it!
Sosyal Mavi, sosyal medya başarınızı hızlandırmanın en güvenilir yolu! Şimdi başlayın ve takipçi sayınızı katlayın.
Hello, I kindly request you to review and publish my blog post. Thank you for your time.
Hello there! Do you know if they make any plugins to
assist with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good gains.
If you know of any please share. Cheers!
I am actually grateful to the owner of this website
who has shared this enormous article at here.
I like what you guys tend to be up too. This sort of clever work and coverage!
Keep up the excellent works guys I’ve included you guys to
our blogroll.
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Amazing lots of superb info!
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ .Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
“Teknoloji dünyasındaki en son yenilikleri, derinlemesine incelemeleri ve kapsamlı analizleri keşfedin, sadece Pandermos.net’te. Akıllı telefonlardan yapay zekaya, bulut bilişimden siber güvenliğe kadar her konuda güncel bilgileri takip edin. Yeni çıkan oyun teknolojilerinden elektrikli araçlara, giyilebilir cihazlardan akıllı ev sistemlerine kadar geniş bir yelpazede, teknolojinin her köşesini keşfetmek isteyenler için Pandermos.net, zengin içeriği ve uzman görüşleriyle ideal bir kaynaktır. Teknoloji meraklıları, geliştiriciler, yatırımcılar ve eğitimciler, güncel teknoloji haberleri ve trendlerini takip etmek için Pandermos.net’i ziyaret edin; teknolojinin geleceği hakkında derinlemesine bilgi edinin.”
Thanks for finally writing about >Shoulder Pain – Rotator Cuff
Tear – MTS Results <Loved it! https://empresarialjardinsdobrasil.com.br/index.php?page=user&action=pub_profile&id=5765
Thanks for finally writing about >Shoulder Pain – Rotator Cuff Tear – MTS
Results <Loved it! https://empresarialjardinsdobrasil.com.br/index.php?page=user&action=pub_profile&id=5765
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button! I’d certainly donate to this brilliant blog!
I guess for now i’ll settle for book-marking and adding your
RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to new
updates and will talk about this website with my Facebook group.
Chat soon! http://can.heuso.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=343583
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button!
I’d certainly donate to this brilliant blog!
I guess for now i’ll settle for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my
Google account. I look forward to new updates and
will talk about this website with my Facebook group.
Chat soon! http://can.heuso.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=343583
Thanks for sharing your thoughts about login vip188slot.
Regards
This is a good tip especially to those fresh to the blogosphere.
Brief but very accurate information… Many thanks for sharing this one.
A must read article!
Your style is very unique compared to other people I’ve read stuff from.
Thank you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I’ll just book mark this
blog.
I have read a few just right stuff here. Certainly
worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how so much attempt you put to create this sort
of wonderful informative site.
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.兒童色情
Cabura site – официальный сайт приглашает Кабура игроков онлайн игры уникальную стратегию игры , привлекать новых геймеров , радуйся каждому , зарабатывай играя
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.活婴儿色情片
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.儿童色情片
Howdy! This post couldn’t be written much better! Going through this article reminds me of my previous roommate!
He continually kept preaching about this. I’ll forward this article to
him. Fairly certain he’ll have a very good read.
I appreciate you for sharing!
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
What’s up to all, the contents present at this site are
actually amazing for people knowledge, well, keep up the nice
work fellows.
Hello there! This blog post couldn’t be written any better!
Looking through this post reminds me of my previous roommate!
He always kept preaching about this. I am going to send this post
to him. Fairly certain he’ll have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article.
I will make sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful info.
Thanks for the post. I will certainly return.
Hello, I’d appreciate it if you could review and approve my blog post. Thanks a lot.
Takipçi sayınızı arttırmak için doğru adrestesiniz! Sosyal Mavi ile hedeflerinize ulaşın.
Emeğinize sağlık, içerikleriniz çok değerli.
Tebrikler, içerikleriniz gerçekten bilgilendirici.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.儿童色情片
I appreciate the effort you’ve put into crafting such an engaging blog post.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.儿童色情
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.儿童色情
Howdy! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a group of volunteers and starting a
new project in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us useful information to
work on. You have done a extraordinary job!
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Twitter Video Dow: Twitter Video Dow is a shorthand term for Twitter Video Downloader. It encompasses various tools and applications that enable users to download videos from Twitter with ease.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.兒童色情
Hello, I’d appreciate it if you could review and approve my blog post. Thank you.
İçeriklerinizin kalitesi beni etkiledi, teşekkür ederim.
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for content. Area rugs and online home decor store. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
When someone writes an post hе/she maintains thhe imɑge of a user in һis/hеr
mind thɑt how а սser can understand it. Therefore that’s why this artiocle
iѕ outstdanding. Thanks!
Feel free to visit my site :: kitchen appliances (spotlight.radiopublic.Com)
Cabura site – официальный сайт приглашает Кабура игроков онлайн игры уникальную стратегию игры , привлекать новых геймеров , радуйся каждому , зарабатывай играя
Street Union Team Production от Suteam – это профессиональная организация и проведение мероприятий под
открытым небом. Мы предлагаем комплексные услуги по разработке
концепции, планированию и проведению успешных и запоминающихся событий, предлагаем съемка спортивных событий
учитывая все пожелания заказчика и актуальные тренды в области
мероприятий. Наши опытные специалисты приложат
все усилия, чтобы ваше мероприятие стало ярким и незабываемым событием, объединяющим всех гостей.
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
hello there and thank you for your info – I’ve certainly picked up anything new
from right here. I did however expertise a few technical issues using this site,
since I experienced to reload the site many times
previous to I could get it to load properly.
I had been wondering if your web hosting is OK? Not that I am complaining, but slow loading instances times will very frequently affect your placement
in google and could damage your high quality score if ads and
marketing with Adwords. Anyway I’m adding this RSS to my e-mail and can look
out for much more of your respective exciting content.
Ensure that you update this again soon.
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this matter to
be really something which I think I would never understand.
It seems too complicated and very broad for me. I am looking
forward for your next post, I will try to get the
hang of it!
İçerikleriniz gerçekten kaliteli, tebrikler.
Wow, this post is good, my sister is analyzing these kinds of things, so I am going to let know her.
AK PARTİ ESKİL BELEDİYE BAŞKAN ADAYI MUSTAFA ZAVLAK’IN HALK PAZARI ZİYARETİ
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hi, i believee tһat i saw you visited my weblog tһus i got here
to go back the favor?.I’m attempting to fіnd thіngs to enhance my website!Ӏ suppoxe its adequate tο ᥙsе a few of youг concepts!!
Ꮮook into myy web site; patritti ราคา
Thank you great posting about essential oil. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
SULTANHANI AKSARAY ARASI DOLMUŞ FİYATLARI GÜNCELLENDİ.
eskil medya
Very good post! We are linking to this great post on our website.
Keep up the great writing. https://bookmarksoflife.com/story2421985/ideesrange
Hello there, You’ve done a great job. I’ll certainly digg it and personally recommend to my friends.
I am confident they’ll be benefited from this web site.
Heating engineers are regularly employed to carry out boiler servicing and set up jobs.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across.国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great content. Hello Administ. 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hello. Allow me to introduce creator. His name is Santo Peck.
I am an administrative assistant. Doing interior decorating is what that I’m totally
endlaved by. My house is now in Minnesota.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information.活婴儿色情片
Cabura site – официальный сайт приглашает Кабура игроков онлайн игры уникальную стратегию игры , привлекать новых геймеров , радуйся каждому , зарабатывай играя
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 現場兒童色情片
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Great post thank you. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
This info is priceless. How can I find out more?
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
This column sticks out for its harmony of records as
well as private idea. Truly a pleasure to read.
Here is my web-site – Ron Spinabella
Quality articles or reviews is the important to invite the visitors to pay
a quick visit the site, that’s what this site is providing.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Türkiye Futbol Federasyonu, 6 Şubat 2024
Nice article inspiring thanks. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
It’s an amazing post designed for all the web viewers; they will obtain benefit from it
I am sure.
It’s really a nice and helpful piece of information. I am glad that
you shared this useful information with us.
Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
CUMHURİYET HALK PARTİSİ ESKİL ADAYI RESUL GÜÇ ESNAFLARI ZİYARET ETTİ
What’s up to every body, it’s my fіrst vvisit of tһіѕ blog; thius weblog contains amazing аnd really g᧐od data designed for
visitors.
Heгe is my page wine หวาน
Spor dünyasından 6 Şubat mesajı! ‘Unutmayacağız’
What’s up, everything is going perfectly here and
ofcourse every one is sharing data, that’s actually good, keep up writing.
Lots of folks overlook the significance of extensive insurance coverage along with their vehicle insurance options in Mundelein insurance coverage in Mundelein. This kind of
insurance defends versus non-collision-related events, which are fairly usual.
When choosing Car insurance in Mundelein, consider adding extensive protection for
total confidence. Speak to an educated broker who can assist you with the a variety of choices offered.
At tһis time I am going ɑway tto dо my breakfast, when having my breakfast
comіng agɑin to reаd օther news.
Μy web site: ขายไวน์ยกลัง
Nevşehir Avukat
First off I want to say fantastic blog! I had a quick question that I’d like
to ask if you don’t mind. I was curious to find out how you center yourself and clear your mind prior
to writing. I have had difficulty clearing my thoughts in getting my thoughts out there.
I truly do enjoy writing but it just seems
like the first 10 to 15 minutes tend to be wasted just trying to figure out how to begin. Any ideas or hints?
Thanks!
What’s uρ it’s me, I am alѕo visiting this web ⲣage on a regular basis, tһіs web
site іs actualⅼy good aand thе users ɑre genuinely sharing nice tһoughts.
Review mу web blog; patritti wine
Hi there, I kindly request you to review and publish my blog post. Thank you!
Harika içerikler, tebrikler.
Takipçi sayınızı anında arttırmanın en hızlı yolu! Sosyal Mavi ile sosyal medya başarınızı garanti altına alın.
Ηi my friend! I wish to ѕay that this article іs awesome, ցreat ԝritten and come
with aⅼmost aⅼl significаnt infos. I’d like
to see mօre posts ⅼike thiis .
Haѵe a look at my web-site … ขาย ไวน์
İçerikleriniz beni etkiledi, teşekkürler.
Kocaeli dijital ile web tasarım ve seo hizmetleri ile tanışın.
Just got just received Funny Dad T-Shirt and it’s the perfect mood booster!
The perfect blend of style and dad humour. We love the quirky vibes and comfortable feel.
A must-have for every dad who appreciates laughter!
Good day, I’m submitting my blog post for your consideration. Appreciate your valuable feedback in advance.
Thank you for great article. Hello Administ .国产线播放免费人成视频播放
İstanbul Avukat
Nakitbahis betgaranti sekabet milanobet 国产线播放免费人成视频播放 lordbahis aresbet betkom
My slouse and І stumbled оver here by a diffeгent web page and tһought I should check things oսt.
I ⅼike whɑt I seee ѕo noᴡ i’m foⅼlowing you. Look forward
t᧐ checking оut үоur web page repeatedly.
Αlso visit mʏ homepɑge – patritti
A fascinating discussion is worth comment. I think that
you should publish more on this topic, it may not be a taboo subject but generally people don’t talk about
these subjects. To the next! All the best!!
eskil
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
ABANT-YEDİGÖLLER- AĞVA –ŞİLE –POLENEZKÖY-HOBBIT EVLERİ 2GÜN-1GECE
İçeriklerinizle ilgili olumlu bir geri bildirimde bulunmak istedim.
Yesterday, while I was at work, my sister stole my
apple ipad and tested to see if it can survive a
thirty foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now destroyed and she has 83
views. I know this is entirely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
I for all time emailed this weblog post page to all my contacts, for the
reason that if like to read it next my contacts
will too.
you are in point of fact a just right webmaster. The site
loading speed is incredible. It sort of feels that you
are doing any distinctive trick. Moreover, The contents are masterwork.
you’ve performed a magnificent job in this matter!
I have to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in writing
this blog. I am hoping to check out the same high-grade blog posts by you in the future as well.
In fact, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own website now 😉
I’m amazed, Ӏ mst say. Seldom ɗo I come aсross a blog tһat’s ƅoth educative ɑnd interesting, аnd withoսt a
doubt, you have hit the nail on the head. The pгoblem
is sometһing that not enough men andd women ɑre speakibg
intelligently abοut. I’m verү happy Ι stumbled ɑcross this ԁuring mу hunt fⲟr
ѕomething сoncerning thіs.
Here is my website :: ร้านจำหน่ายไวน์
Sosyal Mavi, sosyal medya stratejinizi güçlendirmenin en akıllıca yolu! Şimdi keşfedin ve takipçi sayınızı artırın.
Sitenizin içerikleri benim için çok faydalı oldu.
Thanks , I have just been searching for info about this subject for
a while and yours is the greatest I’ve came upon till now.
However, what about the conclusion? Are you certain concerning the source?
Sosyal Mavi ile takipçi sayınızı arttırın ve profilinizin etkileyiciliğini artırın! Hemen keşfedin.
Teşekkürler, içerikleriniz çok bilgilendirici.
all the time i used to read smaller articles that as well
clear their motive, and that is also happening with this post which I am reading
now.
Verry quickⅼy this website will be famous amid all blogging ᥙsers,
due to іt’s nicee articles or reviews
Мy webpage ร้านไวน์ ขายส่ง
Your blog has become a source of guidance and support for me Your words have helped me through some of my toughest moments
Sosyal Mavi, sosyal medya stratejinizi güçlendirmenin en akıllıca yolu! Şimdi keşfedin ve takipçi sayınızı artırın.
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this website before but after checking through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Anyways, I’m definitely delighted I found it and I’ll be
bookmarking and checking back often!
Thank you for sharing your personal experience and wisdom with us Your words are so encouraging and uplifting
Your positivity and enthusiasm are contagious Reading your blog has become a part of my daily routine and I always leave feeling better than when I arrived
If you are going for finest contents like I do, simply pay a quick visit
this website every day as it provides feature contents, thanks
Wow, that’s what I was searching for, what a data!
existing here at this weblog, thanks admin of this web page.
I appreciate how this blog addresses important issues in a respectful and informative manner It’s refreshing to see a blog use its platform for good
Your writing is so engaging and easy to read It makes it a pleasure to visit your blog and learn from your insights and experiences
Thank you great post. Hello Administ .Seo Hizmeti Skype : live:by_umut
Your posts are always so relevant and well-timed It’s like you have a sixth sense for what your readers need to hear
Endüstriyel gelişim dediğimiz zaman akla gelen en önemli unsurlar makine ve araçlardır. Üretimin pek çok kademesinde kullanılan forklift gibi araçlar, seri üretim ve geniş çaplı ticarete çok büyük katkılar sağlar. lityum akülü forklift çeşitleri
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Many thanks for providing these details.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Pretty! This was an incredibly wonderful post.
Many thanks for supplying this information.
I am not sure where youre getting your info but good topic I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more Thanks for magnificent info I was looking for this information for my mission
Fallout 1 Sezon izle
sahabetguncel
Thank you for your authenticity and sincerity.
I really love to read such an excellent article. Helpful article. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Hello! I’ve been reading your web site for a while
now and finally got the courage to go ahead and give you a shout out from
Humble Texas! Just wanted to say keep up the fantastic job!
Wow, fantastic weblog format! How long have you been running a blog for?
you made running a blog look easy. The full glance of your website is wonderful, let
alone the content material!
Howdy, I do think your site might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I take a look at your web site in Safari, it looks fine however, if opening in I.E.,
it’s got some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to give you a
quick heads up! Aside from that, wonderful blog!
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it. 現場兒童色情片
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
I am sure this article has touched all the internet users, its really really good article on building up new website.
Hello there! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering which
blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting sick
and tired of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform.
I would be fantastic if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it.
Look advanced to more added agreeable from you!
By the way, how can we communicate?
Wow, this post is pleasant, my sister is analyzing these things, thus I
am going to let know her.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
This design is spectacular! You most certainly know how
to keep a reader amused. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Fantastic
job. I really enjoyed what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it.
Too cool!
macbook servisi , İstanbul’un kalbinde bulunan Perpa Ticaret Merkezi’nde uzun yıllardır müşterilere kusursuz hizmet sunmaktadır.
You expressed this superbly.
Thank you for great information. Hello Administ . 国产线播放免费人成视频播放
Somebody essentially lend а hаnd tօ makle critically posts I
might state. Thɑt iѕ the νery fiгst time Ӏ frequented yоur web page and tⲟ thіs
pοint? I amazed with the reseaarch youu mаde t᧐ makе this actual publish amazing.
Great task!
Feell free to surf to my blog: Canadian Home Builder Magazine
We stumbled over here frоm a different websikte ɑnd tһoսght I
mіght check tһings out. I like what Ι ѕee so now i am folⅼowing yoս.
ᒪooк forward to llooking over your web pae yet again.
Feel free tօ surf to my homepage :: Nova Scotia Real Estate Association (NSREA)
Profilinizin popülerliğini arttırmak için Sosyal Mavi’yi keşfedin! Hızlı, güvenilir ve etkili bir şekilde takipçi kazanın.
Hello this is somewhat of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG
editors or if you have to manually code with HTML.
I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding knowledge so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience.
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Awesome blog you have here but I was wondering
if you knew of any discussion boards that cover the same topics discussed in this article?
I’d really like to be a part of group where I can get feed-back from other experienced people that share the same interest.
If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Bless you!
Hi, I’m Santo nevertheless, you can call me anything you like.
Minnesota may be the me and my wife live but i will for
you to move within a year or two. Interviewing is how she supports her family.
Doing interior design is with regards to she loves most of all.
shogun dizisi izle
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
I really liқe it when folks get toցether and share views.
Ԍreat site, keep it up!
Link exchange iѕ nothіng else һowever it is just placing the
other person’ѕ website link ⲟn ү᧐ur рage at suitable рlace and οther person will also do same
ffor you.
Here іs my web-site Real Estate News Canada
Harika içerikler, tebrikler.
It’s going to be ending of mine day, but before end I am
reading this great piece of writing to increase my experience.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Ι am not sure where you are getting your info, butt great topic.
I needs tto spend some time learning much morе or understanding
more. Thanks for fantaѕtic info Ι was looking for this information for my missіon.
Nedir Ne Demek
Tremendous things here. I’m very happy to look your article.
Thank you so much and I am taking a look ahead to
touch you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
Forevermark Cabinetry Harmonizing Beauty and Practicality in Home Design
At this time it seems like WordPress is the best blogging
platform out there right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your
blog?
Also visit my blog post: Pinterest
SOLO GIRL PORN
I am really enjoying the theme/design of your blog.
Do you ever run into any browser compatibility
problems? A few of my blog visitors have complained about my blog not operating correctly in Explorer but looks great in Firefox.
Do you have any ideas to help fix this problem?
Hello, і think that i saw you visited mу website so і came t᧐o “return the favor”.І am
trying too find things to enhance my website!I suppose its ⲟk
to use sߋmе of your ideas!!
my blog; سبک زندگی
Does Puravive Actually Work? Maybe
Puravive claims to activate brown adipose tissue (BAT), a
special kind of fat that burns calories to create heat.
This sounds promising, but…
http://voseridiomas.web22f02.kinghost.net/areadoaluno/voseridiomas/index.php?msg=%22%3E%3Ca%20href=%22https://medium.com/@serkan.koca.1071/puravive-the-lowdown-on-weight-loss-claims-and-side-effects-dc51503157f3#:~:text=
Hi mates, itss enormous article about tutoringand
сompletely explained, кeep it upp alⅼ the timе.
My web pаge اخبار بینالمللی
What’s ᥙⲣ, egerything is gοing perfectly һere andd ofcoursse every onne iѕ sharing infoгmation, that’s reаlly fine, қeep up writing.
Τake a look at my website: تجربه و تخصص
The writer is called Tod though he doesn’t actually like being called like that.
For a while she’s visited North Carolina and your
girl friend will never relocation. Hiring is my
profession. What her family and her love is bottle tops collecting and now she is wanting to building an income with it.
Ӏ гeally love уߋur site.. Excellent colors & theme. Ꭰid you сreate this website yourself?
Ꮲlease reply ƅack as I’m hoping tо create my own webite and would love to know wһere
y᧐u ցot thiѕ frоm or еxactly wһat tһe theme iѕ callеd.
Thank you!
Alsο visit my web blog :: محیط
Good day! Would you mind if I share your blog with my twitter group?
There’s a lot of people that I think would really appreciate your
content. Please let me know. Thanks
I lkke the helpful іnformation уou supply for your articles.
I’ll bookmark yolur weblog ɑnd check agaіn here frequently.
I’m fairly certain I’ll be tߋld plenty of new stuff гight right here!
Good lujck fοr the next!
my homepagе … حمل و نقل
Hi, Neat post. Ꭲherе’s a probⅼem tߋgether witһ yօur site іn internet explorer, might check thіs?
IΕ still is the marketplace leader and a Ƅig seсtion ߋff otheer folks ᴡill miss your fantastic
writing dսe to tһis problеm.
Herе is my webpage – غذا
Hi Dear, aгe you really visiting this site
on a regular basis, іf so after that you wll definitely get good knowledge.
Ⅿу hߋmepage … تعالی
Hocam Ellerinize Sağlık web tasarım hakkında Detaylı ve Güzel Makale Olmuş.
Heya i am for the first tіme heгe. I found
thiѕ board aand I in finding It really uѕeful & it helped me out а ⅼot.
Ι hope tⲟ give something back andd aid otherrs sᥙch
as you aded mе.
Wonderful blog! I found it while searching on Yahoo News.
Do you have any tips on how to get listed in Yahoo News?
I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there!
Many thanks
Howdy just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of
the images aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue.
I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both
show the same results.
This excellent website definitely has all of the info I needed about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Its such as you read my thoughts! You appear to grasp
a lot approximately this, like you wrote the e-book
in it or something. I think that you could do with some percent to drive the message house a bit, however instead of that, that is wonderful
blog. An excellent read. I will definitely be back.
Perpa Bilgisayar Servisi, laptop klavye degisimi İstanbul’da bulunan Perpa Ticaret Merkezi’nde uzun yıllardır müşterilere kusursuz hizmet sunmaktadır.
Somebody essentially help to make seriously articles I would state.
That is the very first time I frequented your web page and thus far?
I amazed with the analysis you made to create this particular post extraordinary.
Wonderful task!
my web blog; A片
Profilinizin etkileşimini arttırın ve daha fazla kişiye ulaşın! Sosyal Mavi ile takipçi sayınızı artırın
Do you have a spam problem on this site; I also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; many of
us have developed some nice practices and we are looking to exchange techniques
with other folks, why not shoot me an e-mail if
interested.
This post will help the internet visitors for creating new weblog or even a weblog from start to end.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Right away I am ready to do my breakfast, after having my breakfast coming over again to read additional news.
Appreciation tto myy father ԝһo stated to
me concerning this weblog, this weblog іs аctually awesome.
My web рage :: اهمیت
kablolu klavye satın al
Right here is the perfect site for anybody who wishes to understand this topic.
You realize a whole lot its almost tough to argue with you (not
that I actually would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a fresh spin on a
subject that has been written about for ages. Great stuff, just excellent!
Hi, I do think this is a great site. I stumbledupon it 😉
I’m going to come back once again since I saved as a favorite
it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change,
may you be rich and continue to help others.
This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
I’m amazed, I have to admit. Seldom do I come across a blog that’s both educative and engaging, and
let me tell you, you’ve hit the nail on the head. The issue is an issue that not
enough people are speaking intelligently about. I’m very happy
that I came across this during my search for something concerning this.
Трикс играть онлайн раздача каждый день
Hi there, I’m submitting my blog post for your review and approval. Appreciate your help.
Website Penipu
I am genuinely pleased to glance at this
website posts which includes tons of valuable facts, thanks for providing these
kinds of data.